|
Document revision date: 24 June 2002
|
![[Compaq]](../../images/hp.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/hp_ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
Open
Source Security for OpenVMS Alpha Volume 1:
Common Data Security Architecture AA-RSCUA-TE
This is a new manual.
Common Data Security Architecture
OpenVMS Alpha Versions
7.2–2, 7.3, and 7.3–1
June 2002
Compaq Computer Corporation
Houston Texas
© 2002 Compaq Information Technologies Group,
L.P.
The Common Data Security Architecture (CDSA)
is a multiplatform, industry-standard, open-source security infrastructure.
It provides a stable programming interface that application developers can
use to access OpenVMS Alpha operating system security services. This manual
briefly describes CDSA, gives information about installation, initialization,
and examples, and describes the CDSA application programming interface modules.
Compaq, the Compaq logo, Alpha, OpenVMS, Tru64, VAX, VMS, and
the DIGITAL logo are trademarks of Compaq Information Technologies Group,
L.P. in the U.S. and/or other countries.
Microsoft, MS-DOS, Visual C++, Windows, and Windows NT are trademarks
of Microsoft Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries.
Intel,
Intel Inside, and Pentium are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S.
and/or other countries.
Motif, OSF/1, and UNIX are trademarks of The Open Group in the
U.S. and/or other countries.
All other product names mentioned herein may be trademarks of
their respective companies.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from Compaq required
for possession, use or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial
Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for
Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor’s
standard commercial license.
Compaq shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or
omissions contained herein. The information is provided “as is”
without warranty of any kind and is subject to change without notice. The
warranties for Compaq products are set forth in the express limited warranty
statements accompanying such products. Nothing herein should be construed
as constituting an additional warranty.
ZK6660
The Compaq OpenVMS documentation set is available on CD-ROM.
PrefaceIntended Audience
This
document is for application developers who want to use the Common Data Security
Architecture (CDSA) to add security to their programs.
This
is not a tutorial manual. The reader should already have a basic understanding
of fundamental cryptographic terms and principles, as well as a broad overview
of CDSA services and architecture. The developer who plans to use CDSA should
have a good idea of what he or she wants to accomplish with it.
Document Structure
This
manual consists of the following chapters:
Chapter 1 gives a broad overview of CDSA.
Chapter
2 gives some important information about installation and initialization of
CDSA.
Chapter 3 includes some information on programming
and examples of using CDSA.
Chapter 4 is a reference section that describes
and includes the text of the CDSA application programming interface functions
(API functions).
Related
Documents
The following documents are recommended for further
information:
• Open
Source Security for OpenVMS Alpha Volume 2: Compaq SSL for OpenVMS Alpha.
• DCL Help file for the API functions.
(Enter the HELP CDSA command at the DCL prompt.)
• Release Notes for CDSA. For
Version 7.3–1, the information is included in the OpenVMS
Alpha Version 7.3–1 Release Notes. For Versions 7.2–2 and
7.3, the Release Notes for CDSA can be found in SYS$HELP:CDSA010.RELEASE_NOTES.
• Intel
Common Data Security Architecture Application Developer’s Guide, available
in SYS$HELP:CDSA$APP_DEV_GUIDE.PDF.
• CDSA Technical
Standard, available from The Open Group.
For additional information about Compaq OpenVMS
products and services, see the Compaq web site at the following location:
http://www.openvms.compaq.com/
For
additional information about CDSA, visit the following web sites:
http://sourceforge.net/projects/cdsa
http://developer.intel.com/IAL/security
Reader’s Comments
Compaq
welcomes your comments on this manual. Please send comments to either of the
following addresses:
Internet:
openvmsdoc@compaq.com
Mail:
Compaq Computer Corporation
OSSG Documentation Group, ZKO3-4/U08
110 Spit Brook Rd.
Nashua, NH 03062-2698
How to Order Additional Documentation
Visit
the following World Wide Web address for information about how to order additional
documentation:
http://www.openvms.compaq.com/
Conventions
The
following conventions are used in this manual:
Ctrl/ x
Indicates that you must hold down the key labeled
Ctrl while you press another key or a pointing device button.
PF1x
A sequence such as PF1x indicates
that you must first press and release the key labeled PF1 and then press and
release another key or a pointing device button.
[Return]
In an example, a key name enclosed in a box indicates
that you press that key.
…
A horizontal ellipsis in examples indicates one
of the following possibilities:
• Additional optional arguments
in a statement have been omitted.
• The preceding item or items can be
repeated one or more times.
• Additional parameters, values, or
other information can be entered.
A
vertical ellipsis indicates the omission of items from a code example or command
format; the items are omitted\par because they are not important to the topic
being discussed.
( )
In command format descriptions, parentheses indicate
that you must enclose choices in parentheses if you specify more than one.
[ ]
In command format descriptions, brackets indicate
optional choices. You can choose one or more items or no items. Do not type
the brackets on the command line. However, you must include the brackets in
the syntax for OpenVMS directory specifications and for a substring specification
in an assignment statement.
|
In command format descriptions, vertical bars separate
choices within brackets or braces. Within brackets, the choices are optional;
within braces, at least one choice is required. Do not type the vertical bars
on the command line.
{ }
In command format descriptions, braces indicate
required choices; you must choose at least one of the items listed. Do not
type the braces on the command line.
Type
This typeface represents the introduction of a
new. It also represents the name of argument an attribute, or a reason.
italics
Italic
text indicates important information, complete titles of manuals, or variables.
Variables include information that varies in system output (Internal error number), in command lines (/PRODUCER=name), and in command parameters in text
(where (dd) represents the predefined
par code for the device type.
UPPERCASE TEXT
Uppercase
text indicates a command, the name of a routine, the name of a file, or the
abbreviation for a system privilege.
Monospace text
Monospace
type indicates code examples and interactive screen displays.
In the C programming language, monospace type in
text identifies the following elements: keywords, the names of independently
compiled externalfunctions and files, syntax summaries, and references to
variables or identifiers introduced in an example.
–
A hyphen at the end of a command format description,
command line, or code line indicates that the command or statement continues
on the following line.
numbers
All numbers in text are assumed to be decimal unless
otherwise noted. Nondecimal radixes---binary, octal, or hexadecimal---are
explicitly indicated.
Statement
About OPEN SOURCE LICENSEIMPORTANT: READ BEFORE DOWNLOADING, COPYING, INSTALLING OR USING. By
downloading, copying, installing or using the software you agree to
this license. If you do not agree to this license, do not download,
install, copy or use the software.
Intel Open Source License for CDSA/CSSM Implementation
(BSD License with Export Notice)
Copyright (c) 1996-2000 Intel Corporation
All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
are met:
+ Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
+ Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in
the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
distribution.
+ Neither the name of the Intel Corporation nor the names of its
contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
from this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
"AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL INTEL
OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF
USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED
AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING
IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF
THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
EXPORT LAWS: THIS LICENSE ADDS NO RESTRICTIONS TO THE THE EXPORT
LAWS OF YOUR JURISDICTION. It is licensee’s responsibility to comply
with any export regulations applicable in licensee’s jurisdiction.
Under CURRENT (July 2000) U.S. export regulations this software is
eligible for export from the U.S. and can be downloaded by or
otherwise exported or reexported worldwide EXCEPT to U.S. embargoed
destinations which include Cuba, Iraq, Libya, North Korea, Iran,
Syria, Sudan, Afghanistan and any other country to which the U.S.
has embargoed goods and services.
_____________________________________________________________________
Copyright (c) 1996-2000 Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
* Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
1 Introduction to CDSA1.1 What
Is CDSA?The
Common Data Security Architecture (CDSA) is a multiplatform, industry-standard
security infrastructure. Starting with Version 7.3-1, Compaq provides CDSA
as a part of the OpenVMS Alpha operating system. CDSA is compatible with OpenVMS
Alpha Version 7.2-2 and higher.
CDSA
provides a stable, standards-based programming interface that enables applications
to access operating system security services. With CDSA, developers can create
cross-platform, security-enabled applications. Security services, such as
cryptography and other public key operations, are available through a dynamically
extensible interface to a set of plug-in application programming interface
modules (API functions). These modules can be supplemented or changed as
business needs and technologies evolve.
CDSA is security middleware that provides flexible
mix-and-match solutions across a variety of applications and security services.
CDSA insulates application developers from the issues of incorporating security
into applications, freeing them to focus on the applications themselves. The
security underpinnings are transparent to the user.
CDSA
was originally developed by Intel® Architecture Labs and was released to the OpenSource
community in May 2000. Compaq’s CDSA implementation is based on the
Intel® V2.0
Release 3 reference platform, which implements CDSA V2.0 with Corrigenda,
as defined in The Open Group’s Technical
Standard C914, May 2000.
1.1.1 CDSA Overview
CDSA
contains the following components:
• The Common Security Services
Manager (CSSM) shared library (in SYS$SHARE:CDSA$INCSSM300_SHR.EXE), to which
applications can link to obtain security services. CSSM is the heart of CDSA.
It defines both the API and the service provider interface (SPI) for plug-in
security service modules. CSSM includes a set of core services that are common
to all categories of security services. These services perform functions such
as integrity verification and authentication.
Available
types of plug-in modules include cryptographic services (CSP), certificate
library (CL), data library (DL), trust policy (TP), and authorization computation
(AC).
Applications call functions in the CSSM API, which
is fully specified by the CDSA Technical Standard (located at http://www.opengroup.org/onlinepubs/009609799/).
API function names are prefaced with CSSM_ and are sometimes followed by the
designation of the module that will actually handle the request. For instance,
an application calls CSSM_DL_DbOpen to direct a DL module to open a data store.
The associated service provider interface (SPI) for this module is DL_DbOpen.
An application begins by initializing its connection
to CSSM using the CSSM_Init routine. The application might use Module Directory
Services (MDS) to query for available modules and their supported functionality,
or it might hardcode to a particular module’s global unique identifier
(GUID). The application loads the desired module using the CSSM_ModuleLoad
routine and then attaches to it using the CSSM_ModuleAttach routine.
• The header files (in CDSA_SYSDIR:[INCLUDES]*.H)
that define the CSSM API.
• Module Directory Services (MDS), which
are used by applications to locate service providers.
• A set of Cryptographic Service
Provider (CSP) modules that provide many popular encryption algorithms. The
CSPs are described in Section 1.1.2.
Figure 1–1 The Common Data Security Architecture Extensibility
of CDSA through the Elective Module Manager, shown at the far right of the
figure, is not currently supported.
Chapter 3 describes two sample C programs that
illustrate the use of CDSA.
1.1.2 Overview of CSP
The Cryptographic Service Providers (CSPs) are
add-in modules to the Common Security Services Manager (CSSM). CSPs perform
cryptographic operations and securely store cryptographic keys for the applications
that call them through the CSSM API.
The security services API functions that are defined
by the CSP Module Manager include the following service categories:
SignData
VerifyData
DigestData
EncryptData
DecryptData
GenerateKeyPair
GenerateRandom
WrapKey
UnwrapKey
Applications call these CSPs to provide authentication,
data integrity, data and communication privacy, and nonrepudiation of messages
to users.
Before an application calls a CSP to perform a
cryptographic operation, it uses the Module Directory Service (MDS) to determine
which CSPs are available on the system and what services they provide. The
application uses this information to determine which CSP to use.
The
remaining sections discuss the following topics:
Chapter 3 provides an example of how to use MDS.
1.1.2.1 Establishing
a Session
An application establishes an attach session to
select a particular CSP. Once attached, the application can initiate a cryptographic
login session with the CSP. The application requests additional credentials,
such as a passphrase or PIN, to gain access to specific keys and services
managed by the CSP.
Within a module attach session or a cryptographic
login session, an application creates, uses, and discards cryptographic contexts.
A cryptographic context carries the parameters required to perform a cryptographic
service. The cryptographic context can be used for the following:
• A one-step cryptographic operation,
in which only one call is needed to obtain the result.
• A cryptographic session of
a multistaged cryptographic service, in which an initialization call is followed
by one or more update calls, ending with a completion (final) call. For most
cryptographic operations, the result is available after the final function
completes its execution. An exception is staged encryption/decryption, in
which each update call generates a portion of the result.
Depending
on the class of cryptographic operations, individualized attributes are available
for the cryptographic context. In addition to specifying an algorithm when
creating the context, the application can also initialize a session key, pass
an initialization vector, or pass padding information to complete the description
of the session. A successful return value from the create function indicates
that the desired CSP is available.
Functions are also provided to manage the created
context. The cryptographic context contains most or all of the input parameters
required for an operation. Some cryptographic service functions accept input
parameters in addition to the CSP handle and the context handle. These input
parameters always take precedence over any duplicate or conflicting parameters
in the cryptographic context. When a context is no longer required, the application
calls a DeleteContext function. Resources allocated for that context can then
be reclaimed by the operating system.
CSPs implement many algorithms, including the following,
in one or more modes:
• Bulk encryption algorithm: DES, Triple
DES, RC2, RC4, RC5
• Digital signature algorithm: RSA,
DSS
• Key negotiation algorithm: Diffie-Hellman,
DSA
• Cryptographic hash algorithm: MD4,
MD5, SHA
CSPs also provide the following services:
• Unique identification number: hard
coded or random generated
• Random number generator: attended
and unattended
• Encrypted data: symmetric keys and
private keys
1.1.2.2 Defining a Security Context
The application’s associated security context
defines parameter values for the low-level variables that control the details
of cryptographic operations. For example, an application issuing a request
to the EncryptData call can reference a security context that defines the
following parameters:
• The algorithm to be used (such as
DES)
• Algorithm-specific parameters (such
as key length)
• The object on which the operation
is conducted (such as a set of buffers)
• The cryptographic variables
(such as the key)
Most applications use default (predefined) contexts.
Typically, a distinct context is used for encrypting, hashing, and signing.
For an initialized application, these contexts change little, if at all, during
the application’s execution or between executions. This allows the application
developer to implement security by manipulating certificates, using previously
defined security contexts, and maintaining a high-level view of security operations.
1.1.2.3 KeysIn CDSA, cryptographic keys
are of two types: public and private. These two types are used together.
A public key is for encrypting messages. It is available to multiple users
(for example, the public) and, therefore, is not secret. A private key is
for deciphering or verifying (by digitally signing) messages that have been
encrypted with the public key. The private key is kept secret by its owner.
Every CSP implements its own secure, persistent
storage and management of private keys. To support chains of trust across
application domains, CSPs support importing and exporting of public and private
keys among remote and possibly foreign systems. To transfer keys, the CSP
must be able to convert one key format into any other key format and to secure
the transfer of private and symmetric keys.
Each CSP is responsible for securely storing the
private keys it generates or imports from other sources. Additional storage-related
operations include retrieving a private key when given its corresponding public
key and wrapping private keys as key blobs for secure exportation to other
systems.
On an OpenVMS Alpha system, the CSP stores private
key files in EAYCSP.PRI and MAF_BSAFE.PRI. The protections on the key files
are OWNER:READ,WRITE,DELETE. Any user-specific CDSA files are in the [.CDSA.COMPAQ]
subdirectory in the user’s login directory.
PKI
The
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is the state-of-the-art method, ultimately
to be applied worldwide, for secure and confidential electronic transactions.
It employs public and private keys. The two PKI algorithms in widespread use are:
For
RSA-based algorithms, CDSA uses the PKCS#1 standard for key representation.
For DSA-based algorithms, no organization has published a standard. CDSA’s
representation of the DSA key is based on the DSA algorithm definitions in
the FIPS 186 and FIPS 186a standards.
A DSA public key is represented as a BER-encoding
of a sequence list that contains the following:
PrimeModulus;
/* p */
PrimeDivisor; /* q */
OrderQ; /* g */
PublicKey; /* y */
A DSA private key is represented as a BER-encoded
sequence list that contains the following:
PrimeModulus; /* p */
PrimeDivisor; /* q */
OrderQ; /* g */
PrivateKey; /* x */
These key components are defined as follows by
FIPS 186 and FIPS 186a:
• PrimeModulus. This is the public prime
modulus.
p = A prime modulus, where 2L-1 <
p < 2L for 512 <= L <= 1024,
and L is a multiple of 64.
• PrimeDivisor. Another public prime
number dividing (p-1).
q = A prime divisor of p-1, where 2159 <
q < 2160
• OrderQ. This public number
has order q mod p.
g = h (p-1)/q
mod p, where h is any integer with 1 < h < p-1, such that h (p-1) /q
mod p > 1.
• PrivateKey. The private key.
x = a pseudorandomly generated integer with 0 <
x < q.
• PublicKey. The public key.
y = gx mod
p.
For a better display of these equations, refer
to the CDSA Technical Standard, available
from The Open Group.
A DSA-wrapped private key is defined by the PKCS#8
specification. The PKCS#8 standard specifies the wrapped key format resulting
from encoding an algorithm OID with an encoded private key.
For
additional information about CDSA, visit the following web sites:
http://sourceforge.net/projects/cdsa
http://developer.intel.com/IAL/security 2 Installation and Initialization
This chapter gives important information about
CDSA installation and initialization.
Please note:
• Section
2.1 applies only to OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.3-1. • Section
2.2 applies only to OpenVMS Alpha Versions 7.3 and 7.2-2.  Note
NoteBecause
of the number of opened files used by CDSA, you should increase your FILLM
process quota by 100 before you initialize or use CDSA. You
must have SYSPRV privilege to initialize CDSA. You do not need SYSPRV to use
CDSA.
2.1 Installation
of CDSA on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.3-1
Installation of CDSA occurs automatically when
you install the OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.3-1 operating system. However, you
must consider the following important points.
2.1.1 CDSA
Setup and InitializationAlthough
the CDSA installation is part of the OpenVMS Alpha V7.3-1 installation, setup
and initialization of CDSA are not part of that installation. Before you
can use CDSA, you must perform the following manual procedure, for which you
must have SYSPRV privilege. Enter the following command: $ @SYS$STARTUP:CDSA$INITIALIZE
If
the procedure encounters database inconsistency, you will receive the following
message:
The existing CDSA configuration on this system is
corrupt.
If this occurs, you can recover by deleting the
CDSA_SYSDIR:[CDSAFFDB] and CDSA_SYSDIR:[REGISTRY...] directories and rerunning
the CDSA initialization procedure. However, you will lose any CDSA information
that was stored previously.
When a new version of CDSA is installed (for example,
in an upgrade from a field test to a production version, or an upgrade to
a new version of OpenVMS), the CDSA initialization procedure must be rerun.
Any CDSA application should be shut down before you rerun the initialization
procedure.
It is not necessary to rerun the initialization
procedure when the system is rebooted, and therefore it is not necessary to
add the initialization to the OpenVMS startup procedures.
The CDSA$INITIALIZE procedure
can take 5 minutes or more, depending on your processor and disk speeds. When
the procedure is run interactively, you will see system messages similar to
the following: $ @sys$startup:cdsa$initialize
Installing CDSA
*** Installing MDS
MDS installed successfully.
*** Installing CSSM
Module installed successfully.
*** Installing FFDL
Module installed successfully.
*** Installing 509CL
.
.
.
CDSA Initialization complete
2.1.2 Warning
Against Uninstalling CDSA from OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.3–1
The
POLYCENTER Software Installation utility command PRODUCT REMOVE is not supported
for CDSA on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.3-1, even though there is an apparent
option to remove CDSA. (This option is due to the use of the POLYCENTER Software
Installation utility in the installation.) CDSA is installed together with
the operating system and is tightly bound with it. An attempt to remove it
from Version 7.3-1 would not work cleanly and could create other undesirable
side effects. An attempt to remove CDSA results in the following message:
%PCSI-E-HRDREF, product CPQ AXPVMS CDSA Vx.x is
referenced by DEC AXPVMS OPENVMS V7.3-1
-PCSI-E-HRDRF1, the two products are tightly bound
by this software dependency
2.2 Installation
on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.3 or 7.2-2
On OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.3 or 7.2-2, CDSA is
not included in the operating system installation. However, CDSA is compatible
with these versions and can be installed separately.
Use
the command PRODUCT INSTALL to install CDSA. The following is a log of a
CDSA installation:
$ product install cdsa
The following product has been selected:
CPQ AXPVMS CDSA V1.0 Layered Product
Do you want to continue? [YES]
Configuration phase starting ...
You will be asked to choose options, if any, for each selected product and for
any products that may be installed to satisfy software dependency requirements.
CPQ AXPVMS CDSA V1.0
Do you want the defaults for all options? [YES]
Do you want to review the options? [NO]
Execution phase starting ...
The following product will be installed to destination:
CPQ AXPVMS CDSA V1.0 DISK$SYSTEM:[VMS$COMMON.]
Portion done:
0%...10%...20%...30%...40%...50%...60%...70%...80%...90%...100%
The following product has been installed:
CPQ AXPVMS CDSA V1.0 Layered Product
CPQ AXPVMS CDSA V1.0
CDSA requires post-installation work on OpenVMS V7.2-2 and V7.3
In order to to complete the installation of CDSA, you need to add the
following line to the system startup file:
$ @SYS$STARTUP:CDSA$INSTALL_IMAGES.COM
In addition, you need to add the following logical name definition to
SYS$MANAGER:SYLOGICALS.COM:
$ cdsa_sysdir = f$trnlnm("SYS$COMMON") - "]" + "CDSA.]"
$ Define/system/exec/trans=conc cdsa_sysdir ’cdsa_sysdir
Prior to the first time that CDSA is used, CDSA must be initialized, on a
one-time basis. To accomplish this, execute the following command file as
shown:
$ @SYS$STARTUP:CDSA$INITIALIZE
There is no need to add this to any of the system startup files, as the
initialization does NOT need to be rerun after a system restart.2.2.1 After
Installation on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.3 or 7.2–2Once
CDSA is installed on your OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.3 or 7.2-2 system, you must
perform a manual initialization procedure before you can use CDSA. For details,
see Section 2.1.1.
The installation places the CDSA Release Notes,
help file, and other documentation into the SYS$HELP directory.
To
complete the installation of CDSA, you need to add the following line to the
system startup file:
$ @SYS$STARTUP:CDSA$INSTALL_IMAGES.COM
In
addition, you need to add the following logical name definition to SYS$MANAGER:SYLOGICALS.COM:
$
cdsa_sysdir = f$trnlnm("SYS$COMMON") - "]" + "CDSA.]"
$
Define/system/exec/trans=conc cdsa_sysdir ’cdsa_sysdir
If
you want to remove CDSA from your OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.3 or 7.2–2
system, you can do so with the POLYCENTER Software Installation utility command
PRODUCT REMOVE. (This does not apply
to Version 7.3–1; see Section 2.1.2.)
3 CDSA Programming Concepts
This chapter provides an overview of programming
with CDSA on OpenVMS. This chapter should be read in conjunction with the
Intel Common Data Security Architecture Application
Developer’s Guide.
3.1 Overview of CDSA Programming
CDSA
programming on OpenVMS works much the same as on any other platform. The following
sections indicate differences.
3.1.1 Compiling
a CDSA Program
When you compile your program, you need to add
the /INCLUDE=CDSA_SYSDIR:[INCLUDES] qualifier to your compiler command line.
For example (taken from the BUILD_DES.COM example in this chapter):
$
cc/list/include=cdsa_sysdir:[includes]/prefix=all do_des
3.1.2 Linking a CDSA Program
Most CDSA applications must link with SYS$SHARE:CDSA$INCSSM300_SHR.EXE.
If the application uses MDS, you might need to include SYS$SHARE:CDSA$MDS300_SHR.EXE
and SYS$SHARE:CDSA$MDS_UTIL_API.OLB as well.
Because CDSA routines are located in shareable
libraries, use of a link options file is recommended. For details about using
link options files, refer to the OpenVMS
Linker Utility Manual. The CDSA example programs described in this
chapter provide examples of using link options files for CDSA applications.
3.1.3 Pointer Validation Policy
CDSA
on OpenVMS has set the Pointer Validation Policy to be PVC_POLICY_SPI.
Return addresses are checked across the CSSM service provider interface (SPI)
boundary but not across the application boundary. This value is a parameter
(PvcPolicy) that is passed to CSSM_Init and must be correct. For this version
of CDSA, the only valid value of PvcPolicy is 2 (PVC validation is performed
on SPI modules). This functionality is expected to be expanded in a future
version to allow optional validation of application modules as well. For more
information about pointer validation checking, see the description of the
CSSM_Init API.
3.2 CDSA
Example Programs
This section describes two example CDSA programs.
3.2.1 DES Encryption/Decryption Example
This
example is a simple DES encryption/decryption program that uses CDSA. The
DES example includes two source files (DES.C and DO_DES.C) and two build files
(BUILD_DES.COM and DES.OPT).
Before you run this program, you must initialize
CDSA, unless it has already been initialized. For the initialization procedure,
see Section 2.1.1.
After you enter the @SYS$STARTUP:CDSA$INITIALIZE
command, copy the example files into a local build area and then execute the
BUILD_DES command file, as follows:
$ COPY SYS$SYSROOT:[SYSHLP.EXAMPLES.CDSA.DES]*.* <local-build-area>
$ SET DEF <local-build-area>
$ @BUILD_DES
The resulting DES.EXE file can be run as a foreign
command. Define this file as follows:
$ DES :== $<local-build-area>DES.EXE
You
can now execute the program with the following options:
-e : encrypt with supplied key (requires -k switch)
-d : decrypt with supplied key (requires -k switch)
-h : specifies that the supplied key is a 16-character
hexadecimal number
-k "key" : (double quotation marks if ASCII and case
sensitive; no quotation marks if hex)For example, to encrypt MYFILE.TXT using an ASCII
key with the DES example program, enter the following command, using the
double quotation marks as shown if the key is case sensitive (if not, you
may omit them):
$ DES -e -k "xyzzy" MYFILE.TXT MYFILE.DES
To
decrypt the same file, enter the following command:
$ DES -d -k "xyzzy" MYFILE.DES MYFILE.TXT
To
encrypt or decrypt with a hexadecimal key, use the -h switch and make sure
the key length is exactly 16 typed characters (8 hexadecimal bytes). No quotation
marks, either single or double, are allowed. For example:,
$ DES -e -k 012abcde012abcde -h MYFILE.TXT MYFILE.DES
$ DES -d -k 012abcde012abcde -h MYFILE.DES MYFILE.TXT
3.2.2 MDS Programming Example
This
program uses some of the MDS and CSSM services of CDSA. The MDS example includes
two source files (DECODE_CDSA_ERRORS.C and MDS_EXAMPLE.C) and two build files
(BUILD_MDS_EXAMPLE.COM and MDS_EXAMPLE.OPT).
The program follows the descriptions and code fragments
from the Intel Common Data Security Architecture
Application Developer’s Guide.
Before you run this program, you must initialize
CDSA, unless it has already been initialized. For the initialization procedure,
see Section 2.1.1.
Build the MDS example program by copying the example
files into a local build area and then executing the BUILD_MDS_EXAMPLE command
file, as follows:
$ COPY SYS$SYSROOT:[SYSHLP.EXAMPLES.CDSA.MDS]*.* <local-build-area>
$ SET DEF <local-build-area>
$ @BUILD_MDS_EXAMPLE
The resulting MDS_EXAMPLE.EXE file takes no parameters
and can be executed as follows:
$ RUN <local-build-area>MDS_EXAMPLE
The
following is an excerpt of output from the program:
$ run MDS_EXAMPLE.EXE
Module 0) Name: SSLeay Crypto Based CSP
Module 0) ModuleGuid: {67ef50d0-fe74-11d2-a8e6-0090271d266f}
Module 0) Version: 3.1
Module 0) CompatibleCSSMVersion: 2.1
Module 0) Description: SSLeay Crypto Based CSP
Module 0) Vendor: Compaq Computer Corporation
Module 0) Flags: 0x0
Module 0) ServiceMask: 0x2
Service 0) Description: SSLeay Crypto Based CSP
Service 0) Type: CSSM_SERVICE_CSP
Service 0) Flags: 0x0
SubService 0) ModuleType: 0
SubService 0) SubServiceId: 0
This is a SOFTWARE subservice with 10 capabilities
Context Type: CSSM_ALGCLASS_RANDOMGEN
Algorithm Type: CSSM_ALGID_MD5Random
Attribute Type: CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_BLOCK_SIZE
Attribute Type: CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_DESCRIPTION
Context Type: CSSM_ALGCLASS_DIGEST
Algorithm Type: CSSM_ALGID_MD5
Attribute Type: CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_OUTPUT_SIZE
Attribute Type: CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_DESCRIPTION
Context Type: CSSM_ALGCLASS_DIGEST
Algorithm Type: CSSM_ALGID_SHA1
Attribute Type: CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_OUTPUT_SIZE
Attribute Type: CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_DESCRIPTION
Context Type: CSSM_ALGCLASS_KEYGEN
Algorithm Type: CSSM_ALGID_DSA
Attribute Type: CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_KEY_LENGTH_RANGE
Attribute Type: CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_DESCRIPTION
Attribute Type: CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_KEYUSAGE
Context Type: CSSM_ALGCLASS_SIGNATURE. . .
3.3 CDSA Error Resolution
The MDS example program provides two special routines
for deciphering CDSA error codes. Because the CDSA include file that specifies
error codes (CDSA_SYSDIR:[INCLUDES]CSSMERR.H) does not allow for easy translation
from the numeric code to the associated error string, these routines can make
the job of debugging a CDSA application easier. These routines are as follows:
Decode_CDSA_Error
NAME
Decode_CDSA_Error
Decode_CDSA_Error - Translates CDSA error code to
string
SYNOPSIS
#include <cssmerr.h>
API:
void Decode_CDSA_Error(Error_Code,
Error_Label_String,Error_String)
CSSM_RETURN Error_Code;
char *Error_Label_String;
char *Error_String;
DESCRIPTION
This function accepts a CDSA numeric error code, and returns two
strings: The ASCII name of the error, and a description of the error.
RETURN VALUE
None
Print_CDSA_Error
NAME
Print_CDSA_Error
Print_CDSA_Error - Prints CDSA error message text
SYNOPSIS
#include <cssmerr.h>
API:
void Print_CDSA_Error(Error_Code)
CSSM_RETURN Error_Code;
DESCRIPTION
This function accepts a CDSA numeric error code, calls Decode_CDSA_Error,
and prints the resulting strings to SYS$OUTPUT.
RETURN VALUE
NoneAPI Functions
This reference section contains descriptions of
the CDSA API functions.
These descriptions are also available from online
help. To access help, enter the HELP CDSA command at the system prompt.
The
MDSUTIL API functions are a special group of functions described in the following
paragraphs.
MDS Utility Library API Functions
Although
the MDS API is a required part of any CDSA implementation, the MDSUTIL functions
are not. This library of functions was provided with the Intel CDSA reference
implementation to encapsulate many common queries that applications typically
make to MDS. CDSA on OpenVMS implements the Intel CDSA version of the MDS
utility library. Other vendors may supply their own utility libraries built
on top of MDS.
To use the MDS utility library, you must include
two header files, MDS_UTIL_API.H and MDS_UTIL_HELPER.H, which are in the CDSA_SYDIR:[INCLUDES]
directory. You must also link with the library files CDSA$MDS300_SHR.EXE
and CDSA$MDS_UTIL_API.OLB, which are located in SYS$SHARE.
For
further information, see the Intel Common
Data Security Architecture Application Developer’s Guide, Chapter
2 (Module Directory Services), under the heading MDS Utility Library.
API
Functions Not Currently Supported
The following API functions are not currently supported:
• CSP_EventNotify
• DeregisterDispatchTable
• EventNotifyManager
• Initialize
• MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall
• MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall
• MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall
• MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall
• ModuleManagerAuthenticate
• RefreshFunctionTable
• RegisterDispatchTable
• Terminate
AC_AuthCompute – Compute authorization (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMACI CSSM_AC_AuthCompute
(CSSM_AC_HANDLE ACHandle,
const CSSM_TUPLEGROUP *BaseAuthorizations,
const CSSM_TUPLEGROUP *Credentials,
uint32 NumberOfRequestors,
const CSSM_LIST *Requestors,
const CSSM_LIST *RequestedAuthorizationPeriod,
const CSSM_LIST *RequestedAuthorization,
CSSM_TUPLEGROUP_PTR AuthorizationResult)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMACI AC_AuthCompute
(CSSM_AC_HANDLE ACHandle,
const CSSM_TUPLEGROUP *BaseAuthorizations,
const CSSM_TUPLEGROUP *Credentials,
uint32 NumberOfRequestors,
const CSSM_LIST *Requestors,
const CSSM_LIST *RequestedAuthorizationPeriod,
const CSSM_LIST *RequestedAuthorization,
CSSM_TUPLEGROUP_PTR AuthorizationResult)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
ACHandle (input)
The handle that describes the authorization computation
module used to perform this function.
BaseAuthorizations (input)
A pointer to a CSSM_TUPLEGROUP containing at least
one ACL certificate, specifying the authorization granted to certain root
keys, named entities or combinations thereof. A NULL group of BaseAuthorizations always
results in a NULL AuthorizationResult.
Credentials (input/optional)
A pointer to a CSSM_TUPLEGROUP containing a group
of certificates, in TUPLE form. The tuple-certificates define the delegation
of authorizations from the BaseAuthorizations to the Requestors. If no additional authorization-granting tuples
are provided, then this value is NULL and the BaseAuthorizations are the only source of trusted authorizations
used as input to the authorization computation.
NumberOfRequestors (input)
The number of entries in the Requestors array.
Requestors (input)
A pointer to a list of requestors that define the "who"
portion of the request. The list can be of type CSSM_LIST_TYPE_SEXPR. Typical
exhibits include:
• Public keys
• Hashes of keys
• Hashes of other objects offered for
proof.
RequestedAuthorizationPeriod (input/optional)
A
list defining a validity period or NULL (implying "all time"). This
is the "when" portion of the request.
If
the list is of type CSSM_LIST_TYPE_SEXPR, then the validity interval is specified
as a two-element list containing the values ((not-before <date1>)(not-after <date2
>)). Note that each element is a two-element sublist. The <date> is represented
by an ASCII byte-string, in the format (for example) "1998-11-24_15:06:16"
and is assumed to be GMT. Open-ended time intervals are specified by omitting
either of the interval ends. For example, ((not-before 1997-1-1_00:00:0))
specifies all dates and times beginning on January 1, 1997 going forward indefinitely.
For programming convenience, when testing for authorization at a single point
in time, the date is represented by a one-element list containing (<date>).
RequestedAuthorization (input)
A list defining the "what" portion of
the authorization being requested.
If the list is of type CSSM_LIST_TYPE_SEXPR, then
the list presents an authorization request in SPKI format. If a specific authorization
is being requested, then this input is a two-element SEXPR list containing
(tag <req>). The valid values for <req> are application-specific. If
this is a request to derive all possible authorizations based on the BaseAuthorizations, Credentials, and Requestors, then this input
value must be the two-element list containing (tag (*)). This list corresponds
to "all authorizations". With this input, the function tests the
provided ACL and certificates against the Requestors (and possibly RequestedAuthorizationPeriod) to yield all authorizations for which the provided Exhibits qualify.
AuthorizationResult (output)
A CSSM_TUPLEGROUP structure, giving the result
of the authorization computation. Typically there will be one result, but
there could be as many as there are entries in the BaseAuthorizations. Each of these results says, in effect: "for
this machine, under this ACL and the provided certificates, relative to the
specified Requestors,
the following authorizations have been deduced". Those authorizations
are available only on the current platform (and possibly only for the application
providing the ACL), and are therefore in the form of an ACL. They are not
intended to be used by any other machine or application instance, necessarily,
and need to be converted into certificates signed by some private key available
to the caller if they are to be so used.
This
function performs an authorization computation and returns the results as
a group of tuple certificates. The computation is based on the following input
values:
Requestors
One
or more items that identify the requestor. These items are matched against
subject fields in BaseAuthorizations or Credentials. These will
be of any form that occurs in an ACL or certificate, and the class of entries
is extensible. AuthCompute uses
these fields to compare against Subject fields of TUPLES but does not interpret them,
so it does not need to be aware of these extensions. Requestors, taken together with RequestedAuthorization and RequestedAuthorizationPeriod, form request tuples of the form "who requests
what, when." Requestors can
be public keys that verify some signed request, hashes of objects submitted
for proof of permission, etc. In general, there will be only one Requestor, typically the
public key of some keyholder signing a request or authenticating a connection.
RequestedAuthorization
The
authorization against which the Requestors are being tested in this computation.
RequestedAuthorizationPeriod
The time range of an authorization computation.
BaseAuthorizations
The
group of ACL entries (unsigned certificates) provided as the basis for this
computation.
Credentials
A
group of tuple-certificates used with the BaseAuthorizations to grant authorizations to the Requestors.
Kind of Subject |
Example Requestor |
Public
key |
(public-key
(rsa-pkcs1-sha1 (e #03#) (n ##))) |
Hash
of object, key, template, etc. |
(hash
md5 #900150983cd24fb0d6963f7d28e17f72#) |
The most likely Requestor is a public key that signs a request. In common
practice there will be one Requestor per computation, but it is possible for
an ACL or certificate to require multiple signatures or other forms of identification
before an action is authorized. In that case, there must be multiple Requestors. This function
can be used in the following modes:
• To verify the authorization
of a specific request, backed up by specific Requestors
• To compute the set of authorizations
that a particular set of Requestors has
been granted by the BaseAuthorizations and Credentials.
When using this function to verify an authorization,
the RequestedAuthorization is
the specific authorization being requested and the RequestedAuthorizationPeriod gives the date and time of that request (typically
the current date and time) using both NOT_BEFORE and NOT_AFTER dates. The
result, if any, should be an ACL entry with the same authorization that was
requested. If such an ACL entry is produced by the computation, then the request
is authorized.
Requested
Authorization Example |
(http
http://private.cdsa.hp.com/local-data.html ) |
(ftp
ftp://private.cdsa.hp.com/users/cme/private/test.txt write) |
Requested
Authorization Period Example |
(valid
(not-before "1999-07-28_17:00:44") (not-after "1999-07-28_17:00:44")) |
When using this function to compute the full set
of possible authorizations from a set of credentials, rather than to verify
a specific access request, the inputs should be of the following form:
• RequestedAuthorizationPeriod is either an empty list or the list "valid", indicating "all
time".
• RequestedAuthorization is the list "*", indicating all possible
authorizations.
The result of this computation, if any, will be
one or more ACL entries representing all the granted authorizations for the
indicated requestor.
The scope of ACLs output from this function is
limited to the local system. Each ACL should be interpreted to mean: "for
this machine, under these base authorization ACLs and the provided certificates,
relative to the specified requestors, the following authorizations have been
deduced". Those authorizations are available only on the current platform
(and possibly only for the application providing the ACL) and are therefore
in the form of an ACL. They are not intended to be used by any other machine
or application instance. However, the resulting ACLs can be transferred and
used outside of the local scope by an entity with authority in the target
scope/environment. The transfer and use is a three-step process:
1. Convert the ACL into one or more certificates.
The certificates must be signed by some private key with appropriate authority
in the target scope/environment.
2. Transfer the certificates to the target
environment.
3. Use the signed certificates as input Credentials to this function
in the target scope/environment.
If the function is successful, check (*AuthorizationResult)->NumCerts to
determine the precise number of authorizations granted by this computation.
If 0, then the requestors were
not authorized.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard. .
CSSMERR_AC_INVALID_BASE_ACLS
CSSMERR_AC_INVALID_ENCODING
CSSMERR_AC_INVALID_REQUESTOR
CSSMERR_AC_INVALID_REQUEST_DESCRIPTOR
CSSMERR_AC_INVALID_TUPLE_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_AC_INVALID_VALIDITY_PERIOD
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Reference
Pages
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup, CSSM_TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup
Functions
for the AC SPI:
TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup, TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup
AC_PassThrough:
CSSM_AC_PassThrough – Call exported module-specific
operations (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_AC_PassThrough
(CSSM_AC_HANDLE ACHandle,
CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
uint32 PassThroughId,
const void *InputParams,
void **OutputParams)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMACI AC_PassThrough
(CSSM_AC_HANDLE ACHandle,
CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
uint32 PassThroughId,
const void *InputParams,
void **OutputParams)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
ACHandle (input)
The handle that describes the authorization computation
module used to perform this function.
TPHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the trust policy module
that can be used by the authorization computation service to implement this
function. If no trust policy module is specified, the AC module uses an assumed
TP module, if required.
CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module that can be used to manipulate the subject certificate and
anchor certificates. If no certificate library module is specified, the AC
module uses an assumed CL module, if required.
CCHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the cryptographic context
containing a handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic Service Provider
module that can be used to perform cryptographic operations as required to
perform the requested operation. If no cryptographic context is specified,
the AC module uses an assumed cryptographic context and CSP module, if required.
DBList (input/optional)
A list of handle pairs specifying a data storage
library module and a data store managed by that module. These data stores
can contain certificates, CRLs, and policy objects for use by the AC module.
If no DL and DB handle pairs are specified, the AC module uses an assumed
DL module and an assumed data store for this operation.
PassThroughId (input)
An identifier assigned by the AC module to indicate
the exported function to perform.
InputParams (input)
A pointer to a module, implementation-specific
structure containing parameters to be interpreted in a function-specific manner
by the requested AC module. If the passthrough function requires access to a private key located
in the CSP referenced by CSPHandle,
then InputParams should
contain a passphrase, or a callback or cryptographic context that can be used
to obtain the passphrase.
OutputParams (output/optional)
A
pointer to a module, implementation-specific structure containing the output
data. The service provider will allocate the memory for this structure. The
application must free the memory for the structure.
This
function allows applications to call authorization computation module-specific
operations that have been exported. Such operations might include queries
or services specific to the domain represented by the AC module.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_AC_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_AC_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_AC_INVALID_DBLIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_AC_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_AC_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_AC_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_AC_INVALID_PASSTHROUGH_ID
CSSMERR_AC_INVALID_TP_HANDLE
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
CL_CertAbortCache:
CSSM_CL_CertAbortCache – Terminate a certificate cache
handle (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertAbortCache
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE CertHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertAbortCache
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE CertHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certificate library
module used to perform this function.
CertHandle (input)
The handle that identifies the cached certificate.
This
function terminates a certificate cache handle created and returned by the
function CSSM_CL_CertCache (CSSM
API) or CL_CertCache (CL
SPI). The Certificate Library module releases all cache space and state information
associated with the cached certificate.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CACHE_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Reference Pages
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertCache
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertCache
CL_CertAbortQuery:
CSSM_CL_CertAbortQuery function – Terminate a results handle
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertAbortQuery
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertAbortQuery
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
ResultsHandle (input)
A pointer to the handle that identifies the results
of a CSSM_CL_GetFieldValue (CSSM
API), or CL_GetFieldValue (CLI
SPI) request.
This
function terminates a results handle used to access multiple certificate fields
identified by a single OID. The ResultsHandle was created and returned by CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue (CL SPI), or CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue (CL SPI).
The CL releases all intermediate state information
associated with the repeating-value query. Once this function has been invoked,
the results handle is invalid.
Applications must invoke this function to terminate
the ResultsHandle.
Using CSSM_CL_CertGetNextFieldValue (CSSM
API), or CL_CertGetNextFieldValue (CL
SPI), or CSSM_CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue (CL SPI), to access all of the attributes named
by a single OID does not terminate the ResultsHandle.
This function can be invoked to terminate the results
handle without accessing all values identified by the single OID.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_RESULTS_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertGetNextFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue, CL_CertGetNextFieldValue, CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue
CL_CertCache:
CSSM_CL_CertCache – Cache a copy of a certificate
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertCache
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR CertHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertCache
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR CertHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certificate library
module used to perform this function.
Cert (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the encoded certificate.
CertHandle (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_HANDLE that should be used
in all future references to the cached certificate.
This
function caches a copy of a certificate for subsequent accesses using the
functions CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue (CL SPI), and CSSM_CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue (CL SPI).
The input certificate must be in an encoded representation.
The Certificate Library module can cache the certificate in any appropriate
internal representation. Parsed or incrementally parsed representations are
common. The selected representation is opaque to the caller.
The
application must call CSSM_CL_CertAbortCache (CSSM API), or CL_CertAbortCache (CL SPI), to remove the cached copy when additional get operations will not
be performed on the cached certificate.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERT_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertAbortQuery, CSSM_CL_CertAbortCache
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue, CL_CertAbortQuery, CL_CertAbortCache
CL_CertCreateTemplate:
CSSM_CL_CertCreateTemplate – Allocate and initialize memory
for a certificate template (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertCreateTemplate
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CertFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR CertTemplate)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CertCreateTemplate
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CertFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR CertTemplate)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certificate library
module used to perform this function.
NumberOfFields (input)
The number of certificate field values specified
in the CertFields.
CertFields (input)
A pointer to an array of OID/value pairs that identify
the field values to initialize a new certificate.
CertTemplate (output)
A pointer to a CSSM_DATA structure that will contain
the unsigned certificate template as a result of this function.
This
function allocates and initializes memory for an encoded certificate template
output in CertTemplate->Data.
The template values are specified by the input OID/value pairs contained in CertFields. The initialization
process includes encoding all certificate field values according to the certificate
type and certificate encoding supported by the certificate library module.
