This chapter describes the tasks you perform to set up a disk service:
The first task in setting up a disk service is to create the container file for the service on an OpenVMS disk. To do this, log on to an OpenVMS Alpha node and use the NTDS CREATE CONTAINER command. For example:
$ SET PROCESS /PRIVILEGE=SYSPRV $ NTDS CREATE CONTAINER DISK$MEDIA:[NTDS$CONT]SPORTS.NTDS - _$ /SIZE=2000000
Use the /SIZE qualifier to specify how big you want the virtual disk to be, in blocks. The NTDS CREATE CONTAINER command creates a container file of the specified size.
The second task in setting up a disk service is to configure your OpenVMS Cluster to provide the service. The following table gives an overview of the steps.
Follow these steps first on the node that you want to provide the service, and then on each of the nodes that you want to be standbys for the service.
| Step | Do This | Using This Command |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Log on to the OpenVMS Alpha node and set process privileges | SET PROCESS |
| 2 | Start up the server software | NTDS START SERVER |
| 3 | Start an active or standby disk service | NTDS START SERVICE |
| 4 | Edit the system startup file | |
| 5 | Edit the system shutdown file |
To configure your OpenVMS Cluster to provide a service, follow these steps first on the node that you want to provide the service, and then on each of the nodes that you want to be standbys for the service:
Give your process the SYSNAM and SYSPRV privileges:
$ SET PROCESS /PRIVILEGE=(SYSNAM,SYSPRV)
If you have not already done so, start the server software on the local node, using the NTDS START SERVER command. For example:
$ NTDS START SERVER /CLUSTERNAME="Media"
You must use the /CLUSTERNAME qualifier to define the cluster name for your OpenVMS Cluster. This is the name that Windows NT computers use to identify your OpenVMS Cluster when they connect to the disk services that it provides.
You can use any name you want as your cluster name, provided that it is not longer than 24 characters and does not contain a backslash character (\). For example, you may use the same name as your OpenVMS Cluster alias.
Note that the cluster name is case sensitive, and that the NTDS START SERVER command automatically converts the string you supply to uppercase unless you enclose it in quotation marks.
Use the NTDS START SERVICE command to start the disk service on the local node. For example:
$ NTDS START SERVICE "Sports" - _$ /CONTAINER=DISK$MEDIA:[NTDS$CONT]SPORTS.NTDS
The /CONTAINER qualifier specifies the container file for the service.
The parameter, in this example Sports, specifies the name you want to give to the service. This is the name that the Windows NT computer uses to identify the service when it connects to it.
You can choose any name you want, provided that it is not longer than 24 characters. Note that the service name is case sensitive, and that the NTDS START SERVICE command automatically converts the string you supply to uppercase unless you enclose it in quotation marks.
The first NTDS START SERVICE command starts the active disk service on the local node. Subsequent NTDS START SERVER commands issued on other nodes start standby disk services on those nodes.
To make sure that the disk service is started automatically during system startup, edit the site-specific system startup file to execute the NTDS START SERVER and NTDS START SERVICE commands of Steps 2 and 3.
We recommend that you use a separate command procedure, and edit your site-specific startup file to run this command procedure during system startup.
You will find a template file NTDS$STARTUP.TEMPLATE in SYS$STARTUP. Create a file called NTDS$STARTUP.COM by copying the template file, then edit the new file to add the NTDS commands of Steps 2 and 3.
During system startup, make sure that NTDS$STARTUP.COM is executed after UCX$STARTUP.COM, which starts DIGITAL TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS.
If you have not already done so, edit the site-specific shutdown file, SYSHUTDWN.COM, to add the following line:
$ @SYS$STARTUP:NTDS$SHUTDOWN.COM
During system shutdown, make sure that this line is executed before the line that executes UCX$SHUTDOWN.COM, which stops DIGITAL TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS.
Be careful to type the correct container file when you issue NTDS START SERVICE commands on different nodes in your OpenVMS Cluster.
To avoid this problem we recommend that you make the file name of the container file the same as its service name. For example, if the container file is SPORTS.NTDS, call the service Sports.
