![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 19 July 1999 | |
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
You can use the QUI$_SEARCH_FREEZE_CONTEXT option of the QUI$_SEARCH_FLAGS item code in any wildcard or nested wildcard call to prevent advancement of context to the next object on the list. This allows you to make successive calls for information about the same queue, job, file, characteristic, or form.
The caller must have manage (M) access to the queue, read (R) access to the job, or SYSPRV or OPER privilege to obtain job and file information.
If the caller does not have the privilege required to access a job specified in a QUI$_DISPLAY_JOB or QUI$_DISPLAY_FILE operation, $GETQUI returns a successful condition value. However, it sets the QUI$V_JOB_INACCESSIBLE bit of the QUI$_JOB_STATUS item code and returns information only for the following item codes:
AST limit quota must be sufficient.
$ALLOC, $ASSIGN, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR, $TRNLNM
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The item list or input buffer cannot be read by the caller; or the return length buffer, output buffer, or status block cannot be written by the caller. SS$_BADCONTEXT Context does not exist or must be called from a more privileged mode. SS$_BADPARAM The function code is invalid; the item list contains an invalid item code; a buffer descriptor has an invalid length; or the reserved parameter has a nonzero value. SS$_DEVOFFLINE The job controller process is not running. SS$_EXASTLM The astadr argument was specified, and the process has exceeded its ASTLM quota. SS$_ILLEFC The efn argument specifies an illegal event flag number. SS$_INSFMEM The space for completing the request is insufficient. SS$_MBFULL The job controller mailbox is full. SS$_IVLOGNAM The device name string has a length of 0 or has more than 63 characters. SS$_MBTOOSML The mailbox message is too large for the job controller mailbox. SS$_UNASEFC The efn argument specifies an unassociated event flag cluster.
JBC$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. JBC$_INVFUNCOD The specified function code is invalid. JBC$_INVITMCOD The item list contains an invalid item code. JBC$_INVPARLEN The length of a specified string is outside the valid range for that item code. JBC$_INVQUENAM The queue name is not syntactically valid. JBC$_JOBQUEDIS The request cannot be executed because the system job queue manager has not been started. JBC$_MISREQPAR An item code that is required for the specified function code has not been specified. JBC$_NOJOBCTX No job context has been established for a QUI$_DISPLAY_FILE operation. JBC$_NOMORECHAR No more characteristics are defined, which indicates the termination of a QUI$_DISPLAY_CHARACTERISTIC wildcard operation. JBC$_NOMOREENT There are no more job entries for the specified user or current user name, which indicates termination of a QUI$_DISPLAY_ENTRY wildcard operation. JBC$_NOMOREFILE No more files are associated with the current job context, which indicates the termination of a QUI$_DISPLAY_FILE wildcard operation for the current job context. JBC$_NOMOREFORM No more forms are defined, which indicates the termination of a QUI$_DISPLAY_FORM wildcard operation. JBC$_NOMOREJOB No more jobs are associated with the current queue context, which indicates the termination of a QUI$_DISPLAY_JOB wildcard operation for the current queue context. JBC$_NOMOREQMGR No more queue managers are defined, which indicates the termination of a QUI$_DISPLAY_MANAGER wildcard operation. JBC$_NOMOREQUE No more queues are defined, which indicates the termination of a QUI$_DISPLAY_QUEUE wildcard operation. JBC$_NOQUECTX No queue context has been established for a QUI$_DISPLAY_JOB or QUI$_DISPLAY_FILE operation. JBC$_NOSUCHCHAR The specified characteristic does not exist. JBC$_NOSUCHENT There is no job with the specified entry number, or there is no job for the specified user or current user name. JBC$_NOSUCHFILE The specified file does not exist. JBC$_NOSUCHFORM The specified form does not exist. JBC$_NOSUCHJOB The specified job does not exist. JBC$_NOSUCHQMGR The specified queue manager does not exist. JBC$_NOSUCHQUE The specified queue does not exist.