The
memory for CertTemplate->Data is
allocated by the service provider using the calling application’s memory
management routines. The application must deallocate the memory.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_NUMBER_OF_FIELDS
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertGetAllTemplateFields, CSSM_CL_CertSign
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertGetAllTemplateFields, CL_CertSign
CL_CertDescribeFormat:
CSSM_CL_CertDescribeFormat – Return a list of the CSSM_OID
values (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertDescribeFormat
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 *NumberOfOids,
CSSM_OID_PTR *OidList)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertDescribeFormat
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 *NumberOfOids,
CSSM_OID_PTR *OidList)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
NumberOfOids (output)
The length of the returned array of OIDs.
OidList (output)
A pointer to the array of CSSM_OIDs that represent
the supported certificate format. The OID list is allocated by the service
provider and must be deallocated by the application.
This
function returns a list of the CSSM_OID values this certificate library module
uses to name and reference fields of a certificate. Multiple CSSM_OID values
can correspond to a single field. These OIDs can be provided as input to CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue (CSSM
API), or CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue (CL
SPI), to retrieve field values from the certificate. The OID also implies
the data format of the returned value. When multiple OIDs name the same field
of a certificate, those OIDs have different return data formats associated
with them.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertGetAllFields, CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertGetAllFields, CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue, CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue
CL_CertGetAllFields:
CSSM_CL_CertGetAllFields – Return a list of input certificate
values (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertGetAllFields
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
uint32 *NumberOfFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *FieldList)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CertGetAllFields
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
uint32 *NumberOfFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *FieldList)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
Cert (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the certificate whose fields will be returned.
NumberOfFields (output)
The length of the returned array of fields.
FieldList (output)
A pointer to an array of CSSM_FIELD structures
that contain the values of all fields of the input certificate. The field
list is allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application
by calling CSSM_CL_FreeFields (CSSM
API), or CL_FreeFields (CL
SPI).
This
function returns a list of the values stored in the input certificate.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERT_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
For the CSSM API: CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertDescribeFormat, CSSM_CL_FreeFields
For
the CLI SPI: CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue, CL_CertDescribeFormat, CL_FreeFields
CL_CertGetAllTemplateFields CL_CertGetAllTemplateFields:
CSSM_CL_CertGetAllTemplateFields – Extract and return values stored
in CertTemplate (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertGetAllTemplateFields
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplate,
uint32 *NumberOfFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *CertFields)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CertGetAllTemplateFields
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplate,
uint32 *NumberOfFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *CertFields)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certificate library
module used to perform this function.
CertTemplate (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the packed, encoded certificate template.
NumberOfFields (output)
The length of the output array of fields.
CertFields (output)
A pointer to an array of CSSM_FIELD structures
which contains the OIDs and values of the fields of the input certificate
template.
This
function extracts and returns a copy of the values stored in the encoded CertTemplate. The memory
for the CertFields output
is allocated by the service provider using the calling application’s
memory management routines. The application must deallocate the memory by
calling CSSM_CL_FreeFields (CSSM
API), or CL_FreeFields (CL
SPI).
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_FreeFields, CSSM_CL_CertCreateTemplate
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_FreeFields, CL_CertCreateTemplate
CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue:
CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue – Return values from the cached
certificate (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE CertHandle,
const CSSM_OID *CertField,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR ResultsHandle,
uint32 *NumberOfMatchedFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *FieldValue)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE CertHandle,
const CSSM_OID *CertField,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR ResultsHandle,
uint32 *NumberOfMatchedFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *FieldValue)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
CertHandle (input)
A handle identifying a certificate that the application
has temporarily cached with the Certificate Library module. The referenced
certificate is searched for the field value named by CertField.
CertField (input)
A pointer to an object identifier that identifies
the field value to be extracted from the Cert.
ResultsHandle (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_HANDLE that should be used
to obtain any additional matching fields.
NumberOfMatchedFields (output)
The total number of fields that match the CertField OID. This count
includes the first match, which was returned by this function.
FieldValue (output)
A pointer to the structure containing the value
of the requested field. The structure and the field at I "(*FieldValue)->Data"
are allocated by the service provider. The CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_FreeFieldValue (CL SPI), function can be used to deallocate FieldValue and (*FieldValue)->Data.
This
function returns a single structure containing a set of field values from
the cached certificate identified by CertHandle. The selected fields are designated by the CSSM_OID
CertField and returned in the output parameter FieldValue. The OID also identifies the data format of the
values returned to the caller. If multiple OIDs designate the same certificate
field, then each such OID defines a distinct data format for the returned
values. The function CSSM_CL_CertDescribeFormat (CSSM API), or CL_CertDescribeFormat (CL SPI), provides a list of all CSSM_OID values
supported by a certificate library module for naming fields of a certificate.
The CertField OID can identify
a single occurrence of a set of certificate fields, or multiple occurrences
of a set of certificate fields. If the CertField OID matches more than one occurrence, this function
outputs the total number of matches and a ResultsHandle to be used as input to CSSM_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue (CSM API), or CertGetNextCachedFieldValue (CL SPI), to retrieve the remaining matches. The
first match is returned as the return value of this function.
This
function determines the complete set of matches. The number of matches and
the selected field values do not change between this function and subsequent
calls to CSSM_CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue (CL SPI).
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CACHE_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_CL_NO_FIELD_VALUES
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertAbortCache, CSSM_CL_CertAbortQuery, CSSM_CL_CertGetAllFields, CSSM_CL_CertDescribeFormat, CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue, CL_CertAbortCache, CL_CertAbortQuery, CL_CertGetAllFields, CL_CertDescribeFormat, CL_FreeFieldValue
CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue:
CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue – Return the value of the certificate
field (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
const CSSM_OID *CertField,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR ResultsHandle,
uint32 *NumberOfMatchedFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *Value)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
const CSSM_OID *CertField,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR ResultsHandle,
uint32 *NumberOfMatchedFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *Value)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
Cert (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the certificate.
CertField (input)
A pointer to an object identifier which identifies
the field value to be extracted from the Cert.
ResultsHandle (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_HANDLE that should be used
to obtain any additional matching fields.
NumberOfMatchedFields (output)
The total number of fields that match the CertField OID. This count
includes the first match, which was returned by this function.
Value (output)
A pointer to the structure containing the value
of the requested field. The structure and the field at I "(*Value)->Data"
are allocated by the service provider. The CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue (CSSM API) or CL_FreeFieldValue (CL SPI) function can be used to deallocate *Value and (*Value)->Data.
This
function returns the value of the certificate field designated by the CSSM_OID CertField. The OID also
identifies the data format for the field value returned to the caller. If
multiple OIDs name the same certificate field, then each such OID defines
a distinct data format for the returned field value. The function CSSM_CL_CertDescribeFormat (CSSM
API), or CL_CertDescribeFormat (CL
SPI), provides a list of all CSSM_OID values supported by a certificate library
module for naming fields of a certificate.
If more than one field matches the CertField OID, the first
matching field will be returned. The number of matching fields is an output
parameter, as is the ResultsHandle to
be used to retrieve the remaining matching fields.
The
set of matching fields is determined by this function. The number of matching
fields and the field values do not change between this function and subsequent
calls to CSSM_CL_CertGetNextFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CertGetNextFieldValue (CL SPI).
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERT_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_CL_NO_FIELD_VALUES
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertGetNextFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertAbortQuery, CSSM_CL_CertGetAllField, CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertDescribeFormat, CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertGetNextFieldValue, CL_CertAbortQuery, CL_CertGetAllField, CL_FreeFieldValue, CL_CertDescribeFormat, CL_FreeFieldValue
CL_CertGetKeyInfo:
CSSM_CL_CertGetKeyInfo – Return the public key and integral
information (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertGetKeyInfo
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
CSSM_KEY_PTR *Key)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CertGetKeyInfo
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
CSSM_KEY_PTR *Key)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
Cert (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the certificate from which to extract the public key information.
Key (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_KEY structure containing
the public key and possibly other key information. The CSSM_KEY structure
and its substructures are allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated
by the application.
This
function returns the public key and integral information about the key from
the specified certificate. The key structure returned is a compound object.
It can be used in any function requiring a key, such as creating a cryptographic
context.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERT_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue, CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue, CL_FreeFieldValue
CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue :
CSSM_CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue – Return the value of a certificate
field (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *FieldValue)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *FieldValue)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certificate library
module used to perform this function.
ResultsHandle (input)
The handle that identifies the results of a certificate
query.
FieldValue (output)
A pointer to the structure containing the value
of the requested field. The structure and the field at I "(*FieldValue)->Data"
are allocated by the service provider. The CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_FreeFieldValue (CL SPI) function can be used to deallocate *FieldValue and (*FieldValue)->Data.
This
function returns the value of a certificate field, when that field occurs
multiple times in a certificate. Certificates with repeated fields (such as
multiple signatures) have multiple field values corresponding to a single
OID. A call to the function CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue (CL SPI), returns a ResultsHandle identifying the size and values contained in the
result set. The CSSM_CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue (CSSMAPI), or CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue (CL SPI), function can be called repeatedly to
obtain these values, one at a time. The result set does not change in size
or value between calls to this function.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_RESULTS_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_NO_FIELD_VALUES
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertAbortCache, CSSM_CL_CertAbortQuery, CSSM_CL_CertGetAllFields, CSSM_CL_CertDescribeFormat, CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CL_CertAbortCache, CL_CertAbortQuery, CL_CertGetAllFields, CL_CertDescribeFormat, CL_FreeFieldValue
CL_CertGetNextFieldValue:
CSSM_CL_CertGetNextFieldValue – Return the value of a certificate
field (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertGetNextFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *Value)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CertGetNextFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *Value)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
ResultsHandle (input)
The handle that identifies the results of a certificate
query.
Value (output)
A pointer to the structure containing the value
of the requested field. The structure and the field at I "(*Value)->Data"
are allocated by the service provider. The CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue (CSSM API) or CL_FreeFieldValue (CL SPI), function can be used to deallocate *Value and (*Value)->Data.
This
function returns the value of a certificate field, when that field occurs
multiple times in a certificate. Certificates with repeated fields (such as
multiple signatures) have multiple field values corresponding to a single
OID. A call to the function CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue (CL SPI), returns a results handle identifying
the size and values contained in the result set. The CSSM_CL_CertGetNextFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CertGetNextFieldValue (CL SPI), function can be called repeatedly to
obtain these values, one at a time. The result set does not change in size
or value between calls to this function.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_RESULTS_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_NO_FIELD_VALUES
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertAbortQuery, CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue, CL_CertAbortQuery, CL_FreeFieldValue
CL_CertGroupFromVerifiedBundle CL_CertGroupFromVerifiedBundle:
CSSM_CL_CertGroupFromVerifiedBundle – Verify the signature of a bundle
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertGroupFromVerifiedBundle
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CERT_BUNDLE *CertBundle,
const CSSM_DATA *SignerCert,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *CertGroup)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CertGroupFromVerifiedBundle
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CERT_BUNDLE *CertBundle,
const CSSM_DATA *SignerCert,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *CertGroup)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
CCHandle (input/optional)
The handle of the cryptographic context to control
the verification operation.
CertBundle (input)
A structure containing a reference to a signed,
encoded bundle of certificates and to descriptors of the type and encoding
of the bundle. The bundled certificates are to be separated into a certificate
group (list of individual encoded certificates). If the bundle type and bundle
encoding are not specified, the add-in module might either attempt to decode
the bundle assuming a default type and encoding or might immediately fail.
SignerCert (input/optional)
The certificate to be used to verify the signature
on the certificate bundle. If the bundle is signed but this field is not specified,
then the module will assume a default certificate for verification.
CertGroup (output)
A pointer to the certificate group, represented
as an array of individual, encoded certificates. The certificate group and
CSSM_CERTGROUP substructures are allocated by the serivce provider and must
be deallocated by the application. The group contains all certificates contained
in the certificate bundle.
This
function accepts as input a certificate bundle (a codified and signed aggregation
of the certificates in the group), verifies the signature of the bundle (if
a signature is present), and returns a certificate group (as an array of individual
certificates) including every certificate contained in the bundle. The signature
on the certificate aggregate is verified using the cryptographic context and
possibly using the input signer certificate. The CL module embeds the knowledge
of the verification scope for the bundle types that it supports. A CL module’s
supported bundle types and encodings are available to applications by querying
the CSSM registry. The type and encoding of the certificate bundle must be
specified with the input bundle. If signature verification is successful,
the certificate aggregate will be parsed into a certificate group whose order
corresponds to the certificate aggregate ordering. This certificate group
will then be returned to the calling application.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_BUNDLE_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_BUNDLE_INFO
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERT_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertGroupToSignedBundle
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertGroupToSignedBundle
CL_CertGroupToSignedBundle CL_CertGroupToSignedBundle:
CSSM_CL_CertGroupToSignedBundle – Convert a certificate group
to a certificate bundle (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertGroupToSignedBundle
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBundle,
const CSSM_CERT_BUNDLE_HEADER *BundleInfo,
CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedBundle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CertGroupToSignedBundle
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBundle,
const CSSM_CERT_BUNDLE_HEADER *BundleInfo,
CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedBundle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
CCHandle (input/optional)
The handle of the cryptographic context to control
the signing operation. The operation will fail if a signature is required
for this type of bundle and the cryptographic context is not valid.
CertGroupToBundle (input)
An array of individual, encoded certificates. All
certificates in this list will be included in the resulting certificate bundle.
BundleInfo (input/optional)
A structure containing the type and encoding of
the bundle to be created. If the type and the encoding are not specified,
then the module will use a default bundle type and bundle encoding.
SignedBundle (output)
The function returns a pointer to a signed certificate
bundle containing all certificates in the certificate group. The bundle is
of the type and encoding requested by the caller or is the default type defined
by the library module if the BundleInfo was not specified by the caller. The SignedBundle->Data is allocated
by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
This
function accepts as input a certificate group (as an array of individual certificates)
and returns a certificate bundle (a codified and signed aggregation of the
certificates in the group). The certificate group will first be encoded according
to the BundleInfo input
by the user. If BundleInfo is
NULL, the library will perform a default encoding for its default bundle type.
If possible, the certificate group ordering will be maintained in this certificate
aggregate encoding. After encoding, the certificate aggregate will be signed
using the input context. The CL module embeds knowledge of the signing scope
for the bundle types it supports. The signature is then associated with the
certificate aggregate according to the bundle type and encoding rules and
is returned as a bundle to the calling application.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERT_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_BUNDLE_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_BUNDLE_INFO
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertGroupFromVerifiedBundle
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertGroupFromVerifiedBundle
: CSSM_CL_CertSign – Sign a certificate (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertSign
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplate,
const CSSM_FIELD *SignScope,
uint32 ScopeSize,
CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedCert)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CertSign
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplate,
const CSSM_FIELD *SignScope,
uint32 ScopeSize,
CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedCert)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
CCHandle (input)
A signature context defining the CSP, signing algorithm,
and private key that must be used to perform the operation. The passphrase
for the private key is also provided.
CertTemplate (input)
A pointer to a CSSM_DATA structure containing a
certificate template in the default format supported by this CL. The template
contains values that are currently contained in or will be contained in a
signed certificate.
SignScope (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_FIELD array containing the
OID/value pairs of the fields to be signed. A null input signs all the fields
provided by CertTemplate.
ScopeSize (input)
The number of entries in the SignScope list. If the sign scope is not specified, the
input value for scope size must be zero.
SignedCert (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the signed certificate.
This
function signs a certificate using the private key and signing algorithm specified
in the CCHandle.
The result is a signed, encoded certificate in SignedCert. The certificate field values are specified in
the input certificate template. The template is constructed using CSSM_CL_CertCreateTemplate (CSSM
API), or CL_CertCreateTemplate (CL
SPI). The template is in the default format for this CL.
The CCHandle must be a signature
context created using the function CSSM_CSP_CreateSignatureContext (CSSM API), or CSP_CreateSignatureContext (SPI). The context must specify the Cryptographic
Services Provider (CSP) module, the signing algorithm, and the signing key
that must be used to perform this operation. The context must also provide
the passphrase or a callback function to obtain the passphrase required to
access and use the private key.
The fields included in the signing operation are
identified by the OIDs in the optional SignScope array.
The memory for the SignedCert->Data output is allocated by the service provider using
the calling application’s memory management routines. The application
must deallocate the memory.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_SCOPE
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_NUMBER_OF_FIELDS
CSSMERR_CL_SCOPE_NOT_SUPPORTED
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertVerify, CSSM_CL_CertCreateTemplate
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertVerify, CL_CertCreateTemplate
CL_CertVerify:
CSSM_CL_CertVerify – Verify a signed certificate
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertVerify
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertToBeVerified,
const CSSM_DATA *SignerCert,
const CSSM_FIELD *VerifyScope,
uint32 ScopeSize)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertVerify
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertToBeVerified,
const CSSM_DATA *SignerCert,
const CSSM_FIELD *VerifyScope,
uint32 ScopeSize)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
CCHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation.
CertToBeVerified (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure with a certificate
containing at least one signature for verification. An unsigned certificate
template cannot be verified.
SignerCert (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the certificate used to sign the subject certificate. This certificate provides
the public key to use in the verification process and if the certificate being
verified contains multiple signatures, the signer’s certificate indicates
which signature is to be verified.
VerifyScope (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_FIELD array containing the
tag/value pairs of the fields to be used in verifying the signature. (This
should include all fields that were used to calculate the signature.) If the
verify scope is null, the certificate library module assumes that its default
set of certificate fields were used to calculate the signature, and those
same fields are used in the verification process.
ScopeSize (input)
The number of entries in the verify scope list.
If the verification scope is not specified, the input value for scope size
must be zero.
This
function verifies that the signed certificate has not been altered since it
was signed by the designated signer. Only one signature is verified by this
function. If the certificate to be verified includes multiple signatures,
this function must be applied once for each signature to be verified. This
function verifies a digital signature over the certificate fields specified
by VerifyScope.
If the verification scope fields are not specified, the function performs
verification using a preselected set of fields in the certificate.
The
caller can specify a Cryptographic Service Provider (CSP) and verification
algorithm that the CL can use to perform the verification. The handle for
the CSP is contained in the cryptographic context identified by CCHandle.
The
verification process requires that the caller must specify the necessary verification
algorithm parameters. These parameter values are specified in one of two locations:
• As a field value in the SignerCert parameter
• As a set of algorithm parameters contained
in the cryptographic context identified by CCHandle
If
both of the preceding arguments are supplied, a consistency check is performed
to ensure that they result in the same verification algorithm parameters.
If they are not consistent, an error is returned. If only one of the above
arguments is supplied, that argument is used to generate the verification
algorithm parameters. If no algorithm parameters are found, the certificate
cannot be verified and the operation fails.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERT_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_SCOPE
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_NUMBER_OF_FIELDS
CSSMERR_CL_SCOPE_NOT_SUPPORTED
CSSMERR_CL_VERIFICATION_FAILURE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertSign
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertSign
CL_CertVerifyWithKey:
CSSM_CL_CertVerifyWithKey – Verify
with a key (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CertVerifyWithKey
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertToBeVerified)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CertVerifyWithKey
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertToBeVerified)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certificate library
service module used to perform this function.
CCHandle (input)
A signature verification context defining the CSP,
verification algorithm, and public key that must be used to perform the operation.
CertToBeVerified (input)
A signed certificate whose signature is to be verified.
This
function verifies that the CertToBeVerified parameter was signed using a specific private
key and that the certificate has not been altered since it was signed using
that private key. The public key corresponding to the private signing key
is used in the verification process.
The CCHandle, must be a signature verification context created
using the function CSSM_CSP_CreateSignatureContext (CSSM API), or CSP_CreateSignatureContext (SPI). The context must specify the Cryptographic
Services Provider (CSP) module, the verification algorithm, and the public
verification key that must be used to perform this operation.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERT_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_CL_VERIFICATION_FAILURE
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CertVerify, CSSM_CL_CrlVerify
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CertVerify, CL_CrlVerify
CL_CrlAbortCache:
CSSM_CL_CrlAbortCache – Terminate a CRL cache handle
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlAbortCache
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE CrlHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlAbortCache
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE CrlHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certificate library
module used to perform this function.
CrlHandle (input)
The handle that identifies the cached CRL.
This
function terminates a CRL cache handle created and returned by the function CSSM_CL_CrlCache (CSSM API),
or CL_CrlCache (CL
SPI). The Certificate Library module releases all cache space and state information
associated with the cached CRL.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CACHE_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlCache
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CrlCache
CL_CrlAbortQuery:
CSSM_CL_CrlAbortQuery – Terminate a query (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlAbortQuery
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlAbortQuery
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
ResultsHandle (input)
The handle that identifies the results of a CRL
query.
This
function terminates the query initiated by CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue or CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue function (or their CL SPI equivalents), and allows
the CL to release all intermediate state information associated with the repeating-value get operation. Once this
function has been invoked, the results handle is invalid.
Applications
must invoke this function to terminate the ResultsHandle. Using CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue or CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue (or their CL SPI equivalents), to access all of
the attributes named by a single OID does not terminate the ResultsHandle. This function can be invoked to terminate the
results handle without accessing all of the values identified by the single
OID.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_RESULTS_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue
Functions
for the CL SPI:
CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue, CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue, CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue
CL_CrlAddCert:
CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert – Revoke an input certificate
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CrlEntryFields,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrl,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrl)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlAddCert
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CrlEntryFields,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrl,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrl)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation.
Cert (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the certificate to be revoked.
NumberOfFields (input)
The number of OID/value pairs specified in the
CrlEntryFields input parameter.
CrlEntryFields (input)
An array of OID/value pairs specifying the initial
values for descriptive data fields of the new CRL entry.
OldCrl (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the CRL to which the newly revoked certificate will be added.
NewCrl (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the updated CRL. The NewCrl->Data is
allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
This
function revokes the input certificate by adding a record representing the
certificate to the CRL. The values for the new entry in the CRL are specified
by the list of OID/value input pairs. The reason for revocation is a typical
value specified in the list. The new CRL entry is signed using the private
key and signing algorithm specified in the CCHandle.
The CCHandle must be a context created using the function CSSM_CSP_CreateSignatureContext (CSSM
API), or CSP_CreateSignatureContext (CL
SPI). The context must specify the Cryptographic Services Provider (CSP) module,
the signing algorithm, and the signing key that must be used to perform this
operation. The context must also provide the passphrase or a callback function
to obtain the passphrase required to access and use the private key.
The
operation is valid only if the CRL has not been closed by the process of signing
the CRL, by calling CSSM_CL_CrlSign (CSSM
API), or CL_CrlSign (CL
SPI). Once the CRL has been signed, entries cannot be added or removed.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERT_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_NUMBER_OF_FIELDS
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_CRL_ALREADY_SIGNED
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlRemoveCert
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CrlRemoveCert
CL_CrlCache: CSSM_CL_CrlCache – Cache a copy of a certificate revocation list (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlCache
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Crl,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR CrlHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlCache
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Crl,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR CrlHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certificate library
module used to perform this function.
Crl (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the encoded CRL.
CrlHandle (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_HANDLE that should be used
in all future references to the cached CRL.
This
function caches a copy of a CertificateRevocationList (CRL) for subsequent accesses using the functions CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue and CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue (or
their CL SPI equivalents).
The input CRL must be in an encoded representation.
The Certificate Library module can cache the CRL in any appropriate internal
representation. Parsed or incrementally parsed representations are common.
The selected representation is opaque to the caller.
The
application must call CSSM_CL_CrlCacheAbort (CSSM API), or CL_CrlCacheAbort (CL SPI), to remove the cached copy when additional get operations will not
be performed on the cached CRL.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_IsCertInCachedCrl, CSSM_CL_CrlAbortQuery, CSSM_CL_CrlAbortCache
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue, CL_IsCertInCachedCrl, CL_CrlAbortQuery, CL_CrlAbortCache
CL_CrlCreateTemplate:
CSSM_CL_CrlCreateTemplate – Create an unsigned, memory-resident
CRL (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlCreateTemplate
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CrlTemplate,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrl)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlCreateTemplate
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CrlTemplate,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrl)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
NumberOfFields (input)
The number of OID/value pairs specified in the
CrlTemplate input parameter.
CrlTemplate (input)
An array of OID/value pairs specifying the initial
values for descriptive data fields of the new CRL.
NewCrl (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the new CRL. The NewCrl-> Data is
allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
This
function creates an unsigned, memory-resident CRL. Fields in the CRL are initialized
with the descriptive data specified by the OID/value input pairs. The specified
OID/value pairs can initialize all or a subset of the general attribute fields
in the new CRL. Subsequent values can be set using the CSSM_CL_CrlSetFields (CSSM API) or the CL_CrlSetFields (CL SPI) function. The new CRL contains no revocation
records.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_NUMBER_OF_FIELDS
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlSetFields, CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert, CSSM_CL_CrlSign, CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CrlSetFields, CL_CrlAddCert, CL_CrlSign, CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue
CL_CrlDescribeFormat:
CSSM_CL_CrlDescribeFormat – Return a list of the CSSM_OID
values (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlDescribeFormat
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 *NumberOfOids,
CSSM_OID_PTR *OidList)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlDescribeFormat
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 *NumberOfOid,
CSSM_OID_PTR *OidList)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
NumberOfOids (output)
The length of the returned array of OIDs.
OidList (output)
A pointer to the array of CSSM_OIDs that represent
the supported CRL format. The OID list is allocated by the service provider
and must be deallocated by the application.
This
function returns a list of the CSSM_OID values the Certificate Library module
uses to name and reference fields of a CRL. Multiple CSSM_OID values can correspond
to a single field. These OIDs can be provided as input to CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue (CL SPI), calls to retrieve field values from
the CRL. The OID also implies the data format of the returned value. When
multiple OIDs name the same field of a CRL, those OIDs have different return
data formats associated with them.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
CL_CrlGetAllCachedRecordFields CL_CrlGetAllCachedRecordFields:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetAllCachedRecordFields – Return field values from a
CRL record (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlGetAllCachedRecordFields
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE CrlHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CrlRecordIndex,
uint32 *NumberOfFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *Fields)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlGetAllCachedRecordFields
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE CrlHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CrlRecordIndex,
uint32 *NumberOfFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *Fields)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
CrlHandle (input)
A handle identifying a CRL that the application
has temporarily cached with the Certificate Library module. The referenced
CRL must contain the CRL record identified by CrlRecordIndex.
CrlRecordIndex (input)
An index value identifying a particular revocation
record in a cached CRL.
NumberOfFields (output)
The number of OID-value pairs returned by this
function.
Fields (output)
A pointer to an array of CSSM_FIELD structures,
describing the contents of the preselected CRL record using OID-value pairs.
The field list is allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated
by the application by calling CSSM_CL_FreeFields (CSSM API), or CL_FreeFields (CL SPI).
This
function returns all field values from a prelocated, cached CRL record. The
scanned CRL record is identified by CrlRecordIndex, which is returned by the function CSSM_CL_IsCertInCachedCrl (CSSM
API), or CL_IsCertInCachedCrl (CL
SPI).
Fields are returned as a set of OID-value pairs.
The OID identifies the CRL record field and the data format of the value extracted
from that field. The Certificate Library module defines and uses a preferred
data format for returning field values in this function.
Each
CRL record may be digitally signed when it is added to the CRL using the function CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert (CSSM
API), or CL_CrlAddCert (CL
SPI). This function does not perform any signature verification on the CRL
record.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CACHE_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CRL_INDEX
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_IsCertInCachedCrl, CSSM_CL_CrlCache, CSSM_CL_CrlAbortCache, CSSM_CL_FreeFields
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_IsCertInCachedCrl, CL_CrlCache, CL_CrlAbortCache, CL_FreeFields
CL_CrlGetAllFields:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetAllFields – Get the field values from the
CRL (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlGetAllFields
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Crl,
uint32 *NumberOfCrlFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *CrlFields)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlGetAllFields
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Crl,
uint32 *NumberOfCrlFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *CrlFields)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
Crl (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure that contains
the encoded, packed CRL from which field values are to be extracted.
NumberOfCrlFields (output)
The number of entries in the array CrlFields.
CrlFields (output)
A pointer to an array of OID-value pairs that describe
the contents of the CRL. The extracted CRL fields are returned as the value
portion of each OID-value pair. The field list is allocated by the service
provider and must be deallocated by the application by calling CSSM_CL_FreeFields (CSSM
API), or CL_FreeFields (CL
SPI).
This
function returns one or more structures. Each structure contains a set of
field values from the encoded, packed CRL contained in Crl. Each structure is returned in the FieldValue entry of the
CSSM_FIELD structure CrlFields.
The parameter NumberOfCrlFields indicates
the number of returned structures.
The CRL can be signed or unsigned. This function
does not perform any signature verification on the CRL fields or the CRL records.
Each CRL record can be digitally signed when it is added to the CRL using
the function CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert (CSSM
API), or CL_CrlAddCert (CL
SPI).
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_FreeFields
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_FreeFields
CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue – Get field values from the cached
CRL (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE CrlHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CrlRecordIndex,
const CSSM_OID *CrlField,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR ResultsHandle,
uint32 *NumberOfMatchedFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *FieldValue)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE CrlHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CrlRecordIndex,
const CSSM_OID *CrlField,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR ResultsHandle,
uint32 *NumberOfMatchedFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *FieldValue)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
CrlHandle (input)
A handle identifying a CRL that the application
has temporarily cached with the Certificate Library module. The referenced
CRL is searched for the field values identified by CrlField.
CrlRecordIndex (input/optional)
An index value identifying a particular revocation
record in a cached CRL. If an index value is supplied, the scan for the field
values identified by CrlField is
limited to the preselected revocation record.
CrlField (input)
A pointer to an object identifier that identifies
the field value to be extracted from the CRL.
ResultsHandle (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_HANDLE that should be used
to obtain any additional matching fields.
NumberOfMatchedFields (output)
The total number of fields that match the CrlField OID. This count
includes the first match, which was returned by this function.
FieldValue (output)
A pointer to the structure containing the value
of the requested field. The structure and the field at I "(*FieldValue)->Data" are allocated by the service provider. The CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue (CSSM
API), or CL_FreeFieldValue (CL
SPI), function can be used to deallocate *FieldValue and (*FieldValue)->Data.
This
function returns a single structure containing a set of field values from
the cached CRL identified by CrlHandle parameter. The selected fields are designated
by the CSSM_OID CrlField parameter
and returned in the output parameter FieldValue. The OID also identifies the data format of the
values returned to the caller. If multiple OIDs designate the same CRL field,
then each such OID defines a distinct data format for the returned values.
The function CSSM_CL_CrlDescribeFormat (CSSM API), or CL_CrlDescribeFormat (CL SPI), provides a list of all CSSM_OID values
supported by a CL module for naming fields of a CRL.
The
search can be limited to a particular revocation record within the CRL. A
single record is identified by the CrlRecordIndex parameter, which is returned by the function CSSM_CL_IsCertInCachedCrl (CSSM
API), or CL_IsCertInCachedCrl (CL
SPI). If no record index is supplied, the search is initiated from the beginning
of the CRL.
The CRL can be signed or unsigned. This function
does not perform any signature verification on the CRL fields or the CRL records.
Each CRL record can be digitally signed when it is added to the CRL using
the function CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert (CSSM
API), or CL_CrlAddCert (CL
SPI). The caller can examine fields in the CRL and CRL records at any time
using this function.
The CrlField OID can identify a single occurrence of a set
of CRL fields or multiple occurrences of a set of CRL fields. If the CrlField OID matches more
than one occurrence, this function outputs the total number of matches and
a ResultsHandle to
be used as input to CSSM_CrlGetNextFieldValue (CSSM API), or CrlGetNextFieldValue (CL SPI), to retrieve the remaining matches. The
first match is returned as the return value of this function.
This
function determines the complete set of matches. The number of matches and
the selected field values do not change between this function and subsequent
calls to CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue (CSSM
API), or CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue (CL
SPI).
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CACHE_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CRL_INDEX
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_CL_NO_FIELD_VALUES
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_IsCertInCachedCrl, CSSM_CL_CrlAbortQuery, CSSM_CL_CrlCache, CSSM_CL_CrlAbortCache, CSSM_CL_CrlDescribeFormat, CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue, CL_IsCertInCachedCrl, CL_CrlAbortQuery, CL_CrlCache, CL_CrlAbortCache, CL_CrlDescribeFormat, CL_FreeFieldValue
CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue – Get the value of the first
CRL field (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Crl,
const CSSM_OID *CrlField,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR ResultsHandle,
uint32 *NumberOfMatchedFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *Value)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Crl,
const CSSM_OID *CrlField,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR ResultsHandle,
uint32 *NumberOfMatchedFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *Value)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
Crl (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure that contains
the CRL from which the field is to be retrieved.
CrlField (input)
An object identifier that identifies the field
value to be extracted from the CRL.
ResultsHandle (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_HANDLE that should be used
to obtain any additional matching fields.
NumberOfMatchedFields (output)
The total number of fields that match the CrlField OID. This count
includes the first match, which was returned by this function.
Value (output)
A pointer to the structure containing the value
of the requested field. The structure and the field at I "(*Value)->Data" are allocated by the service provider. The CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue (CSSM
API), or CL_FreeFieldValue (CL
SPI), function can be used to deallocate *Value and (*Value)->Data.
This
function returns the value of the CRL field designated by the CSSM_OID CrlField. The OID also identifies
the data format for the field value returned to the caller. If multiple OIDs
name the same CRL field, then each OID defines a distinct data format for
the returned field value. The function CSSM_CL_CrlDescribeFormat (CSSM API), or CL_CrlDescribeFormat (CL SPI), provides a list of all CSSM_OID values
supported by a Certificate Library module for naming fields of a CRL.
If
more than one field matches the CrlField OID, the first matching field will be returned.
The number of matching fields is an output parameter, as is the ResultsHandle to be used
to retrieve the remaining matching fields.
The set of matching fields is determined by this
function. The number of matching fields and the field values do not change
between this function and subsequent calls to CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue (CL SPI).
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_CL_NO_FIELD_VALUES
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CrlAbortQuery, CSSM_CL_CrlGetAllFields
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue, CL_CrlAbortQuery, CL_CrlGetAllFields
CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue – Get the value of the next cached
CRL field (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *FieldValue)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *FieldValue)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
ResultsHandle (input)
The handle that identifies the results of a CRL
query.
FieldValue (output)
A pointer to the structure containing the value
of the requested field. The structure and the field at I "(*FiledValue)->Data" are allocated by the service provider. The CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue (CSSM
API), or CL_FreeFieldValue (CL
SPI), function can be used to deallocate *FieldValue and (*FieldValue)->Data.
This
function returns the value of a CRL field, when that field occurs multiple
times in a CRL. CRLs with repeated fields (such as revocation records) have
multiple field values corresponding to a single OID. A call to the function CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue (CSSM
API), or CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue (CL SPI), initiates the process and returns a ResultsHandle identifying
the size and values contained in the result set. The CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue (CL SPI), function can be called repeatedly to
obtain these values, one at a time. The result set does not change in size
or value between calls to this function.
The result set selected by CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue (CL SPI), and identified by ResultsHandle can reference CRL fields repeated across multiple
revocation records or within one revocation record. The scope of the scan
was set by an optional CrlRecordIndex input
to the function CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue (CL SPI). If the record index was specified, then
the results set is the revocation record identified by the index. If no record
index was specified, then the results set can include repeated fields from
multiple revocation records in a CRL.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_RESULTS_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_NO_FIELD_VALUES
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CrlAbortQuery, CSSM_CL_IsCertInCachedCrl, CSSM_CL_CrlCache, CSSM_CL_CrlAbortCache, CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CL_CrlAbortQuery, CL_IsCertInCachedCrl, CL_CrlCache, CL_CrlAbortCache, CL_FreeFieldValue
CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue – Get the value of the next CRL
field (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *Value)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR *Value)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
ResultsHandle (input)
The handle that identifies the results of a CRL
query.
Value (output)
A pointer to the structure containing the value
of the requested field. The structure and the field at I "(*Value)->Data" are allocated by the service provider. The CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue (CSSM
API), or CL_FreeFieldValue (CL
SPI), function can be used to deallocate *Value and (*Value)->Data.
This
function returns the value of a CRL field, when that field occurs multiple
times in a CRL. CRLs with repeated fields (such as revocation records) have
multiple field values corresponding to a single OID. A call to the function CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue (CSSM
API), or CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue (CL
SPI), initiates the process and returns a results handle identifying the size
and values contained in the result set. The CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue (CSSM API), or CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue (CL SPI), function can be called repeatedly to
obtain these values, one at a time. The result set does not change in size
or value between calls to this function.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_RESULTS_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_NO_FIELD_VALUES
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CrlAbortQuery
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue, CL_CrlAbortQuery
CL_CrlRemoveCert:
CSSM_CL_CrlRemoveCert – Reinstate a certificate (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlRemoveCert
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrl,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrl)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlRemoveCert
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrl,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrl)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
Cert (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the certificate to be reinstated.
OldCrl (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the CRL from which the certificate is to be removed.
NewCrl (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the updated CRL. The NewCrl->Data is
allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
This
function reinstates a certificate by removing it from the specified CRL. The
operation is valid only if the CRL has not been closed by the process of signing
the CRL by executing CSSM_CL_CrlSign(CSSM
API), or CL_CrlSign (CL
SPI). Once the CRL has been signed, entries cannot be added or removed.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERT_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_CL_CRL_ALREADY_SIGNED
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CrlAddCert
CL_CrlSetFields:
CSSM_CL_CrlSetFields – Set new field values (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlSetFields
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CrlTemplate,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrl,
CSSM_DATA_PTR ModifiedCrl)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlSetFields
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CrlTemplate,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrl,
CSSM_DATA_PTR ModifiedCrl)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
NumberOfFields (input)
The number of OID value pairs specified in the
CrlTemplate input parameter.
CrlTemplate (input)
Any array of field OID value pairs containing the
values to initialize the CRL attribute fields.
OldCrl (input)
The CRL to be updated with the new attribute values.
The CRL must be unsigned and available for update.
ModifiedCrl (output)
A pointer to the modified, unsigned CRL. The ModifiedCrl->Data is allocated
by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
This
function will set the fields of the input CRL to the new values, specified
by the input OID/value pairs. If there is more than one possible instance
of an OID (for example, as in an extension or CRL record), then a new field
with the specified value is added to the CRL.
This
function should be used to update any of the CRL field values. If a specified
field was initialized by CSSM_CL_CrlCreateTemplate (CSSM API), or CL_CrlCreateTemplate (CL SPI), the field value is set to the new specified
value. If a specified field was not initialized by the CSSM_CL_CrlCreateTemplate (CSSM API), or CL_CrlCreateTemplate (CL SPI), the field is set to the new specified
value. The OldCrl must
be unsigned. Once a CRL has been signed using CSSM_CL_CrlSign (CSSM API), or CL_CrlSign (CL SPI), the signed CRL’s field values
cannot be modified. Modification would invalidate the cryptographic signature
of the CRL.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_NUMBER_OF_FIELDS
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_CRL_ALREADY_SIGNED
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlCreateTemplate, CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert, CSSM_CL_CrlSign, CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CrlCreateTemplate, CL_CrlAddCert, CL_CrlSign, CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue
CL_CrlSign: CSSM_CL_CrlSign,
CL_CrlSign – Sign
a CRL (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlSign
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *UnsignedCrl,
const CSSM_FIELD *SignScope,
uint32 ScopeSize,
CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedCrl)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlSign
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *UnsignedCrl,
const CSSM_FIELD *SignScope,
uint32 ScopeSize,
CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedCrl)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation.
UnsignedCrl (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the CRL to be signed.
SignScope (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_FIELD array containing the
tag/value pairs of the fields to be signed. If the signing scope is null,
the Certificate Library module includes a default set of CRL fields in the
signing process.
ScopeSize (input)
The number of entries in the sign scope list. If
the signing scope is not specified, the input scope size must be zero.
SignedCrl (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the signed CRL. The SignedCrl->Data is
allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
This function signs a CRL using the private key
and signing algorithm specified in the CCHandle parameter. The result is a signed, encoded certificate
revocation list in SignedCrl.
The unsigned CRL is specified in the input UnsignedCrl. The UnsignedCrl is constructed using the CSSM_CL_CrlCreateTemplate, CSSM_CL_CrlSetFields, CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert, and CSSM_CL_CrlRemoveCert functions (for the CSSM API), or their CL SPI
equivalents.
The CCHandle must be context created using the function CSSM_CSP_CreateSignatureContext (CSSM
API), or CSP_CreateSignatureContext (SPI).
The context must specify the Cryptographic Services Provider module, the signing
algorithm, and the signing key that must be used to perform this operation.
The context must also provide the passphrase or a callback function to obtain
the passphrase required to access and use the private key.
The
fields included in the signing operation are identified by the OIDs in the
optional SignScope array.
Once
the CRL has been signed it cannot be modified. This means that entries cannot
be added or removed from the CRL through application of the CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert or CSSM_CL_CrlRemoveCertCSSM_CL_CrlRemoveCert (or their CL SPI equivalent operations. A signed
CRL can be verified, applied to a data store, and searched for values.
The
memory for the SignedCrl->Data output
is allocated by the service provider using the calling application’s
memory management routines. The application must deallocate the memory.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_SCOPE
CSSMERR_CL_SCOPE_NOT_SUPPORTED
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_NUMBER_OF_FIELDS
CSSMERR_CL_CRL_ALREADY_SIGNED
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
Functions: CSSM_CL_CrlVerify, CSSM_CL_CrlVerifyWithKey
Functions for the CLI SPI:
CL_CrlVerify, CL_CrlVerifyWithKey
CL_CrlVerify:
CSSM_CL_CrlVerify – Verify a signed CRL has not
been altered (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlVerify
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CrlToBeVerified,
const CSSM_DATA *SignerCert,
const CSSM_FIELD *VerifyScope,
uint32 ScopeSize)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlVerify
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CrlToBeVerified,
const CSSM_DATA *SignerCert,
const CSSM_FIELD *VerifyScope,
uint32 ScopeSize)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
CCHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation.
CrlToBeVerified (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the CRL to be verified.
SignerCert (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the certificate used to sign the CRL.
VerifyScope (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_FIELD array containing the
tag/value pairs of the fields to be verified. If the verification scope is
null, the Certificate Library module assumes that a default set of fields
were used in the signing process and those same fields are used in the verification
process.
ScopeSize (input)
The number of entries in the verify scope list.
If the verification scope is not specified, the input value for scope size
must be zero.
This
function verifies that the signed CRL has not been altered since it was signed
by the designated signer. It does this by verifying the digital signature
over the fields specified by the VerifyScope parameter.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERT_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_SCOPE
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_NUMBER_OF_FIELDS
CSSMERR_CL_SCOPE_NOT_SUPPORTED
CSSMERR_CL_VERIFICATION_FAILURE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlSign
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CrlSign
CL_CrlVerifyWithKey:
CSSM_CL_CrlVerifyWithKey – Verify a CRL with a specific
key (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_CrlVerifyWithKey
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CrlToBeVerified)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_CrlVerifyWithKey
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CrlToBeVerified)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the Certificate Library
service module used to perform this function.
CCHandle (input)
A signature verification context defining the Cryptographic
Services Provider (CSP), verification algorithm, and public key that must
be used to perform the operation.
CrlToBeVerified (input)
A signed certificate revocation list whose signature
is to be verified.
This
function verifies that the CrlToBeVerified parameter was signed using a specific private
key and that the certificate revocation list has not been altered since it
was signed using that private key. The public key corresponding to the private
signing key is used in the verification process.
The
cryptographic context indicated by the CCHandle parameter must be a signature verification context
created using the function CSSM_CSP_CreateSignatureContext (CSSM API) or CSP_CreateSignatureContext (CL SPI). The context must specify the Cryptographic
Services Provider (CSP) module, the verification algorithm, and the public
verification key that must be used to perform this operation.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_CL_VERIFICATION_FAILURE
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlVerify
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CrlVerify
CL_FreeFields:
CSSM_CL_FreeFields – Free fields (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_FreeFields
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *FieldArray)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_FreeFields
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *FieldArray)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
NumberOfFields (input)
The length of the array of fields in FieldArray.
FieldArray (input)
A pointer to an array of CSSM_FIELD structures
that need to be deallocated.
This
function frees the fields in the FieldArray by freeing the data pointers for both the FieldOid and FieldValue fields. It also
frees the top level FieldArray pointer.
This
function should be used only to free CSSM_FIELD_PTR values returned from calls CSSM_TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields, CSSM_CL_CertGetAllTemplateFields, CSSM_CL_CertGetAllFields, CSSM_CL_CrlGetAllFields, CSSM_CL_CrlGetAllCachedRecordFields,
or their SPI equivalent calls.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
CL_FreeFieldValue:
CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue – Free field data (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_FreeFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_OID *CertOrCrlOid,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Value)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_FreeFieldValue
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_OID *CertOrCrlOid,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Value)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
CertOrCrlOid (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_OID structure describing
the type of the Value to
be freed.
Value (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the Data to
be freed.
This
function frees the data specified by Value and Value->Data. CertOrCrlOid indicates the type of the data in Value.
