| Previous | Contents | Index |
The DIVIDE statement divides one or more numeric data items by another and sets the value of the data items equal to the quotient, optionally storing the remainder.

num
is a numeric literal or the identifier of an elementary numeric item.rsult
is the identifier of an elementary numeric item or an elementary numeric edited item. However, in Format 1, rsult must be an elementary numeric item. It is the resultant identifier.stment
is an imperative statement executed when a size error condition has occurred.stment2
is an imperative statement executed when no size error condition has occurred.remaind
is the identifier of an elementary numeric item or an elementary numeric edited item.
The following example shows a run-time message issued for an illegal attempt to divide by zero:
%COB-E-DIVBY-ZER, divide by zero; execution continues |
Each of the examples assume the following data descriptions and initial values. The initial values are listed in the righthand column:
INITIAL VALUES
03 ITEMA PIC 99V99 VALUE 9. 9.00
03 ITEMB PIC 99V99 VALUE 24. 24.00
03 ITEMC PIC 99V99 VALUE 8. 8.00
03 ITEMD PIC 99 VALUE 12. 12
03 ITEME PIC 99V99 VALUE 3. 3.00
03 ITEMF PIC 99 VALUE 47. 47
03 ITEMG PIC 9 VALUE 9. 9
03 ITEMH PIC 9 VALUE 2. 2
03 ITEMI PIC 99 VALUE 4. 4
|
In each of the following examples, the righthand column shows the results of the DIVIDE operation.
DIVIDE ITEMA INTO ITEMB. ITEMB = 2.66 |
DIVIDE ITEMA INTO ITEMB ROUNDED. ITEMB = 2.67 |
DIVIDE ITEMA INTO ITEMB ITEMD = 2 GIVING ITEMD. |
DIVIDE ITEMA INTO ITEMB ITEMD = 3 GIVING ITEMD ROUNDED. |
DIVIDE ITEMA BY ITEMB ITEMD = 0 GIVING ITEMD. |
DIVIDE ITEMA INTO ITEMB ITEMD = 2 GIVING ITEMD REMAINDER ITEMC. ITEMC = 6.00 |
DIVIDE ITEMA INTO ITEMB ITEMD = 3 GIVING ITEMD ROUNDED REMAINDER ITEMC. ITEMC = 6.00 |
DIVIDE ITEMA INTO ITEMB ITEME = 2.66 GIVING ITEME REMAINDER ITEMC. ITEMC = .06 |
DIVIDE ITEMA INTO ITEMB ITEME = 2.67 GIVING ITEME ROUNDED REMAINDER ITEMC. ITEMC = .06 |
DIVIDE ITEME INTO ITEMF
GIVING ITEMG ITEMD ITEMD = 15
ON SIZE ERROR ITEMG = 9
MOVE 0 TO ITEMH. ITEMH = 0
|
DIVIDE ITEMD INTO ITEMF
GIVING ITEMI REMAINDER ITEMG ITEMI = 3
ON SIZE ERROR ITEMG = 9
MOVE 0 TO ITEMH. ITEMH = 0
|
DIVIDE ITEMD INTO ITEMF ITEMI = 3
GIVING ITEMI REMAINDER ITEMC ITEMC = 11.00
ON SIZE ERROR
MOVE 0 TO ITEMH
NOT ON SIZE ERROR
MOVE 1 TO ITEMH. ITEMH = 1
|
The EVALUATE statement selects a program action based on the evaluation of one or more conditions.
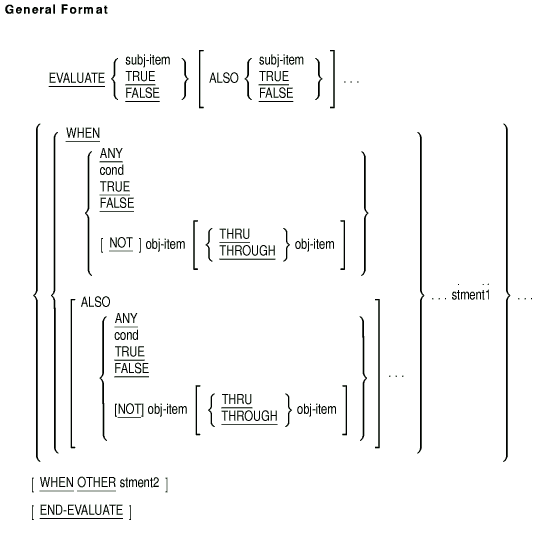
subj-item
is an identifier, an arithmetic or conditional expression, or a literal other than the figurative constant ZERO.cond
is a conditional expression.obj-item
is a literal, an identifier, or an arithmetic expression.stment1
is an imperative statement.stment2
is an imperative statement.
| Condition | Value Assigned | |
|---|---|---|
| a. | An identifier for a subject, or for an object without the NOT or THROUGH phrases | Value and class of the identifier's data item. |
| b. | A literal for a subject, or for an object without the NOT or THROUGH phrases | Value and class of the literal. |
| c. | The figurative constant ZERO for an object without the NOT or THROUGH phrases | Value and class of the corresponding subject. |
| d. | An arithmetic expression for a subject, or for an object without the NOT or THROUGH phrases | Numeric value, according to the rules for evaluating arithmetic expressions. |