| #1 |
|---|
! Declare system service related symbols
INTEGER*4 SYS$GETQUIW,
2 LIB$MATCH_COND,
2 STATUS
INCLUDE '($QUIDEF)'
! Define item list structure
STRUCTURE /ITMLST/
UNION
MAP
INTEGER*2 BUFLEN, ITMCOD
INTEGER*4 BUFADR, RETADR
END MAP
MAP
INTEGER*4 END_LIST
END MAP
END UNION
END STRUCTURE
! Define I/O status block structure
STRUCTURE /IOSBLK/
INTEGER*4 STS, ZEROED
END STRUCTURE
! Declare $GETQUIW item list and I/O status block
RECORD /ITMLST/ GETQUI_LIST(4)
RECORD /IOSBLK/ IOSB
! Declare variables used in $GETQUIW item list
CHARACTER*31 QUEUE_NAME
INTEGER*2 QUEUE_NAME_LEN
INTEGER*4 SEARCH_FLAGS,
2 ENTRY_NUMBER
! Initialize item list
GETQUI_LIST(1).BUFLEN = 4
GETQUI_LIST(1).ITMCOD = QUI$_SEARCH_FLAGS
GETQUI_LIST(1).BUFADR = %LOC(SEARCH_FLAGS)
GETQUI_LIST(1).RETADR = 0
GETQUI_LIST(2).BUFLEN = 4
GETQUI_LIST(2).ITMCOD = QUI$_ENTRY_NUMBER
GETQUI_LIST(2).BUFADR = %LOC(ENTRY_NUMBER)
GETQUI_LIST(2).RETADR = 0
GETQUI_LIST(3).BUFLEN = 31
GETQUI_LIST(3).ITMCOD = QUI$_QUEUE_NAME
GETQUI_LIST(3).BUFADR = %LOC(QUEUE_NAME)
GETQUI_LIST(3).RETADR = %LOC(QUEUE_NAME_LEN)
GETQUI_LIST(4).END_LIST = 0
SEARCH_FLAGS = QUI$M_SEARCH_THIS_JOB
! Call $GETQUIW service to obtain job information
STATUS = SYS$GETQUIW (,
2 %VAL(QUI$_DISPLAY_JOB),,
2 GETQUI_LIST,
2 IOSB,,)
IF (LIB$MATCH_COND (IOSB.STS, %LOC(JBC$_NOSUCHJOB))) THEN
! The search_this_job option can be used only by
! a batch job to obtain information about itself
TYPE *, '<<< this job is not being run in batch mode>>>'
ENDIF
IF (STATUS) STATUS = IOSB.STS
IF (STATUS) THEN
! Display information
TYPE *, 'Job entry number = ', ENTRY_NUMBER
TYPE *, 'Queue name = ', QUEUE_NAME(1:QUEUE_NAME_LEN)
ELSE
! Signal error condition
CALL LIB$SIGNAL (%VAL(STATUS))
ENDIF
END
|
This Fortran program demonstrates how a batch job can obtain information about itself from the system job queue file by using the $GETQUIW system service. Use of the QUI$M_SEARCH_THIS_JOB option in the QUI$_SEARCH_FLAGS input item requires that the calling program run as a batch job; otherwise, the $GETQUIW service returns a JBC$_NOSUCHJOB error.
| #2 |
|---|
! Declare system service related symbols
INTEGER*4 SYS$GETQUIW,
2 STATUS_Q,
2 STATUS_J,
2 NOACCESS
INCLUDE '($QUIDEF)'
! Define item list structure
STRUCTURE /ITMLST/
UNION
MAP
INTEGER*2 BUFLEN, ITMCOD
INTEGER*4 BUFADR, RETADR
END MAP
MAP
INTEGER*4 END_LIST
END MAP
END UNION
END STRUCTURE
! Define I/O status block structure
STRUCTURE /IOSBLK/
INTEGER*4 STS, ZEROED
END STRUCTURE
! Declare $GETQUIW item lists and I/O status block
RECORD /ITMLST/ QUEUE_LIST(4)
RECORD /ITMLST/ JOB_LIST(6)
RECORD /IOSBLK/ IOSB
! Declare variables used in $GETQUIW item lists
CHARACTER*31 SEARCH_NAME
CHARACTER*31 QUEUE_NAME
CHARACTER*39 JOB_NAME
CHARACTER*12 USERNAME
INTEGER*2 SEARCH_NAME_LEN,
2 QUEUE_NAME_LEN,
2 JOB_NAME_LEN,
2 USERNAME_LEN
INTEGER*4 SEARCH_FLAGS,
2 JOB_SIZE,
2 JOB_STATUS
! Solicit queue name to search; it may be a wildcard name
TYPE 9000
ACCEPT 9010, SEARCH_NAME_LEN, SEARCH_NAME