This
function should be used only to free CSSM_DATA values returned from calls CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertGetNextFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CertGetNextCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue,
or their CLI SPI equivalents.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
CL_IsCertInCachedCrl:
CSSM_CL_IsCertInCachedCrl – Search cached CRL for a record
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_IsCertInCachedCrl
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
CSSM_HANDLE CrlHandle,
CSSM_BOOL *CertFound,
CSSM_DATA_PTR CrlRecordIndex)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_IsCertInCachedCrl
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
CSSM_HANDLE CrlHandle,
CSSM_BOOL *CertFound,
CSSM_DATA_PTR CrlRecordIndex)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
Cert (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
an encoded, packed certificate.
CrlHandle (input)
A handle identifying a CRL that the application
has temporarily cached with the Certificate Library module. The referenced
CRL is searched for a revocation record matching the specified Cert.
CertFound (output)
A pointer to a CSSM_BOOL indicating success or
failure in finding the specified certificate in the CRL. CSSM_TRUE signifies
that the certificate was found in the CRL. CSSM_FALSE indicates that the certificate
was not found in the CRL.
CrlRecordIndex (output)
A pointer to a CSSM_DATA structure containing an
index descriptor for direct access to the located CRL record. CrlRecordIndex->Data is
allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
This
function searches the cached CRL for a record corresponding to the certificate.
The result of the search is returned in CertFound. The CRL and the records within the CRL must be
digitally signed. This function does not verify either signature. The caller
should use CSSM_TP_CrlVerify or CSSM_CL_CrlVerify (or their
SPI equivalents) before invoking this function. Once the CRL has been verified,
the caller can invoke this function repeatedly without repeating the verification
process.
If the certificate is found in the CRL, the CL
module returns an index descriptor CrlRecordIndex for use with other Certificate Library CRL functions.
The index provides more direct access to the selected CRL record.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERT_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CACHE_HANDLE
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue, CSSM_CL_CrlGetAllCachedRecordField, CSSM_CL_CrlCache, CSSM_CL_CrlAbortCache
Functions
for the CLI SPI:
CL_CrlGetFirstCachedFieldValue, CL_CrlGetNextCachedFieldValue, CL_CrlGetAllCachedRecordField, CL_CrlCache, CL_CrlAbortCache
CL_IsCertInCrl:
CSSM_CL_IsCertInCrl – Search CRL for a certificate
record (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_IsCertInCrl
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
const CSSM_DATA *Crl,
CSSM_BOOL *CertFound)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_IsCertInCrl
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Cert,
const CSSM_DATA *Crl,
CSSM_BOOL *CertFound)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
Cert (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the certificate to be located.
Crl (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the CRL to be searched.
CertFound (output)
A pointer to a CSSM_BOOL indicating success or
failure in finding the specified certificate in the CRL. CSSM_TRUE signifies
that the certificate was found in the CRL. CSSM_FALSE indicates that the certificate
was not found in the CRL.
This
function searches the CRL for a record corresponding to the certificate. The
result of the search is returned in CertFound. The CRL and the records within the CRL must be
digitally signed. This function does not verify either signature. The caller
should use CSSM_TP_CrlVerify or CSSM_CL_CrlVerify (or their
SPI equivalents) before invoking this function. Once the CRL has been verified,
the caller can invoke this function repeatedly without repeating the verification
process.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CERT_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_CL_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
CL_PassThrough:
CSSM_CL_PassThrough – Extend certificate library
functionality (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CL_PassThrough
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
uint32 PassThroughId,
const void *InputParams,
void **OutputParams)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCLI CL_PassThrough
(CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
uint32 PassThroughId,
const void *InputParams,
void **OutputParams)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Certificate
Library module used to perform this function.
CCHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the context of the cryptographic
operation. If the module-specific operation does not perform any cryptographic
operations, a cryptographic context is not required.
PassThroughId (input)
An identifier assigned by the CL module to indicate
the exported function to perform.
InputParams (input/optional)
A pointer to a module, implementation-specific
structure containing parameters to be interpreted in a function-specific manner
by the requested CL module.
OutputParams (output/optional)
A
pointer to a module, implementation-specific structure containing the output
data. The service provider allocates the memory for substructures. The application
must free the memory for the substructures.
This
function allows applications to call certificate library module-specific operations.
Such operations might include queries or services that are specific to the
domain represented by the CL module.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_PASSTHROUGH_ID
CSSMERR_CL_INVALID_DATA
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
CSP_EventNotify – Notify service module of a
context event (CDSA) (not currently supported) CSSM_RETURN CSSMSPI CSP_EventNotify
(CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CONTEXT_EVENT Event,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Event (input)
One of the following event types listed:
Event |
Description |
CSSM_CONTEXT_EVENT_CREATE |
A
caller using this module attach handle has created a new cryptographic context
using CSSM_Create***Context. |
CSSM_CONTEXT_EVENT_DELETE |
A
caller using this module attach handle has deleted a cryptographic context
using CSSM_DeleteContext. |
CSSM_CONTEXT_EVENT_UPDATE |
A
caller using this module attach handle has updated an existing cryptographic
context. |
CCHandle (input)
The cryptographic context handle for the context
affected by the event.
Context
A
pointer to the cryptographic context affected by the event. The results of
the event are visible in the context.
This
function is used to notify the service module of a context event related to
a particular attach handle. Valid events include creation, deletion, or modification
of a cryptographic context. The service module can examine the new or modified
context referenced by pContext to
determine whether the context is acceptable to the service module.
If
the cryptographic context is acceptable (if the service module examines the
contents of the context only upon use of the context), then the service module
should return CSSM_OK.
If the cryptographic context is not acceptable, then the service module should
return CSSM_FAIL.
Upon receiving a return value of CSSM_OK, CSSM completes the operation signaled by this
event and returns to the calling application. If the return value is CSSM_FAIL, CSSM deletes
a newly created context or modifications to an existing context, and returns
the failed result to the calling application. When deleting a cryptographic
context, CSSM always returns success to the calling application.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error
condition.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_CSP_CreateSignatureContext, CSSM_CSP_CreateDigestContext, CSSM_CSP_CreateSymmetricContext, CSSM_CSP_CreateMacContext, CSSM_CSP_CreateRandomGenContext, CSSM_CSP_CreateAsymmetricContext, CSSM_CSP_CreateDeriveKeyContext, CSSM_CSP_CreateKeyGenContext, CSSM_CSP_CreatePassThroughContext, CSSM_DeleteContext, CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
cssm_CcToHandle – Get the module attach handle
(CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI cssm_CcToHandle
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE Cc,
CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE_PTR ModuleHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
Cc (input)
A handle identifying a cryptographic context.
ModuleHandle (output)
A service provider’s module attach handle.
This value will be set to CSSM_INVALID_HANDLE if the function fails.
This
function returns the module attach handle identifying the service module that
is managing the specified cryptographic context.
The
entry point to this function is provided to a service module in a table of upcall functions passed
to the service provider during module attach processing.
If
the PVC checking for service providers is on, the service provider has to
introduce itself before calling this function.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
CSSM_ChangeKeyAcl – Edit a stored ACL associated
with the target key (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_ChangeKeyAcl
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_ACL_EDIT *AclEdit,
const CSSM_KEY *Key)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The module handle that identifies the Cryptographic
Service Provider to perform this operation
AccessCred (input)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
used to authenticate and validate the caller’s authorization to modify
the ACL associated with the key. Required credentials can include zero or
more certificates, zero or more caller names, and one or more samples. If
certificates and/or caller names are provided as input, these must be provided
as immediate values in this structure. The samples can be provided as immediate
values or can be obtained through a callback function included in the AccessCred structure.
AclEdit (input)
A structure containing information that defines
the edit operation. Valid operations include: adding, replacing, and deleting
entries in an ACL managed by the service provider. The AclEdit can contain information for a new ACL entry and
a handle uniquely identifying an existing ACL entry. The information controls
the edit operation as follows:
Value of AclEdit.EditMode |
Use of AclEdit.NewEntry and AclEdit.OldEntryHandle |
CSSM_ACL_EDIT_MODE_ADD |
Adds
a new ACL entry to the set of ACL entries associated with the specified Key. The new ACL entry is
created from the ACL entry prototype contained in NewEntry. OldEntryHandle is ignored for this edit mode. |
CSSM_ACL_EDIT_MODE_DELETE |
Deletes
the ACL entry identified by OldEntryHandle and associated with the specified Key. NewEntry is ignored for this edit mode. |
CSSM_ACL_EDIT_MODE_REPLACE |
Replaces
the ACL entry identified by OldEntryHandle and associated with the specified Key. The existing ACL is
replaced based on the ACL entry prototype contained in the NewEntry. |
When replacing an existing ACL entry, the caller
must replace all of the items in an ACL entry. The replacement prototype includes:
Subject type and value
A CSSM_LIST structure containing a typed Subject.
The Subject identifies the entity authorized by this ACL entry.
Delegation flag
A CSSM_BOOL value indicating whether the subject
can delegate the permissions recorded in the authorization array.
Authorization array
A CSSM_AUTHORIZATIONGROUP structure defining the
set of operations for which permission is granted to the Subject.
Validity period
A CSSM_ACL_VALIDITY_PERIOD structure containing
two elements, the start time and the stop time for which the ACL entry is
valid.
ACL entry tag
A CSSM_STRING containing a user-defined value associated
with the ACL entry.
Key (input)
A pointer to the target key whose associated ACL
is being modified.
This
function edits the stored ACL associated with the target key. The ACL is modified
according to the edit mode and information provided in AclEdit.
The caller must be authorized to modify the target
ACL. Caller authentication and authorization to edit the ACL is determined
based on the caller-provided AccessCred.
The caller must be authorized to add, delete, or
replace the ACL entries associated with the target key. When adding or replacing
an ACL entry, the service provider must reject the creation of duplicate ACL
entries.
When adding a new ACL entry to an ACL, the caller
must provide a complete ACL entry prototype. All ACL entry items, except the
ACL entry Subject must
be provided as an immediate value in AclEdit->NewEntry. The ACL entry Subject can be provided as an immediate value, from a
verifier with a protected data path, from an external authentication or authorization
service, or through a callback function specified in AclEdit->NewEntry->Callback.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_GetKeyAcl
CSSM_ChangeKeyOwner – Change the owner of a key (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_ChangeKeyOwner
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
const CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE *NewOwner)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The module handle that identifies the Cryptographic
Service Provider to perform this operation.
AccessCred (input)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
used to prove the caller is the current Oowner of the key. Required credentials
can include zero or more certificates, zero or more caller names, and one
or more samples. If certificates and/or caller names are provided as input,
these must be provided as immediate values in this structure. The samples
can be provided as immediate values or can be obtained through a callback
function included in the AccessCred structure.
Key (input)
A pointer to the target key whose associated Owner
is changed.
NewOwner (Input)
A CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE defining the new owner
of the key.
This
function takes a CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE defining the new owner of the key.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_GetKeyOwner
CSSM_CSP_ChangeLoginAcl – Edit a stored CSP ACL login
session (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_ChangeLoginAcl
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_ACL_EDIT *AclEdit)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The module handle that identifies the Cryptographic
Service Provider to perform this operation
AccessCred (input)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
used to authenticate and validate the caller’s authorization to modify
the ACL controlling login sessions with the CSP. Required credentials can
include zero or more certificates, zero or more caller names, and one or more
samples. Traditionally a caller name has been used to establish the context
of a login session. Certificates can be used for the same purpose. If certificates
and/or caller names are provided as input, these must be provided as immediate
values in this structure. The samples can be provided as immediate values
or can be obtained through a callback function included in the AccessCred structure.
AclEdit (input)
A structure containing information that defines
the edit operation. Valid operations include adding, replacing, and deleting
entries in an ACL managed by the service provider. The AclEdit parameter can contain information for a new ACL
entry and a handle uniquely identifying an existing ACL entry. The information
controls the edit operation as follows:
Value of AclEdit.EditMode |
Use of AclEdit.NewEntry
and AclEdit.OldEntryHandle |
CSSM_ACL_EDIT_MODE_ADD |
Adds
a new ACL entry to the set of ACL entries controlling login sessions with
the CSP. The new ACL entry is created from the ACL entry prototype contained
in NewEntry. OldEntryHandle is ignored
for this EditMode. |
CSSM_ACL_EDIT_MODE_DELETE |
Deletes
the ACL entry identified by OldEntryHandle and associated with login sessions with the CSP. NewEntry is ignored for
this EditMode. |
CSSM_ACL_EDIT_MODE_REPLACE |
Replaces
the ACL entry identified by OldEntryHandle and controlling login sessions with the CSP. The
existing ACL is replaced based on the ACL entry prototype contained in the NewEntry. |
When replacing an existing ACL entry, the caller
must replace all items in an ACL entry. The replacement prototype includes:
• Subject type and value – A CSSM_LIST
structure containing a typed subject. The subject identifies the entity authorized
by this ACL entry.
• Delegation flag – A CSSM_BOOL
value indicating whether the subject can delegate the permissions recorded
in the authorization array.
• Authorization array – A CSSM_AUTHORIZATIONGROUP
structure defining the set of operations for which permission is granted to
the subject.
• Validity period – A CSSM_ACL_VALIDITY_PERIOD
structure containing two elements, the start time and the stop time for which
the ACL entry is valid.
• ACL entry tag – A CSSM_STRING
containing a user-defined value associated with the ACL entry.
This
function edits the stored ACL controlling login sessions for a Cryptographic
Service Provider (CSP). The ACL is modified according to the edit mode and
information provided in AclEdit.
The
caller must have a login session in process and must be authorized to modify
the target ACL. Caller authentication and authorization to edit the ACL is
determined based on the caller-provided AccessCred.
The caller must be authorized to add, delete, or
replace the ACL entries controlling login to the CSP. When adding or replacing
an ACL entry, the service provider must reject the creation of duplicate ACL
entries.
When adding a new ACL entry to an ACL, the caller
must provide a complete ACL entry prototype. All ACL entry items, except the
ACL entry Subject, must be provided as an immediate value in AclEdit.NewEntry. The ACL
entry Subject can be provided as an immediate value, from a verifier with
a protected data path, from an external authentication or authorization service,
or through a callback function specified in AclEdit.NewEntry.Callback.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_CSP_GetLoginACLCSSM_CSP_Login, CSSM_CSP_Logout
CSSM_CSP_ChangeLoginOwner CSSM_CSP_ChangeLoginOwner – Define a new login owner (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_ChangeLoginOwner
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE *NewOwner)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The module handle that identifies the Cryptographic
Service Provider to perform this operation.
AccessCred (input)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
used to prove the caller is the current login owner. Required credentials
can include zero or more certificates, zero or more caller names, and one
or more samples. If certificates and/or caller names are provided as input,
these must be provided as immediate values in this structure. The samples
can be provided as immediate values or can be obtained through a callback
function included in the AccessCred structure.
NewOwner (Input)
A CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE defining the new login
owner.
This
function takes a CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE describing the new login owner.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions: CSSM_CSP_GetLoginOwner
CSSM_CSP_CreateAsymmetricContext CSSM_CSP_CreateAsymmetricContext – Create an asymmetric encryption
cryptographic context (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_CreateAsymmetricContext
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS AlgorithmID,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
CSSM_PADDING Padding,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *NewContextHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns an error.
AlgorithmID (input)
The algorithm identification number for the algorithm
used for asymmetric encryption.
AccessCred (input)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
required to unlock the private key. The credentials structure can contain
an immediate value for the credential, such as a passphrase, or the caller
can specify a callback function
the CSP can use to obtain one or more credentials. Credentials can be required
for encryption and decryption operations.
Key (input)
The key used for asymmetric encryption. The caller
passes a pointer to a CSSM_KEY structure containing the key. When the context
is used for a sign operation, AccessCredentials is required to access the private key used for
signing. When the context is used for a verify operation, the public key is
used to verify the signature. When the context is used for a wrapkey operation,
the public key can be used as the wrapping key. When the context is used for
an unwrap operation, AccessCredentials is required to access the private key used to
perform the unwrapping.
Padding (input/optional)
The method for padding. Typically specified for
ciphers that pad.
NewContextHandle (output)
Cryptographic context handle.
This
function creates an asymmetric encryption cryptographic context, given a handle
of a CSP, an algorithm identification number, a key, and padding. The cryptographic
context handle is returned. The cryptographic context handle can be used to
call asymmetric encryption functions and cryptographic wrap or unwrap functions.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_DecryptData, CSSM_DecryptDataInit, CSSM_DecryptDataUpdate, CSSM_DecryptDataFinal, CSSM_DeleteContext, CSSM_EncryptData, CSSM_EncryptDataInit, CSSM_EncryptDataUpdate, CSSM_EncryptDataFinal, CSSM_GetContext, CSSM_GetContextAttribute, CSSM_QuerySize, CSSM_SetContext, CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
CSSM_CSP_CreateDeriveKeyContext CSSM_CSP_CreateDeriveKeyContext – Create a cryptographic context
to derive a symmetric key (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_CreateDeriveKeyContext
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS AlgorithmID,
CSSM_KEY_TYPE DeriveKeyType,
uint32 DeriveKeyLengthInBits,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_KEY *BaseKey,
uint32 IterationCount,
const CSSM_DATA *Salt,
const CSSM_CRYPTO_DATA *Seed,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *NewContextHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns an error.
AlgorithmID (input)
The algorithm identification number for a derived
key algorithm.
DeriveKeyType (input)
The type of symmetric key to derive.
DeriveKeyLengthInBits (input)
The logical length of the key in bits to be derived
( LogicalKeySizeInBits)
AccessCred (input/optional)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
required to access the base key. The credentials structure can contain an
immediate value for the credential, such as a passphrase, or the caller can
specify a callback function the CSP can use to obtain one or more credentials.
If the BaseKey is
NULL, then this parameter is optional.
BaseKey (input/optional)
The base key used to derive the new key. The base
key can be a public key, a private key, or a symmetric key
IterationCount (input/optional)
The number of iterations to be performed during
the derivation process. Used heavily by password-based derivation methods.
Salt (input/optional)
A Salt used in deriving the key.
Seed (input/optional)
A seed used to generate a random number. The caller
can either pass a seed and seed length in bytes or pass a callback function.
If Seed is
NULL, the Cryptographic Service Provider will use its default seed-handling
mechanism.
NewContextHandle (output)
Cryptographic context handle.
This
function creates a cryptographic context to derive a symmetric key, given
a handle of a CSP, an algorithm, the type of symmetric key to derive, the
length of the derived key, and an optional seed or an optional AccessCredentials structure
from which to derive a new key. The cryptographic context handle is returned.
The cryptographic context handle can be used for calling the cryptographic
derive key function.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_DeriveKey
CSSM_CSP_CreateDigestContext CSSM_CSP_CreateDigestContext – Create a digest cryptographic
context (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_CreateDigestContext
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS AlgorithmID,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *NewContextHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns error.
AlgorithmID (input)
The algorithm identification number for message
digests.
NewContextHandle (output)
Cryptographic context handle.
This
function creates a digest cryptographic context, given a handle of a CSP and
an algorithm identification number. The cryptographic context handle is returned.
The cryptographic context handle can be used to call digest cryptographic
functions.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_DigestData, CSSM_DigestDataInit, CSSM_DigestDataUpdate, CSSM_DigestDataFinal, CSSM_GetContext, CSSM_SetContext, CSSM_DeleteContext, CSSM_GetContextAttribute, CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
CSSM_CSP_CreateKeyGenContext CSSM_CSP_CreateKeyGenContext – Create a key generation cryptographic
context (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_CreateKeyGenContext
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS AlgorithmID,
uint32 KeySizeInBits,
const CSSM_CRYPTO_DATA *Seed,
const CSSM_DATA *Salt,
const CSSM_DATE *StartDate,
const CSSM_DATE *EndDate,
const CSSM_DATA *Params,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *NewContextHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns an error.
AlgorithmID (input)
The algorithm identification number of the algorithm
used for key generation.
KeySizeInBits (input)
The logical size of the key (specified in bits).
This refers to either the actual key size (for symmetric key generation) or
the modulus size (for asymmetric key pair generation).
Seed (input/optional)
A seed used to generate the key. The caller can
either pass a seed and seed length in bytes or pass a callback function. If
NULL is passed, the Cryptographic Service Provider will use its default seed-handling
mechanism.
Salt (input/optional)
A salt used to generate the key.
StartDate (input/optional)
A start date for the validity period of the key
or key pair being generated.
EndDate (input/optional)
An end date for the validity period of the key
or key pair being generated.
Params (input/optional)
A data buffer containing parameters required to
generate a key pair for a specific algorithm.
NewContextHandle (output)
Cryptographic context handle.
This
function creates a key generation cryptographic context, given a handle of
a CSP, an algorithm identification number, a passphrase, a modulus size (for
public or private keypair generation), a key size (for symmetric key generation),
a seed, and a salt. The cryptographic context handle is returned. The cryptographic
context handle can be used to call key/ or keypair generation functions.
Additional
attributes can be added to the newly created context using the CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes function.
Incremental attributes of interest for key generation include a handle-pair
identifying a Data Storage Library service module and an open data store for
CSPs that manage multiple persistent key stores. If a CSP does not support
multiple key stores, the CSP ignores the presence or absence of this attribute.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions: CSSM_GenerateKey, CSSM_GenerateKeyPair, CSSM_GetContext, CSSM_SetContext, CSSM_DeleteContext, CSSM_GetContextAttribute, CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
CSSM_CSP_CreateMacContext CSSM_CSP_CreateMacContext – Create a message authentication
code cryptographic context (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_CreateMacContext
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS AlgorithmID,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *NewContextHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns error.
AlgorithmID (input)
The algorithm identification number for the MAC
algorithm.
Key (input)
The key used to generate a message authentication
code. Caller passes a pointer to a CSSM_KEY structure containing the key.
NewContextHandle (output)
Cryptographic context handle.
This
function creates a message authentication code cryptographic context, given
a handle of a CSP, algorithm identification number, and a key. The cryptographic
context handle is returned. The cryptographic context handle can be used to
call message authentication code functions.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions: CSSM_GenerateMac, CSSM_GenerateMacInit, CSSM_GenerateMacUpdate, CSSM_GenerateMacFinal, CSSM_VerifyMac, CSSM_VerifyMacInit, CSSM_VerifyMacUpdate, CSSM_VerifyMacFinal, CSSM_GetContext, CSSM_SetContext, CSSM_DeleteContext, CSSM_GetContextAttribute, CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
CSSM_CSP_CreatePassThroughContext CSSM_CSP_CreatePassThroughContext – Create a custom cryptographic
context (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_CreatePassThroughContext
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *NewContextHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns an error.
Key (input)
The key to be used for the context. The caller
passes a pointer to a CSSM_KEY structure containing the key.
NewContextHandle (output)
Cryptographic context handle.
This
function creates a custom cryptographic context, given a handle of a CSP and
a pointer to a custom input data structure. The cryptographic context handle
is returned. The cryptographic context handle can be used to call the CSSM
pass-through function for the CSP.
A
CSP can create its own set of custom functions. The context information can
be passed through its own data structure. The CSSM_CSP_PassThrough function should be used with the function ID to
call the desired custom function.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_CSP_PassThroughCSSM_GetContext, CSSM_SetContext, CSSM_DeleteContext, CSSM_GetContextAttribute, CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
CSSM_CSP_CreateDeriveKeyContext CSSM_CSP_CreateDeriveKeyContext – Create a cryptographic context
to derive a symmetric key (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_CreateDeriveKeyContext
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS AlgorithmID,
CSSM_KEY_TYPE DeriveKeyType,
uint32 DeriveKeyLengthInBits,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_KEY *BaseKey,
uint32 IterationCount,
const CSSM_DATA *Salt,
const CSSM_CRYPTO_DATA *Seed,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *NewContextHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns an error.
AlgorithmID (input)
The algorithm identification number for a derived
key algorithm.
DeriveKeyType (input)
The type of symmetric key to derive.
DeriveKeyLengthInBits (input)
The logical length of the key in bits to be derived
( LogicalKeySizeInBits)
AccessCred (input/optional)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
required to access the base key. The credentials structure can contain an
immediate value for the credential, such as a passphrase, or the caller can
specify a callback function the CSP can use to obtain one or more credentials.
If the BaseKey is
NULL, then this parameter is optional.
BaseKey (input/optional)
The base key used to derive the new key. The base
key can be a public key, a private key, or a symmetric key
IterationCount (input/optional)
The number of iterations to be performed during
the derivation process. Used heavily by password-based derivation methods.
Salt (input/optional)
A Salt used in deriving the key.
Seed (input/optional)
A seed used to generate a random number. The caller
can either pass a seed and seed length in bytes or pass a callback function.
If Seed is
NULL, the Cryptographic Service Provider will use its default seed-handling
mechanism.
NewContextHandle (output)
Cryptographic context handle.
This
function creates a cryptographic context to derive a symmetric key, given
a handle of a CSP, an algorithm, the type of symmetric key to derive, the
length of the derived key, and an optional seed or an optional AccessCredentials structure
from which to derive a new key. The cryptographic context handle is returned.
The cryptographic context handle can be used for calling the cryptographic
derive key function.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions: CSSM_DeriveKey
CSSM_CSP_CreateDigestContext CSSM_CSP_CreateDigestContext – Create a digest cryptographic
context (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_CreateDigestContext
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS AlgorithmID,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *NewContextHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns error.
AlgorithmID (input)
The algorithm identification number for message
digests.
NewContextHandle (output)
Cryptographic context handle.
This
function creates a digest cryptographic context, given a handle of a CSP and
an algorithm identification number. The cryptographic context handle is returned.
The cryptographic context handle can be used to call digest cryptographic
functions.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_DigestData, CSSM_DigestDataInit, CSSM_DigestDataUpdate, CSSM_DigestDataFinal, CSSM_GetContext, CSSM_SetContext, CSSM_DeleteContext, CSSM_GetContextAttribute, CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
CSSM_CSP_CreateKeyGenContext CSSM_CSP_CreateKeyGenContext – Create a key generation cryptographic
context (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_CreateKeyGenContext
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS AlgorithmID,
uint32 KeySizeInBits,
const CSSM_CRYPTO_DATA *Seed,
const CSSM_DATA *Salt,
const CSSM_DATE *StartDate,
const CSSM_DATE *EndDate,
const CSSM_DATA *Params,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *NewContextHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns an error.
AlgorithmID (input)
The algorithm identification number of the algorithm
used for key generation.
KeySizeInBits (input)
The logical size of the key (specified in bits).
This refers to either the actual key size (for symmetric key generation) or
the modulus size (for asymmetric key pair generation).
Seed (input/optional)
A seed used to generate the key. The caller can
either pass a seed and seed length in bytes or pass a callback function. If
NULL is passed, the Cryptographic Service Provider will use its default seed-handling
mechanism.
Salt (input/optional)
A salt used to generate the key.
StartDate (input/optional)
A start date for the validity period of the key
or key pair being generated.
EndDate (input/optional)
An end date for the validity period of the key
or key pair being generated.
Params (input/optional)
A data buffer containing parameters required to
generate a key pair for a specific algorithm.
NewContextHandle (output)
Cryptographic context handle.
This
function creates a key generation cryptographic context, given a handle of
a CSP, an algorithm identification number, a passphrase, a modulus size (for
public or private keypair generation), a key size (for symmetric key generation),
a seed, and a salt. The cryptographic context handle is returned. The cryptographic
context handle can be used to call key/ or keypair generation functions.
Additional
attributes can be added to the newly created context using the CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes function.
Incremental attributes of interest for key generation include a handle-pair
identifying a Data Storage Library service module and an open data store for
CSPs that manage multiple persistent key stores. If a CSP does not support
multiple key stores, the CSP ignores the presence or absence of this attribute.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions: CSSM_GenerateKey, CSSM_GenerateKeyPair, CSSM_GetContext, CSSM_SetContext, CSSM_DeleteContext, CSSM_GetContextAttribute, CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
CSSM_CSP_CreateMacContext CSSM_CSP_CreateMacContext – Create a message authentication
code cryptographic context (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_CreateMacContext
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS AlgorithmID,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *NewContextHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns error.
AlgorithmID (input)
The algorithm identification number for the MAC
algorithm.
Key (input)
The key used to generate a message authentication
code. Caller passes a pointer to a CSSM_KEY structure containing the key.
NewContextHandle (output)
Cryptographic context handle.
This
function creates a message authentication code cryptographic context, given
a handle of a CSP, algorithm identification number, and a key. The cryptographic
context handle is returned. The cryptographic context handle can be used to
call message authentication code functions.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_GenerateMac, CSSM_GenerateMacInit, CSSM_GenerateMacUpdate, CSSM_GenerateMacFinal, CSSM_VerifyMac, CSSM_VerifyMacInit, CSSM_VerifyMacUpdate, CSSM_VerifyMacFinal, CSSM_GetContext, CSSM_SetContext, CSSM_DeleteContext, CSSM_GetContextAttribute, CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
CSSM_CSP_CreatePassThroughContext CSSM_CSP_CreatePassThroughContext – Create a custom cryptographic
context (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_CreatePassThroughContext
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *NewContextHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns an error.
Key (input)
The key to be used for the context. The caller
passes a pointer to a CSSM_KEY structure containing the key.
NewContextHandle (output)
Cryptographic context handle.
This
function creates a custom cryptographic context, given a handle of a CSP and
a pointer to a custom input data structure. The cryptographic context handle
is returned. The cryptographic context handle can be used to call the CSSM
pass-through function for the CSP.
A
CSP can create its own set of custom functions. The context information can
be passed through its own data structure. The CSSM_CSP_PassThrough function should be used with the function ID to
call the desired custom function.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_CSP_PassThroughCSSM_GetContext, CSSM_SetContext, CSSM_DeleteContext, CSSM_GetContextAttribute, CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
CSSM_CSP_CreateRandomGenContext CSSM_CSP_CreateRandomGenContext – Create a random number generation
cryptographic context (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_CreateRandomGenContext
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS AlgorithmID,
const CSSM_CRYPTO_DATA *Seed,
uint32 Length,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *NewContextHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns AN error.
AlgorithmID (input)
The algorithm identification number for random
number generation.
Seed (input/optional)
A seed used to generate THE random number. The
caller can either pass a seed and seed length in bytes or pass a callback
function. If NULL is passed, the Cryptographic Service Provider will use its
default seed-handling mechanism.
Length (input)
The length of the random number to be generated.
NewContextHandle (output)
Cryptographic context handle.
This
function creates a random number generation cryptographic context, given a
handle of a CSP, an algorithm identification number, a seed, and the length
of the random number in bytes. The cryptographic context handle is returned
and can be used for the random number generation function.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions: CSSM_GenerateRandom, CSSM_GetContext, CSSM_SetContext, CSSM_DeleteContext, CSSM_GetContextAttribute, CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
CSSM_CSP_CreateSignatureContext CSSM_CSP_CreateSignatureContext – Create a signature cryptographic
context (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_CreateSignatureContext
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS AlgorithmID,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *NewContextHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns error.
AlgorithmID (input)
The algorithm identification number for a signature/verification
algorithm.
AccessCred (input/optional)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
required to unlock the private key. The credentials structure can contain
an immediate value for the credential, such as a passphrase, or the caller
can specify a callback function the CSP can use to obtain one or more credentials.
Credentials are required for signature operations, not for verify operations.
Key (input)
The key used to sign and verify. The caller passes
a pointer to a CSSM_KEY structure containing the key and the key length.
NewContextHandle (output)
Cryptographic context handle.
This
function creates a signature cryptographic context for sign and verify, given
a handle of a CSP, an algorithm identification number, a key, and an AccessCredentials structure.
The AccessCredentials structure
will be used to unlock the private key when this context is used to perform
a signing operation. The cryptographic context handle is returned. The cryptographic
context handle can be used to call sign and verify cryptographic functions.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions: CSSM_SignData, CSSM_SignDataInit, CSSM_SignDataUpdate, CSSM_SignDataFinal, CSSM_VerifyData, CSSM_VerifyDataInit, CSSM_VerifyDataUpdate, CSSM_VerifyDataFinal, CSSM_GetContext, CSSM_SetContext, CSSM_DeleteContext, CSSM_GetContextAttribute, CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
CSSM_CSP_CreateSymmetricContext CSSM_CSP_CreateSymmetricContext – Create a symmetric encryption
cryptographic context (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_CreateSymmetricContext
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS AlgorithmID,
CSSM_ENCRYPT_MODE Mode,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
const CSSM_DATA *InitVector,
CSSM_PADDING Padding,
void *Reserved,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *NewContextHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns error.
AlgorithmID (input)
The algorithm identification number for symmetric
encryption.
Mode (input)
The mode of the specified algorithm ID.
AccessCred (input/optional)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
required to unlock the private key. The credentials structure can contain
an immediate value for the credential, such as a passphrase, or the caller
can specify a callback function
the CSP can use to obtain one or more credentials. Credentials may be required
for encryption, decryption, and wrapping operations.
Key (input)
The key used for symmetric encryption. The caller
passes a pointer to a CSSM_KEY structure containing the key.
InitVector (input/optional)
The initial vector for symmetric encryption. This
is typically specified for block ciphers.
Padding (input/optional)
The method for padding. This is typically specified
for ciphers that pad.
Reserved (input)
Reserved for future use.
NewContextHandle (output)
Cryptographic context handle.
This
function creates a symmetric encryption cryptographic context, given a handle
of a CSP, an algorithm identification number, a key, an initial vector, padding,
and the number of encryption rounds. Algorithm-specific attributes must be
added to the context after the initial creation using the CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes function. The cryptographic context handle is
returned. The cryptographic context handle can be used to call symmetric encryption
functions and the cryptographic wrap or unwrap functions.
Additional
attributes can be added to the newly created context using the CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes function
. Incremental attributes of interest when using this context to unwrap a key
include a handle-pair identifying a Data Storage Library service module and
an open data store for CSPs that manage multiple, persistent key stores. If
a CSP does not support multiple key stores, the CSP ignores the presence or
absence of this attribute.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_DecryptData, CSSM_DecryptDataInit, CSSM_DecryptDataUpdate, CSSM_DecryptDataFinal, CSSM_DeleteContext, CSSM_EncryptData, CSSM_EncryptDataInit, CSSM_EncryptDataUpdate, CSSM_EncryptDataFinal, CSSM_GetContext, CSSM_GetContextAttribute, CSSM_QuerySize, CSSM_SetContext, CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
CSSM_CSP_GetLoginAcl – Get description of CSP ACL
entries (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_GetLoginAcl
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_STRING *SelectionTag,
uint32 *NumberOfAclInfos,
CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_INFO_PTR *AclInfos)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The module handle that identifies the Cryptographic
Service Provider to perform this operation.
SelectionTag (input/optional)
A CSSM_STRING value matching the user-defined tag
value associated with one or more ACL entries controlling login sessions.
To retrieve a description of all ACL entries controlling login sessions, this
parameter must be NULL.
NumberOfAclInfos (output)
The number of entries in the AclInfos array. If no ACL entry descriptions are returned,
this value is zero.
AclInfos (output)
An array of CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_INFO structures. The
unique handle contained in this structure can be used during the current attach
session and the current login session to reference specific ACL entries for
editing. The structure is allocated by the service provider and must be released
by the caller when the structure is no longer needed. If no ACL entry descriptions
are returned, this value is NULL.
This
function returns a description of zero or more ACL entries managed by the
CSP and used to control login sessions with the CSP. The optional input SelectionTag parameter restricts
the returned descriptions to those ACL entries with a matching EntryTag value. If a SelectionTag value is specified
and no matches are found, zero descriptions are returned. If no SelectionTag is specified,
a description of all ACL entries used to control login sessions are returned
by this function.
Each AclInfo structure contains:
• Public contents of an ACL entry
• ACL EntryHandle, which is a unique value defined and managed by
the service provider
The public ACL entry information returned by this
function includes:
• Subject type — A CSSM_LIST structure
containing one element identifying the type of subject stored in the ACL entry.
• Delegation flag — A CSSM_BOOL
value indicating whether the subject can delegate the permissions recorded
in the authorization array.
• Authorization array — A CSSM_AUTHORIZATIONGROUP
structure defining the set of operations for which permission is granted to
the subject.
• Validity period — A CSSM_ACL_VALIDITY_PERIOD
structure containing two elements, the start time and the stop time for which
the ACL entry is valid.
• ACL entry tag — A CSSM_STRING
containing a user-defined value associated with the ACL entry.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_CSP_Login, CSSM_CSP_LoginAclCSSM_CSP_Logout
CSSM_CSP_GetLoginOwner – Get login owner data (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_GetLoginOwner
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE_PTR Owner)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The module handle that identifies the Cryptographic
Service Provider to perform this operation.
Owner (output)
A CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE describing the login
owner.
This
function returns a CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE describing the current login owner
of the CSP.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_CSP_ChangeLoginOwner
CSSM_CSP_Login – Log user in to the CSP (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_Login
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_DATA *LoginName,
const void *Reserved)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
Handle of the CSP to log in to.
AccessCred (input)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
required to log in to the token or Cryptographic Service Provider. The credentials
structure can contain an immediate value for the credential, such as a passphrase
or PIN, or the caller can specify a callback function the CSP can use to obtain
one or more credentials.
LoginName (input/optional)
A name or ID of the caller. The value is used with
the provided AccessCred to
authenticate and authorize the caller for login with the CSP. The CSP can
require that a name value be provided. If a name value is not provided, the
CSP can assume a default name under which to perform the authentication and
authorization check, or the login request can fail.
Reserved (input)
This field is reserved for future use. The value
NULL should always be given. (May be used for multiple user support in the
future.)
Logs
the user in to the CSP, allowing for multiple login types.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_INVALID_LOGIN_NAME
CSSMERR_CSP_ALREADY_LOGGED_IN
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_CSP_GetLoginAcl, CSSM_CSP_ChangeLoginAcl, CSSM_CSP_Logout
CSSM_CSP_Logout – Terminate the login session
(CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_Logout
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
Handle for the target CSP.
Terminates
the login session associated with the specified CSP handle.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_CSP_Login, CSSM_CSP_GetLoginAcl, CSSM_CSP_ChangeLoginAcl
CSSM_DeleteContext – Free the context structure
(CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DeleteContext
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes a context to be deleted.
This
function frees the context structure allocated by any of the CSSM_Createxxxxx context functions.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_CSP_CreateAsymmetricContext, CSSM_CSP_CreateKeyGenContext, CSSM_CSP_CreateDigestContext, CSSM_CSP_CreateSignatureContext, CSSM_CSP_CreateSymmetricContext, and others.
CSSM_DeleteContextAttributes CSSM_DeleteContextAttributes – Delete internal data (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DeleteContextAttributes
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
uint32 NumberOfAttributes,
const CSSM_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE *ContextAttributes)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes a context that is to
be deleted.
NumberOfAttributes (input)
The number of attributes to be deleted as specified
in the array of context attributes.
ContextAttributes (input)
The attributes to be deleted from the context.
Only the attribute type is required. Any attribute values in the CSSM_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE
structures are ignored.
This
function deletes internal data associated with the given attribute type of
the context handle.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_GetContextAttributes, CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
cssm_DeregisterManagerServices cssm_DeregisterManagerServices – Deregister manager services void CSSMAPI cssm_DeregisterManagerServices
(const CSSM_GUID *Guid);
GUID (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_GUID structure containing
the global unique identifier for this module.
This
function is used by an elective module manager to deregister its function
table with CSSM core services prior to termination. This function is invoked
by an elective module manager only when exiting due to an error condition
detected by the EMM. This allows CSSM to clean up any state information associated
with the exiting EMM.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
CSSM_FreeContext – Free memory associated with
the context structure (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_FreeContext
(CSSM_CONTEXT_PTR Context)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
Context (input)
The pointer to the memory that describes the context
structure.
This
function frees the memory associated with the context structure.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_GetContext
CSSM_GetAPIMemoryFunctions CSSM_GetAPIMemoryFunctions – Retrieve the memory function
table associated with the security service module CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GetAPIMemoryFunctions
(CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE AddInHandle,
CSSM_API_MEMORY_FUNCS_PTR AppMemoryFuncs)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
AddInHandle (input)
The handle to the security service module that
is associated with the requested memory function table.
AppMemoryFuncs (output)
The pointer to an empty memory functions table.
Upon function return, the table is filled with the memory function pointers
associated with the specified attach handle. Caller has to allocate the buffer.
This
function retrieves the memory function table associated with the security
service module identified by the input handle.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
cssm_GetAppMemoryFunctions cssm_GetAppMemoryFunctions – Get service functions (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI cssm_GetAppMemoryFunctions
(CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE hAddIn,
CSSM_UPCALLS_PTR UpcallTable)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
hAddIn (input)
The handle identifying the attach-session whose
memory management function table is returned by this function.
UpcallTable (output)
The table containing sets of service functions
among them a set of four memory management functions provided by the application
that initiated the attach-session identified by hAddIn.
This
function gets a function table containing sets of service functions. Among
these service functions are four application-provided memory management functions.
The elective module manager can use these functions to manage memory on behalf
of the application. The returned function table is specific to the attach-session
identified by the module handle.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
cssm_GetAttachFunctions – Get SPI function table (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI cssm_GetAttachFunctions
(CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE hAddIn,
CSSM_SERVICE_MASK AddinType,
void **SPFunctions,
CSSM_GUID_PTR Guid)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
hAddIn (input)
The handle identifying the attach-session whose
function table is to be returned by this function.
AddinType (input)
A CSSM_SERVICE_MASK value identifying the type
of service module whose function table is to be returned by this function.
SPFunctions (output)
A pointer to the service module function table,
which CSSM acquired from the service module during module-attach processing.
The module manager should use this table to forward application invocation
of the elective APIs to their corresponding SPIs. The memory pointed to by
the function pointers should not be freed by the EMM.
Guid (output)
A CSSM_GUID value identifying the service module
whose function table is to be returned by this function.
This
function returns an SPI function table for the service module identified by
the module handle. The module must be of the type specified by the service
mask. The SPFunctions parameter
contains the returned function table. The elective module manager must use
this function table to forward an application’s call to the elective
APIs to their corresponding SPIs represented in the function table. The returned Guid identifies the service
module. It can be used to locate credentials and other information about the
service module.
This function sets a lock on the SP functions table.
The CSSM service function cssm_ReleaseAttachFunctions must be used to release the lock.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
CSSM_GetContext – Get context information (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GetContext
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_CONTEXT_PTR *Context)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle to the context information.
Context (output)
The pointer to the CSSM_CONTEXT_PTR structure that
describes the context associated with the CCHandle handle. The pointer will be set to NULL if the
function fails. Use CSSM_FreeContext to
free the memory allocated by the CSSM.
This
function retrieves the context information when provided with a context handle.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_FreeContext, CSSM_SetContext
CSSM_GetContextAttribute – Get context attribute (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GetContextAttribute
(const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
uint32 AttributeType,
CSSM_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE_PTR *ContextAttribute)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
Context (input)
A pointer to the context.
AttributeType (input)
The attribute type of the desired attribute value.
ContextAttribute (output)
The pointer to the CSSM_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE that
describes the context attributes associated with the CCHandle handle and the attribute type. The pointer will
be set to NULL if the function fails. Call CSSM_DeleteContextAttributes to free memory allocated by the CSSM.
This
function returns the value of a context attribute. Context references the
cryptographic context to be searched for the attribute specified by AttributeType. If the specified
attribute is not present, then a NULL pointer is returned.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_NOT_IN_CONTEXT
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_DeleteContextAttributes, CSSM_GetContext
CSSM_GetKeyAcl – Get ACL entries by key (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GetKeyAcl
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
const CSSM_STRING *SelectionTag,
uint32 *NumberOfAclInfos,
CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_INFO_PTR *AclInfos)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The module handle that identifies the Cryptographic
Service Provider to perform this operation.
Key (input)
A pointer to the target key whose associated ACL
entries are scanned and returned.
SelectionTag (input/optional)
A CSSM_STRING value matching the user-defined tag
value associated with one or more ACL entries for the target Key. To retrieve
a description of all ACL entries for the target Key, this parameter must be
NULL.
NumberOfAclInfos (output)
The number of entries in the AclInfos array. If no ACL entry descriptions are returned,
this value is zero.
AclInfos (output)
An array of CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_INFO structures. The
unique handle contained in this structure can be used during the current attach
session to reference specific ACL entries for editing. The structure is allocated
by the service provider and must be released by the caller when the structure
is no longer needed. If no ACL entry descriptions are returned, this value
is NULL.
This
function returns a description of zero or more ACL entries managed by the
CSP and associated with the target key. The optional input SelectionTag restricts the returned descriptions to those ACL
entries with a matching EntryTag value.
If a SelectionTag value
is specified and no matches are found, zero descriptions are returned. If
no SelectionTag is
specified, a description of all ACL entries associated with the key is returned
by this function.
Each AclInfo structure contains:
• Public contents of an ACL entry
• ACL EntryHandle, which is a unique value defined and managed by
the service provider
The public ACL entry information returned by this
function includes:
Subject type and value
A CSSM_LIST structure containing one element identifying
the type of subject stored in the ACL entry.
Delegation flag
A
CSSM_BOOL value indicating whether the subject can delegate the permissions
recorded in the authorization array.
Authorization array
A CSSM_AUTHORIZATIONGROUP structure defining the
set of operations for which permission is granted to the subject.
Validity period
A CSSM_ACL_VALIDITY_PERIOD structure containing
two elements, the start time and the stop time for which the ACL entry is
valid.
ACL entry tag
A
CSSM_STRING containing a user-defined value associated with the ACL entry.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_ChangeKeyAcl
CSSM_GetKeyOwner – Get data describing key owner
(CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GetKeyOwner
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE_PTR Owner)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The module handle that identifies the Cryptographic
service provider to perform this operation.