To avoid the possibility of making typing mistakes when you issue NTDS START SERVICE commands, we recommend that you issue them either:
or
For example, the following command sequence starts the Sports service on three nodes; it starts the active service on GREEN, and standby services on BLUE and YELLOW:
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:SYSMAN SYSMAN> SET ENVIRONMENT /NODE=(GREEN,BLUE,YELLOW) SYSMAN> SET PROFILE /PRIVILEGES=(SYSNAM,SYSPRV) SYSMAN> DO NTDS START SERVICE "Sports" - _SYSMAN> /CONTAINER=DISK$MEDIA:[NTDS$CONT]SPORTS.NTDS
The third and final task in setting up a disk service is to configure the Windows NT computer to connect to the service. The following table gives an overview of the steps.
| Step | Do This | By Using |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Log on to the Windows NT computer as an Administrator | |
| 2 | Add the disk service to the configuration database | NTDS Administrator |
| 3 | If necessary, configure the communication settings | NTDS Administrator |
| 4 | Connect to the disk service | NTDS Administrator |
| 5 | Partition and format the virtual disk | Disk Administrator |
| 6 | Optionally, share the virtual disk | Explorer |
Follow these steps to configure the Windows NT computer to connect to the disk service:
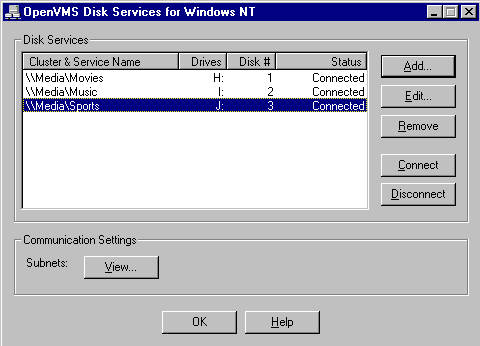
Run NTDS Administrator (by default, from the Windows Start Bar click Programs, then DIGITAL OpenVMS Disk Services, then NTDS Administrator). The following screen appears:
Click Add. The following dialogue box appears:
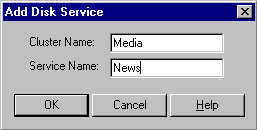
Enter the cluster name and the service name, then click OK.
Type them in uppercase if you did not enclose them in quotation marks when you used NTDS START SERVER and NTDS START SERVICE.
The NTDS commands automatically convert the names to uppercase unless you enclose them in quotation marks.
If you enclosed a name in quotation marks on the NTDS command, do not include the quotation marks when you type the name in this dialogue box.
You can skip this step and accept the default settings if the Windows NT computer only wants to use disk services on OpenVMS Clusters that are in the same subnets as itself.
The first time you run NTDS Administrator, it automatically scans the network cards attached to the computer and configures default settings that allow it to communicate with OpenVMS Clusters that have the same IP subnet addresses as these cards.
If you want the computer to be able to use disk services provided by OpenVMS Clusters in other subnets, click View. The following screen appears:
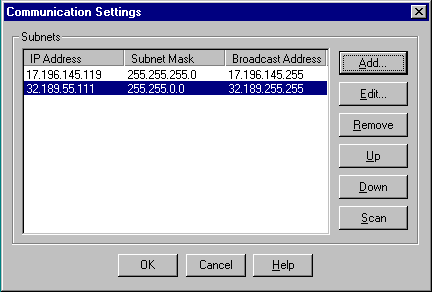
Click Help, then click the Configuring a new disk service Related Topic help button for instructions on how to configure the communications settings so that the computer can communicate with OpenVMS Clusters on other subnets.
When you have finished, click OK to remove the Communication Settings screen and return to the NTDS Administrator's Main screen (Figure 2-1).
Select the disk service that you added in Step 2, then click Connect.
The status of the disk service changes from Disconnected to Connected. The Windows NT computer has just got itself a new disk!
The Disk # column tells you the disk number assigned to the new disk.
Note that when the computer restarts, it automatically connects to all of the disk services it was connected to when it was shut down.
Partition and format the new virtual disk in the normal way, using the Windows NT Disk Administrator (by default, from the Windows Start Bar click Programs, then Administrative Tools (Common), then Disk Administrator).
Make sure you select the right disk; create the partition on the disk whose number was displayed in the Disk # column of the NTDS Administrator's Main screen of Figure 2-1.
Remember not to create a volume, mirror or stripe set on the disk.
Ignore this step if you do not want to share the virtual disk.
Share the virtual disk in the normal way. For example, using Windows NT Explorer, click the right mouse button on the disk and select Sharing.
Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1997. All Rights Reserved.