| e. | A conditional expression for a subject or a conditional expression for an object | Truth value, according to the rules for evaluating conditional expressions. |
| f. | TRUE or FALSE as a subject or object | Truth value: true for the word TRUE and false for the word FALSE. |
| g. | ANY for an object | No further evaluation. |
| h. | THROUGH phrase for an object without the NOT phrase | The range of values is all values that, when compared to the subject, are greater than or equal to the first obj-item and less than or equal to the second obj-item. If the first obj-item is greater than the second obj-item, there are no values in the range. |
| i. | Object with the NOT phrase | All values not equal to the value (or range of values) that would be assigned without the NOT phrase. |
In these examples, the results are shown as either data item values or procedure branches. However, stment can be any imperative statement, including multiple statements.
EVALUATE ITEMA
WHEN "A01" MOVE 1 TO ITEMB
WHEN "A02" THRU "C16" MOVE 2 TO ITEMB
WHEN "C20" THRU "L86" MOVE 3 TO ITEMB
WHEN "R20" ADD 1 TO R-TOT
GO TO PROC-A
WHEN OTHER MOVE 0 TO ITEMB
END-EVALUATE.
|
| ITEMA | Result |
|---|---|
| "A15" | ITEMB = 2 |
| "P80" | ITEMB = 0 |
| "F01" | ITEMB = 3 |
| "M19" | ITEMB = 0 |
| "A01" | ITEMB = 1 |
| "R20" | PROC-A |
EVALUATE LOW-STOK WEEK-USE LOC-VNDR ON-ORDER WHEN "Y", 16 THRU 999, ANY, "N" GO TO RUSH-ORDER WHEN "Y", 16 THRU 999, ANY, "Y" GO TO NORMAL-ORDER WHEN "Y", 8 THRU 15, "N", "N" GO TO RUSH-ORDER WHEN "Y", 8 THRU 15, "N", "Y" GO TO NORMAL-ORDER WHEN "Y", 8 THRU 15, "Y", "N" GO TO NORMAL-ORDER WHEN "Y", 0 THRU 7, ANY, "N" GO TO NORMAL-ORDER WHEN "N", ANY, ANY, "Y" GO TO CANCEL-ORDER END-EVALUATE. |
| LOW-STOK | WEEK-USE | LOC-VNDR | ON-ORDER | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| "Y" | 38 | "N" | "Y" | NORMAL-ORDER |
| "N" | 20 | "Y" | "Y" | CANCEL-ORDER |
| "N" | 12 | "Y" | "N" | next statement |
| "Y" | 12 | "Y" | "N" | NORMAL-ORDER |
| "Y" | 12 | "Y" | "Y" | next statement |
| "Y" | 40 | "N" | "N" | RUSH-ORDER |
EVALUATE-ITEM-ROUTINE.
*
* After the imperative statement in the selected WHEN phrase
* executes (for example PERFORM PROC-A), control then
* transfers to the first statement following the end of the
* EVALUATE statement (MOVE A TO B).
*
EVALUATE ITEMA > 6 AND < 30, 8 * ITEMB - 1
WHEN TRUE, 5 * ITEMC PERFORM PROC-A
WHEN FALSE, ITEMC PERFORM PROC-B
WHEN ITEMC > 12, -1 PERFORM PROC-C
WHEN TRUE, NOT 7 THRU 40 PERFORM PROC-D
WHEN OTHER PERFORM PROC-E
END-EVALUATE.
MOVE A TO B.
|
| ITEMA | ITEMB | ITEMC | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 2 | 3 | PROC-A |
| 25 | 0 | 14 | PROC-C |
| 30 | 0 | 14 | PROC-E |
| 6 | 3 | 23 | PROC-B |
| 14 | 0 | 5 | PROC-D |
| 5 | 0 | 11 | PROC-C |
Consider how the EVALUATE statement works using the values in the previous sample:
The EXIT statement provides a common logical end point for a series of procedures.

The EXIT statement must appear in a sentence by itself and be the only sentence in the paragraph.
The EXIT statement associates a procedure-name with a point in the program. It has no other effect on program compilation or execution.
REPORT-INVALID-ADD.
DISPLAY " ".
DISPLAY "INVALID ADDITION".
DISPLAY "RECORD ALREADY EXISTS".
DISPLAY "UPDATE ATTEMPT: " UPDATE-REC.
DISPLAY "EXISTING RECORD: " OLD-REC.
REPORT-INVALID-ADD-EXIT.
EXIT.
|
The EXIT PROGRAM statement marks the logical end of a called program.

TEST-RETURN.
IF ITEMA NOT = ITEMB
MOVE ITEMA TO ITEMB
EXIT PROGRAM.
|
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |