![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 19 July 1999 | |
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
On Alpha systems, allows a process to create a memory-resident global demand-zero section and to map a section of its address space to the global section. Shared page table sections can also be created.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 gs_name_64 ,ident_64 ,prot ,length_64 ,region_id_64 ,section_offset_64 ,acmode ,flags ,return_va_64 ,return_length_64 [,start_va_64 [,map_length_64] [reserved_length_64]]
int sys$crmpsc_gdzro_64 (void *gs_nam_64, struct _secid *ident_64, unsigned int prot, unsigned __int64 length_64, struct _generic_64 *region_id_64, unsigned __int64 section_offset_64, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, void *(*(return_va_64)), unsigned __int64 *return_length_64,...);
gs_name_64
OpenVMS usage: section_name type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Name of the global section. The gs_name_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned 32- or 64-bit string descriptor pointing to this name string.ident_64
OpenVMS usage: section_id type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Identification value specifying the version number of a global section. The ident_64 argument is a quadword containing three fields. The ident_64 argument is the 32- or 64-bit virtual address of a naturally aligned quadword that contains the identification value.The first longword specifies the matching criteria in its low-order 2 bits. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified, and their meanings are as follows:
Value Symbolic Name Match Criteria 0 SEC$K_MATALL Match all versions of the section. 1 SEC$K_MATEQU Match only if major and minor identifications match. 2 SEC$K_MATLEQ Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor identification of the global section. When a section is mapped at creation time, the match control field is ignored. If you specify the ident_64 argument as 0, the version number and match control fields default to 0.
The version number is in the second longword. The version number contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a section is created, processes that specify a version number when mapping cannot access the global section.
prot
OpenVMS usage: file_protection type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Protection to be applied to the global demand-zero section. The mask contains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to left in each field. The following diagram depicts the mask:
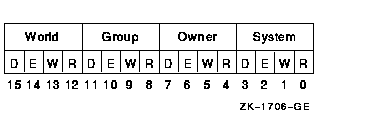
Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, in that order, are granted to the particular category of user. Only read, write, and execute access are meaningful for section protection. Delete access bits are ignored. Read access also grants execute access for those situations where execute access applies. If zero is specified, read access and write access are granted to all users.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
Creating a memory-resident global section with shared page table does not imply that the global section must have an even multiple of CPU-specific page table pages. The global section might not fully use the last page table page. |
| OpenVMS usage: | region identifier |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
The file VADEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB and the $VADEF macro in STARLET.MLB define a symbolic name for each of the three default regions in P0, P1, and P2 space. The following region IDs are defined:
| Symbol | Region |
|---|---|
| VA$C_P0 | Program region |
| VA$C_P1 | Control region |
| VA$C_P2 | 64-bit program region |
Other region IDs, as returned by the $CREATE_REGION_64 service, can be specified.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte offset |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
If a shared page table region is specified by the region_id_64 argument, section_offset_64 must be an even multiple of the number of bytes that can be mapped by a CPU-specific page table page.
| OpenVMS usage: | access_mode |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
If the memory-resident global section is created with shared page tables, this is the access mode that is stored in the owner, read, and write fields of the corresponding shared page table entries (PTEs).
The $PSLDEF macro in STARLET.MLB and the file PSLDEF.H in SYS$STARLET_C.TLB define the following symbols and their values for the four access modes:
| Value | Symbolic Name | Access Mode |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | PSL$C_KERNEL | Kernel |
| 1 | PSL$C_EXEC | Executive |
| 2 | PSL$C_SUPER | Supervisor |
| 3 | PSL$C_USER | User |
The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller. The calling process can delete pages only if those pages are owned by an access mode equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the calling process.
Address space cannot be created within a region that has a create mode associated with it that is more privileged than the caller's mode. The condition value SS$_IVACMODE is returned if the caller is less privileged than the create mode for the region.
| OpenVMS usage: | mask_longword |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The following table describes each flag that is valid for the $CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 service:
| Flag | Description |
|---|---|
| SEC$M_DZRO | Pages are demand-zero pages. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. |
| SEC$M_EXPREG |
Pages are mapped into the first available space at the current end of
the specified region.
