If a request received from a DUA cannot be fulfilled by the receiving DSA, that DSA can send a referral back to the initiating DUA over DAP. Alternatively, the DSA can chain the request over DSP, asking another DSA to perform the requested function. That DSA can perform the function or can send back a referral of its own. In either case, the first DSA eventually responds to the originating DUA with either the results of the completed operation or a referral.
Chaining can go deeper than one level. To prevent lengthy searches, a user can request no chaining or specify a limit on the total elapsed time for an operation.
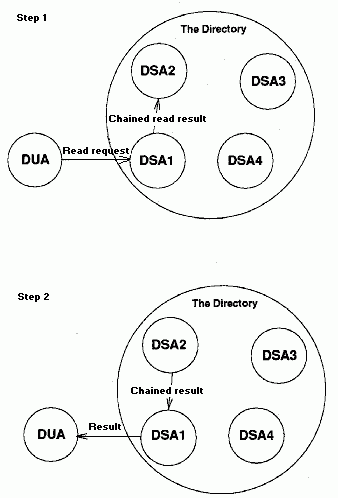
The following figure shows an example of chaining. The DUA makes a request of DSA1. DSA1 is unable to service the request and passes it to DSA2. DSA2 services the request, passes the result back to DSA1, and DSA1 passes the result back to the DUA.
An Example of Chaining