Key (input)
A pointer to the target key whose associated Owner
is returned.
Owner (output)
A CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE describing the current
Owner of the Key.
This
function returns a CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE describing the current Owner of
the Key.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions: CSSM_ChangeKeyOwner
CSSM_GetModuleGUIDFromHandle CSSM_GetModuleGUIDFromHandle – Get GUID of the attached module
(CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GetModuleGUIDFromHandle
(CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE ModuleHandle,
CSSM_GUID_PTR ModuleGUID)
ModuleHandle (input)
The handle of the module for which the GUID should
be returned.
ModuleGUID (output)
The GUID of the module associated with ModuleHandle.n.
This function returns the GUID of the attached
module identified by the specified handle.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_GetSubserviceUIDFromHandle
cssm_GetModuleInfo – Get the module handle state
information CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI cssm_GetModuleInfo
(CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE Module,
CSSM_GUID_PTR Guid,
CSSM_VERSION_PTR Version,
uint32 *SubServiceId,
CSSM_SERVICE_TYPE *SubServiceType,
CSSM_ATTACH_FLAGS *AttachFlags,
CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY *KeyHierarchy,
CSSM_API_MEMORY_FUNCS_PTR AttachedMemFuncs,
CSSM_FUNC_NAME_ADDR_PTR FunctionTable,
uint32 NumFunctionTable);
Module (input)
The handle to a service provider module.
GUID (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_GUID structure containing
the global unique identifier for this module.
Version (output)
The version number set on ModuleAttach.
SubServiceId (output)
The slot number of the reader to which the module
is attached.
SubServiceType (output)
A CSSM_SERVICE_TYPE value identifying the class
of security service
AttachFlags (output)
This parameter provides the caller with session
specific information asso- ciated with the module handle.
KeyHierarchy (output)
The key hierarchy supplied when the module was
attached.
AttachedMemFuncs (output)
The memory functions supplied when the module was
attached.
FunctionTable (input/output optional)
A
table of function-name and API function-pointer pairs. The caller provides
the name of the functions as input. The corresponding API function pointers
are returned on output.
The function table allows dynamic linking of CDSA
interfaces, including interfaces to Elective Module Managers, which are transparently
loaded by CSSM during the CSSM_ModuleAttach function. The caller of this function should allocate
the memory for the number of slots required.
NumFunctionTable (input)
The number of entries in the FunctionTable parameter.
If no FunctionTable is provided, this value must be zero.
This function returns the state information associated
with the module handle. The information returned by this function is that
set by the call to the CSSM_ModuleAttach function. The entry point to this function is
provided to a service module in a table of upcall functions passed to the
service provider during module attach processing.
If
the PVC checking for service providers is on, the service provider has to
introduce itself before calling this function.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
CSSM_GetPrivilege – Get CSSM privilege value (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GetPrivilege
(CSSM_PRIVILEGE *Privilege);
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
Privilege (output)
The CSSM_PRIVILEGE value currently set.
The CSSM_GetPrivilege function
returns the CSSM_PRIVILEGE value currently established in the framework.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
CSSM_GetSubserviceUIDFromHandle CSSM_GetSubserviceUIDFromHandle – Complete a subservice unique
identifier structure (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GetSubserviceUIDFromHandle
(CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE ModuleHandle,
CSSM_SUBSERVICE_UID_PTR SubserviceUID)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
ModuleHandle (input)
Handle of the module subservice for which the subservice
unique identifier should be returned.
SubserviceUID (output)
Subservice UID value associated with ModuleHandle. The caller
has to allocate the buffer.
This
function completes a structure containing the persistent unique identifier
of the attached module subservice, as identified by the input handle.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions: CSSM_GetModuleGUIDFromHandle
CSSM_Init – Initialize CSSM (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_Init(
const CSSM_VERSION *Version,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE_SCOPE Scope,
const CSSM_GUID * CallerGuid,
CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY KeyHierarchy,
CSSM_PVC_MODE *PvcPolicy,
const void *Reserved)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
Version (input)
The major and minor version number of the CSSM
release the application is compatible with.
Scope (input)
The scope of the global privilege value. The scope
may either process scope wide (CSSM_PRIVILEGE_SCOPE_PROCESS) or thread wide
(CSSM_PRIVILEGE_SCOPE_THREAD). This parameter is ignored after the first call
to CSSM_Init.
CallerGuid (input)
The GUID associated with the caller. This GUID
is used to locate the caller’s credentials when evaluating the request
for privileges.
KeyHierarchy (input)
The CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY option directing CSSM what
embedded key to use when verifying integrity of the named module.
PvcPolicy (input/output)
Configures the way in which pointer validation
checks will be performed. If not the first call to CSSM_Init, the previously configured policy is returned
in the PvcPolicy bitmask
and the CSSM_Init call
continues processing. If successfully completed, the error code CSSMERR_CSSM_PVC_ALREADY_CONFIGURED
is returned.
Value |
Description |
0 |
PVC
validation is not performed |
1 |
PVC
validation is performed on application modules |
2 |
PVC
validation is performed on service provider modules |
3 |
Both
types of PVC validations are performed |
Reserved (input)
A reserved input.
This
function initializes CSSM and verifies that the version of CSSM expected by
the application is compatible with the version of CSSM on the system. This
function should be called at least once by the application. It is an error
to call any function of the CSSM API other than CSSM_Init before a call to CSSM_Init has returned successfully (that is, with CSSM_OK).
Implementations
of CSSM might have platform specific characteristics associated with the implementation
of CSSM_SetPrivilege API.
The privilege value might have thread specific scope or process specific scope.
The application can specify the anticipated scope at CSSM_Init. If the anticipated scope is not appropriate for
the implementation, an error is returned. The scope can be configured only
once. Subsequent attempts to configure scope are ignored.
CSSM
integrity model includes the ability to make and check assertions about trusted
dynamically loaded libraries. Checking assertions happens while the program
executes. It is known as Pointer Validation Checking (PVC). Pointer validation
checking can be applied every time execution flow crosses the CSSM API or
SPI interfaces.
Performing pointer validation checks has two purposes:
• It allows exportation of CSSM.
• It aids in detering unanticipated
run-time modification of the program.
The CSSM can be configured to bypass pointer validation
under some circumstances. Pointer validation cannot be bypassed when privileged
operations are being performed.
The prerequisites for performing PVC on another
module, be it service provider, CSSM, or other library, are:
• The module must have been signed and
have an accompanying signed manifest.
• The module must be loaded into
process address space.
• An entry-point into the module must
be available.
Typically, the entry points are discovered when
a module’s functions are called by another module. The CSSM performs
pointer validation checks based on the configured checking policy. Checking
policies are established by the manufacturers of CSSM and other libraries.
The checking policy to be applied during execution is configured using the CSSM_Init call. The policy
can be configured once during the life of the process and occurs the first
time CSSM_Init is
called.
PVC POLICY
CONFIGURATION OPTIONS Pointer validation checking can be applied at the
CSSM API interface, the CSSM SPI interface, or both. The CSSM vendor can configure
a default policy through instructions contained in the CSSM signed manifest.
Manifest attributes pertaining to pointer validation checking are defined
as follows:
Module |
Tag |
Value |
Description |
CSSM |
CDSA_PVC_API |
unspecified |
CSSM
will perform PVC checks at the API boundary. |
CSSM |
CDSA_PVC_API |
OFF |
CSSM
will not perform PVC checks at the API boundary. |
CSSM |
CDSA_PVC_SPI |
unspecified |
CSSM
will perform PVC checks at the SPI boundary. |
CSSM |
CDSA_PVC_SPI |
OFF |
CSSM
will not perform PVC checks at the SPI boundary. |
App |
CDSA_PVC_API |
EXEMPT |
The
calling module is allowed to override the CSSM policy for the API boundary. |
App |
CDSA_PVC_API |
unspecified |
The
calling module cannot weaken the CSSM API policy. |
App |
CDSA_PVC_SPI |
EXEMPT |
The
calling module is allowed to override the CSSM policy for the SPI boundary. |
App |
CDSA_PVC_SPI |
unspecified |
The
calling module cannot weaken the CSSM SPI policy. |
The PvcPolicy parameter to CSSM_Init configures the run-time policy for the process.
The PvcPolicy parameter
is a bitmask allowing both API and SPI policies to be specified simultaneously.
Unspecified policies default to the most conservative operational mode. CSSM
performs pointer validation checks unless explicitly disabled. Application
modules cannot override CSSM policy unless exemptions are explicitly granted.
The following table shows the what policies can be configured for various
manifest attribute values:
CSSM
Manifest |
Calling
Module Manifest |
Acceptable
PvcPolicy Values |
| |
|
|
CDSA_PVC_API=<n/a> |
CDSA_PVC_API=EXEMPT |
API
checks: off (0) or on (1) |
CDSA_PVC_API=OFF |
CDSA_PVC_API=EXEMPT |
API
checks: off (0) or on (1) |
CDSA_PVC_API=<n/a> |
CDSA_PVC_API=<n/a> |
API
checks: on (1) |
CDSA_PVC_API=OFF |
CDSA_PVC_API=<n/a> |
API
checks: off (0) or on (1) |
The following table shows the PvcPolicy configuations available for the SPI:
SSM
Manifest |
Calling
Module Manifest |
Acceptable
PvcPolicy Values |
| |
|
|
CDSA_PVC_SPI=<n/a> |
CDSA_PVC_SPI=EXEMPT |
SPI
checks: off (0) or on (2) |
CDSA_PVC_SPI=OFF |
CDSA_PVC_SPI=EXEMPT |
SPI
checks: off (0) or on (2) |
CDSA_PVC_SPI=<n/a> |
CDSA_PVC_SPI=<n/a> |
SPI
checks: on (2) |
CDSA_PVC_SPI=OFF |
CDSA_PVC_SPI=<n/a> |
SPI
checks: off (0) or on (2) |
If an application module does not have a manifest
and CSSM requires the application module be subject to pointer validation
checks, then pointer validation checks fail and CSSM will not operate with
the anonymous module. All service provider modules are expected to have signed
manifests.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_SCOPE_NOT_SUPPORTED
CSSMERR_CSSM_PVC_ALREADY_CONFIGURED
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_PVC
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
CSSM_Introduce – Identify an executable module
(CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_Introduce
(const CSSM_GUID *ModuleID,
CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY KeyHierarchy)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
ModuleID (input)
The CSSM_GUID of the calling library or other library
that might call CDSA interfaces. The GUID is used to locate the signed manifest
credentials of the named module to calculate module integrity information.
KeyHierarchy (input)
The CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY option directing CSSM what
embedded key to use when verifying integrity of the named module.
The CSSM_Introduce function
identifies a dynamically loadable executable module (for example, DLL) to
the CSSM framework. CSSM uses the ModuleID information to locate the signed manifest and
library on the host platform. The Module Directory Service (MDS) should be
used to obtain the information. CSSM performs an integrity cross-check on
the module identified by ModuleID and
caches the result in an internal structure. The integrity cross-check uses
the KeyHierarchy information
to determine which classes of embedded public keys must serve as anchors when
doing certificate path validation. If the export key hierarchy is specified,
the set of export privileges contained in the manifest are retrieved from
the manifest and saved with the integrity state information in the cache.
Privileges granted to a module are accepted only if the manifest sections
containing the privilege set have been signed by a principal in the export
key hierarchy class and that hash of the module binary is part of the hash
of the privilege attributes.
The CSSM_Introduce can be called at any time after CSSM_Init, by any module, on behalf of any module.
Once
a module is introduced into CSSM the load location of the module must not
change. If the load location changes then the module must be reintroduced.
Once introduced, the module load location, integrity, and privilege information
is held until CSSM_Terminate is
called or the process terminates. Initialization of internal data structures
maintaining the table of introductions is performed when CSSM_Init is called.
If CSSM_Introduce is called on behalf of another module, then the
caller needs to make sure that the other module is loaded into the process
address space. If the library is already loaded into process address space,
but a reference to the library cannot be obtained, a different error is returned
(CSSMERR_CSSM_LIB_REF_NOT_FOUND).
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_KEY_HIERARCHY
CSSMERR_CSSM_LIB_REF_NOT_FOUND
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
cssm_IsFuncCallValid – Check secure linkage (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI cssm_IsFuncCallValid
(CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE hAddin,
CSSM_PROC_ADDR SrcAddress, /* application */,
CSSM_PROC_ADDR DestAddress,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE InPriv,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE *OutPriv,
CSSM_BITMASK Hints,
CSSM_BOOL * IsOK)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
hAddIn (input)
The handle identifying the attach-session whose
caller and callee scope is being tested by this function.
SrcAddress (input/optional)
An address to be tested for containment within
the application that requested and created the attach-session identified by
the module handle.
DestAddress (input/optional)
An address within a service module. The destination
address must be valid for the service provider associated with the attach-session
identified by the module handle.
InPriv (input)
The privilege value to be checked. Privilege checks
apply to both SrcAddress and DestAddress.
OutPriv (output)
If non-NULL, the global privilege will be checked
and returned in OutPriv.
Hints (input)
A flag providing search hints.
IsOK (output)
CSSM_TRUE if success, CSSM_FALSE if fail.
This
function checks secure linkage between an application and a service module.
Based on address scope of the application and the service module associated
with the attach handle, CSSM determines whether the SrcAddress is within an associated application and DestAddress is within the
associated service module. The scope of the application and the service module
is determined by their respective signed manifest credentials, which attest
to the integrity of each entity.
This function uses the input privilege value InPriv to compare against
the privilege range associated with the ranges for SrcAddress and DestAddres. The privilege check is performed when the InPriv privilege value is
non-NULL. If the EMM wants the global privilege value to be checked, InPriv is zero and OutPriv is non-NULL. CSSM
will return the privilege value in OutPriv. If integrity only checks are to be performed, InPriv is zero and OutPriv is NULL.
Another
parameter called Hints is
used to help CSSM efficiently perform the integrity and privilege verification
operations. Hints helps
CSSM know where to look to find the desired state information. In the regular
case, CSSM will look for SrcAddress in
the CallerList and DestAddress in the AttachList. For callback
functions, the SrcAddress and DestAddress are likely to
be in AttachList.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
CSSM_ListAttachedModuleManagers CSSM_ListAttachedModuleManagers – Get a list of GUIDs for the
attached module manager(CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_ListAttachedModuleManagers
(uint32 *NumberOfModuleManagers,
CSSM_GUID_PTR ModuleManagerGuids)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
NumberOfModuleManagers (input/output)
The number of GUIDs in the array. If the array
is not large enough, then the actual number needed is returned and the error
CSSMERR_CSSM_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL is returned. The caller should then allocate
an appropriately sized list and call the function again. If the supplied list
is larger than needed, the number of module managers found is returned and
no error is set.
ModuleManagerGuids (input/output)
A pointer to an array of CSSM_GUID structures,
one per active module manager. The caller allocates this array.
This
function returns a list of GUIDs for the currently attached and active module
managers in the CSSM environment.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_GUID
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
CSSM_ModuleAttach – Attach and verify a service
provider module (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_ModuleAttach
(const CSSM_GUID *ModuleGuid,
const CSSM_VERSION *Version,
const CSSM_API_MEMORY_FUNCS *MemoryFuncs,
uint32 SubserviceID,
CSSM_SERVICE_TYPE SubServiceType,
CSSM_ATTACH_FLAGS AttachFlags,
CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY KeyHierarchy,
CSSM_FUNC_NAME_ADDR *FunctionTable,
uint32 NumFunctionTable,
const void *Reserved,
CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE_PTR NewModuleHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
ModuleGuid (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_GUID structure containing
the global unique identifier for the CSP module.
Version (input)
The major and minor version number of CDSA that
the application is compatible with.
MemoryFuncs (input)
A structure containing pointers to the memory routines.
SubserviceID (input)
A SubServiceID identifying a particular subservice within the
module. Subservice IDs can be obtained from MDS or gleaned from insertion
events reported through the callback function
installed through CSSM_ModuleLoad.
Modules that provide only one service can use zero as their subservice ID.
SubServiceType (input)
A service mask describing the type of service the
caller is requesting of the service provider module.
AttachFlags (input)
A mask representing the caller’s request
for session-specific services.
KeyHierarchy (input)
The CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY option directing CSSM what
embedded key to use when verifying integrity of the named module.
FunctionTable (input/output/optional)
A table of function-name and API function-pointer
pairs. The caller provides the name of the functions as input. The corresponding
API function pointers are returned on output. The function table allows dynamic
linking of CDSA interfaces, including interfaces to Elective Module Managers
(EMMs), which are transparently loaded by CSSM during CSSM_ModuleAttach.
NumFunctionTable (input)
The number of entries in the FunctionTable parameter. If no FunctionTable is provided, this value must be zero.
Reserved (input)
This field is reserved for future use. It should
always be set to zero
NewModuleHandle (output)
A new module handle that can be used to interact
with the requested service provider. The value will be set to CSSM_INVALID_HANDLE
if the function fails.
This
function attaches the service provider module and verifies that the version
of the module expected by the application is compatible with the version on
the system. The module can implement subservices (described in your service
provider’s documentation). The caller can specify a specific subservice
provided by the module.
If the subservice is supported as part of the CSSM
framework as well as by an EMM, ModuleAttach attaches the Service Provider to the CSSM framework.
If the subservice is supported only by an EMM, ModuleAttach loads the appropriate EMM. The service provider
is given an indication of whether it is being attached to the CSSM framework
or an EMM.
The caller can provide a function table containing
function names for the desired services. On output each function name is matched
with an API function pointer. The caller can use the pointers to invoke service
module operations through CSSM.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_ADDIN_FUNCTION_TABLE
CSSMERR_CSSM_EMM_AUTHENTICATE_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSSM_ADDIN_AUTHENTICATE_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_SERVICE_MASK
CSSMERR_CSSM_MODULE_NOT_LOADED
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_SUBSERVICEID
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_KEY_HIERARCHY
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_GUID
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_ModuleDetach
CSSM_ModuleDetach – Detach application from service
provider module (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_ModuleDetach
(CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE ModuleHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
ModuleHandle (input)
The handle that describes the service provider
module.
This
function detaches the application from the service provider module.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_ModuleAttach
CSSM_ModuleLoad – Initialize the security service
module (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_ModuleLoad
(const CSSM_GUID *ModuleGuid,
CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY KeyHierarchy,
CSSM_API_ModuleEventHandler AppNotifyCallback,
void* AppNotifyCallbackCtx)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
ModuleGuid (input)
The GUID of the module selected for loading.
KeyHierarchy (input)
The CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY option directing CSSM what
embedded key to use when verifying integrity of the named module.
AppNotifyCallback (input/optional)
The event notification function provided by the
caller. This defines the callback for event notifications from the loaded
(and later attached) service module.
AppNotifyCallbackCtx (input/optional)
When
the selected service module raises an event, this context is passed as an
input to the event handler specified by AppNotifyCallback. CSSM does not interpret or modify the value of AppNotifyCallbackCtx.
This
function initializes the security service module. Initialization includes
registering the application’s module-event handler and enabling events
with the security service service module. The application can choose to provide
an event handler function to receive notification of insert, remove, and fault
events. The specified event handler is the single callback point for all attached
sessions with the specified service module.
The function CSSM_Init must be invoked prior to calling CSSM_ModuleLoad. The function CSSM_ModuleAttach can be
invoked multiple times per call to CSSM_ModuleLoad.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_GUID
CSSMERR_CSSM_ADDIN_LOAD_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSSM_EMM_LOAD_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_KEY_HIERARCHY
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
CSSM_ModuleUnload – Deregister event notification
callbacks (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_ModuleUnload
(const CSSM_GUID *ModuleGuid,
CSSM_API_ModuleEventHandler AppNotifyCallback,
void* AppNotifyCallbackCtx)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
ModuleGuid (input)
The GUID of the module selected for unloading.
AppNotifyCallback (input/optional)
The event notification function to be deregistered.
The function must have been provided by the caller in CSSM_ModuleLoad.
AppNotifyCallbackCtx (input/optional)
The
event notification context that was provided in the corresponding call to CSSM_ModuleLoad.
The
function deregisters event notification callbacks for the caller identified
by ModuleGuid.
The CSSM_ModuleUnload function
is the analog call to CSSM_ModuleLoad.
If all callbacks registered with CSSM are removed, then CSSM unloads the service
module that was loaded by calls to CSSM_ModuleLoad. Calls to CSSM_ModuleUnload that are not matched with a previous call to CSSM_ModuleLoad result in
an error.
The CSSM uses the three input parameters ModuleGuid, AppNotifyCallback, and AppNotifyCallbackCtx to
uniquely identify registered callbacks.
This function should be invoked after all necessary
calls to CSSM_ModuleDetach have
been performed.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_ADDIN_UNLOAD_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSSM_EMM_UNLOAD_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSSM_EVENT_NOTIFICATION_CALLBACK_NOT_FOUND
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
cssm_ReleaseAttachFunctions cssm_ReleaseAttachFunctions – Release lock on the SP function
table (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI cssm_ReleaseAttachFunctions
(CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE hAddIn)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
hAddIn (input)
The handle identifying the attach-session whose
function table is to be released by this function.
This
function releases the lock on the SP function table for the service module
identified by the module handle. The SPI function table was obtained by the
elective module manager through the cssm_GetAttachFunctions operation.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
CSSM_SetContext – Replace all context information
(CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_SetContext
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle to the context.
Context (input)
The context data describing the service to replace
the current service associated with context handle CCHandle.
This
function replaces all context information associated with an existing context
specified by CCHandle.
The contents of the basic context structure and all attributes included in
that structure are replaced by the context structure and attribute values
contained in the Context input
parameter .
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_ATTRIBUTE
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_GetContext
CSSM_SetPrivilege – Store privilege value in CSSM
framework (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_SetPrivilege
(CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
Privilege (input)
The CSSM_PRIVILEGE value to be applied to subsequent
calls to CSSM interfaces.
The CSSM_SetPrivilege function
accepts as input a privilege value and stores it in the CSSM framework. The
integrity credentials of the module calling CSSM_SetPrivilege must be verified by CSSM before the privilege
value is updated. Integrity credentials are established using CSSM_Introduce. CSSM will
perform a pointer validation check to ensure the caller has been previously
introduced. The CSSM_SetPrivilege function
will fail if no integrity information can be found for the caller.
After
pointer validation checks, CSSM verifies the requested privilege is authorized.
This is done by comparing Privilege with
the set of privileges contained in the caller manifest. If Privilege is not a member, the CSSM_SetPrivilege call fails.
Subsequent calls to the framework that require
privileges inherit the privilege value previously established by CSSM_SetPrivilege. CSSM
will perform pointer validation checks on the API caller before servicing
the API call. If OK, then the Privilege value is supplied to the SPI function.
Internally,
CSSM builds and maintains privilege information based on the chosen scope
of the implementation. The scope may be dictated by the capabilities of the
platform hosting the CSSM. If threading is available, the privilege value
can be associated with the thread ID of the currently executing thread. In
this scenario, CSSM can manage a table of tuples consisting of threadID and privilege value.
If threading is not available, the privilege value can be global to the process.
Because
the selected privilege value is shared, the application programmer should
take precautions to reset the privilege value whenever program flow leaves
the caller’s module and again when control flow returns. In general,
any time there is a possibility for CSSM_SetPrivilege to be called while within the context of the security
critical section, CSSM_SetPrivilege should
be called again. Otherwise, the module receiving execution control could have
called CSSM_SetPrivilege,
resulting in the privilege value being reset.
Data
structures used to maintain the global privilege value should be initialized
in CSSM_Init.
This includes lock initialization and preliminary resource allocation. The CSSM_Init function is assumed
to be idempotent with respect to shared structure initialization. This means CSSM_Init will ensure a
single thread initializes the shared structure and subsequent calls to CSSM_Init will not reinitialize
it. A reference count of calls to CSSM_Init is needed to ensure matching calls to CSSM_Terminate are handled.
Resource
cleanup is performed at CSSM_Terminate after the reference count falls to zero. The last
call to CSSM_Terminate results
in shared resources being freed and lock structures being released.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
CSSM_SPI_ModuleAttach – Attach a service provider module(CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMSPI CSSM_SPI_ModuleAttach
(const CSSM_GUID *ModuleGuid,
const CSSM_VERSION *Version,
uint32 SubserviceID,
CSSM_SERVICE_TYPE SubServiceType,
CSSM_ATTACH_FLAGS AttachFlags,
CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE ModuleHandle,
CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY KeyHierarchy,
const CSSM_GUID *CssmGuid,
const CSSM_GUID *ModuleManagerGuid,
const CSSM_GUID *CallerGuid,
const CSSM_UPCALLS *Upcalls,
CSSM_MODULE_FUNCS_PTR *FuncTbl)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
ModuleGuid (input)
The CSSM_GUID of the invoked service provider module.
Version (input)
The major and minor version number of the required
level of system services and features. The service module must determine whether
its services are compatible with the required version.
SubserviceId (input)
The identifier for the requested subservice within
this module. If only one service is provided by the module, then subserviceId can be zero.
SubServiceType (output)
A CSSM_SERVICE_MASK indicating the type of services
provided by the service module and the ordering of the function table returned
in the output parameter FuncTbl.
AttachFlags (input)
A mask representing the caller’s request
for session-specific services.
ModuleHandle (input)
The CSSM_HANDLE value assigned by CSSM and associated
with the attach session being created by this function.
KeyHierarchy (input)
The CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY option directing CSSM which
embedded key or keys to use when verifying integrity of the named modules.
CssmGuid (input)
The CSSM_GUID of the CSSM invoking this function.
ModuleManagerGuid (input)
The CSSM_GUID of the module that will route calls
to the service provider.
CallerGuid (input)
The CSSM_GUID of the caller who invoked CSSM_ModuleAttach, which
resulted in CSSM invoking this function.
Upcalls (input)
A set of function pointers the service module must
use to obtain selected CSSM services and to manage application memory. The
memory management functions are provided when the application invokes CSSM_ModuleAttach. CSSM
forwards these function pointers with CSSM service function pointers to the
module.
FuncTbl (output)
A CSSM_MODULE_FUNCS table containing pointers to
the service module functions the caller can use. CSSM uses this table to proxy
calls from an application caller to the add-in service module.
This
function is invoked by CSSM once for each invocation of CSSM_ModuleAttach, specifying the module identified by ModuleGuid. Four entities
are stakeholders in this function and each is identified by a CSSM_GUID value:
Service Module
The executing service provider performing the CSSM_SPI_ModuleAttach operation.
The module is identified by ModuleGuid.
CSSM
The CSSM that invoked the service module. CSSM
is identified by CssmGuid.
ModuleManagerGuid
The
module that will be routing calls to the service provider. This value will
be the same as CssmGuid if
CSSM is managing the calls to this service provider.
Caller
The entity that invoked CSSM through the CSSM_ModuleAttach function.
The caller is identified by CallerGuid.
The service provider module should perform an integrity
check of CSSM. CssmGuid can
be used to locate CSSM’s signed manifest credentials. The service provider
can require an integrity check of the Caller. The CallerGuid parameter can be used to locate the Caller’s
signed manifest credentials. The KeyHierarchy flag identifies the class of embedded public keys
CSSM will use to check the integrity of the service provider. If the manifest
for the target module does not encounter an embedded key for all the key classes
in KeyHierarchy,
the integrity cross-check fails.
The service module must verify compatibility with
the system version level specified by Version. If the version is not compatible, then this function
fails. The service module should perform all initializations required to support
the new attached session and should return a function table for the SPI entry
points that can be invoked by CSSM in response to API invocations by CallerGuid. CSSM uses this
function table to dispatch requests for the attach session created by this
function. Each attach session has its own function table.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions: CSSM_SPI_ModuleDetach, CSSM_SPI_ModuleLoad
CSSM_SPI_ModuleDetach – Notify service module of a
context event (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMSPI CSSM_SPI_ModuleDetach
(CSSM_MODULE_HANDLE ModuleHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
ModuleHandle (input)
The CSSM_HANDLE value associated with the attach
session being terminated by this function.
This
function is invoked by CSSM once for each invocation of CSSM_ModuleDetach specifying the attach-session identified by ModuleHandle. The function
entry point for CSSM_SPI_ModuleDetach is
included in the module function table CSSM_MODULE_FUNCS returned to CSSM as output of a successful CSSM_SPI_ModuleAttach.
The
service module must perform all cleanup operations associated with the specified
attach handle.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions: CSSM_SPI_ModuleAttach, CSSM_SPI_ModuleUnload
CSSM_SPI_ModuleLoad – Initialize process between
CSSM and the add-in service module (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMSPI CSSM_SPI_ModuleLoad
(const CSSM_GUID *CssmGuid,
const CSSM_GUID *ModuleGuid,
CSSM_SPI_ModuleEventHandler CssmNotifyCallback,
void* CssmNotifyCallbackCtx)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CssmGuid (input)
The CSSM_GUID of the caller. Used to locate the
caller’s signed manifest credentials.
ModuleGuid (input)
The CSSM_GUID of the invoked service provider module.
Used to locate the module’s signed manifest credentials.
CssmNotifyCallback (input)
A function pointer for the CSSM event handler that
manages events of type CSSM_MODULE_EVENT.
CssmNotifyCallbackCtx (input)
The context to be returned to CSSM as input on
each callback to the event handler defined by CssmNotifyCallback.
This
function completes the module initialization process between CSSM and the
add-in service module. Before invoking this function, CSSM verifies the add-in
service module’s manifest credentials. If the credentials verify this
module is loaded (physically if required), the CSSM_SPI_ModuleLoad function is invoked.
The CssmGuid parameter identifies
the caller and should be used by the module to locate the caller’s signed
manifest credentials and to complete integrity verification and secure linkage
checks on the caller. The ModuleGuid identifies
the invoked module and should be used by the module to locate its credentials
and to complete an integrity self-check.
The CssmNotifyCallback and CssmNotifyCallbackCtx parameters define a callback and callback context
respectively. The module must retain this information for later use. The module
should use the callback to notify CSSM of module events of type CSSM_MODULE_EVENT
in any ongoing, attached sessions.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions: CSSM_SPI_ModuleAttach, CSSM_SPI_ModuleUnload
CSSM_SPI_ModuleUnload – Disable events and deregister
CSSM event notification (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMSPI CSSM_SPI_ModuleUnload
(const CSSM_GUID *CssmGuid,
const CSSM_GUID *ModuleGuid,
CSSM_SPI_ModuleEventHandler CssmNotifyCallback,
void* CssmNotifyCallbackCtx)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CssmGuid (input)
The CSSM_GUID of the caller.
ModuleGuid (input)
The CSSM_GUID of the invoked service provider module.
CssmNotifyCallback (input)
A function pointer for the CSSM event handler that
manages events of type CSSM_MODULE_EVENT.
CssmNotifyCallbackCtx (input)
The context to be returned to CSSM as input on
each callback to the event handler defined by CssmNotifyCallback.
This
function disables events and deregisters the CSSM event-notification function. The add-in service module can perform
cleanup operations, reversing the initialization performed in CSSM_SPI_ModuleLoad.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_SPI_ModuleDetach, CSSM_SPI_ModuleLoad
CSSM_Terminate – Terminate the use of CSSM (CDSA) Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
None
This
function terminates the caller’s use of CSSM. CSSM can clean up all
internal states associated with the calling application. This function must
be called once by each application.
CSSM_Terminate must be called
one time for each time CSSM_Init was
previously called.
CSSM services remain available to the program until
the final call to CSSM_Terminate completes.
After that final call, all information introduced by the caller (including
privileges, handles, contexts, introduced libraries, and so forth) is lost,
and it is an error to subsequently call any CSSM API function other than CSSM_Init.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions CSSM_Init
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult – Return the results of the credentials
request (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier,
const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthCredentials,
sint32 *EstimatedTime,
CSSM_BOOL *ConfirmationRequired,
CSSM_TP_RESULT_SET_PTR *RetrieveOutput)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certification authority
module used to perform this function.
ReferenceIdentifier (input)
A reference identifier that uniquely identifies
the CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest call
that initiated the certificate service request whose results are returned
by this function. The identifier persists across application executions and
becomes undefined when all local processing of the request has completed.
Local processing is completed in one of two ways:
• For certificate services that do not
require explicit confirmation by the requester, the reference identifier is
invalidated when the corresponding CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult function completes (by returning valid results
or by failure, which blocks returned results).
• For certificate services that
require explicit confirmation by the requester, the reference identifier is
invalidated by successfully invoking the function CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult.
CallerAuthCredentials (input/optional)
This
structure contains a set of caller authentication credentials. The authentication
information can be a passphrase, a PIN, a completed registration form, a certificate,
or a template of user-specific data. The required set of credentials is defined
by the service provider module and recorded in a record in the MDS Primary
relation. Multiple credentials can be required. If the local service provider
module does not require credentials from a caller, then the Credentials field of this verification context structure can
be NULL. The structure optionally contains additional credentials that can
be used to support the authentication process. Authentication credentials
required by the authority should be included in the RequestInput. The local TP module can forward information from CallerAuthCredentials to
the authority, as appropriate, but is not required to do so.
EstimatedTime (output)
The number of seconds estimated before the results
of a requested service will be returned to the requester. When the local TP
module or the authority process cannot estimate the time required to perform
the requested service, the output value for estimated time is CSSM_ESTIMATED_TIME_UNKNOWN.
ConfirmationRequired (output)
A Boolean value indicating whether the caller must
invoke CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult to
acknowledge retrieving the results of the service request. CSSM_TRUE indicates
the caller must call CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult. CSSM_FALSE indicates that the caller must not
call CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult.
The value of this output parameter is not applicable until CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult completes by returning results of the request
or terminates in unrecoverable failure.
RetrieveOutput (output)
A pointer to the results returned by the authority
in response to the service requests submitted by CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest. The output results are ordered corresponding
to the requests. The structure of the response set is determined by the type
of request. The caller and the service provider must retain knowledge of the
request type associated with the ReferenceIdentifier.
This
function returns the results of a CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest call.
The single identifier ReferenceIdentifier denotes the CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest invocation that initiated the request.
It
is possible that the results are not ready to be retrieved when this call
is made. In that case, an EstimatedTime to complete processing is returned. The caller
must attempt to retrieve the results again after the estimated time to completion
has elapsed.
This function can fail in total for any one of
the following reasons:
• The reference identifier is invalid.
• The TP process cannot be located.
• The TP process encountered a fatal
error when attempting to process the requests.
When
this function completes, the set of return results is ordered corresponding
to the order of the originating request.
Some certificate services require the requester
to confirm retrieval of the results. The ConfirmationRequired parameter indicates whether the caller must confirm
completion of CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult by calling CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult.
A CSSM_RETURN value combined with estimated time
to indicate one of three results:
Complete Function |
Function Return |
RetrieveOutput |
EstimatedTime |
Result |
Value |
|
|
Request
results returned to caller |
CSSM_OK |
Non-NULL
pointer |
NA |
Request
results not ready, but expected in the future |
CSSM_OK |
NULL
pointer |
CSSM_ESTIMATED_TIME_
UNKNOWN or <estimated seconds> |
Fatal
Error, results will never be returned |
(!CSSM_OK) |
NA |
NA |
The (!CSSM_OK) return value represents a specific
error code.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_IDENTIFIER_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_IDENTIFIER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_REQUEST_LOST
CSSMERR_TP_REQUEST_REJECTED
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest
Functions
for the TP SPI:
TP_SubmitCredRequest
CSSM_Unintroduce – Remove module (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSM_Unintroduce
(const CSSM_GUID *ModuleID)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
ModuleID (input)
The CSSM_GUID of the calling library or other library
that can call CDSA interfaces. The GUID is used to locate the module integrity
and privilege information. If the ModuleID is NULL, then the caller will be unintroduced.
The CSSM_Unintroduce function
removes the module referenced by ModuleID from the list of module information maintained
by the CSSM framework.
A caller can unintroduce modules other than itself
if the caller has been previously introduced.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_GUID
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes – Update context attribute values
(CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_UpdateContextAttributes
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
uint32 NumberOfAttributes,
const CSSM_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE *ContextAttributes)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle to the existing context.
NumberOfAttributes (input)
The number of CSSM_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE structures
to allocate.
ContextAttributes (input)
Pointer to data that describes the attributes to
be associated with this context.
This
function updates one or more context attribute values stored as part of an
existing context specified by CCHandle. The basic context structure is not modified by
this function. Only the context attributes are updated.
The NumberOfAttributes parameter
specifies the number of attributes to update. The new attribute values are
specified in ContextAttributes.
If an attribute provided in ContextAttributes is already present in the existing context, the
existing value is replaced by the new value. If an attribute provided in ContextAttributes is not
present in the existing context, then the new attribute is added. Attribute
values are never deleted from the existing context.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_ATTRIBUTE
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_DeleteContextAttributes, CSSM_GetContextAttribute
DecryptData: CSSM_DecryptData,
CSP_DecryptData – Decrypt buffer data (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DecryptData
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CipherBufs,
uint32 CipherBufCount,
CSSM_DATA_PTR ClearBufs,
uint32 ClearBufCount,
uint32 *bytesDecrypted,
CSSM_DATA_PTR RemData)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_DecryptData
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
const CSSM_DATA *CipherBufs,
uint32 CipherBufCount,
CSSM_DATA_PTR ClearBufs,
uint32 ClearBufCount,
uint32 *bytesDecrypted,
CSSM_DATA_PTR RemData,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
CipherBufs (input)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the data to be decrypted.
CipherBufCount (input)
The number of CipherBufs.
ClearBufs (output)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the decrypted data resulting from the decryption operation.
ClearBufCount (input)
The number of ClearBufs.
bytesDecrypted (output)
A pointer to uint32 for the size of the decrypted data in bytes.
RemData (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure for the remaining
plain text if there is not enough buffer space available in the output data
structures.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
A pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
Privilege (input)
The export privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation. This parameter is forwarded to the CSP after CSSM verifies the
caller and service provider privilege set includes the specified PRIVILEGE.
This function decrypts all data contained in the
set of input buffers using information in the context. The CSSM_QuerySize (CSSM API), or CSP_QuerySize (CSP SPI), function can be used to estimate the
output buffer size required. The minimum number of buffers required to contain
the resulting plain text is produced as output. If the plain text result does
not fit within the set of output buffers, the remaining plain text is returned
in the single output buffer RemData.
The
CSP can require that the cryptographic context include access credentials
for authentication and authorization checks when using a private key or a
secret key.
The output is returned to the caller either by
filling the caller-specified buffer or by using the application’s declared
memory allocation functions to allocate buffer space. To specify a specific,
pre-allocated output buffer, the caller must provide an array of one or more
CSSM_DATA structures, each containing a Length field value greater than zero
and a non-NULL data pointer field value. To specify automatic output buffer
allocation by the CSP, the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA
structures, each containing a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL
data pointer field value. The application is always responsible for deallocating
the memory when it is no longer needed. In-place decryption can be done by
supplying the same input and output buffers.
The output is returned to the caller as specified
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_BLOCK_SIZE_MISMATCH
CSSMERR_CSP_OUTPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_QuerySize, CSSM_EncryptData, CSSM_DecryptDataInit, CSSM_DecryptDataUpdate, CSSM_DecryptDataFinal, CSSM_DecryptP, CSSM_DecryptDataInitP
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_QuerySize, CSP_EncryptData, CSP_DecryptDataInit, CSP_DecryptDataUpdate, CSP_DecryptDataFinal
DecryptDataFinal:
CSSM_DecryptDataFinal, CSP_DecryptDataFinal – Finalize staged decryption
process (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DecryptDataFinal
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR RemData)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_DecryptDataFinal
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR RemData)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
RemData (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure for the last
decrypted block, if necessary.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function finalizes the staged decryption process by returning any remaining
plain text not returned in the previous staged decryption call. The plain
text is returned in a single buffer.
The output is returned to the caller either by
filling the caller-specified buffer or by using the application’s declared
memory allocation functions to allocate buffer space. To specify a specific,
pre-allocated output buffer, the caller must provide an array of one or more
CSSM_DATA structures, each containing a Length field value greater than zero
and a non-NULL data pointer field value. To specify automatic output buffer
allocation by the CSP, the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA
structures, each containing a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL
data pointer field value. The application is always responsible for deallocating
the memory when it is no longer needed.
The output is returned to the caller as specified
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_BLOCK_SIZE_MISMATCH
CSSMERR_CSP_OUTPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DecryptData, CSSM_DecryptDataInit, CSSM_DecryptDataUpdate
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_DecryptData, CSP_DecryptDataInit, CSP_DecryptDataUpdate
DecryptDataInit:
CSSM_DecryptDataInit, CSP_DecryptDataInit – Initialize the staged decrypt
function(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DecryptDataInit
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSSM_CSP_DecryptDataInit
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
Privilege (input)
The export privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation. This parameter is forwarded to the CSP after CSSM verifies the
caller and service provider privilege set includes the specified PRIVILEGE.
This
function initializes the staged decrypt function.
The
CSP can require that the cryptographic context include access credentials
for authentication and authorization checks when using a private key or a
secret key.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DecryptData, CSSM_DecryptDataUpdate, CSSM_DecryptDataFinal, CSSM_DecryptDataP, CSSM_DecryptDataInitP
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_DecryptData, CSP_DecryptDataUpdate, CSP_DecryptDataFinal
DecryptDataInitP – Intialize the staged decrypt
function with privilege (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DecryptDataInitP
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
Privilege (input)
The privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation.
See CSSM_DecryptDataInit for other parameters.
This
function is similar to CSSM_DecryptDataInit. It also accepts a USEE tag as a privilege request
parameter. CSSM checks that either its own privilege set or the application’s
privilege set (if the application is signed) includes the tag. If the tag
is found and the service provider privilege set indicates that it is supported,
the tag is forwarded to the service provider.
For
staged operations using privilege initialization functions CSSM_DecryptDataInitP, the completion functions CSSM_DecryptDataUpdate and CSSM_DecryptDataFinalize are used.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_DecryptData, CSSM_EncryptDataInit, CSSM_EncryptDataUpdate, CSSM_EncryptDataFinal, CSSM_EncryptDataP, CSSM_EncryptDataInitP, CSSM_DecryptP, CSSM_DecryptDataInitP, CSSM_QuerySize
DecryptDataP – Decrypt data with privilege
(CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DecryptDataP
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CipherBufs,
uint32 CipherBufCount,
CSSM_DATA_PTR ClearBufs,
uint32 ClearBufCount,
uint32 *bytesDecrypted,
CSSM_DATA_PTR RemData,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
Privilege (input)
The privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation.
See CSSM_DecryptData for other parameters.
This
function is similar to CSSM_DecryptData. It also accepts a USEE tag as a privilege request
parameter. CSSM checks that either its privilege set or the application’s
privilege set (if the application is signed) includes the tag. If the tag
is found and the service provider privilege set indicates that it is supported,
the tag is forwarded to the service provider.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_BLOCK_SIZE_MISMATCH
CSSMERR_CSP_OUTPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_DecryptData, CSSM_EncryptDataInit, CSSM_EncryptDataUpdate, CSSM_EncryptDataFinal, CSSM_EncryptDataP, CSSM_EncryptDataInitP, CSSM_DecryptP, CSSM_DecryptDataInitP, CSSM_QuerySize
DecryptDataUpdate:
CSSM_DecryptDataUpdate, CSP_DecryptDataUpdate – Continue the staged decryption
process (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DecryptDataUpdate
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CipherBufs,
uint32 CipherBufCount,
CSSM_DATA_PTR ClearBufs,
uint32 ClearBufCount,
uint32 *bytesDecrypted)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_DecryptDataUpdate
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CipherBufs,
uint32 CipherBufCount,
CSSM_DATA_PTR ClearBufs,
uint32 ClearBufCount,
uint32 *bytesDecrypted)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
CipherBufs (input)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the data to be operated on.
CipherBufCount (input)
The number of CipherBufs.
ClearBufs (output)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the decrypted data resulting from the decryption operation.
ClearBufCount (input)
The number of ClearBufs.
bytesDecrypted (output)
A pointer to uint32 for the size of the decrypted data in bytes.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function continues the staged decryption process over all data in the set
of input buffers. There can be algorithm-specific and token-specific rules
restricting the lengths of data in CSSM_DecryptUpdate calls, but multiple input buffers are supported.
The minimum number of buffers required to contain the resulting plain text
is produced as output. Excess output buffer space is not remembered across
staged decryption calls. Each staged call begins filling one or more new output
buffers. The CSSM_QuerySize (CSSM
API), or CSP_QuerySize (CSP
SPI), function can be used to estimate the output buffer size required for
each update call.
The output is returned to the caller either by
filling the caller-specified buffer or by using the application’s declared
memory allocation functions to allocate buffer space. To specify a specific,
preallocated output buffer, the caller must provide an array of one or more
CSSM_DATA structures, each containing a Length field value greater than zero
and a non-NULL data pointer field value. To specify automatic output buffer
allocation by the CSP, the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA
structures, each containing a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL
data pointer field value. The application is always responsible for deallocating
the memory when it is no longer needed. In-place decryption can be done by
supplying the same input and output buffers.
The output is returned to the caller as specified
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_QuerySize, CSSM_DecryptData, CSSM_DecryptDataInit, CSSM_DecryptDataFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_QuerySize, CSP_DecryptData, CSP_DecryptDataInit, CSP_DecryptDataFinal
DeregisterDispatchTable – Invalidate CSSM pointers to
EMM (CDSA) (not currently supported) Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
None.
This
EMM-defined function is invoked by CSSM once for each CSSM_ModuleDetach operation issued against a service provider of
the type managed by the EMM. CSSM uses this function to inform the EMM that
the set of CSSM function pointers provided to the EMM when the session was
attached are no longer valid.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions: RegisterDispatchTable
DeriveKey: CSSM_DeriveKey,
CSP_DeriveKey – Derive new symmetric key (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DeriveKey
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Param,
uint32 KeyUsage,
uint32 KeyAttr,
const CSSM_DATA *KeyLabel,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry,
CSSM_KEY_PTR DerivedKey)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_DeriveKey
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Param,
uint32 KeyUsage,
uint32 KeyAttr,
const CSSM_DATA *KeyLabel,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry,
CSSM_KEY_PTR DerivedKey)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation.
Param (input/output)
This parameter varies depending on the derivation
algorithm. Password based derivation algorithms use this parameter to return
a cipher block chaining initialization vector. Concatenation algorithms use
this parameter to get the second item to concatenate.
KeyUsage (input)
A bit mask indicating all permitted uses for the
new derived key.
KeyAttr (input)
A bit mask defining other attribute values for
the new derived key.
KeyLabel (input/optional)
Pointer to a byte string that will be used as the
label for the derived key.
CredAndAclEntry (input/optional)
A structure containing one or more credentials
authorized for creating a key and the prototype ACL entry that will control
future use of the newly created key. The credentials and ACL entry prototype
can be presented as immediate values or callback functions can be provided
for use by the CSP to acquire the credentials and/or the subject of the ACL
entry interactively. If the CSP provides public access for creating a key,
then the credentials can be NULL. If the CSP defines a default initial ACL
entry for the new key, then the ACL entry prototype can be empty.
DerivedKey (output)
A pointer to a CSSM_KEY structure that returns
the derived key.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
This
function derives a new symmetric key using the context and/or information
from the base key in the context. The CSP can require that the cryptographic
context include access credentials for authentication and authorization checks
when using a private key or a secret key.
Authorization policy can restrict the set of callers
who can create a new resource. In this case, the caller must present a set
of access credentials for authorization. Upon successfully authenticating
the credentials, the template that verified the presented samples identifies
the ACL entry that will be used in the authorization computation. If the caller
is authorized, the new resource is created.
The caller must provide an initial ACL entry to
be associated with the newly created resource. This entry is used to control
future access to the new resource and (since the subject is deemed to be the "Owner")
exercise control over its associated ACL. The caller can specify the following
items for initializing an ACL entry:
Subject
A CSSM_LIST structure, containing the type of the
subject and a template value that can be used to verify samples that are presented
in credentials when resource access is requested.
Delegation flag
A
value indicating whether the Subject can delegate the permissions recorded
in the AuthorizationTag.
(This item only applies to public key subjects).
Authorization tag
The
set of permissions that are granted to the Subject.
Validity period
The
start time and the stop time for which the ACL entry is valid.
ACL entry tag
A user-defined string value associated with the
ACL entry.
The service provider can modify the caller-provided
initial ACL entry to conform to any innate resource-access policy that the
service provider may be required to enforce. If the initial ACL entry provided
by the caller contains values or permissions that are not supported by the
service provider, then the service provider can modify the initial ACL appropriately
or can fail the request to create the new resource. Service providers list
their supported AuthorizationTag values
in their Module Directory Services primary record.
The
CSP can require that the cryptographic context include access credentials
for authentication and authorization checks when using a private key or a
secret key.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_KEY_LABEL_ALREADY_EXISTS
The KeyData field of the CSSM_KEY
structure is allocated by the CSP. The application is required to free this
memory using the CSSM_FreeKey (CSSM
API), or CSP_FreeKey (CSP
SPI) call, or with the memory functions registered for the CSPHandle.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_CSP_CreateDeriveKeyContext
DigestData: CSSM_DigestData,
CSP_DigestData – Compute message digest (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DigestData
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Digest)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_DigestData
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Digest)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
DataBufs (input)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the data to be operated on.
DataBufCount (input)
The number of DataBufs.
Digest (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure for the message
digest.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
This
function computes a message digest for all data contained in the set of input
buffers.
The output is returned to the caller either by
filling the caller-specified buffer or by using the application’s declared
memory allocation functions to allocate buffer space. To specify a specific,
preallocated output buffer, the caller must provide an array of one or more
CSSM_DATA structures, each containing a Length field value greater than zero
and a non-NULL data pointer field value. To specify automatic output buffer
allocation by the CSP, the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA
structures, each containing a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL
data pointer field value. The application is always responsible for deallocating
the memory when it is no longer needed.
The output is returned to the caller as specifed
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_OUTPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DigestDataInit, CSSM_DigestDataUpdate, CSSM_DigestDataFinal, CSSM_DigestDataClone
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_DigestDataInit, CSP_DigestDataUpdate, CSP_DigestDataFinal, CSP_DigestDataClone
DigestDataClone:
CSSM_DigestDataClone, CSP_DigestDataClone – Clone a staged message digest
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DigestDataClone
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE *ClonednewCCHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_DigestDataClone
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE ClonednewCCHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of a staged
message digest operation.
ClonednewCCHandle (output)
The cloned digest context handle. The handle will
be set to CSSM_INVALID_HANDLE if the function fails.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function clones a given staged message digest context with its cryptographic
attributes and intermediate result.
When
a digest context is cloned, a new context is created with data associated
with the parent context. Changes made to the parent context after calling
this function will not be reflected in the cloned context. The cloned context
could be used with the CSSM_DigestDataUpdate and CSSM_DigestDataFinal functions.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard. .
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DigestData, CSSM_DigestDataInit, CSSM_DigestDataUpdate, CSSM_DigestDataFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_DigestData, CSP_DigestDataInit, CSP_DigestDataUpdate, CSP_DigestDataFinal
DigestDataFinal:
CSSM_DigestDataFinal, CSP_DigestDataFinal – Finalize the staged message
digest (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DigestDataFinal
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Digest)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_DigestDataFinal
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Digest)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
Digest (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure for the message
digest.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function finalizes the staged message digest function.
The output is returned to the caller either by
filling the caller-specified buffer or by using the application’s declared
memory allocation functions to allocate buffer space. To specify a specific,
preallocated output buffer, the caller must provide an array of one or more
CSSM_DATA structures, each containing a Length field value greater than zero
and a non-NULL data pointer field value. To specify automatic output buffer
allocation by the CSP, the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA
structures, each containing a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL
data pointer field value. The application is always responsible for deallocating
the memory when it is no longer needed.
The output is returned to the caller as specified
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard. .
CSSMERR_CSP_OUTPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DigestData, CSSM_DigestDataInit, CSSM_DigestDataUpdate, CSSM_DigestDataClone
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_DigestData, CSP_DigestDataInit, CSP_DigestDataUpdate, CSP_DigestDataClone
DigestDataInit:
CSSM_DigestDataInit, CSP_DigestDataInit – Initialize the staged message
digest (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DigestDataInit
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_DigestDataInit
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
This
function initializes the staged message digest function.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
.
None specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DigestData, CSSM_DigestDataUpdate, CSSM_DigestDataClone, CSSM_DigestDataFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_DigestData, CSP_DigestDataUpdate, CSP_DigestDataClone, CSP_DigestDataFinal
DigestDataUpdate:
CSSM_DigestDataUpdate – Continue the staged process
of digesting (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DigestDataUpdate
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_DigestDataUpdate
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
DataBufs (input)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the data to be operated on.
DataBufCount (input)
The number of DataBufs.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function continues the staged process of digesting all data contained in the
set of input buffers. The resulting digest value will be returned as part
of the staged digesting process.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DigestData, CSSM_DigestDataInit, CSSM_DigestDataClone, CSSM_DigestDataFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
Functions: CSP_DigestData, CSP_DigestDataInit, CSP_DigestDataClone, CSP_DigestDataFinal
DL_Authenticate:
CSSM_DL_Authenticate – Provide authentication credentials
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_Authenticate
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_DB_ACCESS_TYPE AccessRequest,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_Authenticate
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_DB_ACCESS_TYPE AccessRequest,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the add-in data
storage library module used to perform this function and the data store to
which access is being requested. If the form of authentication being requested
is authentication to the DL module in general, then the data store handle
must be NULL.
AccessRequest (input)
An indicator of the requested access mode for the
data store or DL module in general.
AccessCred (input)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
being presented for authentication by the caller. The credentials can apply
to the DL module in general or to a particular data store managed by this
service module. The credentials required for creating new data stores is defined
by the DL and recorded in a record in the MDS Primary DL relation. The required
set of credentials to access a particular data store is defined by the DbInfo record containing
meta-data for the specified data store.
The credentials structure can contain multiple
types of credentials, as required for multi-factor authentication. The credential
data can be an immediate value, such as a passphrase, PIN, certificate, or
template of user-specific data, or the caller can specify a callback function
the DL can use to obtain one or more credentials.
This
function allows the caller to provide authentication credentials to the DL
module at a time other than data store creation, deletion, open, import, and
export. AccessRequest defines the type of access to be associated with the
caller. If the authentication credential applies to access and use of a DL
module in general, then the data store handle specified in the DLDBHandle must be NULL.
When the authorization credential is to apply to a specific data store, the
handle for that data store must be specified in the DLDBHandle pair.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_ACCESS_REQUEST
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
DL_ChangeDbAcl:
CSSM_DL_ChangeDbAcl – Edit stored ACL (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_ChangeDbAcl
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_ACL_EDIT *AclEdit)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_ChangeDbAcl
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_ACL_EDIT *AclEdit)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the data storage
library module to be used to perform this function, and the open data store
whose associated ACL entries are to be updated.
AccessCred (input)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
used to authenticate and validate the caller’s authorization to modify
the ACL associated with the target data base. Required credentials can include
zero or more certificates, zero or more caller names, and one or more samples.
If certificates and/or caller names are provided as input these must be provided
as immediate values in this structure. The samples can be provided as immediate
values or can be obtained through a callback function included in the AccessCred structure.
AclEdit (input)
A structure containing information that defines
the edit operation. Valid operations include adding, replacing and deleting
entries in the set of ACL entries managed by the service provider. The AclEdit can contain information
for a new ACL entry and a unique handle identifying an existing ACL entry.
The information controls the edit operation as follows:
Value of AclEdit.EditMode |
Use of AclEdit.NewEntry and AclEdit.OldEntryHandle |
CSSM_ACL_EDIT_MODE_ADD |
Adds
a new ACL entry to the set of ACL entries associated with the specified data
base. The new ACL entry is created from the prototype ACL entry contained
in NewEntry. OldEntryHandle is ignored
for this EditMode. |
CSSM_ACL_EDIT_MODE_DELETE |
Deletes
the ACL entry identified by OldEntryHandle and associated with the specified data base. NewEntry is ignored for
this EditMode. |
CSSM_ACL_EDIT_MODE_REPLACE |
Replaces
the ACL entry identified by OldEntryHandle and associated with the specified data base. The
existing ACL is replaced based on the ACL entry prototype contained in NewEntry. |
When replacing an existing ACL entry, the caller
must replace all of the items in an ACL entry. The replacement prototype includes:
Subject type and value
A CSSM_LIST structure containing a typed Subject.
The Subject identifies the entity authorized by this ACL entry.
Delegation flag
A CSSM_BOOL value indicating whether the subject
can delegate the permissions recorded in the authorization array.
Authorization array
A CSSM_AUTHORIZATIONGROUP structure defining the
set of operations for which permission is granted to the Subject.
Validity period
A CSSM_ACL_VALIDITY_PERIOD structure containing
two elements, the start time and the stop time for which the ACL entry is
valid.
ACL entry tag
A CSSM_STRING containing a user-defined value associated
with the ACL entry.
This
function edits the stored ACL associated with the target data base identified
by DLDBHandle.DBHandle.
The ACL is modified according to the edit mode and information provided in AclEdit.
The
caller must be authorized to modify the target ACL. Caller authentication
and authorization to edit the ACL is determined based on the caller-provided AccessCred.
The
caller must be authorized to add, delete or replace the ACL entries associated
with the target data base. When adding or replacing an ACL entry, the service
provider must reject the creation of duplicate ACL entries.
When
adding a new ACL entry to an ACL, the caller must provide a complete ACL entry
prototype. All ACL entry items, except the ACL entry TypedSubject must be provided as an immediate value in AclEdit->NewEntry. The ACL
entry Subject can be provided as an immediate value, from a verifier with
a protected data path, from an external authentication or authorization service,
or through a callback function specified in AclEdit->NewEntry->Callback.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_GetDbAcl
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_GetDbAcl
DL_ChangeDbOwner:
CSSM_DL_ChangeDbOwner – Define a new data base owner
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_ChangeDbOwner
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE *NewOwner)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_ChangeDbOwner
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE *NewOwner)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the data storage
library module to be used to perform this function, and the open data store
whose associated Owner is to be updated.
AccessCred (input)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
used to prove the caller is the current Owner of the Data Base. Required credentials
can include zero or more certificates, zero or more caller names, and one
or more samples. If certificates and/or caller names are provided as input
these must be provided as immediate values in this structure. The samples
can be provided as immediate values or can be obtained through a callback
function included in the AccessCred structure.
NewOwner (input)
A CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE defining the new Owner of the Data Base.
This
function takes a CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE defining the new Owner of the Data Base.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_NEW_OWNER
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_GetDbOwner
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_GetDbOwner
DL_CreateRelation:
CSSM_DL_CreateRelation – Create a new persistent relation
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_CreateRelation
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_DB_RECORDTYPE RelationID,
const char *RelationName,
uint32 NumberOfAttributes,
const CSSM_DB_SCHEMA_ATTRIBUTE_INFO *pAttributeInfo,
uint32 NumberOfIndexes,
const CSSM_DB_SCHEMA_INDEX_INFO *pIndexInfo)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_CreateRelation
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_DB_RECORDTYPE RelationID,
const char *RelationName,
uint32 NumberOfAttributes,
const CSSM_DB_SCHEMA_ATTRIBUTE_INFO *pAttributeInfo,
uint32 NumberOfIndexes,
const CSSM_DB_SCHEMA_INDEX_INFO *pIndexInfo)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the add-in data
storage library module to be used to perform this function and the open data
store in which to insert the new relation record. The database should be opened
in administrative mode using the CSSM_DB_ACCESS_PRIVILEGED flag.
RelationID (input)
Indicates the type of relation record being added
to the data store.
RelationName (input)
Indicates the name of the relation being added
to the data store.
NumberOfAttributes (input)
Indicates the number of attributes specified in pAttributeInfo.
pAttributeInfo (input)
A list of structures containing the meta information
(schema) describing the attributes for the relation being added to the specified
data store. The list contains at most one entry per attribute in the specified
record type.
NumberOfIndexes (input)
Indicates the number of indexes specified in pIndexInfo.
pIndexInfo (input)
A list of structures containing the meta information
(schema) describing the indexes for the relation being added to the specified
data store. The list contains at most one entry per index in the specified
record type.
This
function creates a new persistent relation of the specified type by inserting
it into the specified data store. The pAttributeInfo and pIndexInfo specify the values contained in the new relation
record.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_FIELD_SPECIFIED_MULTIPLE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_ATTRIBUTE_INFO
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_INDEX_INFO
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORDTYPE
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_DestroyRelation
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_DestroyRelation
DL_DataAbortQuery:
CSSM_DL_DataAbortQuery – Terminate DL_DataGetFirst query
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_DataAbortQuery
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_DataAbortQuery
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the add-in data
storage library module to be used to perform this function and the open data
store from which records were selected by the initiating query.
ResultsHandle (input)
The selection handle returned from the initial
query function.
This
function terminates the query initiated by DL_DataGetFirst and allows a DL to release all intermediate state
information associated with the query, and release any locks on the resource.
The user/application must call CSSM_DL_DataAbortQuery at the termination.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RESULTS_HANDLE
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_DataGetFirst, CSSM_DL_DataGetNext
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_DataGetFirst, dL_DataGetNext
DL_DataDelete:
CSSM_DL_DataDelete – Remove data record (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_DataDelete
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
const CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD *UniqueRecordIdentifier)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_DataDelete
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
const CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD *UniqueRecordIdentifier)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the add-in data
storage library module to be used to perform this function and the open data
store from which to delete the specified data record.
UniqueRecordIdentifier (input)
A pointer to a CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD identifier
containing unique identification of the data record to be deleted from the
data store. Once the associated record has been deleted, this unique record
identifier cannot be used in future references, except as an argument to DL_FreeUniqueRecord which
must still be called.
This
function removes the data record specified by the unique record identifier
from the specified data store.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORD_UID
CSSMERR_DL_RECORD_NOT_FOUND
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_DataInsert
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_DataInsert
DL_DataGetFirst:
CSSM_DL_DataGetFirst – Get first data record (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_DataGetFirst
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
const CSSM_QUERY *Query,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR ResultsHandle,
CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE_DATA_PTR Attributes,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Data,
CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR *UniqueId)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_DataGetFirst
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
const CSSM_QUERY *Query,
CSSM_HANDLE_PTR ResultsHandle,
CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE_DATA_PTR Attributes,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Data,
CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR *UniqueId)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the add-in data
storage library module to be used to perform this function and the open data
store to search for records satisfying the query.
Query (input/optional)
The query structure specifying the selection predicate(s)
used to query the data store. The structure contains meta information about
the search fields and the relational and conjunctive operators forming the
selection predicate. The comparison values to be used in the search are specified
in the Attributes field of this Query structure. If a search attribute is
of type CSSM_DB_ATTRIBUTE_FORMAT_STRING and the search value specified for
that string includes a null-terminator, then the length count for that string
should include the terminating character. (If null-terminators are used they
should be used consistently, storing the terminator as part of the string
in the data store, otherwise selection predicates will not locate expected
matches.) The Query structure attributes also identify the particular attributes
to be searched by this query. If no query is specified, the DL module can
return the first record in the data store, performing sequential retrieval,
or return an error. If no selection predicates are specified, the DL module
can return the first record in the data store, performing sequential retrieval,
or return an error (CSSM_DL_UNSUPPORTED_NUM_SELECTION_PREDS). When selection
predicates are specified, the NumberOfValues of the Attribute of each selection predicate must be 1. If any
selection predicate does not satisfy this requirement, the error CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_QUERY
is returned.
ResultsHandle (output)
This handle should be used to retrieve subsequent
records that satisfied this query.
Attributes (optional-input/output)
If
the Attributes structure
pointer is NULL, no values are returned.
Otherwise, the DataRecordType, NumberOfAttributes and AttributeData fields are read. AttributeData must be an array of NumberOfAttributes CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE elements. Only the Info field of each element
is used on input. The AttributeFormat field
of the Info field
is ignored on input.
On output, a CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE structure
containing a list of all or the requested attribute values (subset) from the
retrieved record. The SemanticInformation field is set. For each CSSM_DB_ATTRIBUTE_DATA
contained in the AttributeData array,
the NumberOfValues field
is set to reflect the size of the Value array which is allocated by the DL using the application
specified allocators. Each CSSM_DATA in the Value array will have it’s Data field as a pointer to data allocated using the
application specified allocators containing the attributes value, and have
it’s Length set
to the length of the value.
All values for an attribute are returned (this
could be 0). All fields in the Info field
of the CSSM_DB_ATTRIBUTE_DATA are left unchanged except for the AttributeFormat field, which
is set to reflect the schema.
Data (optional-input/output)
Data values contained in the referenced memory
are ignored during processing and are overwritten with the retrieved opaque
object. On output, a CSSM_DATA structure containing the opaque object stored
in the retrieved record.
UniqueId (output)
If successful and (at least) a record satisfying
the query has been found, then this parameter returns a pointer to a CSSM_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR
structure containing a unique identifier associated with the retrieved record.
This unique identifier structure can be used in future references to this
record using this DLDBHandle pairing.
It may not be valid for other DLHandles targeted to this DL module or to other DBHandles targeted to this
data store. If there are no records satisfying the query, then this pointer
is NULL and CSSM_DL_DataGetFirst must
return CSSM_DL_ENDOFDATA; in this case a normal termination condition has
occurred. The CSSM_DL_FreeUniqueRecord must be used to deallocate this structure.
This
function retrieves the first data record in the data store that matches the
selection criteria. The selection criteria (including selection predicate
and comparison values) is specified in the Query structure. If the Query specifies
an attribute that is not defined in the database’s meta-information,
an error condition is returned. The DL module can use internally-managed indexing
structures to enhance the performance of the retrieval operation. This function
selects the first record satisfying the query based on the list of Attributes
and the opaque Data object. The output buffers for the retrieved record are
allocated by this function using the memory management functions provided
during the module attach operation. This function also returns a results handle
to be used when retrieving subsequent records satisfying the query.
Additional
matching records are iteratively retrieved using the CSSM_DL_DataGetNext function . The data storage module supports one
of two retrieval models:
• Transactional - all query results
are determined at initial query evaluation. Results do not change during an
incremental retrieval process.
• File System Scan - query results are
selected during the incremental retrieval process. Records matching the query
may be added to or deleted from the underlying data store during the iterative
retrieval. The caller may receive the new matching records and not received
the deleted records.
The caller can determine which retrieval model
is supported by examining the encapsulated product description for this data
storage module.
If the query selection criteria also specifies
time for space limits for executing the query, those limits also apply ro
retrieval of the additional selected data records retrieved using the CSSM_DL_DataGetNext function.
Finally, this function returns a unique record identifier associated with
the retrieved record. This structure can be used in future references to the
retrieved data record. Once a user has finished using a certain query, it
must call CSSM_DataAbortQuery for
releasing resources that CSSM uses. If all records satisfying the query have
been retrieved, then query is automatically terminated.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_ENDOFDATA
CSSMERR_DL_FIELD_SPECIFIED_MULTIPLE
CSSMERR_DL_INCOMPATIBLE_FIELD_FORMAT
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_FIELD_NAME
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_PARSING_MODULE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_QUERY
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORDTYPE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORD_UID
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_FIELD_FORMAT
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_NUM_SELECTION_PREDS
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_OPERATOR
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_QUERY
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_QUERY_LIMITS
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_DataGetNext, CSSM_DL_DataAbortQuery
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_DataGetNext, DL_DataAbortQuery
DL_DataGetFromUniqueRecordId DL_DataGetFromUniqueRecordId:
CSSM_DL_DataGetFromUniqueRecordId – Get data record (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_DataGetFromUniqueRecordId
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
const CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR UniqueRecord,
CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE_DATA_PTR Attributes,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Data)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_DataGetFromUniqueRecordId
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
const CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR UniqueRecord,
CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE_DATA_PTR Attributes,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Data)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the add-in data
storage library module to be used to perform this function and the open data
store to search for the data record.
UniqueRecord (input)
The pointer to a unique record structure returned
from a DL_DataInsert, DL_DataGetFirst, or DL_DataGetNext operation.
Attributes (optional-input/output)
If the Attributes structure pointer is NULL, no values are returned.
Otherwise, the DataRecordType, NumberOfAttributes and AttributeData fields are read. AttributeData must be an array of NumberOfAttributes CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE elements. Only the Info field of each element
is used on input. The AttributeFormat field
of the Info field
is ignored on input.
On output, a CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE structure
containing a list of all or the requested attribute values (subset) from the
retrieved record. The SemanticInformation field is set. For each CSSM_DB_ATTRIBUTE_DATA
contained in the AttributeData array,
the NumberOfValues field
is set to reflect the size of the Value array which is allocated by the DL using the application
specified allocators. Each CSSM_DATA in the Value array will have it’s Data field as a pointer to data allocated using the
application specified allocators containing the attributes value, and have
it’s Length set
to the length of the value.
All values for an attribute are returned (this
could be 0). All fields in the Info field
of the CSSM_DB_ATTRIBUTE_DATA are left unchanged except for the AttributeFormat field, which
is set to reflect the schema.
Data (optional-input/output)
Data values contained in the referenced memory
are ignored during processing and are overwritten with the retrieved opaque
object. On output, a CSSM_DATA structure containing the opaque object stored
in the retrieved record. If the pointer is data structure pointer is NULL,
the opaque object is not returned.
This
function retrieves the data record and attributes associated with this unique
record identifier. The Attributes parameter
can specify a subset of the attributes to be returned. If Attributes specifies an attribute that is not defined in
the database’s meta-information, an error condition is returned. The
output buffers for the retrieved record are allocated by this function using
the memory management functions provided during the module attach operation.
The DL module can use an indexing structure identified in the UniqueRecordId to enhance
the performance of the retrieval operation.
The DL should assume that the value of CSSM_QUERY_FLAGS
is when performing this operation. In particular this means that if the data
of a key record is being retrieved, the DL will return a CSSM_KEY structure
with a key reference.
If the record referenced by UniqueRecordIdentifier has been modified since the last time it was retrieved,
the error (warning) CSSMERR_DL_RECORD_MODIFIED is returned but the requested
attributes and data of the new record is returned. The caller should be advised
that other attributes (or the data) might have changed that were not fetched
from the DL with this call.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_FIELD_SPECIFIED_MULTIPLE
CSSMERR_DL_INCOMPATIBLE_FIELD_FORMAT
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_FIELD_NAME
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORDTYPE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORD_UID
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_DataInsert, CSSM_DL_DataGetFirst, CSSM_DL_DataGetNext
Functions
for the DL SPI:
CSSM_DL_DataInsert, CSSM_DL_DataGetFirst, CSSM_DL_DataGetNext
DL_DataGetNext:
CSSM_DL_DataGetNext – Get next data record (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_DataGetNext
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle,
CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE_DATA_PTR Attributes,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Data,
CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR *UniqueId)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_DataGetNext
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_HANDLE ResultsHandle,
CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE_DATA_PTR Attributes,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Data,
CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR *UniqueId)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the add-in data
storage library module to be used to perform this function, and the open data
store from which records were selected by the initiating query.
ResultsHandle (input)
The handle identifying a set of records retrieved
by a query executed by the CSSM_DL_DataGetFirst function.
Attributes (optional-input/output)
If
the Attributes structure
pointer is NULL, no values are returned.
Otherwise, the DataRecordType, NumberOfAttributes and AttributeData fields are read. AttributeData must be an array of NumberOfAttributes CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE elements. Only the Info field of each element
is used on input. The AttributeFormat field
of the Info field
is ignored on input.
On output, a CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE structure
containing a list of all or the requested attribute values (subset) from the
retrieved record. The SemanticInformation field is set. For each CSSM_DB_ATTRIBUTE_DATA
contained in the AttributeData array,
the NumberOfValues field
is set to reflect the size of the Value array which is allocated by the DL using the application
specified allocators. Each CSSM_DATA in the Value array will have it’s Data field as a pointer to data allocated using the
application specified allocators containing the attributes value, and have
it’s Length set
to the length of the value.
All values for an attribute are returned (this
could be 0). All fields in the Info field
of the CSSM_DB_ATTRIBUTE_DATA are left unchanged except for the AttributeFormat field, which
is set to reflect the schema.
Data (optional-input/output)
Data values contained in the referenced memory
are ignored during processing and are overwritten with the retrieved opaque
object. On output, a CSSM_DATA structure containing the opaque object stored
in the retrieved record. If the pointer is data structure pointer is NULL,
the opaque object is not returned.
UniqueId (output)
If successful and (at least) a record satisfying
the query has been found, then this parameter returns a pointer to a CSSM_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR
structure containing a unique identifier associated with the retrieved record.
This unique identifier structure can be used in future references to this
record using this DLDBHandle pairing.
It may not be valid for other DLHandles targeted to this DL module or to other DBHandles targeted to this
data store. If there are no more records satisfying the query, then this pointer
is NULL and CSSM_DL_DataGetNext must
return CSSM_DL_ENDOFDATA; in this case a normal termination condition has
occurred. The CSSM_DL_FreeUniqueRecord must be used to deallocate this structure.
This
function returns the next data record referenced by the ResultsHandle. The ResultsHandle references a set of records selected by an invocation
of the DataGetFirst function.
The Attributes parameter can specify a subset of the attributes to be returned.
If Attributes specifies
an attribute that is not defined in the database’s meta-information,
an error condition is returned. The record values are returned in the Attributes and Data parameters. The output
buffers for the retrieved record are allocated by this function using the
memory management functions provided during the module attach operation. The
function also returns a unique record identifier for the return record.
The
data storage module supports one of two retrieval models: transactional or
file system scan. The transactional model freezes the set of records to be
retrieved at query initiation. The file system scan model selects from a potentially
changing set of records during the retrieval process. The EndOfDataStore function indicates when all matching records have
been retrieved. The caller can determine which retrieval model is supported
by examining the encapsulated product description for this data storage module.
Once a user has finished using a certain query, it must call CSSM_DataAbortQuery for
releasing resources that CSSM uses. If all records satisfying the query have
been retrieved, then query is automatically terminated.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_ENDOFDATA
CSSMERR_DL_FIELD_SPECIFIED_MULTIPLE
CSSMERR_DL_INCOMPATIBLE_FIELD_FORMAT
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_FIELD_NAME
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORDTYPE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORD_UID
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RESULTS_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_DataGetFirst, CSSM_DL_DataAbortQuery
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_DataGetFirst, DL_DataAbortQuery
DL_DataInsert:
CSSM_DL_DataInsert – Create new persistent data
record (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_DataInsert
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_DB_RECORDTYPE RecordType,
const CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE_DATA *Attributes,
const CSSM_DATA *Data,
CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR *UniqueId)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_DataInsert
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_DB_RECORDTYPE RecordType,
const CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE_DATA *Attributes,
const CSSM_DATA *Data,
CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR *UniqueId)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the add-in data
storage library module to be used to perform this function and the open data
store in which to insert the new data record.
RecordType (input)
Indicates the type of data record being added to
the data store
Attributes (input/optional)
A list of structures containing the attribute values
to be stored in that attribute, and the meta information (schema) describing
those attributes. The list contains at most one entry per attribute in the
specified record type. The specified AttributeFormat for each attribute must match that of the database
schema, otherwise the error CSSMERR_DL_INCOMPATIBLE_FIELD_FORMAT is returned.
If an attribute is of type CSSM_DB_ATTRIBUTE_FORMAT_STRING and the value specified
for that string includes a null-terminator, then the length count in the CSSM_DATA
structure containing the input string should include the terminating character.
(If null-terminators are used, they should be used consistently when storing,
searching, and retrieving the string value, otherwise selection predicates
will not locate expected matches.) For those attributes that are not assigned
values by the caller, the DL module may assume the values to be the empty
set, or assume default values, or return an error. If the specified record
type does not contain any attributes, this parameter must be NULL.
Data (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure which contains
the opaque data object to be stored in the new data record. If the specified
record type does not contain an opaque data object, this parameter must be
NULL.
UniqueId (output)
A pointer to a CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR containing
a unique identifier associated with the new record. This unique identifier
structure can be used in future references to this record during the current
open data base session. The pointer will be set to NULL if the function fails.
The CSSM_DL_FreeUniqueRecord function
must be used to deallocate this structure.
This
function creates a new persistent data record of the specified type by inserting
it into the specified data store. The values contained in the new data record
are specified by the Attributes and
the Data. The
attribute value list contains zero or more attribute values. The Attributes parameter also
specifies a record type. This type must be the same as the type specified
by the RecordType input
parameter. The DL module may require initial values for the CSSM pre-defined
attributes. The DL module can assume default values for any unspecified attribute
values or can return an error condition when DLM-required attribute values
are not specified by the caller. The Data is an opaque object to be stored
in the new data record.
If a primary key (concatination of all unique indexes
in the relation) exists, the error CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_UNIQUE_INDEX_DATA is
returned. The client should call CSSM_DL_DataGetFirst, followed by CSSM_DL_DataModify to change an existing record.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_FIELD_SPECIFIED_MULTIPLE
CSSMERR_DL_INCOMPATIBLE_FIELD_FORMAT
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_FIELD_NAME
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_PARSING_MODULE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORDTYPE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORD_UID
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_UNIQUE_INDEX_DATA
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_VALUE
CSSMERR_DL_MISSING_VALUE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_DataDelete
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_DataDelete
DL_DataModify:
CSSM_DL_DataModify – Modify persistent data record
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_DataModify
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_DB_RECORDTYPE RecordType,
CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR UniqueRecordIdentifier,
const CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE_DATA *AttributesToBeModified,
const CSSM_DATA *DataToBeModified,
CSSM_DB_MODIFY_MODE ModifyMode)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_DataModify
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_DB_RECORDTYPE RecordType,
CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR UniqueRecordIdentifier,
const CSSM_DB_RECORD_ATTRIBUTE_DATA *AttributesToBeModified,
const CSSM_DATA *DataToBeModified,
CSSM_DB_MODIFY_MODE ModifyMode)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the add-in data
storage library module to be used to perform this function and the open data
store to search for records satisfying the query.
RecordType (input)
Indicates the type of data record being modified.
UniqueRecordIdentifier (input/output)
A pointer to a CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD containing
a unique identifier associated with the record to modify. If the modification
succeeds, the UniqueRecordIdentifier points
to a CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD containing a unique identifier associated with
the updated record. If the modification fails, the UniqueRecordIdentifier is not modified.
AttributesToBeModified (input/optional)
A
list of structures containing the attribute values to be stored in that attribute
and the meta information (schema) describing those attributes. The list contains
at most one entry per attribute in the specified record type. The specified AttributeFormat for each
attribute must match that of the database schema, otherwise the error CSSMERR_DL_INCOMPATIBLE_FIELD_FORMAT
is returned. If an attribute is of type CSSM_DB_ATTRIBUTE_FORMAT_STRING and
the value specified for that string includes a null-terminator, then the length
count in the CSSM_DATA structure containing the input string should include
the terminating character. (If null-terminators are used, they should be used
consistently when storing, searching, and retrieving the string value, otherwise
selection predicates will not locate expected matches.) Each attribute specified
is modified according to the value of ModifyMode (see table in the DESCRIPTION section of this definition). Those attributes
that are not specified as part of this parameter remain unchanged. If the AttributesToBeModified parameter
is NULL, no attribute modification occurs.
DataToBeModified (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure which contains
the opaque data object to be stored in the data record. If this parameter
is NULL, no Data modification occurs.
ModifyMode (input)
A CSSM_DB_MODIFY_MODE value indicating the type
of modification to be performed on the record attributes identified by AttributesToBeModified.
If no attributes are specified, then this value must be CSSM_DB_MODIFY_ATTRIBUTE_NONE.
This
function modifies the persistent data record identified by the UniqueRecordIdentifier.
The modifications are specified by the Attributes and Data parameters.
The ModifyMode indicates
how the attributes are to be updated. The ModifyMode has no affect on updating the data blob contained
in the record. If the data blob is the only record attribute being updated
by this function call, then the modification mode must be 0. The current modification
modes behave as follows:
ModifyMode
Value |
Function
Behavior |
CSSM_DB_MODIFY_ATTRIBUTE_NONE |
No
Attributes are being updated. |
CSSM_DB_MODIFY_ATTRIBUTE_ADD |
The
specified values are added to the set of current values for each attribute.
If 0 values are specified then the error CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_MODIFY_MODE is
returned. If a DL does not support multiple values per attribute, the error
CSSMERR_DL_MULTIPLE_VALUES_UNSUPPORTED is returned. |
CSSM_DB_MODIFY_ATTRIBUTE_DELETE |
The
specified values are removed from the set of current values for each attribute.
If 0 values are specified then all values are deleted or the attributes value
is replaced with the default for this attribute. If a DL does not support
multiple values per attribute, the error CSSMERR_DL_MULTIPLE_VALUES_UNSUPPORTED
is returned. |
CSSM_DB_MODIFY_ATTRIBUTE_REPLACE |
The
values for each attribute are replaced with the specified set of values for
each attribute. If no values are specified then all values are deleted or
the attributes value is replaced with the default for this attribute. If a
DL does not support multiple values per attribute, the error CSSMERR_DL_MULTIPLE_VALUES_UNSUPPORTED
is returned when more than 1 value is specified. |
If the attribute lists specifies an attribute that
is not defined in the database’s meta-information, an error condition
is returned. For each attribute-value pair, the value replaces the corresponding
attribute value in the record. If a data value is specified, the record’s
data value is replaced with the specified value. A record’s data value
or attribute values can be set to NULL or zero to represent deletion or the
lack of a known value.
If the record referenced by UniqueRecordIdentifier has been modified since the last time it was updated,
the error CSSMERR_DL_STALE_UNIQUE_RECORD is returned and no modification takes
place.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_FIELD_SPECIFIED_MULTIPLE
CSSMERR_DL_INCOMPATIBLE_FIELD_FORMAT
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_FIELD_NAME
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_MODIFY_MODE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORDTYPE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORD_UID
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_UNIQUE_INDEX_DATA
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_VALUE
CSSMERR_DL_MULTIPLE_VALUES_UNSUPPORTED
CSSMERR_DL_STALE_UNIQUE_RECORD
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_DataInsert, CSSM_DL_DataDelete
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_DataInsert, DL_DataDelete
DL_DbClose: CSSM_DL_DbClose – Close open data store (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_DbClose
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_DbClose
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
A handle structure containing the DL handle for
the attached DL module and the DB handle for an open data store managed by
the DL. This specifies the open data store to be closed.
This function closes an open data store.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_DbOpen
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_DbOpen
DL_DbCreate: CSSM_DL_DbCreate – Create and open new data store (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_DbCreate
(CSSM_DL_HANDLE DLHandle,
const char *DbName,
const CSSM_NET_ADDRESS *DbLocation,
const CSSM_DBINFO *DBInfo,
CSSM_DB_ACCESS_TYPE AccessRequest,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry,
const void *OpenParameters,
CSSM_DB_HANDLE *DbHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_DbCreate
(CSSM_DL_HANDLE DLHandle,
const char *DbName,
const CSSM_NET_ADDRESS *DbLocation,
const CSSM_DBINFO *DBInfo,
CSSM_DB_ACCESS_TYPE AccessRequest,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry,
const void *OpenParameters,
CSSM_DB_HANDLE *DbHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in data storage
library module used to perform this function.
DbName (input)
The logical name for the new data store.
DbLocation (input/optional)
A pointer to a network address directly or indirectly
identifying the location of the storage service process. If the input is NULL,
the module can assume a default storage service process location. If the DbName does not distinguish
the storage service process, the service cannot be performed and the operation
fails.
DBInfo (input)
A pointer to a structure describing the format/schema
of each record type that will be stored in the new data store.
AccessRequest (input)
An indicator of the requested access mode for the
data store, such as read-only or read-write.
CredAndAclEntry (input/optional)
A structure containing one or more credentials
authorized for creating a data base and the prototype ACL entry that will
control future use of the newly created key. The credentials and ACL entry
prototype can be presented as immediate values or callback functions can be
provided for use by the DL to acquire the credentials and/or the ACL entry
interactively. If the DL provides public access for creating a data base,
then the credentials can be NULL. If the DL defines a default initial ACL
entry for the new data base, then the ACL entry prototype can be an empty
list.
OpenParameters (input/optional)
A pointer to a module-specific set of parameters
required to open the data store.
DbHandle (output)
The handle to the newly created and open data store.
The value will be set to CSSM_INVALID_HANDLE if the function fails.
This function creates and opens a new data store.
The name of the new data store is specified by the input parameter DbName. The record schema
for the data store is specified in the DBINFO structure. If any RecordType defined in the
DBINFO structure does not have an associated parsing module, then the ModuleSubserviceUid specified
for that record type must be zero.
The newly created data store is opened under the
specified access mode. If user authentication credentials are required, they
must be provided. Also, additional open parameters may be required and are
supplied in OpenParameters.
If user authentication credentials are required, they must be provided.
Authorization
policy can restrict the set of callers who can create a new resource. In this
case, the caller must present a set of access credentials for authorization.
Upon successfully authenticating the credentials, the template that verified
the presented samples identifies the ACL entry that will be used in the authorization
computation. If the caller is authorized, the new resource is created.
The
caller must provide an initial ACL entry to be associated with the newly created
resource. This entry is used to control future access to the new resource
and (since the subject is deemed to be the "Owner") exercise control
over its associated ACL. The caller can specify the following items for initializing
an ACL entry:
Subject
A CSSM_LIST structure, containing the type of the
subject and a template value that can be used to verify samples that are presented
in credentials when resource access is requested.
Delegation flag
A
value indicating whether the Subject can delegate the permissions recorded
in the AuthorizationTag.
(This item only applies to public key subjects).
Authorization tag
The
set of permissions that are granted to the Subject.
Validity period
The
start time and the stop time for which the ACL entry is valid.
ACL entry tag
A user-defined string value associated with the
ACL entry.
The service provider can modify the caller-provided
initial ACL entry to conform to any innate resource-access policy that the
service provider may be required to enforce. If the initial ACL entry provided
by the caller contains values or permissions that are not supported by the
service provider, then the service provider can modify the initial ACL appropriately
or can fail the request to create the new resource. Service providers list
their supported AuthorizationTag values
in their Module Directory Services primary record.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_DATASTORE_ALREADY_EXISTS
CSSMERR_DL_FIELD_SPECIFIED_MULTIPLE
CSSMERR_DL_INCOMPATIBLE_FIELD_FORMAT
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_ACCESS_REQUEST
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_LOCATION
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_NAME
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_FIELD_NAME
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_OPEN_PARAMETERS
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_PARSING_MODULE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORDTYPE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORD_INDEX
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_FIELD_FORMAT
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_INDEX_INFO
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_LOCALITY
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_NUM_ATTRIBUTES
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_NUM_INDEXES
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_NUM_RECORDTYPES
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_RECORDTYPE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_DbOpen, CSSM_DL_DbClose, CSSM_DL_DbDelete
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_DbOpen, DL_DbClose, DL_DbDelete
DL_DbDelete: CSSM_DL_DbDelete – Delete all records (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_DbDelete
(CSSM_DL_HANDLE DLHandle,
const char *DbName,
const CSSM_NET_ADDRESS *DbLocation,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_DbDelete
(CSSM_DL_HANDLE DLHandle,
const char *DbName,
const CSSM_NET_ADDRESS *DbLocation,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in data storage
library module to be used to perform this function.
DbName (input)
A pointer to the string containing the logical
name of the data store.
DbLocation (input/optional)
A pointer to a network address directly or indirectly
identifying the location of the storage service process. If the input is NULL,
the module can assume a default storage service process location. If the DbName does not distinguish
the storage service process, the service cannot be performed and the operation
fails.
AccessCred (input/optional)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
being presented for authentication by the caller. These credentials are required
to obtain access to the specified data store. The credentials structure can
contain multiple types of credentials, as required for multi-factor authentication.
The credential data can be an immediate value, such as a passphrase, PIN,
certificate, or template of user-specific data, or the caller can specify
a callback function the DL can use to obtain one or more credentials. The
required set of credentials to access a particular data store is defined by
the DbInfo record
containing meta-data for the specified data store. If credentials are not
required to access the specified data store, then this field can be NULL.
This function deletes all records from the specified
data store and removes all state information associated with that data store.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_DATASTORE_DOESNOT_EXIST
CSSMERR_DL_DATASTORE_IS_OPEN
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_LOCATION
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_NAME
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_DbCreate, CSSM_DL_DbOpen, CSSM_DL_DbClose
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_DbCreate, DL_DbOpen, DL_DbClose
DL_DbOpen: CSSM_DL_DbOpen – Open a data store (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_DbOpen
(CSSM_DL_HANDLE DLHandle,
const char *DbName,
const CSSM_NET_ADDRESS *DbLocation,
CSSM_DB_ACCESS_TYPE AccessRequest,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const void *OpenParameters,
CSSM_DB_HANDLE *DbHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_DbOpen
(CSSM_DL_HANDLE DLHandle,
const char *DbName,
const CSSM_NET_ADDRESS *DbLocation,
CSSM_DB_ACCESS_TYPE AccessRequest,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const void *OpenParameters,
CSSM_DB_HANDLE *DbHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in data storage
library module to be used to perform this function.
DbName (input)
A pointer to the string containing the logical
name of the data store.
DbLocation (input/optional)
A pointer to a network address directly or indirectly
identifying the location of the storage service process. If the input is NULL,
the module can determine a storage service process and its location based
on the DbName (for existing data stores) or can assume a default storage service
process location. If the DbName does not distinguish the storage service process,
the service cannot be performed and the operation fails.
AccessRequest (input)
An indicator of the requested access mode for the
data store, such as read-only or read-write.
AccessCred (input/optional)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
being presented for authentication by the caller. These credentials are required
to obtain access to the specified data store. The credentials structure can
contain multiple types of credentials, as required for multi-factor authentication.
The credential data can be an immediate value, such as a passphrase, PIN,
certificate, or template of user-specific data, or the caller can specify
a callback function the DL can use to obtain one or more credentials. The
required set of credentials to access a particular data store is defined by
the DbInfo record
containing meta-data for the specified data store. If credentials are not
required to access the specified data store, then this field can be NULL.
OpenParameters (input/optional)
A pointer to a module-specific set of parameters
required to open the data store.
DbHandle (output)
The handle to the opened data store. The value
will be set to CSSM_INVALID_HANDLE if the function fails.
This function opens the data store with the specified
logical name under the specified access mode. If user authentication credentials
are required, they must be provided. Also, additional open parameters may
be required to open a given data store, and are supplied in the OpenParameters.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_DB_LOCKED
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_ACCESS_REQUEST
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_LOCATION
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_NAME
CSSMERR_DL_DATASTORE_DOESNOT_EXIST
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_PARSING_MODULE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_OPEN_PARAMETERS
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_DbClose
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_DbClose
DL_DestroyRelation:
CSSM_DL_DestroyRelation – Destroy an existing relation
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_DestroyRelation
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_DB_RECORDTYPE RelationID)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_DestroyRelation
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_DB_RECORDTYPE RelationID)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the add-in data
storage library module to be used to perform this function and the open data
store from which to delete the relation record.
RelationID (input)
Indicates the type of relation record being deleted
from the data store.
This
function destroys an existing relation of the specified type by removing its
entry from the specified data store.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORDTYPE
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_CreateRelation
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_CreateRelation
DL_FreeNameList:
CSSM_DL_FreeNameList – Free the list of the logical
data store names (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_FreeNameList
(CSSM_DL_HANDLE DLHandle,
CSSM_NAME_LIST_PTR NameList)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_FreeNameList
(CSSM_DL_HANDLE DLHandle,
CSSM_NAME_LIST_PTR NameList)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in data storage
library module to be used to perform this function.
NameList (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_NAME_LIST.
This
function frees the list of the logical data store names that was returned
by CSSM_DL_GetDbNames.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_GetDbNames
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_GetDbNames
DL_FreeUniqueRecord:
CSSM_DL_FreeUniqueRecord – Free data store memory (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_FreeUniqueRecord
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR UniqueRecord)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_FreeUniqueRecord
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_DB_UNIQUE_RECORD_PTR UniqueRecord)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the add-in data
storage library module to be used to perform this function and the open data
store from which the UniqueRecord identifier was assigned.
UniqueRecord(input)
The pointer to the memory that describes the data
store unique record structure.
This
function frees the memory associated with the data store unique record structure.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORD_UID
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_DataInsert, CSSM_DL_DataGetFirst, CSSM_DL_DataGetNext
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_DataInsert, DL_DataGetFirst, DL_DataGetNext
DL_GetDbAcl: CSSM_DL_GetDbAcl – Get ACL description (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_GetDbAcl
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
const CSSM_STRING *SelectionTag,
uint32 *NumberOfAclInfos,
CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_INFO_PTR *AclInfos)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_GetDbAcl
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
const CSSM_STRING *SelectionTag,
uint32 *NumberOfAclInfos,
CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_INFO_PTR *AclInfos)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that identifies the Data Storage
service provider to perform this operation and the target data store whose
associated ACL entries are scanned and returned.
SelectionTag (input/optional)
A CSSM_STRING value matching the user-defined tag
value associated with one or more ACL entries for the target data base. To
retrieve a description of all ACL entries for the target data base, this parameter
must be NULL.
NumberOfAclInfos (output)
The number of entries in the AclInfos array. If no ACL entry descriptions are returned,
this value is zero.
AclInfos (output)
An array of CSSM_ACL_ENTRY_INFO structures. The
unique handle contained in each structure can be used during the current attach
session to reference the ACL entry for editing. The structure is allocated
by the service provider and must be released by the caller when the structure
is no longer needed. If no ACL entry descriptions are returned, this value
is NULL.
This
function returns a description of zero or more ACL entries managed by the
data storage service provider module and associated with the target database
identified by DLDBHandle.DBHandle.
The optional input SelectionTag restricts
the returned descriptions to those ACL entries with a matching EntryTag value. If a SelectionTag value is specified
and no matches are found, zero descriptions are returned. If no SelectionTag is specified,
a description of all ACL entries associated with the target data base are
returned by this function.
Each AclInfo structure contains:
• Public contents of an ACL entry
• ACL EntryHandle, which is a unique value defined and managed by
the service provider
The public ACL entry information returned by this
function includes:
The subject type
A
CSSM_LIST structure containing one element identifying the type of subject
stored in the ACL entry.
Delegation flag
A
CSSM_BOOL value indicating whether the subject can delegate the permissions
recorded in Authorization
Authorization array
A CSSM_AUTHORIZATIONGROUP structure defining the
set of operations for which permission is granted to the Subject.
Validity period
A CSSM_ACL_VALIDITY_PERIOD structure containing
two elements, the start time and the stop time for which the ACL entry is
valid.
ACL entry tag
A
CSSM_STRING containing a user-defined value associated with the ACL entry.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_ChangeDbAcl
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_ChangeDbAcl
DL_GetDbNameFromHandle:
CSSM_DL_GetDbNameFromHandle – Get data source name (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_GetDbNameFromHandle
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
char **DbName)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_GetDbNameFromHandle
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
char **DbName)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that identifies the add-in data
storage library module and the open data store whose name should be retrieved.
DbName (output)
Returns a zero terminated string which contains
a data store name. The memory is allocated by the service provider and must
be deallocated by the application.
This
function retrieves the data source name corresponding to an opened data store
handle.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_GetDbNames
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_GetDbNames
DL_GetDbNames:
CSSM_DL_GetDbNames – Get list of logical data store names (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_GetDbNames
(CSSM_DL_HANDLE DLHandle,
CSSM_NAME_LIST_PTR *NameList)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_GetDbNames
(CSSM_DL_HANDLE DLHandle,
CSSM_NAME_LIST_PTR *NameList)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in data storage
library module to be used to perform this function.
NameList (output)
Returns a list of data store names in a CSSM_NAME_LIST_PTR
structure.
This
function returns the list of logical data store names for all data stores
that are known by and accessible to the specified DL module. This list also
includes the number of data store names in the return list.
The CSSM_DL_FreeNameList function
must be called to deallocate memory containing the list.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_GetDbNameFromHandle, CSSM_DL_FreeNameList
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_GetDbNameFromHandle, DL_FreeNameList
DL_GetDbOwner:
CSSM_DL_GetDbOwner – Get data base owner (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_GetDbOwner
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE_PTR Owner)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_GetDbOwner
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE_PTR Owner)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the data storage
library module to be used to perform this function, and the open data store
whose associated Owner is to be retrieved.
Owner (output)
A CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE describing the current
Owner of the Data Base.
This
function returns a CSSM_ACL_OWNER_PROTOTYPE describing the current Owner of
the Data Base.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_DL_ChangeDbOwner
Functions
for the DL SPI:
DL_ChangeDbOwner
DL_PassThrough:
CSSM_DL_PassThrough – Extend data storage module
functionality (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_DL_PassThrough
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
uint32 PassThroughId,
const void *InputParams,
void **OutputParam)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMDLI DL_PassThrough
(CSSM_DL_DB_HANDLE DLDBHandle,
uint32 PassThroughId,
const void *InputParams,
void **OutputParam)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
DLDBHandle (input)
The handle pair that describes the add-in data
storage library module to be used to perform this function and the open data
store upon which the function is to be performed.
PassThroughId (input)
An identifier assigned by a DL module to indicate
the exported function to be performed.
InputParams (input)
A pointer to a module implementation-specific structure
containing parameters to be interpreted in a function-specific manner by the
requested DL module.
OutputParams (output)
A pointer to a module, implementation-specific
structure containing the output data. The service provider will allocate the
memory for this structure. The application should free the memory for the
structure.
This
function allows applications to call data storage library module-specific
operations that have been exported. Such operations may include queries or
services that are specific to the domain represented by a DL module.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_PASSTHROUGH_ID
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
EncryptData: CSSM_EncryptData,
CSP_EncryptData – Encrypts all buffer data (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_EncryptData
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ClearBufs,
uint32 ClearBufCount,
CSSM_DATA_PTR CipherBufs,
uint32 CipherBufCount,
uint32 *bytesEncrypted,
CSSM_DATA_PTR RemData)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_EncryptData
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
const CSSM_DATA *ClearBufs,
uint32 ClearBufCount,
CSSM_DATA_PTR CipherBufs,
uint32 CipherBufCount,
uint32 *bytesEncrypted,
CSSM_DATA_PTR RemData,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
ClearBufs (input)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the data to be operated on.
ClearBufCount (input)
The number of ClearBufs.
CipherBufs (output)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the results of the operation on the data.
CipherBufCount (input)
The number of CipherBufs.
bytesEncrypted (output)
A pointer to uint32 for the size of the encrypted data in bytes.
RemData (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure for the remaining
cipher text if there is not enough buffer space available in the output data
structures.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
Privilege (input)
The export privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation. This parameter is forwarded to the CSP after CSSM verifies the
caller and service provider privilege set includes the specified PRIVILEGE.
This function encrypts all data contained in the
set of input buffers using information in the context. The CSSM_QuerySize function can be used to estimate the output buffer
size required. The minimum number of buffers required to contain the resulting
cipher text is produced as output. If the cipher text result does not fit
within the set of output buffers, the remaining cipher text is returned in
the single output buffer RemData.
The
CSP can require that the cryptographic context include access credentials
for authentication and authorization checks when using a private key or a
secret key.
The output is returned to the caller either by
filling the caller-specified buffer or by using the application’s declared
memory allocation functions to allocate buffer space. To specify a specific,
preallocated output buffer, the caller must provide an array of one or more
CSSM_DATA structures, each containing a Length field value greater than zero
and a non-NULL data pointer field value. To specify automatic output buffer
allocation by the CSP, the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA
structures, each containing a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL
Data pointer field value. The application is always responsible for deallocating
the memory when it is no longer needed. In-place encryption can be done by
supplying the same input and output buffers.
The output is returned to the caller as specified
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_BLOCK_SIZE_MISMATCH
CSSMERR_CSP_OUTPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_QuerySize, CSSM_DecryptData, CSSM_EncryptDataInit, CSSM_EncryptDataUpdate, CSSM_EncryptDataFinal, CSSM_EncryptDataP, CSSM_EncryptDataInitP, CSSM_DecryptP, CSSM_DecryptDataInitP
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_QuerySize, CSP_DecryptData, CSP_EncryptDataInit, CSP_EncryptDataUpdate, CSP_EncryptDataFinal
EncryptDataFinal:
CSSM_EncryptDataFinal, CSP_EncryptDataFinal – Finalize staged encryption
process (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_EncryptDataFinal
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR RemData)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_EncryptDataFinal
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR RemData)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
RemData (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure for the last
encrypted block containing padded data, if necessary.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function finalizes the staged encryption process by returning any remaining
cipher text not returned in the previous staged encryption call. The cipher
text is returned in a single buffer.
The output is returned to the caller either by
filling the caller-specified buffer or by using the application’s declared
memory allocation functions to allocate buffer space. To specify a specific,
preallocated output buffer, the caller must provide an array of one or more
CSSM_DATA structures, each containing a Length field value greater than zero
and a non-NULL data pointer field value. To specify automatic output buffer
allocation by the CSP, the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA
structures, each containing a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL
data pointer field value. The application is always responsible for deallocating
the memory when it is no longer needed.
The output is returned to the caller as specified
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_BLOCK_SIZE_MISMATCH
CSSMERR_CSP_OUTPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_QuerySize, CSSM_DecryptData, CSSM_EncryptDataInit, CSSM_EncryptDataUpdate, CSSM_EncryptDataFinal, CSSM_EncryptDataP, CSSM_EncryptDataInitP, CSSM_DecryptP, CSSM_DecryptDataInitP
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_EncryptData, CSP_EncryptDataInit, CSP_EncryptDataUpdate
EncryptDataInit:
CSSM_EncryptDataInit, CSP_EncryptDataInit – Initialize the staged encrypt
funciton (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_EncryptDataInit
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_EncryptDataInit
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
Privilege (input)
The export privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation. This parameter is forwarded to the CSP after CSSM verifies the
caller and service provider privilege set includes the specified PRIVILEGE.
This
function initializes the staged encrypt function. There may be algorithm-specific
and token-specific rules restricting the lengths of data following data update
calls making use of these parameters.
The CSP can require that the cryptographic context
include access credentials for authentication and authorization checks when
using a private key or a secret key.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_QuerySize, CSSM_DecryptData, CSSM_EncryptDataInit, CSSM_EncryptDataUpdate, CSSM_EncryptDataFinal, CSSM_EncryptDataP, CSSM_EncryptDataInitP, CSSM_DecryptP, CSSM_DecryptDataInitP
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_QuerySize, CSP_DecryptData, CSP_EncryptDataInit, CSP_EncryptDataUpdate, CSP_EncryptDataFinal
EncryptDataInitP – Initialize the staged encrypt
function with privilege (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_EncryptDataInitP
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
Privilege (input)
The privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation.
See CSSM_EncryptDataInit for other parameters.
This
function is similar to CSSM_EncryptDataInit. It also accepts a USEE tag as a privilege request
parameter. CSSM checks that either its privilege set or the application’s
privilege set (if the application is signed) includes the tag. If the tag
is found and the service provider privilege set indicates that it is supported,
the tag is forwarded to the service provider.
For
staged operations using privilege initialization functions CSSM_EncryptDataInitP, the completion functions CSSM_EncryptDataUpdate and CSSM_EncryptDataFinalize are used.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_DecryptData, CSSM_EncryptDataInit, CSSM_EncryptDataUpdate, CSSM_EncryptDataFinal, CSSM_EncryptDataP, CSSM_EncryptDataInitP, CSSM_DecryptP, CSSM_DecryptDataInitP, CSSM_QuerySize
EncryptDataP – Encrypt data with privilege
(CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_EncryptDataP
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ClearBufs,
uint32 ClearBufCount,
CSSM_DATA_PTR CipherBufs,
uint32 CipherBufCount,
uint32 *bytesEncrypted,
CSSM_DATA_PTR RemData,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
Privilege (input)
The privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation.
See CSSM_EncryptData for other parameters.
This
function is similar to CSSM_EncryptData. It also accepts a USEE tag as a privilege request
parameter. CSSM checks that either its own privilege set or the application’s
privilege set (if the application is signed) includes the tag. If the tag
is found and the service provider privilege set indicates that it is supported,
the tag is forwarded to the service provider.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_BLOCK_SIZE_MISMATCH
CSSMERR_CSP_OUTPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions: CSSM_DecryptData, CSSM_EncryptDataInit, CSSM_EncryptDataUpdate, CSSM_EncryptDataFinal, CSSM_EncryptDataP, CSSM_EncryptDataInitP, CSSM_DecryptP, CSSM_DecryptDataInitP, CSSM_QuerySize
EncryptDataUpdate:
CSSM_EncryptDataUpdate, CSP_EncryptDataUpdate – Continue the staged encryption
process (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_EncryptDataUpdate
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ClearBufs,
uint32 ClearBufCount,
CSSM_DATA_PTR CipherBufs,
uint32 CipherBufCount,
uint32 *bytesEncrypted)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_EncryptDataUpdate
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ClearBufs,
uint32 ClearBufCount,
CSSM_DATA_PTR CipherBufs,
uint32 CipherBufCount,
uint32 *bytesEncrypted)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
ClearBufs (input)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the data to be operated on.
ClearBufCount (input)
The number of ClearBufs.
CipherBufs (output)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the encrypted data resulting from the encryption operation.
CipherBufCount (input)
The number of CipherBufs.
bytesEncrypted (output)
A pointer to uint32 for the size of the encrypted data in bytes.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function continues the staged encryption process over all data in the set
of input buffers. There can be algorithm-specific and token-specific rules
restricting the lengths of data in CSSM_EncryptUpdate calls, but multiple input buffers are supported.
The minimum number of buffers required to contain the resulting cipher text
is produced as output. Excess output buffer space is not remembered across
staged encryption calls. Each staged call begins filling one or more new output
buffers. The CSSM_QuerySize function
can be used to estimate the output buffer size required for each update call.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
The output is returned to the caller either by
filling the caller-specified buffer or by using the application’s declared
memory allocation functions to allocate buffer space. To specify a specific,
preallocated output buffer, the caller must provide an array of one or more
CSSM_DATA structures, each containing a Length field value greater than zero
and a non-NULL Data pointer field value. To specify automatic output buffer
allocation by the CSP, the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA
structures, each containing a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL
data pointer field value. The application is always responsible for deallocating
the memory when it is no longer needed. In-place encryption can be done by
supplying the same input and output buffers.
The output is returned to the caller as specified
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_QuerySize, CSSM_DecryptData, CSSM_EncryptDataInit, CSSM_EncryptDataUpdate, CSSM_EncryptDataFinal, CSSM_EncryptDataP, CSSM_EncryptDataInitP, CSSM_DecryptP, CSSM_DecryptDataInitP
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_QuerySize, CSP_DecryptData, CSP_EncryptDataInit, CSP_EncryptDataFinal
EventNotifyManager – Receive an event notification
(CDSA) (not currently supported) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI EventNotifyManager
(const CSSM_MANAGER_EVENT_NOTIFICATION *EventDescription)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
EventDescription
A
structure containing the following fields:
DestinationModuleManagerType (input)
The unique service mask identifying the destination
module manager.
SourceModuleManagerType (input)
The unique service mask identifying the source
module manager.
Event (input)
An identifier indicating the event that has or
will take place.
EventId (input/optional)
A unique identifier associated with this event
notification. It must be used in any reply notification that results from
this event notification.
EventData (input/optional)
Arbitrary data (required or informational) for
this event.
This
function receives an event notification from another module manager. The source
manager is identified by its service mask. The specified event type is interpreted
by the received and the appropriate actions must be taken in response. EventId and EventData are optional.
The EventId is
specified by the source module manager when a reply is expected. The destination
module manager must use this identifier when replying to the event notification.
The EventData is
additional data or descriptive information provided to the destination manager.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_MODULE_MANAGER_NOT_FOUND
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
FreeKey: CSSM_FreeKey,
CSP_FreeKey – Clean
up keys (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_FreeKey
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
CSSM_KEY_PTR KeyPtr,
CSSM_BOOL Delete)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_FreeKey
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
CSSM_KEY_PTR KeyPtr,
CSSM_BOOL Delete)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the module to perform
this operation.
AccessCred (input/optional)
If the target key referenced by KeyPtr is protected and Delete has the value CSSM_TRUE, this parameter must contain
the certificates and samples required to access the target key. The certificates
must be presented as immediate values in the input structure. The samples
can be immediate values, be obtained through a protected mechanism, or be
obtained through a callback function.
KeyPtr (input)
The key whose associated keying material can be
discarded at this time.
Delete (input)
If this value is CSSM_TRUE, the key data in the
key structure will be removed and any internal storage related to that key
will also be removed. In this case the key no longer exists in any form, unless
previously wrapped out of the CSP by the application. If this value is CSSM_FALSE,
then only the resources related to the key structure are released. The key
may still be accessible by other means internally to the CSP.
This
function requests the Cryptographic Service Provider to clean up any key material
associated with the key, and to possibly delete the key from the CSP completely.
This function also releases the internal storage referenced by the KeyData
field of the key structure, which can hold the actual key value. The key reference
by KeyPtr can
be a persistent key or a transient key. This function clears the cached copy
of the key and can have an effect on the long term persistence or transience
of the key.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
GenerateAlgorithmParams:
CSSM_GenerateAlgorithmParams, CSP_GenerateAlgorithmParams – Generate algorithm parameters
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GenerateAlgorithmParams
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
uint32 ParamBits,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Param)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_GenerateAlgorithmParams
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
uint32 ParamBits,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Param,
uint32 *NumberOfUpdatedAttributes,
CSSM_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE_PTR *UpdatedAttributes)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
ParamBits (input)
Used to generate parameters for the algorithm (for
example, Diffie-Hellman).
Param (output)
Pointer to a CSSM_DATA structure used to provide
information to the parameter generation process, or to receive information
resulting from the generation process that is not required as a parameter
to the algorithm. For instance, phase 2 of the KEA algorithm requires a private
random value, rA, and a public version, Ra, to be generated. The private value,
rA, is added to the context and the public value, Ra, is returned to the caller.
In some cases, when both input and output is required, a data structure is
passed to the algorithm. In this situation, Param->Data references the structure and Param->Length is set to the length of the structure.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context. Modifying this structure has no effect on
the internal structure maintained by the CSSM. It is only a copy of the actual
data. Changes to the context attributes must be returned using the UpdatedAttributes return
parameter.
NumberOfUpdatedAttributes (output)
The number of CSSM_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE structures
contained in the UpdatedAttributes array.
If this value is zero, UpdatedAttributes should be set to NULL.
UpdatedAttributes (output)
An array of attributes that will be added to the
context should be returned using this parameter. Memory for the attribute
structures should be allocated using the CSSM_UPCALLS callbacks provided to
the service provider module when CSSM_SPI_ModuleAttach is called.
This
function generates algorithm parameters for the specified context. These parameters
include Diffie-Hellman key
agreement parameters and DSA key generation parameters. In most cases the
algorithm parameters will be added directly to the cryptographic context (by
returning an array of CSSM_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE structures), but an algorithm
may return some data to the caller via the Param parameter. The generated parameters are added
to the context as an attribute of type CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_ALG_PARAMS. Other attributes
returned are added to the context, or replace existing values in the context.
The
output is returned to the caller either by filling the caller-specified buffer
or by using the application’s declared memory allocation functions to
allocate buffer space. To specify a specific, pre-allocated output buffer,
the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA structures each,
containing a Length field value greater than zero and a non-NULL data pointer
field value. To specify automatic output buffer allocation by the CSP, the
caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA structures, each containing
a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL data pointer field value. The
application is always responsible for deallocating the memory when it is no
longer needed.
The output is returned to the caller as specified
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
GenerateKey: CSSM_GenerateKey,
CSP_GenerateKey – Generate a symmetric key (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GenerateKey
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
uint32 KeyUsage,
uint32 KeyAttr,
const CSSM_DATA *KeyLabel,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry,
CSSM_KEY_PTR Key)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_GenerateKey
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
uint32 KeyUsage,
uint32 KeyAttr,
const CSSM_DATA *KeyLabel,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry,
CSSM_KEY_PTR Key)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
KeyUsage (input)
A bit mask indicating all permitted uses for the
new key.
KeyAttr (input)
A bit mask defining attribute values for the new
key.
KeyLabel (input/optional)
Pointer to a byte string that will be used as the
label for the key.
CredAndAclEntry (input/optional)
A structure containing one or more credentials
authorized for creating a key and the prototype ACL entry that will control
future use of the newly created key. The credentials and ACL entry prototype
can be presented as immediate values or callback functions can be provided
for use by the CSP to acquire the credentials and/or the ACL entry interactively.
If the CSP provides public access for creating a key, then the credentials
can be NULL. If the CSP defines a default initial ACL entry for the new key,
then the ACL entry prototype can be an empty list.
Key (output)
Pointer to CSSM_KEY structure used to hold the
new key. The CSSM_KEY structure should be empty upon input to this function.
The CSP will ignore any values residing in this structure at function invocation.
Input values should be supplied in the cryptographic context, KeyUsage, KeyAttr, and KeyLabel input parameters.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up-calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
Key (output)
Pointer to CSSM_KEY structure used to obtain the
key. Upon function invocation, any values in the CSSM_Key structure should
be ignored. All input values should be supplied in the cryptographic Context, KeyUsage, KeyAttr,
and KeyLabel input
parameters.
This
function generates a symmetric key. The KeyUsage, and KeyAttr are used to initialize the keyheader for the newly
created key. These values are not retained in the cryptographic Context, which
contains additional parameters for this operation. The CSP may cache keying
material associated with the new symmetric key. When the symmetric key is
no longer in active use, the application can invoke the CSSM_FreeKey interface to allow cached keying material associated
with the symmetric key to be removed.
Authorization policy can restrict the set of callers
who can create a new resource. In this case, the caller must present a set
of access credentials for authorization. Upon successfully authenticating
the credentials, the template that verified the presented samples identifies
the ACL entry that will be used in the authorization computation. If the caller
is authorized, the new resource is created.
The caller must provide an initial ACL entry to
be associated with the newly created resource. This entry is used to control
future access to the new resource and (since the subject is deemed to be the "Owner")
exercise control over its associated ACL. The caller can specify the following
items for initializing an ACL entry:
• Subject - A CSSM_LIST structure,
containing the type of the subject and a template value that can be used to
verify samples that are presented in credentials when resource access is requested.
• Delegation flag - A value indicating
whether the Subject can delegate the permissions recorded in the AuthorizationTag. (This
item only applies to public key subjects).
• Authorization tag - The set
of permissions that are granted to the Subject.
• Validity period - The start
time and the stop time for which the ACL entry is valid.
• ACL entry tag - A user-defined string
value associated with the ACL entry.
The service provider can modify the caller-provided
initial ACL entry to conform to any innate resource-access policy that the
service provider may be required to enforce. If the initial ACL entry provided
by the caller contains values or permissions that are not supported by the
service provider, then the service provider can modify the initial ACL appropriately
or can fail the request to create the new resource. Service providers list
their supported AuthorizationTag values
in their Module Directory Services primary record.
The KeyData field of the CSSM_KEY
structure is allocated by the CSP. The application is required to free this
memory using the CSSM_FreeKey (CSSM
API), or CSP_FreeKey (CSP
SPI), function or with the memory functions registered for the CSPHandle.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_KEY_LABEL_ALREADY_EXISTS
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_GenerateRandom, CSSM_GenerateKeyPair
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_GenerateRandom, CSP_GenerateKeyPair
GenerateKeyP – Generate a key with privilege
(CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GenerateKeyP
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
uint32 KeyUsage,
uint32 KeyAttr,
const CSSM_DATA *KeyLabel,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry,
CSSM_KEY_PTR Key,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
Privilege (input)
The privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation.
See CSSM_GenerateKey for other parameters.
This
function is similar to the CSSM_GenerateKey function. It also accepts a USEE tag as a privilege
request parameter. CSSM checks that either its own privilege set or the application’s
privilege set (if the application is signed) includes the tag. If the tag
is found and the service provider privilege set indicates that it is supported,
the tag is forwarded to the service provider.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions: CSSM_GenerateKeyPairP, CSSM_GenerateRandom
GenerateKeyPair:
CSSM_GenerateKeyPair, CSP_GenerateKeyPair – Generate an asymmetric key
pair (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GenerateKeyPair
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
uint32 PublicKeyUsage,
uint32 PublicKeyAttr,
const CSSM_DATA *PublicKeyLabel,
CSSM_KEY_PTR PublicKey,
uint32 PrivateKeyUsage,
uint32 PrivateKeyAttr,
const CSSM_DATA *PrivateKeyLabel,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry,
CSSM_KEY_PTR PrivateKey)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_GenerateKeyPair
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
uint32 PublicKeyUsage,
uint32 PublicKeyAttr,
const CSSM_DATA *PublicKeyLabel,
CSSM_KEY_PTR PublicKey,
uint32 PrivateKeyUsage,
uint32 PrivateKeyAttr
const CSSM_DATA *PrivateKeyLabel,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry,
CSSM_KEY_PTR PrivateKey,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
PublicKeyUsage (input)
A bit mask indicating all permitted uses for the
new public key.
PublicKeyAttr (input)
A bit mask defining attribute values for the new
public key.
PublicKeyLabel (input/optional)
Pointer to a byte string that will be used as the
label for the public key.
PublicKey (output)
Pointer to CSSM_KEY structure used to hold the
new public key. The CSSM_KEY structure should be empty upon input to this
function. The CSP will ignore any values residing in this structure at function
invocation. Input values should be supplied in the cryptographic Context, PublicKeyUsage, PublicKeyAttr, and PublicKeyLabel input parameters.
PrivateKeyUsage (input)
A bit mask indicating all permitted uses for the
new private key.
PrivateKeyAttr (input)
A bit mask defining attribute values for the new
private key.
PrivateKeyLabel (input/optional)
Pointer to a byte string that will be used as the
label for the private key.
CredAndAclEntry (input/optional)
A structure containing one or more credentials
authorized for creating a key and the prototype ACL entry that will control
future use of the newly created key. The credentials and ACL entry prototype
can be presented as immediate values or callback functions can be provided
for use by the CSP to acquire the credentials and/or the ACL entry interactively.
If the CSP provides public access for creating a key, then the credentials
can be NULL. If the CSP defines a default initial ACL entry for the new key,
then the ACL entry prototype can be an empty list.
PrivateKey (output)
Pointer to CSSM_KEY structure used to obtain the
private key. Upon function invocation, any values in the CSSM_Key structure
should be ignored. All input values should be supplied in the cryptographic Context, PrivateKeyUsage, PrivateKeyAttr, and PrivateKeyLabel input parameters.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
Privilege (input)
The export privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation. This parameter is forwarded to the CSP after CSSM verifies the
caller and service provider privilege set includes the specified privilege.
This
function generates an asymmetric key pair. The CSP may cache keying material
associated with the new asymmetric keypair. When one or both of the keys are
no longer in active use, the application can invoke the CSSM_FreeKey interface to allow cached keying material associated
with the key to be removed.
Authorization policy can restrict the set of callers
who can create a new resource. In this case, the caller must present a set
of access credentials for authorization. Upon successfully authenticating
the credentials, the template that verified the presented samples identifies
the ACL entry that will be used in the authorization computation. If the caller
is authorized, the new resource is created.
The caller must provide an initial ACL entry to
be associated with the newly created resource. This entry is used to control
future access to the new resource and (since the subject is deemed to be the "Owner")
exercise control over its associated ACL. The caller can specify the following
items for initializing an ACL entry:
Subject
A CSSM_LIST structure, containing the type of the
subject and a template value that can be used to verify samples that are presented
in credentials when resource access is requested.
Delegation flag
A
value indicating whether the Subject can delegate the permissions recorded
in the AuthorizationTag.
(This item applies only to public key subjects).
Authorization tag
The
set of permissions that are granted to the Subject.
Validity period
The
start time and the stop time for which the ACL entry is valid.
ACL entry tag
A user-defined string value associated with the
ACL entry.
The service provider can modify the caller-provided
initial ACL entry to conform to any innate resource-access policy that the
service provider may be required to enforce. If the initial ACL entry provided
by the caller contains values or permissions that are not supported by the
service provider, then the service provider can modify the initial ACL appropriately
or can fail the request to create the new resource. Service providers list
their supported AuthorizationTag values
in their Module Directory Services primary record.
The KeyData fields of the CSSM_KEY
structures are allocated by the CSP. The application is required to free this
memory using the CSSM_FreeKey (CSSM
API), or CSP_FreeKey (CSP
SPI), function or with the memory functions registered for the CSPHandle.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_KEY_LABEL_ALREADY_EXISTS
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_GenerateKey, CSSM_GenerateRandom
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_GenerateKey, CSP_GenerateRandom
GenerateKeyPairP – Generate an asymmetric key
pair with privilege (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GenerateKeyPairP
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
uint32 PublicKeyUsage,
uint32 PublicKeyAttr,
const CSSM_DATA *PublicKeyLabel,
CSSM_KEY_PTR PublicKey,
uint32 PrivateKeyUsage,
uint32 PrivateKeyAttr,
const CSSM_DATA *PrivateKeyLabel,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry,
CSSM_KEY_PTR PrivateKey,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
Privilege (input)
The privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation.
See CSSM_GenerateKeyPair.
This
function is similar to the CSSM_GenerateKeyPair function. It also accepts a USEE tag as a privilege
request parameter. CSSM checks that either its own privilege set or the application’s
privilege set (if the application is signed) includes the tag. If the tag
is found and the service provider privilege set indicates that it is supported,
the tag is forwarded to the service provider.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_KEY_LABEL_ALREADY_EXISTS
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions: CSSM_GenerateKeyPair
GenerateMac: CSSM_GenerateMac,
CSP_GenerateMac – Compute a message authentication code (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GenerateMac
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Mac)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_GenerateMac
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Mac)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
DataBufs (input)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the data to be operated on.
DataBufCount (input)
The number of DataBufs.
Mac (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure for the Message
Authentication Code.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
This
function computes a message authentication code for all data contained in
the set of input buffers.
The output is returned to the caller either by
filling the caller-specified buffer or by using the application’s declared
memory allocation functions to allocate buffer space. To specify a specific,
preallocated output buffer, the caller must provide an array of one or more
CSSM_DATA structures, each containing a Length field value greater than zero
and a non-NULL data pointer field value. To specify automatic output buffer
allocation by the CSP, the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA
structures, each containing a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL
data pointer field value. The application is always responsible for deallocating
the memory when it is no longer needed.
The output is returned to the caller as specified
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_OUTPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_GenerateMacInit, CSSM_GenerateMacUpdate, CSSM_GenerateMacFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_GenerateMacInit, CSP_GenerateMacUpdate, CSP_GenerateMacFinal
GenerateMacFinal:
CSSM_GenerateMacFinal, CSP_GenerateMacFinal – Finalize the staged message
authentication code (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GenerateMacFinal
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Mac)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_GenerateMacFinal
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Mac)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
Mac (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure for the message
authentication code.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function finalizes the staged message authentication code function.
The
output is returned to the caller either by filling the caller-specified buffer
or by using the application’s declared memory allocation functions to
allocate buffer space. To specify a specific, preallocated output buffer,
the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA structures, each
containing a Length field value greater than zero and a non-NULL data pointer
field value. To specify automatic output buffer allocation by the CSP, the
caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA structures, each containing
a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL data pointer field value. The
application is always responsible for deallocating the memory when it is no
longer needed.
The output is returned to the caller as specified
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_OUTPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_GenerateMac, CSSM_GenerateMacInit, CSSM_GenerateMacUpdate
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_GenerateMac, CSP_GenerateMacInit, CSP_GenerateMacUpdate
GenerateMacInit:
CSSM_GenerateMacInit, CSP_GenerateMacInit – Initialize the staged message
authentication code (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GenerateMacInit
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_GenerateMacInit
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
This
function initializes the staged message authentication code function.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_GenerateMac, CSSM_GenerateMacUpdate, CSSM_GenerateMacFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_GenerateMac, CSP_GenerateMacUpdate, CSP_GenerateMacFinal
GenerateMacUpdate:
CSSM_GenerateMacUpdate, CSP_GenerateMacUpdate – Continue the staged process
of computing a message authentication code (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GenerateMacUpdate
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_GenerateMacUpdate
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
DataBufs (input)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the data to be operated on.
DataBufCount (input)
The number of DataBufs.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function continues the staged process of computing a message authentication
code over all data contained in the set of input buffers. The authentication
code will be returned as a result of the final code generation step.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_GenerateMac, CSSM_GenerateMacInit, CSSM_GenerateMacFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_GenerateMac, CSP_GenerateMacInit, CSP_GenerateMacFinal
GenerateRandom:
CSSM_GenerateRandom, CSP_GenerateRandom function – Generate random data (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GenerateRandom
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR RandomNumber)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_GenerateRandom
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
CSSM_DATA_PTR RandomNumber)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
RandomNumber (output)
Pointer to CSSM_DATA structure used to obtain the
random number and the size of the random number in bytes.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
This
function generates random data.
The output is returned to the caller either by
filling the caller-specified buffer or by using the application’s declared
memory allocation functions to allocate buffer space. To specify a specific,
preallocated output buffer, the caller must provide an array of one or more
CSSM_DATA structures, each containing a Length field value greater than zero
and a non-NULL data pointer field value. To specify automatic output buffer
allocation by the CSP, the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA
structures, each containing a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL
data pointer field value. The application is always responsible for deallocating
the memory when it is no longer needed.
The output is returned to the caller as specified
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
GetOperationalStatistics:
CSSM_CSP_GetOperationalStatistics, CSP_GetOperationalStatistics – Get
operational values of a subservice (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_GetOperationalStatistics
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CSP_OPERATIONAL_STATISTICS *Statistics)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSSM_CSP_GetOperationalStatistics
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CSP_OPERATIONAL_STATISTICS *Statistics)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
Handle of the Cryptographic Service Provider that
will perform the operation.
Statistics (output)
Structure containing the subservice’s current
statistics.
Obtain
the current operational values of a subservice. The information is returned
in a structure of type CSSM_CSP_OPERATIONAL_STATISTICS. This information includes
login status and available storage space. The data structure to hold the returned
results must be provided by the caller. The CSP does not allocate memory on
behalf of the caller.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
GetTimeValue:
CSSM_GetTimeValue, CSP_GetTimeValue – Get a CSP time value (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_GetTimeValue
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS TimeAlgorithm,
CSSM_DATA *TimeData)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_GetTimeValue
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS TimeAlgorithm,
kCSSM_DATA *TimeData)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
Handle of the Cryptographic Service Provider that
will perform the operation.
TimeAlgorithm (input)
A CSSM algorithm type that indicates the method
for fetching the time. The following algorithm types are currently supported:
CSSM_ALGID_UTC Returns a time value in the form
YYYYMMDDhhmmss (4 characters for the year; 2 characters each for the month,
the day, the hour, the minute, and the second). The time returned is GMT.
CSSM_ALGID_RUNNING_COUNTER The current value of
a running hardware counter that operates while the device is in operation.
This value can be read from a processor counter provided by some platform
architectures.
TimeData (output)
The time value of counter value returned in response
to the request.
This
function returns a time value maintained by a CSP. This feature will be supported
primarily by hardware tokens with an onboard real time clock.
The
output is returned to the caller either by filling the caller-specified buffer
or by using the application’s declared memory allocation functions to
allocate buffer space. To specify a specific, preallocated output buffer,
the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA structures, each
containing a Length field value greater than zero and a non-NULL data pointer
field value. To specify automatic output buffer allocation by the CSP, the
caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA structures, each containing
a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL data pointer field value. The
application is always responsible for deallocating the memory when it is no
longer needed.
Some tokens require authentication before returning
a time value.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Initialize – Verify module version (CDSA)
(not currently supported) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI Initialize
(uint32 VerMajor,
uint32 VerMinor)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
VerMajor (input)
The major version number of the CSSM that is invoking
this module manager.
VerMinor (input)
The minor version number of the CSSM that is invoking
this module manager.
This
function checks whether the current version of the module is compatible with
the CSSM version specified as input and performs any module-manager-specific
setup activities.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_MODULE_MANAGER_INITIALIZE_FAIL
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: Terminate
MDS_Initialize – Initiate service context with
MDS (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDS_Initialize
(const CSSM_GUID *pCallerGuid,
const CSSM_DATA *pCallerManifest,
const CSSM_MEMORY_FUNCS *pMemoryFunctions,
MDS_FUNCS_PTR pDlFunctions,
MDS_HANDLE *hMds)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
pCallerGuid (input/optional)
The GUID of the module calling MDS.
pCallerManifest (input/optional)
The Manifest of the module calling MDS.
pMemoryFunctions (input)
The memory-management routines MDS uses to allocate
query results on behalf of the caller.
pDlFunctions (output)
The function table containing MDS programming interfaces
for database access.
hMds (output)
A new handle that can be used to interact with
the MDS. The value will be set to CSSM_INVALID_HANDLE if the function fails.
This
function initiates a service context with MDS and returns an opaque handle
corresponding to that context. The caller provides memory functions that MDS
can use to manage memory in the caller’s space on behalf of the caller.
The caller also provides input/output table pDlFunctions to get access to
MDS databases.
If the caller is a CDSA service provider that will
require write-access to an MDS database, (such as a module that supports dynamic
insertion and removal events), then the caller can provide the caller’s
GUID as input parameter pCallerGuid.
When provided as input, the GUID is associated with the MDS handle and is
used during DbOpen processing.
If write-access is requested during DbOpen, MDS uses the associated GUID to locate the service
provider’s signed manifest credentials in the DS
Common relation. The service provider
module and its credentials are verified to ensure that write-access is permitted
on this database by this module.
The installers will have to provide the pCallerManifest instead
of pCallerGuid,
as GUID cannot be used to locate an application unless it is installed. Only
one of the two parameters pCallerGuid and pCallerManifest should be
non NULL in an MDS_Initialize call,
otherwise an error will be returned.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_POINTER
CSSMERR_DL_INTERNAL_ERROR
CSSMERR_DL_MEMORY_ERROR
CSSMERR_DL_FUNCTION_FAILED
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
MDS_Install – Create the object directory
database (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDS_Install
(MDS_HANDLE MdsHandle)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
MdsHandle (input)
The MDS handle identifying an MDS context.
This function creates the Object Directory database
containing the Object relation,
and the CDSA Directory database containing the set of CDSA-specific relations
defined in this specification. The MdsHandle identifies an MDS context created by invoking MDS_Initialize. The context
contains information about the access rights of the caller. Write-access is
required to perform this operation.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_DL_DATASTORE_ALREADY_EXISTS
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_ACCESS_REQUEST
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_LOCATION
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_NAME
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_OPEN_PARAMETERS
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORD_INDEX
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_RECORDTYPE
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_FIELD_NAME
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_FIELD_FORMAT
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_INDEX_INFO
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_LOCALITY
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_NUM_ATTRIBUTES
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_NUM_INDEXES
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_NUM_RECORDTYPES
CSSMERR_DL_UNSUPPORTED_RECORDTYPE
CSSMERR_DL_FIELD_SPECIFIED_MULTIPLE
CSSMERR_DL_INCOMPATIBLE_FIELD_FORMAT
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_PARSING_MODULE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
MDS_Terminate – Terminate the MDS service context
(CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDS_Terminate
(MDS_HANDLE MdsHandle)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
MdsHandle (input)
The MDS handle corresponding to the context being
terminated.
This
function terminates the MDS service context identified by the opaque MdsHandle. The MDS handle
is invalidated and MDS frees all internal resources associated with the context.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
MDS_Uninstall – Delete the object directory
database (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDS_Uninstall
(MDS_HANDLE MdsHandle)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
MdsHandle (input)
The MDS handle identifying a valid MDS context.
This
function deletes the Object Directory database containing the Object relation, and the
CDSA Directory database containing the set of CDSA-specific relations defined
in this specification. The MdsHandle identifies
the MDS context created by invoking MDS_Initialize. The context contains information about the access
rights of the caller. Write-access is required to perform this operation.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DL_HANDLE CSSMERR_DL_DATASTORE_IS_OPEN
CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_LOCATION CSSMERR_DL_INVALID_DB_NAME
CSSMERR_DL_DATASTORE_DOESNOT_EXIST
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo – Frees memory associated with
the MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo function. # include <mds_util_api.h>
# include <mds_util_helper.h>
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo
(MDSUTIL_MODULE_INFO_PTR ModuleInfo)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
ModuleInfo (input)
A pointer to the data to be freed.
This
routine frees the list of module information that was returned by MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo.
All substructures within the info structure are freed by this function.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The
value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_POINTER
CSSMERR_CSSM_NOT_INITIALIZED
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions:MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall, MDSUTIL_ListModules, MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo , MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList, MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers, MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall, MDSUTIL_Init, MDSUTIL_Term
MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList – Frees the list of add-in modules
that was returned by MDSUTIL_ListModules. # include <mds_util_api.h>
# include <mds_util_helper.h>
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList
(MDSUTIL_LIST_PTR List)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
List (input)
A pointer to a MDSUTIL_LIST pointer.
This
routine frees the list of add-in modules that was returned by MDSUTIL_ListModules.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The
value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_POINTER
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions:MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall, MDSUTIL_ListModules, MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo , MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo, MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers, MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall, MDSUTIL_Init, MDSUTIL_Term
MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID – Returns the location of the
add-in module, and the associated credentials file for the add-in module. # include <mds_util_api.h>
# include <mds_util_helper.h>
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID
(const CSSM_GUID *ModuleGUID,
CSSM_DATA *pModulePath,
CSSM_DATA *pModuleCredentialPath,
CSSM_API_MEMORY_FUNCS_PTR MemoryFuncs)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
ModuleGUID (input)
A pointer to the module’s Globally Unique
ID.
pModulePath (output)
A pointer to the module’s full filespec location.
pModuleCredentialPath (output)
A pointer to the module’s credential full
filespec location.
MemoryFuncs (input)
The memory-management routines MDS uses to allocate
query results on behalf of the caller.
This
function returns the location of the add-in module, and the associated credentials
file for the add-in module. The caller is responsible for freeing the memory
in the output parameters.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_GUID
CSSMERR_CSSM_MDS_ERROR
CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_OUTPUT_POINTER
CSSM_ERRCODE_MEMORY_ERROR
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions:MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall, MDSUTIL_ListModules, MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo , MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList, MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers, MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall, MDSUTIL_Init, MDSUTIL_Term
MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo – Gets information from the MDS
registry for the add-in module. # include <mds_util_api.h>
# include <mds_util_helper.h>
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo
(const CSSM_GUID *ModuleGUID,
CSSM_SERVICE_MASK UsageMask,
uint32 SubserviceID,
CSSM_USEE_TAG USEERequest,
MDSUTIL_MODULE_INFO_PTR *pModuleInfo)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
ModuleGUID (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_GUID structure containing
the Globally Unique ID of the add-in module.
UsageMask (input)
A bit mask specifying the module usage types used
to restrict the capabilities information returned by this function. An input
value of zero specifies all usages for the specified module.
SubserviceID (input)
A single subservice ID. Note that the operation
may already be limited by a service mask. If so, the subservice ID applies
to all service categories selected by the service mask.
USEERequest (input)
United States Export Exemption tag; should be set
to CSSM_USEE_NONE.
pModuleInfo (output)
A pointer to the module information.
This
function gets a list of descriptive information from the MDS registry for
the add-in module identified by the ModuleGUID. The information returned can
include all of the capability information for each of the subservices for
each of the service types implemented by the selected module. The request
for information can be limited to a particular set of services, as specified
by the UsageMask. The request may be further limited to one or all of the
subservices implemented in one or all of the service categories. The MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo
function must be called to deallocate memory containing the list.
NULL —
Error in retrieving information from the MDS registry.
Not
NULL — A pointer to a module info structure containing a pointer to
an array of zero or more service information structures. Each structure contains
type information identifying the service description as representing certificate
library services, data storage library services, and so on. The service descriptions
are sub-classed into subservice descriptions that describe the attributes
and capabilities of a subservice.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard. CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_POINTER
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_GUID
CSSM_INVALID_SUBSERVICEID
CSSMERR_CSSM_MEMORY_ERROR
CSSMERR_CSSM_NOT_INITIALIZED
CSSM_ERRCODE_MDS_ERROR
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions:MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall, MDSUTIL_ListModules, MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList, MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers, MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall, MDSUTIL_Init, MDSUTIL_Term
MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo – Returns descriptive information
about the elective module manager identified by the GUID or the service mask. # include <mds_util_api.h>
# include <mds_util_helper.h>
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo
(const CSSM_GUID *ModuleGUID,
CSSM_SERVICE_MASK ServiceType,
MDSUTIL_MODULE_MANAGER_INFO_PTR *ModuleManagerInfo)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
ModuleGUID (input)
A pointer to a GUID identifying the module manager.
ServiceType (input)
A unique service mask identifying the module manager.
ModuleManagerInfo (output)
A pointer to the returned module manager information.
This
function returns descriptive information about the elective module manager
identified by the GUID or the service mask.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. NULL indicates
that the routine was unable to get the module manager information.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_POINTER
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_GUID
CSSM_ERRCODE_MDS_ERROR
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_SERVICE_MASK
CSSM_ERRCODE_MEMORY_ERROR
CSSMERR_CSSM_MEMORY_ERROR
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions:MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall, MDSUTIL_ListModules, MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo , MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList, MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall, MDSUTIL_Init, MDSUTIL_Term
MDSUTIL_Init – Initializes the MDS registry in preparation for a series
of MDSUTIL operations. # include <mds_util_api.h>
# include <mds_util_helper.h>
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDSUTIL_Init
(CSSM_BOOL ReadWrite)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
ReadWrite (input)
A Boolean flag indicating whether the MDS registry
is to be enabled for writing as well as reading. CSSM_TRUE indicates that
the registry should be enabled for writing.
This
function initializes the MDS registry in preparation for a series of MDSUTIL
operations.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values indicate an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions:MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall, MDSUTIL_ListModules, MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo , MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList, MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers, MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall, MDSUTIL_Term
MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers – Returns the number of module
managers and a list of GUIDs associated with those module managers. # include <mds_util_api.h>
# include <mds_util_helper.h>
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers
(CSSM_GUID_PTR *ModuleManagerGuids,
uint32 *NumberOfModuleManagers)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
ModuleManagerGuids (output)
A pointer to a list of GUIDs.
NumberOfModuleManagers (output)
A pointer to the number of module managers.
This
function returns the number of module managers and a list of GUIDs associated
with those module managers. The caller is responsible for freeing the memory
associated with the GUID list.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_POINTER
CSSM_ERRCODE_MEMORY_ERROR
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions:MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall, MDSUTIL_ListModules, MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo , MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList, MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall, MDSUTIL_Init, MDSUTIL_Term
MDSUTIL_ListModules – Returns a list containing the
GUID/version/name for each of the currently installed service provider modules
that provide services in any of the CSSM functional categories selected in
the usage mask. The MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList function must be called to deallocate
memory containing the list. # include <mds_util_api.h>
# include <mds_util_helper.h>
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDSUTIL_ListModules
(CSSM_SERVICE_MASK UsageMask,
CSSM_BOOL MatchAll,
MDSUTIL_LIST_PTR *pList)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
UsageMask (input)
A bit mask selecting CSSM functional categories
of interest for selecting information about potential service provider modules.
MatchAll (input)
A Boolean value to indicate if the add-in has to
match all of the conditions expressed in UsageMask. TRUE means all conditions
must be met. FALSE means one or more conditions must be met.
pList (output)
Pointer to a list of modules. Each item contains
a CSSM_GUID, the module version, and a descriptive string name of the module.
This
function returns a list containing the GUID/version/name for each of the currently
installed service provider modules that provide services in any of the CSSM
functional categories selected in the usage mask. The MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList
function must be called to deallocate memory containing the list.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The
value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSM_ERRCODE_MDS_ERROR
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_POINTER
CSSM_ERRCODE_INVALID_OUTPUT_POINTER
CSSM_ERRCODE_MEMORY_ERROR
CSSMERR_NOT_INITIALIZED
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions:MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall, MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo , MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList, MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers, MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall, MDSUTIL_Init, MDSUTIL_Term
MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall – Updates the MDS registry with
information on the add-in module (not currently supported) # include <mds_util_api.h>
# include <mds_util_helper.h>
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall
(const char *ModuleName,
const char *ModuleFileNames,
const char *ModulePathName,
const char *ModuleCredentialName,
const char *ModulCredentialPath,
const CSSM_GUID *GUID,
const MDSUTIL_MODULE_INFO *ModuleDescription,
const void *Reserved1,
const CSSM_DATA *Reserved2)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
ModuleName (input)
The name of the add-in module.
ModuleFileNames (input)
The name of the file implementing the add-in module.
ModulePathName (input)
The path to the file implementing the add-in module.
ModuleCredentialName (input)
The name of the credential file for the add-in
module.
ModuleCredentialPath (input)
The path to the credential file for the add-in
module.
GUID (input)
The Globally Unique ID of the add-in module.
ModuleDescription (input)
A pointer to a structure that describes the add-in
module.
Reserved1 (input)
Reserved data.
Reserved2 (input)
Reserved data.
This
function updates the MDS registry with information on the add-in module.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The
value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_POINTER
CSSMERR_DL_OS_ACCESS_DENIED
CSSMERR_CSSM_INTERNAL_ERROR
CSSM_ERRCODE_INTERNAL_ERROR
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions: MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall, MDSUTIL_ListModules, MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo , MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList, MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers, MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall, MDSUTIL_Init, MDSUTIL_Term
MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall – Updates the MDS registry with
information about the Extensible Module Manager (not currently supported) # include <mds_util_api.h>
# include <mds_util_helper.h>
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall
(const char *ModuleManagerName,
const char *ModuleManagerFileName,
const char *ModuleManagerPathName,
const char *ModuleManager CredentialName,
const char *ModuleManagerCredentialPath,
const CSSM_GUID *ModuleManagerGuid,
const MDSUTIL_MODULE_MANAGER_INFO *ModuleManagerDescription,
const void *Reserved1,
const CSSM_DATA *Reserved2)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
ModuleManagerName (input)
A pointer to the name of the Extensible Module
Manager (EMM).
ModuleManagerFileName (input)
A pointer to the filename of the Extensible Module
Manager.
ModuleManagerPathname (input)
A pointer to the directory path to the file implementing
the EMM.
ModuleManagerCredentialName (input)
A pointer to the name of the credential file of
the EMM.
ModuleManagerCredentialPath (input)
A pointer to the directory path to the credential
file of the EMM.
ModuleManagerGuid (input)
A pointer to the Globally Unique ID of the EMM.
ModuleManagerDescription (input)
A pointer to the structure that describes the EMM.
Reserved1 (input)
TBD
Reserved2 (input)
TBD
This
function updates the MDS registry with information about the Extensible Module
Manager.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_POINTER
CSSMERR_CSSM_INTERNAL_ERROR
CSSMERR_CSSM_FUNCTION_FAILED
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions:MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall, MDSUTIL_ListModules, MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo , MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList, MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers, MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall, MDSUTIL_Init, MDSUTIL_Term
MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall – Removes from the MDS registry the information associated
with the Globally Unique ID of the EMM (not currently supported) # include <mds_util_api.h>
# include <mds_util_helper.h>
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall
(const CSSM_GUID *ModuleManagerGuid)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
ModuleManagerGuid (input)
A pointer to the Globally Unique ID of the Extensible
Module Manager.
This
function removes from the MDS registry the information associated with the
Globally Unique ID of the EMM.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_INVALID_GUID
CSSMERR_CSSM_FUNCTION_FAILED
CSSM_ERRCODE_MDS_ERROR
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions:MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall, MDSUTIL_ListModules, MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo , MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList, MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers, MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall, MDSUTIL_Init, MDSUTIL_Term
MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall – Removes from the MDS registry
the information associated with GUID (not currently supported) # include <mds_util_api.h>
# include <mds_util_helper.h>
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall
(const CSSM_GUID *ModuleGUID)
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
ModuleGUID (input)
The Globally Unique ID of the add-in module.
This
function removes from the MDS registry the information associated with GUID.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The
value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_MEMORY_ERROR
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions: MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall, MDSUTIL_ListModules, MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo , MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList, MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers, MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall, MDSUTIL_Init, MDSUTIL_Term
MDSUTIL_Term – Closes the MDS registry after a series of operations. # include <mds_util_api.h>
# include <mds_util_helper.h>
void CSSMAPI MDSUTIL_Term()
Module
Directory Services library (cdsa$mds300_shr.exe)
None
This
function closes the MDS registry after a series of operations.
None
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions:MDSUTIL_ModuleInstall MDSUTIL_ModuleUninstall, MDSUTIL_ListModules, MDSUTIL_GetModuleInfo , MDSUTIL_GetCredLocationFromGUID, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleInfo, MDSUTIL_FreeModuleList, MDSUTIL_ListModuleManagers, MDSUTIL_GetModuleManagerInfo, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerInstall, MDSUTIL_ModuleManagerUninstall, MDSUTIL_Init
ModuleManagerAuthenticate ModuleManagerAuthenticate – Module manager authentication
(CDSA) (not currently supported) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI ModuleManagerAuthenticate
(CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY KeyHierarchy,
const CSSM_GUID *CssmGuid,
const CSSM_GUID *AppGuid,
CSSM_MANAGER_REGISTRATION_INFO_PTR FunctionTable)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
KeyHierarchy (input)
The CSSM_KEY_HIERARCHY flag indicating which embedded
key(s) CSSM should use when verifying the integrity of the module manager.
CssmGuid (input)
A CSSM_GUID value identifying the calling CSSM.
The elective module manager can use this value to locate the signed manifest
credentials for CSSM.
AppGuid (input/optional)
A CSSM_GUID value identifying the application who
invoked the calling CSSM. The elective module manager can use this value to
locate the signed manifest credentials for the application.
FunctionTable (output)
A set of function pointers for EMM-defined functions
used by CSSM to communicate state changes related to module attach and module
detach operations.
This
function should perform the elective module manager’s half of the bilateral
authentication procedure with CSSM. The CssmGuid is used to locate the CSSM’s credentials
to be verified. The credentials are a zipped, signed manifest.
The KeyHierarchy indicates which
public key should be used as the root when checking the integrity of the module
manager. The AppGuid is
used to locate the application’s signed manifest credentials. The elective
module manager must check the application’s credentials to verify the
application’s authorization. If no privileges are requested, then the
application is not required to provide a GUID nor a set of signed manifest
credentials.
Upon successful completion, the elective module
manager returns its function table to the calling CSSM. The EMM function table
contains the set of EMM entry points that CSSM uses to notify the module manager
of significant events such as module attach and module detach requests issued
by an application, and event notifications issued by other module managers.
This
function symbol must be exported by the elective module manager, so CSSM can
invoke this function upon completion of the loading process.
This
function is the first module manager interface invoked by CSSM after loading
and invoking the main entry point. In particular, the elective module manager’s
initialize function is invoked by CSSM after this function has successfully
completed execution.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
ObtainPrivateKeyFromPublicKey ObtainPrivateKeyFromPublicKey:
CSSM_CSP_ObtainPrivateKeyFromPublicKey, CSP_ObtainPrivateKeyFromPublicKey – Convert
public key to private key (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_ObtainPrivateKeyFromPublicKey
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle
const CSSM_KEY *PublicKey,
CSSM_KEY_PTR PrivateKey)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_ObtainPrivateKeyFromPublicKey
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_KEY *PublicKey,
CSSM_KEY_PTR PrivateKey)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the module to perform
this operation.
PublicKey (input)
The public key corresponding to the private key
being sought.
PrivateKey (output)
A reference to the private key corresponding to
the public key.
Given
a public key this function returns a reference to the private key. The private
key and its associated passphrase can be used as an input to any function
requiring a private key value.
The KeyData field of the CSSM_KEY
structure is allocated by the CSP. The application is required to free this
memory using the CSSM_FreeKey (CSSM
API), or CSP_FreeKey (CSP
SPI), function or with the memory functions registered for the CSPHandle.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_PRIVATE_KEY_NOT_FOUND
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
PassThrough: CSSM_CSP_PassThrough,
CSP_PassThrough – Extend crypto functionality (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_CSP_PassThrough
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
uint32 PassThroughId,
const void *InData,
void **OutData)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_PassThrough
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
uint32 PassThroughId,
const void *InData,
void **OutData)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation.
PassThroughId (input)
An identifier specifying the custom function to
be performed.
InData (input)
A pointer to a module, implementation-specific
structure containing the input data.
OutData (output)
A pointer to a module, implementation-specific
structure containing the output data. The service provider will allocate the
memory for this structure. The application should free the memory for the
structure.
CSPHandle (input)
Handle of the CSP supporting the PassThrough function.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this custom context structure.
The CSSM_CSP_PassThrough (CSSM
API), or CSP_PassThrough (CSP
SPI), function is provided to allow CSP developers to extend the crypto functionality
of the CSSM API.
The CSP_EventNotify function
is used by the CSSM Core to interact with the CSP module.
Because
this function is only exposed to CSSM as a function pointer, the function
name internal to the CSP can be assigned at the discretion of the CSP module
developer. However, the parameter list and return value types must match those
defined for this function.
The error codes given in this section constitute
the generic error codes, which may be used by all CSP libraries to describe
common error conditions. CSP module developers may also define their own module-specific
error codes.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_INVALID_PASSTHROUGH_ID
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
QueryKeySizeInBits:
CSSM_QueryKeySizeInBits, CSP_QueryKeySizeInBits – Get CSP logical and effective
sizes (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_QueryKeySizeInBits
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
CSSM_KEY_SIZE_PTR KeySize)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_QueryKeySizeInBits
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
CSSM_KEY_SIZE_PTR KeySize)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the Cryptographic Service
Provider module used to perform this function.
For
the API, this parameter is ignored if a valid cryptographic context handle
is specified.
CCHandle (input/optional)
A handle to a context that describes a cryptographic
operation. The cryptographic context should contain a handle to the CSP that
is being queried and the key about which key-size information is being requested.
Key (input/optional)
A pointer to a CSSM_KEY structure containing the
key about which key-size information is being requested. This parameter is
ignored if a valid cryptographic context handle is specified.
KeySize (output)
Pointer to a CSSM_KEY_SIZE data structure. The
logical and effective sizes (in bits) for the key are returned in this structure.
For the API, if no context handle is provided,
only the CSSM_KEY_SIZE LogicalKeySizeInBits field is set.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
This
function queries a Cryptographic Service Provider (CSP) for the logical and
effective sizes of a specified key.
The Cryptographic Service Provider (handle) and
the key can be specified either in the cryptographic context or as parameters
to the function call. If a valid cryptographic context handle parameter is
specified, the CSP handle and key parameters are ignored.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_QUERY_SIZE_UNKNOWN
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_GenerateRandom, CSSM_GenerateKeyPair, CSSM_GenerateKey
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_GenerateRandom, CSP_GenerateKeyPair, CSP_GenerateKey
QuerySize: CSSM_QuerySize,
CSP_QuerySize – Get size of the output data (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_QuerySize
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_BOOL Encrypt,
uint32 QuerySizeCount,
CSSM_QUERY_SIZE_DATA_PTR DataBlockSizes)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_QuerySize
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
CSSM_BOOL Encrypt,
uint32 QuerySizeCount,
CSSM_QUERY_SIZE_DATA_PTR DataBlockSizes)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle for an encryption and decryption context.
Encrypt (input)
A boolean indicating whether encryption is the
operation for which the output data size should be calculated. If CSSM_TRUE,
the operation is encryption. If CSSM_FALSE the operation is decryption.
QuerySizeCount (input)
The number of entries in the array of DataBlockSizes.
DataBlockSizes (input/output)
An array of data block input sizes and corresponding
entries for the data block output sizes that are returned by this function.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
This
function queries for the size of the output data for a cryptographic operation.
If the context is an encryption or decryption context type then the Encrypt parameter will determine
which operation is being performed. If Encrypt is set to CSSM_TRUE then it is an encrypt operation,
otherwise it is a decrypt operation. For all other context types the Encrypt parameter is ignored.
This function can also be used to query the output size requirements for the
intermediate steps of a staged cryptographic operation. There may be algorithm-specific
and token-specific rules restricting the lengths of data following data update
calls.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_QUERY_SIZE_UNKNOWN
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_EncryptData, CSSM_EncryptDataUpdate, CSSM_DecryptData, CSSM_DecryptDataUpdate, CSSM_SignData, CSSM_VerifyData, CSSM_DigestData, CSSM_GenerateMac
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_EncryptData, CSP_EncryptDataUpdate, CSP_DecryptData, CSP_DecryptDataUpdate, CSP_SignData, CSP_VerifyData, CSP_DigestData, CSP_GenerateMac
RefreshFunctionTable – Gets EMM-defined API function
(CDSA) (not currently supported) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI RefreshFunctionTable
(CSSM_FUNC_NAME_ADDR_PTR FuncNameAddrPtr,
uint32 NumOfFuncNameAddr)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
FuncNameAddrPtr (input/output)
A pointer to a table mapping function names to
EMM-defined APIs.
NumOfFuncNameAddr (input)
The number of entries in the table referenced by FuncNameAddrPtr.
CSSM
invokes this function to obtain the EMM-defined API function. The table is
returned to CSSM in FuncNameAddrPtr and
CSSM returns the table to the application. The application uses this table
to invoke the security services defined by the EMM’s service category.
CSSM must obtain and forward the API table to the application on behalf of
the EMM because the application is not aware of the optional nature of the
EMM. Applications use CSSM to obtain the API function table for basic module
managers and elective module managers, providing a uniform application programming
model.
If the Elective Module Manager needs the service
provider’s SPI function table in order to initialize the API function
table, the EMM can obtain the SPI function table by invoking the CSSM-provided
service cssm_GetAttachFunctions.
The service module may implement only a subset of the defined functions and
the EMM may wish to manage these functions in a particular manner through
the API mapping. The elective module manager uses the SPI function table to
dispatch application calls for service to attached modules.
Multiple
applications and multiple instances of a service module can be concurrently
active. The single elective module manager is responsible for managing all
of these concurrent sessions. After completing initialization of the API function
table, the EMM returns the refreshed API table to CSSM.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
RegisterDispatchTable – Provide the EMM with CSSM function
pointers (CDSA) (not currently supported) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI RegisterDispatchTable
(CSSM_STATE_FUNCS_PTR CssmStateCallTable)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CssmStateCallTable (input)
A table of function pointers for the set of CSSM-defined
functions the elective module manager can use to query and control the state
of an attach-session between an application and a service provider managed
by the module manager.
This
EMM-defined function is invoked by CSSM once for each CSSM_ModuleAttach, operation requesting a service provider of the
type managed by the EMM. CSSM uses this function to provide the EMM with a
set of CSSM function pointers. The EMM invokes these functions at anytime
during the life cycle of the attach-session to obtain information about the
current state and to modify the current state of the attach session.
When
the attach-session is terminated, CSSM informs the module manager by invoking
the EMM function DeregisterDispatchTable. The corresponding set of CSSM state functions
become invalid at that time.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions: DeregisterDispatchTable
RetrieveCounter:
CSSM_RetrieveCounter, CSP_RetrieveCounter – Get the value of a tamper resistant
clock (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_RetrieveCounter
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Counter)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_RetrieveCounter
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Counter)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns error.
Counter (output)
Pointer to CSSM_DATA structure that contains data
of the tamper resistant clock/counter of the cryptographic device.
This
function returns the value of a tamper resistant clock/counter of the cryptographic
device.
The output is returned to the caller as specified
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
RetrieveUniqueId:
CSSM_RetrieveUniqueId, CSP_RetrieveUniqueId – Get identifier (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_RetrieveUniqueId
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR UniqueID)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_RetrieveUniqueId
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR UniqueID)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns error.
UniqueID (output)
Pointer to CSSM_DATA structure that contains data
that uniquely identifies the cryptographic device.
This
function returns an identifier that could be used to uniquely differentiate
the cryptographic device from all other devices from the same vendor or different
vendors.
The output is returned to the caller as specified
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
SignData: CSSM_SignData,
CSP_SignData – Sign all buffer data (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_SignData
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS DigestAlgorithm,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Signature)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_SignData
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS DigestAlgorithm,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Signature)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
DataBufs (input)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the data to be signed.
DataBufCount (input)
The number of DataBufs to be signed.
DigestAlgorithm (input)
If signing just a digest, specifies the type of
digest. In this case, the context should only specify the encryption algorithm.
If not signing just a digest, it must be CSSM_ALGID_NONE. In this case, the
context should specify the combination digest/encryption algorithm.
Signature (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure for the signature.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
This
function signs all data contained in the set of input buffers using the private
key specified in the context. The CSP can require that the cryptographic context
include access credentials for authentication and authorization checks when
using a private key or a secret key.
Signing can include digesting the data and encrypting
the digest or signing just the digest (already calculated by the application).
If digesting the data and encrypting the digest, then the context should specify
the combination digest/encryption algorithm (for example, CSSM_ALGID_MD5WithRSA).
In this case, the DigestAlgorithm parameter
must be set to CSSM_ALGID_NONE. If signing just the digest, then the context
should specify just the encryption algorithm and the DigestAlgorithm parameter should specify the type of digest (for
example, CSSM_ALGID_MD5). Also, DataBufCount must be 1.
If the signing algorithm is not reversible or strictly
limits the size of the signed data, then the algorithm can specify signing
without digesting. In this case, the sign operation is performed on the input
data and the size of the input data is restricted by the service provider.
The
output is returned to the caller either by filling the caller-specified buffer
or by using the application’s declared memory allocation functions to
allocate buffer space. To specify a specific, preallocated output buffer,
the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA structures each,
containing a Length field value greater than zero and a non-NULL data pointer
field value. To specify automatic output buffer allocation by the CSP, the
caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA structures, each containing
a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL data pointer field value. The
application is always responsible for deallocating the memory when it is no
longer needed.
The output is returned to the caller as specifed
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_OUTPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
CSSMERR_CSP_INVALID_DIGEST_ALGORITHM
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_VerifyData, CSSM_SignDataInit, CSSM_SignDataUpdate, CSSM_SignDataFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_VerifyData, CSP_SignDataInit, CSP_SignDataUpdate, CSP_SignDataFinal
SignDataFinal:
CSSM_SignDataFinal, CSP_SignDataFinal – Complete the final stage of
the sign data (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_SignDataFinal
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Signature)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_SignDataFinal
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
CSSM_DATA_PTR Signature)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
Signature (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure for the signature.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function completes the final stage of the sign data function.
The
output is returned to the caller either by filling the caller-specified buffer
or by using the application’s declared memory allocation functions to
allocate buffer space. To specify a specific, preallocated output buffer,
the caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA structures, each
containing a Length field value greater than zero and a non-NULL data pointer
field value. To specify automatic output buffer allocation by the CSP, the
caller must provide an array of one or more CSSM_DATA structures, each containing
a Length field value equal to zero and a NULL data pointer field value. The
application is always responsible for deallocating the memory when it is no
longer needed.
The output is returned to the caller as specifed
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_OUTPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_SignData, CSSM_SignDataInit, CSSM_SignDataUpdate
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_SignData, CSP_SignDataInit, CSP_SignDataUpdate
SignDataInit:
CSSM_SignDataInit, CSP_SignDataInit – Initialize the staged sign data (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_SignDataInit
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_SignDataInit
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
This
function initializes the staged sign data function.
For
staged operations, a combination operation selecting both a digesting algorithm
and a signing algorithm must be specified.
The CSP can require that the cryptographic context
include access credentials for authentication and authorization checks when
using a private key or a secret key.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_SignData, CSSM_SignDataUpdate, CSSM_SignDataFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_SignData, CSP_SignDataUpdate, CSP_SignDataFinal
SignDataUpdate:
CSSM_SignDataUpdate, CSP_SignDataUpdate – Continue the staged signing
process input buffer data (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_SignDataUpdate
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_SignDataUpdate
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
DataBufs (input)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the data to be operated on.
DataBufCount (input)
The number of DataBufs to be signed.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function continues the staged signing process over all data contained in the
set of input buffers. Signing is performed using the private key specified
in the context.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_SignData, CSSM_SignDataInit, CSSM_SignDataFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
Funcitons: CSP_SignData, CSP_SignDataInit, CSP_SignDataFinal
Terminate – Clean up module-manager-specific
activities (CDSA) (not currently supported) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI Terminate
(void)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
None.
This function performs any module-manager-specific
cleanup activities in preparation for unloading of the elective module manager.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_EMM_AUTHENTICATE_FAILED.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions: Initialize
TP_ApplyCrlToDb:
CSSM_TP_ApplyCrlToDb – Update persistent storage (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_ApplyCrlToDb
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeApplied,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *ApplyCrlVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR ApplyCrlVerifyResult)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_ApplyCrlToDb
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeApplied,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *ApplyCrlVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR ApplyCrlVerifyResult)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy
module used to perform this function.
CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module that can be used to manipulate the CRL as it is applied to
the data store and to manipulate the certificates effected by the CRL, if
required. If no certificate library module is specified, the TP module uses
an assumed CL module, if required.
CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle referencing a Cryptographic Service
Provider to be used to verify signatures on the CRL determining whether to
trust the CRL and apply it to the data store. The TP module is responsible
for creating the cryptographic context structures required to perform the
verification operation. If no CSP is specified, the TP module uses an assumed
CSP to perform these operations. If optional, the caller will set this value
to 0.
CrlToBeApplied (input)
A pointer to a structure containing the encoded
certificate revocation list to be applied to the data store. The CRL type
and encoding are included in this structure.
SignerCertGroup (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_CERTGROUP structure containing
one or more related certificates that partially or fully represent the signer
of the certificate revocation list. The first certificate in the group is
the target certificate representing the CRL signer. Use of subsequent certificates
is specific to the trust domain. For example, in a hierarchical trust model
subsequent members are intermediate certificates of a certificate chain.
ApplyCrlVerifyContext (input/optional)
A structure containing credentials, policy information,
and contextual information to be used in the verification process. All of
the input values in the context are optional. The service provider can define
default values or can attempt to operate without input for all the other fields
of this input structure. The operation can fail if a necessary input value
is omitted and the service module can not define an appropriate default value.
ApplyCrlVerifyResult (output/optional)
A
pointer to a structure containing information generated during the verification
process. The information can include:
Evidence |
(output/optional) |
NumberOfEvidences |
(output/optional) |
This
function updates persistent storage to reflect entries in the certificate
revocation list. The TP module determines whether the memory-resident CRL
is trusted, and if it should be applied to one or more of the persistent databases.
Side effects of this function can include saving a persistent copy of the
CRL in a data store, or removing certificate records from a data store.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_ENCODING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION_DATA
CSSMERR_TP_VERIFY_ACTION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_CERTIFICATE_CANT_OPERATE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlGetFirstItem, CSSM_CL_CrlGetNextItem, CSSM_DL_CertRevoke
Functions
for the TP SPI:
CL_CrlGetFirstItem, CL_CrlGetNextItem, DL_CertRevoke
TP_CertCreateTemplate:
CSSM_TP_CertCreateTemplate – Allocate and initialize template
memory (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertCreateTemplate
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CertFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR CertTemplate)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertCreateTemplate
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CertFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR CertTemplate)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy
module used to perform this function.
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certificate library
module used to perform this function.
NumberOfFields (input)
The number of certificate field values specified
in the CertFields.
CertFields (input)
A pointer to an array of OID/value pairs that identifies
the field values to initialize a new certificate.
CertTemplate (output)
A pointer to a CSSM_DATA structure that will contain
the unsigned certificate template as a result of this function.
This
function allocates and initializes memory for an encoded certificate template
output in CertTemplate->Data.
The template values are specified by the input OID/value pairs contained in CertFields. The initialization
process includes encoding all certificate field values according to the certificate
type and certificate template encoding supported by the trust policy library
module. The CertTemplate output
is an unsigned certificate template in the format supported by the TP.
The
memory for CertTemplate->Data is
allocated by the service provider using the calling application’s memory
management routines. The application must deallocate the memory.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NUMBER_OF_FIELDS
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields, CSSM_TP_CertSign
Functions
for the TP SPI:
TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields, TP_CertSign
TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields:
CSSM_TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields – Get CertTemplate field values
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplate,
uint32 *NumberOfFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *CertFields)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGetAllTemplateFields
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplate,
uint32 *NumberOfFields,
CSSM_FIELD_PTR *CertFields)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy
module used to perform this function.
CLHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certificate library
module used to perform this function.
CertTemplate (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the packed, encoded certificate template.
NumberOfFields (output)
The length of the output array of fields.
CertFields (output)
A pointer to an array of CSSM_FIELD structures
which contains the OIDs and values of the fields of the input certificate
template.
This
function extracts and returns all field values from CertTemplate. The CertTemplate parameter is an unsigned certificate template
in the format supported by the TP. Fields are returned as a set of OID-value
pairs. The OID identifies the TP certificate template field and the data format
of the value extracted from that field. The Trust Policy module defines and
uses a preferred data format for returning field values from this function.
Memory for the CertFields output
is allocated by the service provider using the calling application’s
memory management routines. The application must deallocate the memory, by
calling CSSM_CL_FreeFields (CSSM
API), or CL_FreeFields (TP
SPI).
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CertCreateTemplate, CSSM_TP_CertSign
Functions
for the TP SPI:
TP_CertCreateTemplate, TP_CertSign
TP_CertGroupConstruct:
CSSM_TP_CertGroupConstruct – Construct credential (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertGroupConstruct
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
const void *ConstructParams,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupFrag,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *CertGroup)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGroupConstruct
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
const void *ConstructParams,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupFrag,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *CertGroup)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle to the trust policy module to perform
this operation.
CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle to the certificate library module that
can be used to manipulate and parse values in stored in the certgroup certificates.
If no certificate library module is specified, the TP module uses an assumed
CL module.
CSPHandle (input./optional)
A handle specifying the Cryptographic Service Provider
to be used to verify certificates as the certificate group is constructed.
If the a CSP handle is not specified, the trust policy module can assume a
default CSP. If the module cannot assume a default, or the default CSP is
not available on the local system, an error occurs.
DBList (input)
A list of handle pairs specifying a data storage
library module and a data store, identifying certificate databases containing
certificates (and possibly other security objects) that are managed by that
module. certificates (and possibly other security objects). The data stores
should be searched to complete construction of a semantically-related certificate
group.
ConstructParams (input/optional)
A pointer to data that can be used by the add-in
trust policy module in constructing the CertGroup.Thesemanticsofthisparameteraredefinedby
the trust policy and the credential model supported by that policy. The input
parameter can consist of a set of values, each guiding some aspect of the
construction process. Parameter values can:
• Limit the certificates that
are added to the constructed set.
• Identify other sources of certificates
for inclusion in the constructed set.
CertGroupFrag (input)
A list of certificates that form a possibly incomplete
set of certificates. The first certificate in the group represents the target
certificate for which a group of semantically related certificates will be
assembled. Subsequent intermediate certificates can be supplied by the caller.
They need not be in any particular order.
CertGroup (output)
A pointer to a complete certificate group based
on the original subset of certificates and the certificate data stores. The
CSSM_CERTGROUP and its sub-structure is allocated by the service provider
and must be deallocated by the application.
This
function builds a collection of certificates that together make up a meaningful
credential for a given trust domain. For example, in a hierarchical trust
domain, a certificate group is a chain of certificates from an end entity
to a top level certification authority. The constructed certificate group
format (such as ordering) is implementation specific. However, the subject
or end-entity is always the first certificate in the group.
A
partially constructed certificate group is specified in CertGroupFrag. The first certificate is interpreted to be the
subject or end-entity certificate. Subsequent certificates in the CertGroupFrag structure
may be used during the construction of a certificate group in conjunction
with certificates found in the data stores specified in DBList. The trust policy defines the certificates that
will be included in the resulting set.
The output set is a sequence of certificates ordered
by the relationship among them. The result set can be augmented by adding
semantically-related certificates obtained by searching the certificate data
stores specified in DBList.
The data stores are searched in order of appearance in DBList. If the TP supports a hierarchical model of certificates,
the function output is an uninterrupted, ordered chain of certificates based
on the first certificate as the leaf of the certificate chain. If the certificate
is multiply-signed, then the ordered chain will follow the first signing certificate.
The function should also detect cross-certificate pairs and should include
both certificates without duplicating either certificate.
Extraneous
certificates in the CertGroupFrag fragment
or contained in the DBList data
stores are ignored. The certificate group returned by this function can be
used as input to the function CSSM_TP_CertGroupVerify (CSSM API), or TP_CertGroupVerify (TP SPI).
The constructed certificate group can be consistent
locally or globally. Consistency can be limited to the local system if locally-defined
points of trust are inserted into the group.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CertGroupPrune, CSSM_TP_CertGroupVerify
Functions
for the TP SPI:
TP_CertGroupPrune, TP_CertGroupVerify
TP_CertGroupPrune:
CSSM_TP_CertGroupPrune – Remove locally issued anchor
certificates (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertGroupPrune
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *OrderedCertGroup,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *PrunedCertGroup)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGroupPrune
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *OrderedCertGroup,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *PrunedCertGroup)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle to the trust policy module to perform
this operation.
CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle to the certificate library module that
can be used to manipulate and parse the certgroup certificates and the certificates
in the specified data stores. If no certificate library module is specified,
the TP module uses an assumed CL module.
DBList (input)
A list of handle pairs specifying a data storage
library module and a data store, identifying certificate databases containing
certificates (and possibly other security objects) that are managed by that
module. The data stores are searched for anchor certificates restricted to
have local scope. These certificates are candidates for removal from the subject
certificate group.
OrderedCertGroup (input)
The initial complete set of semantically-related
certificates - for example, the result of a CSSM_TP_CertGroupConstruct (CSSM API), or TP_CertGroupConstruct (TP SPI), call - from which certificates will
be selectively removed.
PrunedCertGroup (output)
A pointer to a certificate group containing those
certificates which are verifiable credentials outside of the local system.
The CSSM_CERTGROUP and its substructure is allocated by the service provider
and must be deallocated by the application.
This
function removes any locally issued anchor certificates from a constructed
certificate group. The prune operation can remove those certificates that
have been signed by any local certificate authority, as it is possible that
these certificates will not be meaningful on other systems.
This
operation can also remove additional certificates that can be added to the
certificate group again using the CSSM_TP_CertGroupConstruct (CSSM API), or TP_CertGroupConstruct (TP SPI), operation. The pruned certificate group
should be suitable for export to external hosts/entities, which can in turn
reconstruct and verify the certificate group.
The DBList parameter specifies
a set of data stores containing certificates that should be pruned from the
group.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CertGroupConstruct, CSSM_TP_CertGroupVerify
Functions
for the TP SPI:
TP_CertGroupConstruct, TP_CertGroupVerify
TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup:
CSSM_TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup – Create a set of authorization
tuples (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroup,
CSSM_TUPLEGROUP_PTR *TupleGroup)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroup,
CSSM_TUPLEGROUP_PTR *TupleGroup)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the trust policy service
module used to perform this function.
CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the certificate library
module that can be used to scan the certificate fields for values. If no certificate
library module is specified, the TP module uses an assumed CL module.
CertGroup (input)
A group of certificates in the native certificate
format supported by the Trust Policy module. The certificates carry authorizations
for one or more certificate subjects.
TupleGroup (output)
A pointer to a structure containing references
to one or more tuples resulting from the translation process. Storage for
structure and the tuples is allocated by the service provider and must be
deallocated by the application.
This
function creates a set of authorization tuples based on a set of input certificates.
The certificates must be of the type managed by the Trust Policy module. The
trust policy module may require that the input certificates be successfully
verified before being translated to tuples. It is assumed that the certificates
carry authorizations. The trust policy service provider interprets the certificate
authorization fields and generates one or more tuples corresponding to those
authorizations. The certificates of the type managed by the Trust Policy module.
The resulting tuples can be input to an authorization evaluation function,
such as CSSM_AC_AuthCompute (CSSM
API), or AC_AuthCompute (AC
SPI), which determines whether a particular action is authorized under a basic
set of authorization assumptions.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup, CSSM_AC_AuthCompute
Functions
for the TP SPI:
TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup, AC_AuthCompute
TP_CertGroupVerify:
CSSM_TP_CertGroupVerify – Determine if a certificate
is trusted (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertGroupVerify
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeVerified,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *VerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR VerifyContextResult)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertGroupVerify
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeVerified,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *VerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR VerifyContextResult)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy
module used to perform this function.
CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module that can be used to manipulate the subject certificate and
anchor certificates. If no certificate library module is specified, the TP
module uses an assumed CL module, if required.
CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module that can be used to perform the cryptographic operations
required to carry out the verification. If no CSP handle is specified, the
TP module allocates a suitable CSP.
CertGroupToBeVerified (input)
A group of one or more certificates to be verified.
The first certificate in the group is the primary target certificate for verification.
Use of the subsequent certificates during the verification process is specific
to the trust domain.
VerifyContext (input/optional)
A structure containing credentials, policy information,
and contextual information to be used in the verification process. All of
the input values in the context are optional except Action. The service provider can define default values
or can attempt to operate without input for all the other fields of this input
structure. The operation can fail if a necessary input value is omitted and
the service module can not define an appropriate default value.
VerifyContextResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information
generated during the verification process. The information can include:
Evidence |
(output/optional) |
NumberOfEvidences |
(output/optional) |
This
function determines whether the certificate is trusted. The actions performed
by this function differ based on the trust policy domain. The factors include
practices, procedures and policies defined by the certificate issuer.
Typically
certificate verification involves the verification of multiple certificates.
The first certificate in the group is the target of the verification process.
The other certificates in the group are used in the verification process to
connect the target certificate with one or more anchors of trust. The supporting
certificates can be contained in the provided certificate group or can be
stored in the data stores specified in the VerifyContext DBList. This allows the trust policy module to
construct a certificate group and perform verification in one operation. The
data stores specified by DBList can also contain certificate revocation lists
used in the verification process. It is also possible to provide a data store
of anchor certificates. Typically the points of Trust are few in number and
are embedded in the caller or in the TPM during software manufacturing or
at runtime
The caller can select to be notified incrementally
as each certificate is verified. The CallbackWithVerifiedCert parameter (in the VerifyContext) can specify a caller function to be invoked at
the end of each certificate verification, returning the verified certificate
for use by the caller.
Anchor certificates are a list of implicitly trusted
certificates. These include root certificates, cross certified certificates,
and locally defined sources of trust. These certificates form the basis to
determine trust in the subject certificate.
A policy identifier can specify an additional set
of conditions that must be satisfied by the subject certificate in order to
meet the trust criteria. The name space for policy identifiers is defined
by the application domains to which the policy applies. This is outside of
CSSM. A list of policy identifiers can be specified and the stopping condition
for evaluating that set of conditions.
The evaluation and verification process can produce
a list of evidence. The evidence can be selected values from the certificates
examined in the verification process, entire certificates from the process
or other pertinent information that forms an audit trail of the verification
process. This evidence is returned to the caller after all steps in the verification
process have been completed.
If verification succeeds, the trust policy module
may carry out the action on the specified data or may return approval for
the action requiring the caller to perform the action. The caller must consult
TP module documentation outside of this specification to determine all module-specific
side effects of this operation.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION_DATA
CSSMERR_TP_VERIFY_ACTION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
TP_CertReclaimAbort:
CSSM_TP_CertReclaimAbort – Terminate the process of reclaiming
certificates (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertReclaimAbort
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_LONG_HANDLE KeyCacheHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertReclaimAbort
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_LONG_HANDLE KeyCacheHandle)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the service provider
module used to perform this function.
KeyCacheHandle (input)
An opaque handle that identifies the cache of protected
private keys reclaimed from a certificate authority for potentially recovery
on the local system.
This
function terminates the iterative process of reclaiming certificates and recovering
their associated private keys from a protected key cache. This function must
be called even if all private keys are recovered from the cache. This function
destroys all intermediate state and secret information used during the reclamation
process. At completion of this function, the cache handle is invalid.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_KEYCACHE_HANDLE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CertReclaimKey
Functions
for the TP SPI:
TP_CertReclaimKey
TP_CertReclaimKey:
CSSM_TP_CertReclaimKey – Get private key associated
with a certificate (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertReclaimKey
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroup,
uint32 CertIndex,
CSSM_LONG_HANDLE KeyCacheHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertReclaimKey
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroup,
uint32 CertIndex,
CSSM_LONG_HANDLE KeyCacheHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the service provider
module used to perform this operation.
CertGroup (input)
A pointer to a structure containing a reference
to a group of certificates and the number of certificates contained in that
group. The certificate group contains all certificates that are candidates
for reclamation.
CertIndex (input)
An index value that identifies the certificate
whose associated private key is to be recovered and stored in the local CSP.
This index value I references the I-th certificate in CertGroup.
KeyCacheHandle (input)
A reference handle that uniquely identifies the
cache of protected private keys associated with the reclaimed certificates
contained in CertGroup.
The structure of the cache is opaque to the caller.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the CSP module where
the private key is to be stored. Optionally, the CA service provider can use
this CSP to perform additional cryptographic operations or may use another
default CSP for that purpose.
CredAndAclEntry (input/optional)
A structure containing one or more credentials
authorized for creating a key and the prototype ACL entry that will control
future use of the newly created key. The credentials and ACL entry prototype
can be presented as immediate values or callback functions can be provided
for use by the CSP to acquire the credentials and/or the ACL entry interactively.
If the CSP provides public access for creating a key, then the credentials
can be NULL. If the CSP defines a default initial ACL entry for the new key,
then the ACL entry prototype can be an empty list.
This
function recovers the private key associated with a certificate and securely
stores that key in the specified Cryptographic Service Provider. The key and
its associated certificate are among a set of certificates and private keys
reclaimed from a certificate authority.
The particular private key to be recovered to the
local system is identified by its associated certificate. The certificate
is identified by its CertIndex position
within the CertGroup.
The
reclamation process associates the private key with the public key contained
in the certificate, and securely stores the private key in the specified Cryptographic
Service Provider. The CSP can require that the caller provide access credentials
authorizing inserting a new key into the CSP through an UnwrapKey operation. The caller should also provide an initial
Access Control List (ACL) entry for the newly inserted key. The ACL entry
is used to control future use of the recovered private key. These inputs are
provided in CredAndAclEntry.
When
all required private keys have been reclaimed, the key cache can be discarded
using the function CSSM_TP_CertReclaimAbort (CSSM API), or TP_CertReclaimAbort (TP SPI). The caller must free the CertGroup when it is no
longer needed.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_INDEX
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_KEYCACHE_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult, CSSM_TP_Cert_ReclaimAbort
Functions
for the TP SPI:
TP_RetrieveCredResult, TP_Cert_ReclaimAbort
TP_CertRemoveFromCrlTemplate TP_CertRemoveFromCrlTemplate:
CSSM_TP_CertRemoveFromCrlTemplate – Determine if the revoking certificate
group can remove the subject certificate group from the CRL template (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertRemoveFromCrlTemplate
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrlTemplate,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeRemoved,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *RevokerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *RevokerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertRemoveFromCrlTemplate
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrlTemplate,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeRemoved,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *RevokerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *RevokerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy
module used to perform this function.
CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function.
OldCrlTemplate (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
an existing certificate revocation list. If this input is NULL, a new list
is created or the operation fails.
CertGroupToBeRemoved (input)
A group of one or more certificates to be removed
from the the CRL template.
RevokerCertGroup (input)
A group of one or more certificates that partially
or fully represent the revoking entity for this operation. The first certificate
in the group is the target certificate representing the revoker. The use of
subsequent certificates is specific to the trust domain.
RevokerVerifyContext (input)
A structure containing policy elements useful in
verifying certificates and their use with respect to a security policy. Optional
elements in the verify context left unspecified will cause the internal default
values to be used. Default values are specified in the TP module vendor release
documents. This context is used to verify the revoker certificate group.
RevokerVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information
generated during the verification process. The information can include:
Evidence |
(output/optional) |
NumberOfEvidences |
(output/optional) |
NewCrlTemplate (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the updated certificate revocation list. If the pointer is NULL, an error
has occurred.
The
TP module determines whether the revoking certificate group can remove the
subject certificate group from the CRL template. The revoker certificate group
is first authenticated and its applicability to perform this operation is
determined. Once the trust is established, the TP removes the certificates
from the CRL template.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL
CSSMERR_TP_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_TP_CRL_ALREADY_SIGNED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION_DATA
CSSMERR_TP_VERIFY_ACTION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_CERTIFICATE_CANT_OPERATE
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert
Functions
for the TP SPI:
CL_CrlAddCert
TP_CertRevoke:
CSSM_TP_CertRevoke – Determine if the revoking certificate
group can revoke the subject certificate group (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertRevoke
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrlTemplate,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeRevoked,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *RevokerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *RevokerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult,
CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON Reason,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertRevoke
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *OldCrlTemplate,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *CertGroupToBeRevoked,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *RevokerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *RevokerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult,
CSSM_TP_CERTCHANGE_REASON Reason,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy
module used to perform this function.
CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function.
OldCrlTemplate (input/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
an existing certificate revocation list. If this input is NULL, a new list
is created or the operation fails.
CertGroupToBeRevoked (input)
A group of one or more certificates that partially
or fully represent the certificate to be revoked by this operation. The first
certificate in the group is the target certificate. The use of subsequent
certificates is specific to the trust domain. For example, in a hierarchical
trust model subsequent members are intermediate certificates of a certificate
chain.
RevokerCertGroup (input)
A group of one or more certificates that partially
or fully represent the revoking entity for this operation. The first certificate
in the group is the target certificate representing the revoker. The use of
subsequent certificates is specific to the trust domain.
RevokerVerifyContext (input)
A structure containing policy elements useful in
verifying certificates and their use with respect to a security policy. Optional
elements in the verify context left unspecified will cause the internal default
values to be used. Default values are specified in the TP module vendor release
documents. This context is used to verify the revoker certificate group.
RevokerVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information
generated during the verification process. The information can include:
Evidence |
(output/optional) |
NumberOfEvidences |
(output/optional) |
Reason (input/optional)
The reason for revoking the subject certificate.
NewCrlTemplate (output/optional)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the updated certificate revocation list. If the pointer is NULL, an error
has occurred.
The
TP module determines whether the revoking certificate group can revoke the
subject certificate group. The revoker certificate group is first authenticated
and its applicability to perform this operation is determined. Once the trust
is established, the TP revokes the subject certificate by adding it to the
certificate revocation list.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL
CSSMERR_TP_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_TP_CRL_ALREADY_SIGNED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION_DATA
CSSMERR_TP_VERIFY_ACTION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_CERTIFICATE_CANT_OPERATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_REASON
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlAddCert
Functions
for the TP SPI:
CL_CrlAddCert
TP_CertSign: CSSM_TP_CertSign – Determine if signer certificate is trusted (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CertSign
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplateToBeSigned,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *SignerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR SignerVerifyResult,
CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedCert)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CertSign
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *CertTemplateToBeSigned,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *SignerVerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR SignerVerifyResult,
CSSM_DATA_PTR SignedCert)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy
module used to perform this function.
CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
CCHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the cryptographic context
for signing the certificate. This context also identifies the Cryptographic
Service Provider to be used to perform the signing operation. If this handle
is not provided by the caller, the trust policy module can assume a default
signing algorithm and a default CSP. If the trust policy module does not assume
defaults or the default CSP is not available on the local system, an error
occurs.
CertTemplateToBeSigned (input)
A pointer to a structure containing a certificte
template to be signed. The CRL type and encoded are included in this structure.
SignerCertGroup (input)
A group of one or more certificates that partially
or fully represent the signer for this operation. The first certificate in
the group is the target certificate representing the signer. Use of subsequent
certificates is specific to the trust domain. For example, in a hierarchical
trust model subsequent members are intermediate certificates of a certificate
chain.
SignerVerifyContext (input/optional)
A structure containing credentials, policy information,
and contextual information to be used in the verification process. All of
the input values in the context are optional. The service provider can define
default values or can attempt to operate without input for all the other fields
of this input structure. The operation can fail if a necessary input value
is omitted and the service module can not define an appropriate default value.
SignerVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information
generated during the verification process. The information can include:
Evidence |
(output/optional) |
NumberOfEvidences |
(output/optional) |
SignedCert (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the signed certificate. The SignedCert->Data is allocated by the service provider and must
be deallocated by the application.
The
TP module decides whether the signer certificate is trusted to sign the CertTemplateToBeSigned.
The signer certificate group is first authenticated and its applicability
to perform this operation is determined. Once the trust is established, this
operation signs the entire certificate. The caller must provide a credential
that permits the caller to use the private key for this signing operation.
The credential can be provided in the cryptographic context CCHandle. If CCHandle is NULL, the credentials in the SignerVerifyContext specify the credential value.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_UNKNOWN_FORMAT
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION_DATA
CSSMERR_TP_VERIFY_ACTION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_CERTIFICATE_CANT_OPERATE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CertCreateTemplate, CSSM_TP_CrlSign
Functions
for the TP SPI:
TP_CertCreateTemplate, TP_CrlSign
TP_ConfirmCredResult:
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult – Confirm credentials (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier,
const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthCredentials,
const CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE *Responses,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_ConfirmCredResult
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier,
const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthCredentials,
const CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE *Responses,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certification authority
module used to perform this function.
ReferenceIdentifier (input)
A reference identifier that uniquely identifies
execution of the call sequence CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest and CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult (or the equivalent TP SPI call pair) to submit
a set of requests and to retrieve the results of those requests.
CallerAuthCredentials (input/optional)
This structure contains a set of caller authentication
credentials. The authentication information can be a passphrase, a PIN, a
completed registration form, a certificate, or a template of user-specific
data. The required set of credentials is defined by the service provider module
and recorded in a record in the MDS Primary relation. Multiple credentials
can be required. If the local service provider module does not require credentials
from a caller, then the Credentials field
of this verification context structure can be NULL. The structure optionally
contains additional credentials that can be used to support the authentication
process. Authentication credentials required by the authority should be included
in the RequestInput.
The local TP module can forward information from the CallerAuthCredentials to the authority, as appropriate, but is not required
to do so.
Responses (input)
An ordered vector of acknowledges indicating the
caller’s acceptance or rejection of results. The vector contains one
acknowledgement per result returned by CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult (CSSM API), or TP_RetrieveCredResult (TP SPI).
PreferredAuthority (input/optional)
The identifier which uniquely describes the Authority
to receive the acknowledgements. The structure can include:
• An identity certificate for the authority
• The location of the authority
This
function submits a vector of acknowledgements to a Certificate Authority for
a set of requests and corresponding results identified by ReferenceIdentifier. The caller must execute the call sequence CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest and CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult(or
the equivalent TP SPI calls) to submit a set of requests and to retrieve the
results of those requests. Some Certificate Authority services accessed through
the request and retrieve functions require confirmation. The function CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult (CSSM
API), or TP_RetrieveCredResult (TP
SPI), returns a value indicating whether the caller must invoke CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult,
(CSSM API), or TP_ConfirmCredResult (TP
SPI), to successfully complete the service.
The Responses vector accepts or rejects each result independently.
If the caller rejects a returned result, the action taken by the authority
depends on the requested type of service.
The ReferenceIdentifier also identifies the authority process state associated
with the function pair CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest and CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult (or the equivalent TP SPI calls). The PreferredAuthority information
can be used to further identify the authority to receive the acknowledgement.
After successful execution of this function, the value of the ReferenceIdentifier is undefined
and should not be used in subsequent operations in the current module attach
session.
This function fails if ReferenceIdentifier is invalid or the Authority process can not be
located.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_IDENTIFIER_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_IDENTIFIER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_RESPONSE_VECTOR
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_NO_DEFAULT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_UNSUPPORTED_ADDR_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NETWORK_ADDR
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest, CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult, CSSM_TP_ReceiveConfirmation
Functions
for the TP SPI:
TP_SubmitCredRequest, TP_RetrieveCredResult, TP_ReceiveConfirmation
TP_CrlCreateTemplate:
CSSM_TP_CrlCreateTemplate – Create an unsigned memory-resident
CRL template (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CrlCreateTemplate
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CrlFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CrlCreateTemplate
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
uint32 NumberOfFields,
const CSSM_FIELD *CrlFields,
CSSM_DATA_PTR NewCrlTemplate)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy
module used to perform this function.
CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module used to perform this function.
NumberOfFields (input)
The number of OID/value pairs specified in the CrlFields input parameter.
CrlFields (input)
Any array of field OID/value pairs containing the
values to initialize the CRL attribute fields
NewCrlTemplate (output)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the new CRL. The NewCrl->Data is
allocated by the service provider and must be deallocated by the application.
This
function creates an unsigned, memory-resident CRL template. Fields in the
CRL are initialized based on the descriptive data specified by the OID/value
input pairs in CrlFields and
the local domain policy of the TP. The specified OID/value pairs can initialize
all or a subset of the general attribute fields in the new CRL, though the
module developer may specify a set of fields that must be or cannot be set
using this operation. The NewCrlTemplate output is an unsigned CRL template in the format
supported by the TP.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_FIELD_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_UNKNOWN_TAG
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NUMBER_OF_FIELDS
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_CrlSignWithKey, CSSM_TP_CrlSignWithCert
Functions
for the TP SPI:
TP_CrlSignWithKey, TP_CrlSignWithCert
TP_CrlVerify:
CSSM_TP_CrlVerify – Verify integrity of the certificate
revocation list (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_CrlVerify
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeVerified,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *VerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_CrlVerify
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_ENCODED_CRL *CrlToBeVerified,
const CSSM_CERTGROUP *SignerCertGroup,
const CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT *VerifyContext,
CSSM_TP_VERIFY_CONTEXT_RESULT_PTR RevokerVerifyResult)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy
module used to perform this function.
CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module that can be used to manipulate the certificates to be verified.
If no certificate library module is specified, the TP module uses an assumed
CL module, if required.
CSPHandle (input/optional)
The handle referencing a Cryptographic Service
Provider to be used to verify signatures on the signer’s certificate
and on the CRL. The TP module is responsible for creating the cryptographic
context structure required to perform the verification operation. If no CSP
is specified, the TP module uses an assumed CSP to perform the operations.
CrlToBeVerified (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
a signed certificate revocation list to be verified. The CRL type and encoding
are included in this structure.
SignerCertGroup (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_CERTGROUP structure containing
one or more related certificates that paretially or fully represent the signer
of the certificate revocation list. The first certificate in the group is
the target certificate representing the CRL signer. Use of subsequent certificates
is specific to the trust domain. For example, in a hierarchical trust model
subsequent members are intermediate certificates of a certificate chain -
the caller can specify additional points of trust represented by anchor certificates
in the VerifyContext.
The trust policy module can use these additional points of trust in the verification
process.
VerifyContext (input/optional)
A structure containing credentials, policy information,
and contextual information to be used in the verification process. All of
the input values in the context are optional. The service provider can define
default values or can attempt to operate without input for all the other fields
of this input structure. The operation can fail if a necessary input value
is omitted and the service module can not define an appropriate default value
RevokerVerifyResult (output/optional)
A pointer to a structure containing information
generation during the verification process. The information can include:
Evidence |
(output/optional) |
NumberOfEvidences |
(output/optional) |
This
function verifies the integrity of the certificate revocation list and determines
whether it is trusted. The conditions for trust are part of the trust policy
module. It can include conditions such as validity of the signer’s certificate,
verification of the signature on the CRL, the identity of the signer, the
identity of the sender of the CRL, date the CRL was issued, the effective
dates on the CRL, and so on.
The caller can specify additional points of trust
represented by anchor certificates in the VerifyContext. The trust policy module can use these additional
points of trust in the verification process.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CSP_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_ENCODING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERTIFICATE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ACTION_DATA
CSSMERR_TP_VERIFY_ACTION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRLGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CRL_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
CSSMERR_TP_CERTIFICATE_CANT_OPERATE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_CL_CrlVerify
Functions
for the TP SPI:
CL_CrlVerify
TP_FormRequest:
CSSM_TP_FormRequest – Get form from authority (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_FormRequest
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority,
CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE FormType,
CSSM_DATA_PTR BlankForm)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_FormRequest
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority,
CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE FormType,
CSSM_DATA_PTR BlankForm)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certification authority
module used to perform this function.
PreferredAuthority (input/optional)
A CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID structure containing either
a certificate that identifies the Authority process, or a network address
directly or indirectly identifying the location of the authority. If the input
is NULL, the module can assume a default authority location. If a default
authority can not be assumed, the request can not be initiated and the operation
fails.
FormType (input)
Indicates the type of form being requested.
BlankForm (output)
A CSSM_DATA structure containing the requested
form. The caller must have knowledge of the structure of the form based on FormType.
This
function returns a blank form of type FormType from an Authority. If the PreferredAuthority list is NULL, the CA module can use a default
authority name and location based on FormType. The CA module must incorporate knowledge of the
interface protocol for communicating with the authority.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_NO_DEFAULT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_UNSUPPORTED_ADDR_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NETWORK_ADDR
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_FORM_TYPE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_FormSubmit
Functions
for the TP SPI:
TP_FormSubmit
TP_FormSubmit:
CSSM_TP_FormSubmit – Submit form to ClearanceAuthority
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_FormSubmit
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE FormType,
const CSSM_DATA *Form,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *ClearanceAuthority,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *RepresentedAuthority,
CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS_PTR Credentials)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_FormSubmit
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_TP_FORM_TYPE FormType,
const CSSM_DATA *Form,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *ClearanceAuthority,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *RepresentedAuthority,
CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS_PTR Credentials)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
A handle for the service provider module that will
perform the operation.
FormType (input)
Indicates the type of form being submitted.
Form (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the completed form to be submitted to the ClearanceAuthority.
ClearanceAuthority (input/optional)
A CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID structure containing either
a certificate that identifies the clearance authority process, or a network
address directly or indirectly identifying the location of the authority.
If the input is NULL, the service provider module can assume a default authority
based on the FormType and
contents of Form.
If a default authority can not be assumed, the request can not be initiated
and the operation fails.
RepresentedAuthority (input/optional)
A
CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID structure containing either a certificate that identifies
the authority represented by the ClearanceAuthority, or a network address directly or indirectly identifying
the location of the authority. If the input is NULL, the service provider
module can assume a default authority based on the FormType and contents of Form. If a default authority can not be assumed, the
request can not be initiated and the operation fails.
Credentials (output/optional)
A
pointer to a structure containing one or more credentials issued in response
to the contents of the Form.
If the output is NULL, either no credentials were returned or an error occurred.
The
completed Form is submitted to a ClearanceAuthority, who is acting on behalf of a RepresentedAuthority. Typically the submitted form is requesting an
authorization credential required as input to future service requests to the RepresentedAuthority.
If
the form is honored by the ClearanceAuthority, then a set of one or more Credentials is returned to the requester. These credential
can be used as the input credential in future service requests submitted to
the RepresentedAuthority.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_FORM_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_NO_DEFAULT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_UNSUPPORTED_ADDR_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NETWORK_ADDR
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_REJECTED_FORM
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_FormRequest
Functions
for the TP SPI:
TP_FormRequest
TP_PassThrough:
CSSM_TP_PassThrough – Extend trust policy functionality API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_PassThrough
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
uint32 PassThroughId,
const void *InputParams,
void **OutputParams)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_PassThrough
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DL_DB_LIST *DBList,
uint32 PassThroughId,
const void *InputParams,
void **OutputParams)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in trust policy
module used to perform this function.
CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the add-in certificate
library module that can be used to manipulate the subject certificate
and anchor certificates. If no certificate library module is specified, the
TP module uses an assumed CL module, if required.
CCHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the context of the cryptographic
operation. If the module-specific operation does not perform any cryptographic
operations, a cryptographic context is not required
DBList (input/optional)
A list of handle pairs specifying a data storage
library module and a data store, identifying certificate databases containing
certificates (and possibly other security objects) that may be used by the
pass-through function. If no DL and DB handle pairs are specified, the TP
module can use an assumed DL module and an assumed data store for this operation.
PassThroughId (input)
An identifier assigned by a TP module to indicate
the exported function to be performed.
InputParams (input/optional)
A pointer to a module, implementation-specific
structure containing parameters to be interpreted in a function-specific manner
by the requested TP module.
OutputParams (output/optional)
A
pointer to a module, implementation-specific structure containing the output
data. The service provider allocates the memory for substructures. The application
must free the memory for the substructures.
This
function allows applications to call trust policy module-specific operations
that have been exported. Such operations may include queries or services specific
to the domain represented by the TP module.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CONTEXT_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_PASSTHROUGH_ID
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
TP_ReceiveConfirmation:
CSSM_TP_ReceiveConfirmation – Poll for confirmation (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_ReceiveConfirmation
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier,
CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE_PTR *Responses,
sint32 *ElapsedTime)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_ReceiveConfirmation
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *ReferenceIdentifier,
CSSM_TP_CONFIRM_RESPONSE_PTR *Responses,
sint32 *ElapsedTime)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certification authority
module used to perform this function.
ReferenceIdentifier (input)
A reference identifier that uniquely identifies
a set of service requests and the results created in response to those requests.
Responses (output)
An ordered vector of acknowledges indicating the
caller’s acceptance or rejection of results. The vector contains one
acknowledgement per result created by the certificate authority.
ElapsedTime (output)
If the confirmation has not been received, this
output value is the number of seconds elapsed since the certificate authority
created the results or CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_UNKNOWN. If the confirmation has
been received, this output value is CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_COMPLETE.
A
certificate authority uses this function to poll for confirmation from a requester
who has been served by the authority. A requester sends a confirmation to
the authority by successfully invoking the function CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult (CSSM API), or TP_ConfirmCredResult (TP SPI).
The ReferenceIdentifier uniquely identifies the service request and corresponding
results for which confirmation is expected. This reference identifier need
not be identical to the reference identifier used by the requester, but a
one-to-one mapping between the two name spaces must be well-defined.
Responses is an ordered vector of acknowledgements indicating,
for each returned result, whether the result was accepted or rejected by the
original requester for whom the service was performed.
If
a result is rejected by the receiver, then the authority process must undo
the service if a reverse operation is possible and available.
If
a fatal error occurs, this function returns an error code, indicating that
the function call can never be completed. If confirmation has not been received,
the function return value is CSSM_OK and the ElapsedTime is returned to the caller of this function. The
time represents elapsed seconds since the service results were produced by
the authority process. Note that there can be a difference between the time
the authority process produces the results and the time the results are actually
received by the requester. Elapsed time is relative and should increase with
consecutive calls using the same ReferenceIdentifier. If the TP module has no knowledge of the elapsed
time, the value CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_UNKNOWN must be returned. If the service
requester has confirmed receipt of the service results, this function returns
CSSM_OK and ElapsedTime is
CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_COMPLETE.
This function can be invoked repeatedly until the
confirmation is received or until the caller decides the acknowledgement may
be lost and chooses to undo the results of the original service request.
This
function fails if the ReferenceIdentifier is invalid or does not match any requested service
for which confirmation is expected.
A CSSM return value combined with elapsed time
to indicate one of three results:
Complete Function |
Function Return |
RetrieveOutput |
EstimatedTime |
Result |
Value |
|
|
Confirmation
Received |
CSSM_OK |
CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_COMPLETE |
|
Confirmation
not received, but expected in the future |
CSSM_OK |
CSSM_ELAPSED_TIME_UNKNOWN
or <elapsed seconds> |
|
Fatal
Error, Confirmation is not expected |
(!CSSM_OK) |
NA |
|
For a return value of (!CSSM_OK) the return value
is an error code.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_IDENTIFIER_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_IDENTIFIER
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult
Functions
for the TP SPI:
CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult
TP_SubmitCredRequest:
CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest – Submit credential request (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_SubmitCredRequest
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority,
CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_TYPE RequestType,
const CSSM_TP_REQUEST_SET *RequestInput,
const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthContext,
sint32 *EstimatedTime,
CSSM_DATA_PTR ReferenceIdentifier)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_SubmitCredRequest
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
const CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_ID *PreferredAuthority,
CSSM_TP_AUTHORITY_REQUEST_TYPE RequestType,
const CSSM_TP_REQUEST_SET *RequestInput,
const CSSM_TP_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT *CallerAuthContext,
sint32 *EstimatedTime,
CSSM_DATA_PTR ReferenceIdentifier)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the certification authority
module used to perform this function.
PreferredAuthority (input/optional)
The identifier which uniquely describes the Certificate
Service Authority to submit the request to.
RequestType (input)
The identifier of the type of request to submit.
RequestInput (input)
A pointer to the input parameters to be submitted
to the authority who will perform the requested service.
CallerAuthContext (input/optional)
This structure contains a set of caller authentication
credentials. The authentication information can be a passphrase, a PIN, a
completed registration form, a certificate, or a template of user-specific
data. The required set of credentials is defined by the service provider module
and recorded in the MDS Primary relation. Multiple credentials can be required.
If the local service provider module does not require credentials from a caller,
then the CallerCredentials field
of this verification context structure can be NULL. The structure optionally
contains additional credentials that can be used to support the authentication
process. Authentication credentials required by the authority should be included
in the RequestInput.
The local service provider module can forward this credential information
to the authority, as appropriate, but is not required to do so.
EstimatedTime (output)
The number of estimated seconds before the service
results are ready to be retrieved. A (default) value of zero indicates that
the results can be retrieved immediately via the corresponding CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult (CSSM
API), or TP_RetrieveCredResult (TP
SPI), function call. When the local service provider module or the authority
cannot estimate the time required to perform the requested service, the output
value for estimated time is CSSM_ESTIMATED_TIME_UNKNOWN.
ReferenceIdentifier (output)
A reference identifier, which uniquely identifies
this specific request. The handle persists across application executions and
becomes undefined when all local processing of the request has completed.
Local processing is completed in one of two ways:
• For certificate services that do not
require explicit confirmation by the requester, the reference identifier is
invalidated when the corresponding CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult (CSSM API), or TP_RetrieveCredResult (TP SPI), function completes (by returning valid
results or by failure, which blocks returned results)
• For certificate services that
require explicit confirmation by the requester, the reference identifier is
invalidated by successfully invoking the function CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResu (CSSM API), or CSSM_TP_ConfirmCredResult (TP SPI).
If
the caller is successfully authenticated, then this function submits a request
to the Authority identified by PreferredAuthority. The authority service can be local or remote.
If the Authority is not specified, then the TP module can assume a default
authority based on the RequestType and
the CallerAuthContext. RequestType indicates the
type of Authority request and RequestInput specifies the input parameters needed by the authority
to perform the request.
The request is submitted to the authority only
if the TP module can successfully authenticate the caller. The CallerAuthContext presents
the caller’s credentials and a list of one or more policies under which
the caller should be authenticated. Caller credentials can be presented in
several forms:
• Memory-resident credential values,
directly referenced by the structure
• Data bases containing credentials
• Callback functions that can be invoked
to obtain credentials from an active entity
The local service provider must select and forward
the credentials required by the Authority. The caller must provide all necessary
credentials through the CallerAuthContext parameter.
If the caller can not be authenticated by the local
service provider, the function fails and the request is not submitted to the
selected authority.
This function returns a ReferenceIdentifier and an EstimatedTime (specified in seconds). ReferenceIdentifier is an ID for the submitted request. EstimatedTime defines the
expected time to process the request. This time may be substantial when the
request requires offline authentication procedures by the Authority process.
In contrast, the estimated time can be zero, meaning the result can be obtained
immediately using CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult (CSSM API), or TP_RetrieveCredResult (TP SPI). After the specified time has elapsed,
the caller must use the function CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult (CSSMAPI), or TP_RetrieveCredResult (TP SPI), with the reference identifier, to obtain
the result of the request.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_NO_DEFAULT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_UNSUPPORTED_ADDR_TYPE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NETWORK_ADDR
CSSMERR_TP_UNSUPPORTED_SERVICE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_REQUEST_INPUTS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLERAUTH_CONTEXT_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_POLICY_IDENTIFIERS
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TIMESTRING
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_STOP_ON_POLICY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CALLBACK
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_ANCHOR_CERT
CSSMERR_TP_CERTGROUP_INCOMPLETE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_DB_LIST
CSSMERR_TP_AUTHENTICATION_FAILED
CSSMERR_TP_INSUFFICIENT_CREDENTIALS
CSSMERR_TP_NOT_TRUSTED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_REVOKED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_SUSPENDED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_EXPIRED
CSSMERR_TP_CERT_NOT_VALID_YET
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CERT_AUTHORITY
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_NAME
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_TP_RetrieveCredResult
Functions
for the TP SPI:
TP_RetrieveCredResult
TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup:
CSSM_TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup – Create a set of certificate
templates (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_TUPLEGROUP *TupleGroup,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *CertTemplates)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMTPI TP_TupleGroupToCertGroup
(CSSM_TP_HANDLE TPHandle,
CSSM_CL_HANDLE CLHandle,
const CSSM_TUPLEGROUP *TupleGroup,
CSSM_CERTGROUP_PTR *CertTemplates)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
This
function creates a set of certificate templates based on a set of input tuples.
The tuples describe a set of authorizations for one or more subjects. The
trust policy service provider maps these authorizations to appropriate template
values for one or more certificates of the type managed by the Trust Policy
module. The resulting certificate templates can be input to a certificate
creation function, such as CSSM_CL_CertSign, (CSSM API), or CL_CertSign, (TP SPI). The signed certificates created by
these functions should carry the authorizations described in the input tuples.
TPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the trust policy service
module used to perform this function.
CLHandle (input/optional)
The handle that describes the certificate library
module that can be used to assist in the creation of field values. If no certificate
library module is specified, the TP module uses an assumed CL module, if required.
TupleGroup (input)
A pointer to a group of CSSM_TUPLE describing authorizations
for one or more subjects.
CertTemplates (output)
A pointer to a structure containing references
to one or more certificate templates resulting from the translation process.
Storage for the structure and certificate templates is allocated by the service
provider and must be deallocated by the application.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_CL_HANDLE
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TUPLEGROUP_POINTER
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TUPLEGROUP
CSSMERR_TP_INVALID_TUPLE
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
For the CSSM API: CSSM_TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup, CSSM_AC_AuthCompute
For
the TP SPI: TP_CertGroupToTupleGroup, AC_AuthCompute
Terminate – Clean up module-manager-specific
activities (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI Terminate
(void)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
None.
This function performs any module-manager-specific
cleanup activities in preparation for unloading of the elective module manager.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSSM_EMM_AUTHENTICATE_FAILED.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions: Initialize
UnwrapKey: CSSM_UnwrapKey,
CSP_UnwrapKey – Unwrap the wrapped key (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_UnwrapKey
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_KEY *PublicKey,
const CSSM_WRAP_KEY *WrappedKey,
uint32 KeyUsage,
uint32 KeyAttr,
const CSSM_DATA *KeyLabel,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry,
CSSM_KEY_PTR UnwrappedKey,
CSSM_DATA_PTR DescriptiveData)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_UnwrapKey
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
const CSSM_KEY *PublicKey,
const CSSM_WRAP_KEY *WrappedKey,
uint32 KeyUsage,
uint32 KeyAttr,
const CSSM_DATA *KeyLabel,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry,
CSSM_KEY_PTR UnwrappedKey,
CSSM_DATA_PTR DescriptiveData,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation.
PublicKey (input/optional)
The public key corresponding to the private key
being unwrapped. If a symmetric key is being unwrapped, then this parameter
must be NULL.
WrappedKey (input)
A pointer to the wrapped key. The wrapped key may
be a symmetric key or the private key of a public/private key pair. The unwrapping
method is specified as meta data within the wrapped key and is not specified
outside of the wrapped key.
KeyUsage (input)
A bit mask indicating all permitted uses for the
unwrapped key. If no value is specified, the CSP defines the usage mask for
the unwrapped key.
KeyAttr (input)
A bit mask defining other attribute values to be
associated with the unwrapped key.
KeyLabel (input/optional)
Pointer to a byte string that will be used as the
label for the unwrapped key.
CredAndAclEntry (input/optional)
A structure containing one or more credentials
authorized for creating a key and the prototype ACL entry that will control
future use of the newly created key. The credentials and ACL entry prototype
can be presented as immediate values or callback functions can be provided
for use by the CSP to acquire the credentials and/or the ACL entry interactively.
If the CSP provides public access for creating a key, then the credentials
can be NULL. If the CSP defines a default initial ACL entry for the new key,
then the ACL entry prototype can be an empty list.
UnwrappedKey (output)
A pointer to a CSSM_KEY structure that returns
the unwrapped key.
DescriptiveData (output)
A pointer to a CSSM_DATA structure that returns
any additional descriptive data that was associated with the key during the
wrapping operation. It is assumed that the caller incorporated knowledge of
the structure of this data. If no additional data is associated with the imported
key, this output value is NULL.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
Privilege (input)
The export privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation. This parameter is forwarded to the CSP after CSSM verifies the
caller and service provider privilege set includes the specified PRIVILEGE.
This function unwraps the wrapped key using the
context. The wrapped key can be a symmetric key or a private key. If the unwrapping
algorithm is a symmetric algorithm, then a symmetric context must be provided.
If the unwrapping algorithm is an asymmetric algorithm, then an asymmetric
context must be provided. If the key is a private key, then an asymmetric
context must be provide describing the unwrapping algorithm. The CSP can require
the caller to provide credentials authorizing the caller to store the unwrapped
key within the CSP. The CSP can also require that the caller provide an initial
ACL entry to control future access to the newly stored key. These credentials
and the initial ACL entry value are provided in CredAndAclEntry parameter. If the unwrapping algorithm is CSSM_ALGID_NONE
and the wrapped key is actually a raw key (as indicated by its key attributes),
then the key is imported into the CSP. Support for a CSSM_ALGID_NONE unwrapping
algorithm is at the option of the CSP. The unwrapped key is restored to its
original pre-wrap state based on the key attributes recorded by the wrapped
key during the wrap operation. These attributes must not be modified by the
caller.
Authorization policy can restrict the set of callers
who can create a new resource. In this case, the caller must present a set
of access credentials for authorization. Upon successfully authenticating
the credentials, the template that verified the presented samples identifies
the ACL entry that will be used in the authorization computation. If the caller
is authorized, the new resource is created.
The caller must provide an initial ACL entry to
be associated with the newly created resource. This entry is used to control
future access to the new resource and (since the subject is deemed to be the "Owner")
exercise control over its associated ACL. The caller can specify the following
items for initializing an ACL entry:
Subject
A CSSM_LIST structure, containing the type of the
subject and a template value that can be used to verify samples that are presented
in credentials when resource access is requested.
Delegation flag
A
value indicating whether the Subject can delegate the permissions recorded
in the AuthorizationTag.
(This item only applies to public key subjects).
Authorization tag
The
set of permissions that are granted to the Subject.
Validity period
The
start time and the stop time for which the ACL entry is valid.
ACL entry tag
A user-defined string value associated with the
ACL entry.
The service provider can modify the caller-provided
initial ACL entry to conform to any innate resource-access policy that the
service provider may be required to enforce. If the initial ACL entry provided
by the caller contains values or permissions that are not supported by the
service provider, then the service provider can modify the initial ACL appropriately
or can fail the request to create the new resource. Service providers list
their supported AuthorizationTag values
in their Module Directory Services primary record.
The KeyData field of the CSSM_KEY
structure is allocated by the CSP. The application is required to free this
memory using the CSSM_FreeKey (CSSM
API), or CSP_FreeKey (CSP
SPI), function or with the memory functions registered for the CSPHandle.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_KEY_LABEL_ALREADY_EXISTS
CSSMERR_CSP_PUBLIC_KEY_INCONSISTENT
CSSMERR_CSP_PRIVATE_KEY_ALREADY_EXIST
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_WrapKey
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_WrapKey
UnwrapKeyP – Unwrap the wrapped keys with
privilege (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_UnwrapKeyP
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_KEY *PublicKey,
const CSSM_WRAP_KEY *WrappedKey,
uint32 KeyUsage,
uint32 KeyAttr,
const CSSM_DATA *KeyLabel,
const CSSM_RESOURCE_CONTROL_CONTEXT *CredAndAclEntry,
CSSM_KEY_PTR UnwrappedKey,
CSSM_DATA_PTR DescriptiveData,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
Privilege (input)
The privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation.
See CSSM_UnwrapKey.
This
function is similar to CSSM_UnwrapKey.
It also accepts a USEE tag as a privilege request parameter. CSSM checks that
either its own privilege set or the Application’s privilege set (if
the Application is signed) includes the tag. If the tag is found and the service
provider privilege set indicates that it is supported, the tag is forwarded
to the service provider.
The KeyData field of the CSSM_KEY
structure is allocated by the CSP. The application is required to free this
memory using the CSSM_FreeKey function
or with the memory functions registered for the CSPHandle.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_KEY_LABEL_ALREADY_EXISTS
CSSMERR_CSP_PUBLIC_KEY_INCONSISTENT
CSSMERR_CSP_PRIVATE_KEY_ALREADY_EXIST
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
VerifyData: CSSM_VerifyData,
CSP_VerifyData – Verify input buffer data (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_VerifyData
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS DigestAlgorithm,
const CSSM_DATA *Signature)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_VerifyData
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount,
CSSM_ALGORITHMS DigestAlgorithm,
const CSSM_DATA *Signature)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
DataBufs (input)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the data to be operated on.
DataBufCount (input)
The number of DataBufs to be verified.
DigestAlgorithm (input)
If verifying just a digest, specifies the type
of digest. In this case, the context should only specify the encryption algorithm.
If not verifying just a digest, it must be CSSM_ALGID_NONE. In this case,
the context should specify the combination digest/encryption algorithm.
Signature (input)
A pointer to a CSSM_DATA structure which contains
the signature and the size of the signature.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
This
function verifies all data contained in the set of input buffers based on
the input signature.
Verifying can include digesting the data and decrypting
the digest (from the signature) or verifying just the digest (already calculated
by the application). If digesting the data and decrypting the digest, then
the context should specify both digest and decryption algorithms (for example,
CSSM_ALGID_MD5WithRSA). In this case, the DigestAlgorithm parameter must be set to CSSM_ALGID_NONE. If signing
just the digest, then the context should specify just the decryption algorithm
and the DigestAlgorithm parameter
should specify the type of digest (for example, CSSM_ALGID_MD5). Also, DataBufCount must be 1.
If
the signing algorithm is not reversible or strictly limits the size of the
signed data, then the algorithm can specify verification without digesting.
In this case, the verify operation is performed on the input data and the
size of the input data is restricted by the service provider.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_INPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
CSSMERR_CSP_VERIFY_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
CSSMERR_CSP_INVALID_DIGEST_ALGORITHM
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_SignData, CSSM_VerifyDataInit, CSSM_VerifyDataUpdate, CSSM_VerifyDataFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_SignData, CSP_VerifyDataInit, CSP_VerifyDataUpdate, CSP_VerifyDataFinal
VerifyDataFinal:
CSSM_VerifyDataFinal, CSP_VerifyDataFinal – Finalize the staged verify
data (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_VerifyDataFinal
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Signature)
SPI:
CSSM_BOOL CSSMCSPI CSP_VerifyDataFinal
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Signature)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
Signature (input)
A pointer to a CSSM_DATA structure which contains
the starting address for the signature to verify against and the length of
the signature in bytes.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function finalizes the staged verify data function.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_INPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
CSSMERR_CSP_VERIFY_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_VerifyData, CSSM_VerifyDataInit, CSSM_VerifyDataUpdate
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_VerifyData, CSP_VerifyDataInit, CSP_VerifyDataUpdate
VerifyDataInit:
CSSM_VerifyDataInit, CSP_VerifyDataInit – Initialize the staged verify
data (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_VerifyDataInit
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_VerifyDataInit
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
This
function initializes the staged verify data function.
For
staged operations, a combination operation selecting both a digesting algorithm
and a verification algorithm must be specified.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_VerifyDataUpdate, CSSM_VerifyDataFinal, CSSM_VerifyData
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_VerifyDataUpdate, CSP_VerifyDataFinal, CSP_VerifyData
VerifyDataUpdate:
CSSM_VerifyDataUpdate, CSP_VerifyDataUpdate – Continue the staged verification
(CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_VerifyDataUpdate
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_VerifyDataUpdate
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
DataBufs (input)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the data to be operated on.
DataBufCount (input)
The number of DataBufs to be verified.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function continues the staged verification process over all data contained
in the set of input. Verification will be based on the signature presented
as input when finalizing the staged verification process.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None specific to this call.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_VerifyData, CSSM_VerifyDataInit, CSSM_VerifyDataFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_VerifyData, CSP_VerifyDataInit, CSP_VerifyDataFinal
VerifyDevice:
CSSM_VerifyDevice, CSP_VerifyDevice – Cause the cryptographic module to perform a self verification
and integrity check (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_VerifyDevice
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DeviceCert)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_VerifyDevice
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DeviceCert)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform this function. If a NULL handle is
specified, CSSM returns error.
DeviceCert (input)
Pointer to CSSM_DATA structure that contains data
that identifies the cryptographic device.
This
function triggers the cryptographic module to perform self verification and
integrity checking.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_DEVICE_VERIFY_FAILED
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online
Help
VerifyMac: CSSM_VerifyMac,
CSP_VerifyMac – Verify the message authentication code (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_VerifyMac
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount,
const CSSM_DATA *Mac)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_VerifyMac
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount,
const CSSM_DATA *Mac)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
DataBufs (input)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the data to be operated on.
DataBufCount (input)
The number of DataBufs.
Mac (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the MAC to verify.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
This
function verifies the message authentication code over all data contained
in the set of input buffers based on the input signature.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_INPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
CSSMERR_CSP_VERIFY_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_VerifyMacInit, CSSM_VerifyMacUpdate, CSSM_VerifyMacFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_VerifyMacInit, CSP_VerifyMacUpdate, CSP_VerifyMacFinal
VerifyMacFinal:
CSSM_VerifyMacFinal, CSP_VerifyMacFinal – Finalize the staged message
authentication code (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_VerifyMacFinal
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Mac)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_VerifyMacFinal
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *Mac)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
Mac (input)
A pointer to the CSSM_DATA structure containing
the MAC to verify.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function finalizes the staged message authentication code verification function.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
CSSMERR_CSP_INPUT_LENGTH_ERROR
CSSMERR_CSP_VERIFY_FAILED
CSSMERR_CSP_INVALID_SIGNATURE
The output is returned to the caller as specified
in Buffer Management for Cryptographic Services.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_VerifyMac, CSSM_VerifyMacInit, CSSM_VerifyMacUpdate
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_VerifyMac, CSP_VerifyMacInit, CSP_VerifyMacUpdate
VerifyMacInit:
CSSM_VerifyMacInit, CSP_VerifyMacInit – Initialize the staged message
authentication code (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_VerifyMacInit
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_VerifyMacInit
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
This
function initializes the staged message authentication code verification function.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_VerifyMac, CSSM_VerifyMacUpdate, CSSM_VerifyMacFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_VerifyMac, CSP_VerifyMacUpdate, CSP_VerifyMacFinal
VerifyMacUpdate:
CSSM_VerifyMacUpdate, CSP_VerifyMacUpdate – Continue the staged process
of verifying the message authentication code (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_VerifyMacUpdate
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_VerifyMacUpdate
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_DATA *DataBufs,
uint32 DataBufCount)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle that describes the context of this cryptographic
operation used to link to the CSP-managed information.
DataBufs (input)
A pointer to a vector of CSSM_DATA structures that
contain the data to be operated on.
DataBufCount (input)
The number of DataBufs.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
This
function continues the staged process of verifying the message authentication
code over all data in the set of input buffers. Verification will be based
on the authentication code presented as input when finalizing the staged verification
process.
A CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying
a particular error condition. The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other
values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online
Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_VerifyMac, CSSM_VerifyMacInit, CSSM_VerifyMacFinal
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_VerifyMac, CSP_VerifyMacInit, CSP_VerifyMacFinal
WrapKey: CSSM_WrapKey,
CSP_WrapKey – Wrap
a key using the context (CDSA) API:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_WrapKey
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
const CSSM_DATA *DescriptiveData,
CSSM_WRAP_KEY_PTR WrappedKey)
SPI:
CSSM_RETURN CSSMCSPI CSP_WrapKey
(CSSM_CSP_HANDLE CSPHandle,
CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_CONTEXT *Context,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
const CSSM_DATA *DescriptiveData,
CSSM_WRAP_KEY_PTR WrappedKey,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
CCHandle (input)
The handle to the context that describes this cryptographic
operation.
AccessCred (input)
A pointer to the set of one or more credentials
required to access the private or secret key to be exported from the CSP.
The credentials structure can contain an immediate value for the credential,
such as a passphrase, or the caller can specify a callback function the CSP
can use to obtain one or more credentials.
Key (input)
A pointer to the key to be wrapped.
DescriptiveData (input/optional)
A pointer to a CSSM_DATA structure containing additional
descriptive data to be associated and included with the key during the wrapping
operation. The caller and the wrapping algorithm incorporate knowledge of
the structure of the descriptive data. If the wrapping algorithm does not
accept additional descriptive data, then this parameter must be NULL. If the
wrapping algorithm accepts descriptive data, the corresponding unwrapping
algorithm can be used to extract the descriptive data and the key.
WrappedKey (output)
A pointer to a CSSM_WRAP_KEY structure that returns
the wrapped key.
CSPHandle (input)
The handle that describes the add-in Cryptographic
Service Provider module used to perform up-calls to CSSM for the memory functions
managed by CSSM.
Context (input)
Pointer to CSSM_CONTEXT structure that describes
the attributes with this context.
Privilege (input)
The export privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation. This parameter is forwarded to the CSP after CSSM verifies the
caller and service provider privilege set includes the specified PRIVILEGE.
This
function wraps the supplied key using the context. It allows a key to be exported
from a CSP. Four types of wrapping exist:
1. Wrap a symmetric key with a symmetric
key.
2. Wrap a symmetric key with an asymmetric
public key.
3. Wrap an asymmetric private key with a symmetric
key.
4. Wrap an asymmetric private key with an
asymmetric public key.
For types 1 and 3, a symmetric context should be
provided. For types 2 and 4, an asymmetric context is provided. If there is
a CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_WRAPPED_KEY_FORMAT argument in the context represented by
the CCHandle,
the value of the attribute specifies the format of the wrapped key. If this
argument is not present, the symmetric key is wrapped according to CMS for
types 1 and 3, and according to PKCS8 for types 2 and 4. If the wrapping algorithm
in the context is CSSM_ALGID_NONE, then the key is returned in raw format,
if permitted and supported by the CSP (in this case the CSSM_ATTRIBUTE_WRAPPED_KEY_FORMAT
attribute is ignored). All significant key attributes are incorporated into
the KeyHeader of
the returned WrappedKey,
such that the state of the key can be fully restored by the unwrap process.
The CSP can require that the cryptographic context
includes access credentials for authentication and authorization checks when
using the secret or private key.
The KeyData field of the CSSM_KEY
structure is allocated by the CSP. The application is required to free this
memory using the CSSM_FreeKey (CSSM
API), or CSP_FreeKey (CSP
SPI) function, or with the memory functions registered for the CSPHandle.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors
are described in the CDSA technical standard.
None
specific to this call.
Books
Intel
CDSA Application Developer’s Guide
Online Help
Functions for the CSSM API:
CSSM_UnwrapKey
Functions
for the CSP SPI:
CSP_UnwrapKey
WrapKeyP – Wrap a key with privilege (CDSA) CSSM_RETURN CSSMAPI CSSM_WrapKeyP
(CSSM_CC_HANDLE CCHandle,
const CSSM_ACCESS_CREDENTIALS *AccessCred,
const CSSM_KEY *Key,
const CSSM_DATA *DescriptiveData,
CSSM_WRAP_KEY_PTR WrappedKey,
CSSM_PRIVILEGE Privilege)
Common
Security Services Manager library (cdsa$incssm300_shr.exe)
Privilege (input)
The privilege to be applied during the cryptographic
operation.
See CSSM_WrapKey.
This
function is similar to CSSM_WrapKey.
It also accepts a USEE tag as a privilege request parameter. CSSM checks that
either its own privilege set or the application’s privilege set (if
the application is signed) includes the tag. If the tag is found, and the
service provider privilege set indicates that it is supported, the tag is
forwarded to the service provider.
The KeyData field of the CSSM_KEY
structure is allocated by the CSP. The application is required to free this
memory using the CSSM_FreeKey functon,
or with the memory functions registered for the CSPHandle.
A
CSSM_RETURN value indicating success or specifying a particular error condition.
The value CSSM_OK indicates success. All other values represent an error condition.
Errors are described in the CDSA technical standard.
Books
Intel CDSA Application Developer’s
Guide
Online Help
Index
a
b
c
CSSM_CL_FreeFields function (1), (2) CSSM_CSP_CreateDeriveKeyContext function (1), (2) CSSM_CSP_CreateDigestContext function (1), (2) CSSM_CSP_CreateKeyGenContext function (1), (2) CSSM_CSP_CreateMacContext function (1), (2) CSSM_CSP_CreatePassThroughContext function (1), (2) CSSM_DL_GetDbNames function (1), (2) d
e
f
g
i
k
m
o
p
q
r
s
t
u
v
w
![[Compaq]](../../images/hp.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/hp_ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
![[Compaq]](../../images/hp.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/hp_ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
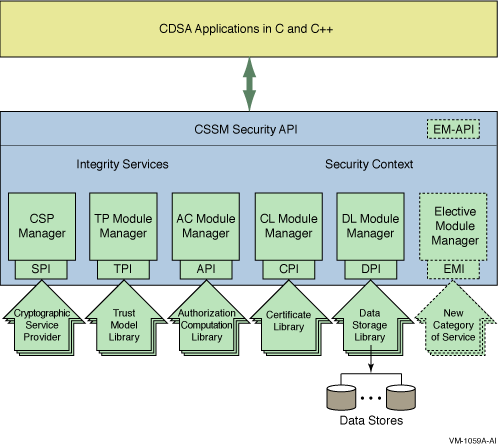
 Note
Note![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_comments.gif)