If the /ALLOCATE qualifier was specified when the global section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, virtually aligned addresses after the first available space are chosen for the mapping. |
| SEC$M_GBL | Pages form a global section. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. |
| SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP | Pages cannot overmap existing address space. |
| SEC$M_PERM | Global section is permanent. |
| SEC$M_SYSGBL | Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group global section. |
| SEC$M_MRES | Pages form a memory-resident section. By default, this page is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. |
| SEC$M_WRT | Pages form a read/write section. By default, this flag is always present in this service and cannot be disabled. |
All other bits in the flags argument are reserved for future use by Compaq and should be specified as 0. The condition value SS$_IVSECFLG is returned if any undefined bits are set or if an invalid combination of flags is set.
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
If a shared page table region is specified by the region_id_64 argument and the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is set, the returned virtual address is aligned to a CPU-specific page table page boundary.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference |
| OpenVMS usage: | address |
| type: | quadword address |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
If SEC$M_EXPREG is clear, start_va_64 is nonzero, and a shared page table region is specified, the specified starting address must be aligned to a natural page table page boundary; otherwise, the condition value SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN is returned.
If the /ALLOCATE qualifier was specified when the memory-resident global section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry and start_va_64 is aligned to a multiple of CPU-specific pages appropriate for taking advantage of granularity hints (8, 64, or 512 pages), then granularity hints are used to map to the global section.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
If a shared page table region is specified by the region_id_64 argument, map_length_64 must be an even multiple of the number of bytes that can be mapped by a CPU-specific page table page or must include the last page within the global section.
| OpenVMS usage: | byte count |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | 32- or 64-bit reference |
If reserved_length_64 is not specified or is specified as 0, no reserved length is returned to the caller.
If the memory-resident global section is not registered, reserved_length_64 is written with the value 0.
The Create and Map to Global Demand-Zero Section service allows a process to create and map to a memory-resident global demand-zero section. Memory-resident global demand-zero sections contain demand-zero allocation pages that are writable and memory resident. If the $CRMPSC_GDZRO_64 service specifies a global section that already exists, the service maps to it only if it is a memory-resident global section. All pages in the memory-resident global section are shared by all processes that map to the global section.The global demand-zero pages are always resident in memory and are not backed up by any file on any disk. The global pages are not charged against any page file quota. The process must have the rights identifier VMS$MEM_RESIDENT_USER to create a memory-resident global section; otherwise, the error status SS$_NOMEMRESID is returned.
The memory-resident global pages are not placed into the process's working set list when the process references the virtual addresses mapping the global section. The pages are not charged against the process's working set quota.
If the memory-resident global section is either not registered in the Reserved Memory Registry or if the /NOALLOCATE qualifier was specified when the global section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, invalid global PTEs are written to the global page table and invalid PTEs are placed in the process page table. Physical memory is not allocated until the virtual memory is referenced. If the global section is registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, the size of the global section need not match the reserved size. If the global section is not registered in the Reserved Memory Registry or if the reserved size is smaller than the size of the global section, the error status SS$_INSFLPGS is returned if there are not enough fluid pages in the system to satisfy the request.
If the /ALLOCATE qualifier was specified when the global section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, contiguous, aligned physical pages are preallocated during system initialization for this global section. Valid page table entries are placed in the global page table and in the process page table. If the reserved preallocated memory is smaller than the size of the global section, the error SS$_MRES_PFNSMALL is returned and the global section is not created.
If the memory-resident global section is not registered in the Reserved Memory Registry or if the /PAGE_TABLES qualifier was specified when the global section was registered in the Reserved Memory Registry, shared page tables are created for the global section.
For more information about using the SYSMAN utility to create entries to the Reserved Memory Registry, see the OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.
Shared page tables consume the same internal OpenVMS data structures as a global section. The system parameters GBLPAGES and GBLSECTIONS must account for the additional global pages and the additional global section.
To use the shared page tables associated with a memory-resident global section, you must first create a shared page-table region (with $CREATE_REGION_64). To map to the memory-resident global section using the shared page tables, you must do the following:
- Specify a shared page-table region in the region_id_64 argument.
- Set the flag SEC$M_EXPREG or provide a CPU-specific page table page aligned virtual address in the start_va_64 argument.
- Specify a value for the section_offset_64 argument that is an even multiple of bytes mapped by a CPU-specific page table page or zero.
- Specify a value for the map_length_64 argument that is an even multiple of bytes mapped by a CPU-specific page table page or zero, or include the last page of the section.
See the description of the $CREATE_REGION_64 service for information about calculating virtual addresses that are aligned to a CPU-specific page table page boundary.
The memory-resident global section can be mapped with shared page tables or private page tables. The following table lists the factors associated with determining whether the mapping occurs with shared page tables or with private page tables.
Global Section Created with Shared Page Tables Shared Page Table Region Specified by region_id_64 Type of Page Tables Used in Mapping No No Private No Yes Private Yes No Private Yes Yes Shared In general, if the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set, the first free virtual address within the specified region is used to map to the global section.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set and the region_id_64 argument indicates a shared page table region, the first free virtual address within the specified region is rounded up to a CPU-specific page table page boundary and used to map to the global section.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is set and if the /ALLOCATE qualifier was specified with the SYSMAN command RESERVED_MEMORY ADD for the memory-resident global section, the first free virtual address within the specified region is rounded up to the same virtual alignment as the physical alignment of the preallocated pages and used to map to the global section. Granularity hints are set appropriately for each process private PTE.
In general, if the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is clear, the virtual address in the start_va_64 argument is used to map to the global section.
If the flag SEC$M_EXPREG is clear, the value specified in the start_va_64 argument can determine if the mapping is possible and if granularity hints are used in the private page tables. If a shared page table region is specified by the region_id_64 argument, the virtual address specified by the start_va_64 argument must be on an even CPU-specific page table page boundary or an error is returned by this service. If the region_id_64 argument does not specify a shared page table region and /ALLOCATE was specified with the SYSMAN command RESERVED_MEMORY ADD for this global section, granularity hints are used only if the virtual alignment of start_va_64 is appropriate for the use of granularity hints (either 8-page, 64-page, or 512-page alignment).
Whenever granularity hints are being used within the mapping of a memory-resident global section, if the length_64 argument is not an exact multiple of the alignment factor, lower granularity hints factors are used as appropriate at the higher addressed portion of the global section. If the section_offset_64 argument is specified, a lower granularity hint factor can be used throughout the mapping of the global section to match the physical alignment of the first page mapped.
If the condition value SS$_ACCVIO is returned by this service, a value cannot be returned in the memory locations pointed to by the return_va_64 and return_length_64 arguments and, if specified as a nonzero value, the reserved_length_64 argument.
If a condition value other than SS$_ACCVIO is returned, the returned address and returned length indicate the pages that were successfully mapped before the error occurred. If no pages were mapped, the return_va_64 argument contains the value --1.
If the service returns an error status value other than SS$_INSFLPGS or SS$_MRES_PFNSMALL, a value is not returned in the reserved_length_64 argument.
If the service returns a successful condition value or if SS$_INSFLPGS or SS$_MRES_PFNSMALL is returned and the reserved_length_64 argument is specified as a nonzero address, the length in bytes of the global section as registered in the Reserved Memory Registry is returned in the reserved_length_64 argument.
To create a global section, the process must have the following privileges:
- SYSGBL privilege to create a system global section (if flag SEC$M_SYSGBL is set)
- PRMGBL privilege to create a permanent global section
- VMS$MEM_RESIDENT_USER rights identifier to create a memory-resident section
If private page tables are used to map to the memory-resident global section, the working set limit quota (WSQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to accommodate the increased size of the process page tables required by the increase in virtual address space.
If private page tables are used to map to the memory-resident global section, the page file quota (PGFLQUOTA) of the process must be sufficient to accommodate the increased size of the process page tables required by the increase in virtual address space.
$CREATE_GDZRO, $CREATE_GPFILE, $CREATE_REGION_64, $CRMPSC, $CRMPSC_FILE_64, $CRMPSC_GFILE_64, $CRMPSC_GPFN_64, $CRMPSC_PFN_64, $DELETE_REGION_64, $DELTVA_64, $DGBLSC, $LCKPAG_64, $LKWSET_64, $MGBLSC_64, $PURGE_WS, $SETPRT_64, $ULKPAG_64, $ULWSET_64, $UPDSEC_64, $UPDSEC_64W
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. The specified global section already exists and has been mapped. SS$_CREATED The service completed successfully. The global section has been created. SS$_CREATED_SHPT Global section has been created with shared page tables. SS$_ACCVIO The gs_name_64 argument cannot be read by the caller, or the return_va_64 or return_length_64 argument cannot be written by the caller. SS$_EXPGFLQUOTA The process's page file quota is not large enough to accommodate the increased virtual address space. SS$_GBLSEC_MISMATCH Global section type mismatch. The specified global section was found; however, it is not a memory-resident section. SS$_GPTFULL There is no more room in the system global page table to set up page table entries for the global section or for the shared page tables. SS$_GSDFULL There is no more room in the system space allocated to maintain control information for global sections. SS$_INSFWSL The process's working set limit is not large enough to accommodate the increased virtual address space. SS$_IVACMODE The specified access mode is greater than PSL$_USER, or the caller's mode is less privileged than the create mode associated with the region. SS$_IVLOGNAM The specified global section name has a length of 0 or has more than 43 characters. SS$_IVPROTECT The protection argument format is invalid. SS$_IVREGID An invalid region ID was specified. SS$_IVSECFLG An invalid flag, a reserved flag, or an invalid combination of flags was specified. SS$_IVSECIDCTL The match control field of the global section identification is invalid. SS$_LEN_NOTPAGMULT The length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specified pages. Or, if a shared page table region is specified by the region_id_64 argument, the map_length_64 argument is not a multiple of CPU-specific page table pages. SS$_MRES_PFNSMALL Preallocated, contiguous, aligned physical memory specified in the Reserved Memory Registry is smaller than the length specified for the memory-resident global section by the length_64 argument. SS$_NOMEMRESID The process attempted to create a memory-resident section, but was not holding the right identifier VMS$MEM_RESIDENT_USER. SS$_NOPRMGBL The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a permanent group global section (PRMGBL). SS$_NOSYSGBL The process does not have the privileges to create or delete a system global section (SYSGBL). SS$_OFF_NOTPAGALGN The section_offset_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned. Or, if a shared page table region is specified by the region_id_64 argument, the section_offset_64 argument is not CPU-specific page table page aligned. SS$_OFFSET_TOO_BIG The section_offset_64 argument specified is beyond the logical end-of-file. SS$_PAGNOTINREG A page in the specified input address range is not within the specified region. SS$_PAGOWNVIO A page in the specified input address range is owned by a more privileged access mode. SS$_REGISFULL The specified virtual region is full; no space is available in the region for the pages created to contain the mapped section. SS$_SECREFOVF The maximum number of references for a global section has been reached (2,147,483,647). SS$_SECTBLFUL There are no entries available in the system global section table for the global section or for the shared page tables. SS$_TOOMANYLNAM The logical name translation of the gs_name_64 argument exceeded the allowed depth of 10. SS$_VA_IN_USE A page in the specified input address range is already mapped and the flag SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP is set, or a page in the specified input address range is in another region, in system space, or inaccessible; or, the existing underlying page cannot be deleted because it is associated with a buffer object. SS$_VA_NOTPAGALGN The start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page aligned. Or, if a shared page table region is specified by the region_id_64 argument, the start_va_64 argument is not CPU-specific page table page aligned.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
| privacy and legal statement | ||
| 4527PRO_021.HTML | ||