! Initialize item list for the display queue operation
QUEUE_LIST(1).BUFLEN = SEARCH_NAME_LEN
QUEUE_LIST(1).ITMCOD = QUI$_SEARCH_NAME
QUEUE_LIST(1).BUFADR = %LOC(SEARCH_NAME)
QUEUE_LIST(1).RETADR = 0
QUEUE_LIST(2).BUFLEN = 4
QUEUE_LIST(2).ITMCOD = QUI$_SEARCH_FLAGS
QUEUE_LIST(2).BUFADR = %LOC(SEARCH_FLAGS)
QUEUE_LIST(2).RETADR = 0
QUEUE_LIST(3).BUFLEN = 31
QUEUE_LIST(3).ITMCOD = QUI$_QUEUE_NAME
QUEUE_LIST(3).BUFADR = %LOC(QUEUE_NAME)
QUEUE_LIST(3).RETADR = %LOC(QUEUE_NAME_LEN)
QUEUE_LIST(4).END_LIST = 0
! Initialize item list for the display job operation
JOB_LIST(1).BUFLEN = 4
JOB_LIST(1).ITMCOD = QUI$_SEARCH_FLAGS
JOB_LIST(1).BUFADR = %LOC(SEARCH_FLAGS)
JOB_LIST(1).RETADR = 0
JOB_LIST(2).BUFLEN = 4
JOB_LIST(2).ITMCOD = QUI$_JOB_SIZE
JOB_LIST(2).BUFADR = %LOC(JOB_SIZE)
JOB_LIST(2).RETADR = 0
JOB_LIST(3).BUFLEN = 39
JOB_LIST(3).ITMCOD = QUI$_JOB_NAME
JOB_LIST(3).BUFADR = %LOC(JOB_NAME)
JOB_LIST(3).RETADR = %LOC(JOB_NAME_LEN)
JOB_LIST(4).BUFLEN = 12
JOB_LIST(4).ITMCOD = QUI$_USERNAME
JOB_LIST(4).BUFADR = %LOC(USERNAME)
JOB_LIST(4).RETADR = %LOC(USERNAME_LEN)
JOB_LIST(5).BUFLEN = 4
JOB_LIST(5).ITMCOD = QUI$_JOB_STATUS
JOB_LIST(5).BUFADR = %LOC(JOB_STATUS)
JOB_LIST(5).RETADR = 0
JOB_LIST(6).END_LIST = 0
! Request search of all jobs present in output queues; also force
! wildcard mode to maintain the internal search context block after
! the first call when a non-wild queue name is entered--this preserves
! queue context for the subsequent display job operation
SEARCH_FLAGS = (QUI$M_SEARCH_WILDCARD .OR.
2 QUI$M_SEARCH_SYMBIONT .OR.
2 QUI$M_SEARCH_ALL_JOBS)
! Dissolve any internal search context block for the process
STATUS_Q = SYS$GETQUIW (,%VAL(QUI$_CANCEL_OPERATION),,,,,)
! Locate next output queue; loop until an error status is returned
DO WHILE (STATUS_Q)
STATUS_Q = SYS$GETQUIW (,
2 %VAL(QUI$_DISPLAY_QUEUE),,
2 QUEUE_LIST,
2 IOSB,,)
IF (STATUS_Q) STATUS_Q = IOSB.STS
IF (STATUS_Q) TYPE 9020, QUEUE_NAME(1:QUEUE_NAME_LEN)
STATUS_J = 1
! Get information on next job in queue; loop until error return
DO WHILE (STATUS_Q .AND. STATUS_J)
STATUS_J = SYS$GETQUIW (,
2 %VAL(QUI$_DISPLAY_JOB),,
2 JOB_LIST,
2 IOSB,,)
IF (STATUS_J) STATUS_J = IOSB.STS
IF ((STATUS_J) .AND. (JOB_SIZE .GE. 500)) THEN
NOACCESS = (JOB_STATUS .AND. QUI$M_JOB_INACCESSIBLE)
IF (NOACCESS .NE. 0) THEN
TYPE 9030, JOB_SIZE
ELSE
TYPE 9040, JOB_SIZE,
2 USERNAME(1:USERNAME_LEN),
2 JOB_NAME(1:JOB_NAME_LEN)
ENDIF
ENDIF
ENDDO
ENDDO
9000 FORMAT (' Enter queue name to search: ', $)
9010 FORMAT (Q, A31)
9020 FORMAT ('0Queue name = ', A)
9030 FORMAT (' Job size = ', I5, ' <no read access privilege>')
9040 FORMAT (' Job size = ', I5,
2 ' Username = ', A, T46,
2 ' Job name = ', A)
END
|
This Fortran program demonstrates how any job can obtain information about other jobs from the system job queue file by using the $GETQUIW system service. This program lists all print jobs in output queues with a job size of 500 blocks or more. It also displays queue name, job size, user name, and job name information for each job listed.
Returns information about queues and jobs initiated from those queues. The $SNDJBC service is the major interface to the Job Controller, which is the queue and accounting manager. For a discussion of the different types of job and queue, see the Description section of $SNDJBC.The $GETQUIW service completes synchronously; that is, it returns to the caller with the requested information. For asynchronous completion, use the Get Queue Information ($GETQUI) service; $GETQUI returns to the caller after queuing the information request, without waiting for the information to be returned.
In all other respects, $GETQUIW is identical to $GETQUI. For more information about $GETQUIW, refer to the description of $GETQUI in this manual.
For additional information about system service completion, refer to the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
SYS$GETQUIW [efn] ,func [,context] [,itmlst] [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm]
int sys$getquiw (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int func, unsigned int *context, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
Returns information about the local system or about other systems in an OpenVMS Cluster system. The $GETSYI service completes asynchronously; for synchronous completion, use the Get Systemwide Information and Wait ($GETSYIW) service.For additional information about system service completion, refer to the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$GETSYI [efn] ,[csidadr] ,[nodename] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm]
int sys$getsyi (unsigned int efn, unsigned int *csidadr, void *nodename, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), unsigned __int64 astprm);
efn
OpenVMS usage: ef_number type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Number of the event flag to be set when the $GETSYI request completes. The efn argument is a longword containing this number; however, $GETSYI uses only the low-order byte.Upon request initiation, $GETSYI clears the specified event flag (or event flag 0 if efn was not specified). Then, when the request completes, the specified event flag (or event flag 0) is set.
csidadr
OpenVMS usage: process_id type: longword (unsigned) access: modify mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
OpenVMS Cluster system identification of the node about which $GETSYI is to return information. The csidadr argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a longword containing this identification value.The cluster-connection software assigns the OpenVMS Cluster system identification of a node. You can obtain this information by using the DCL command SHOW CLUSTER. The value of the cluster system identification for a node is not permanent; a new value is assigned to a node whenever it joins or rejoins the cluster.
You can also specify a node to $GETSYI by using the nodename argument. If you specify csidadr, you need not specify nodename, and vice versa. If you specify both, they must identify the same node. If you specify neither argument, $GETSYI returns information about the local node. However, for wildcard operations, you must use the csidadr argument.
If you specify csidadr as --1, $GETSYI assumes a wildcard operation and returns the requested information for each node in the cluster, one node per call. In this case, the program should test for the condition value SS$_NOMORENODE after each call to $GETSYI and should stop calling $GETSYI when SS$_NOMORENODE is returned.
nodename
OpenVMS usage: process_name type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (VAX)
Name of the node about which $GETSYI is to return information. The nodename argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a character string descriptor pointing to this name string.The node name string must contain from 1 to 15 characters and must correspond exactly to the node name; no trailing blanks or abbreviations are permitted.
You can also specify a node to $GETSYI by using the csidadr argument. See the description of csidadr.
itmlst
OpenVMS usage: 32-bit item_list_3 or 64-bit item_list_64b type: longword (unsigned) for 32-bit; quadword (unsigned) for 64-bit access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
Item list specifying which information is to be returned about the node or nodes. The itmlst argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a list of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of information. An item list in 32-bit format is terminated by a longword of 0; an item list in 64-bit format is terminated by a quadword of 0. All items in an item list must be of the same format---either 32-bit or 64-bit.The following diagram depicts the 32-bit format of a single item descriptor.
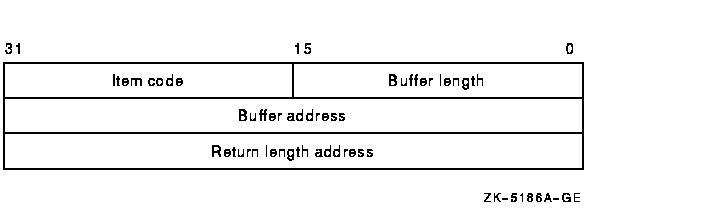
The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 32-bit item list entries.
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| Buffer length | A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer in which $GETSYI is to write the information. The length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of the buffer length field is too small, $GETSYI truncates the data. |
| Item code | A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of information that $GETSYI is to return. The $SYIDEF macro defines these codes. A description of each item code is given in the Item Codes section. |
| Buffer address | A longword containing the user-supplied 32-bit address of the buffer into which $GETSYI is to write the information. |
| Return length address | A longword containing the user-supplied 32-bit address of a word in which $GETSYI writes the length in bytes of the information it actually returned. |
The following diagram depicts the 64-bit format of a single item descriptor.
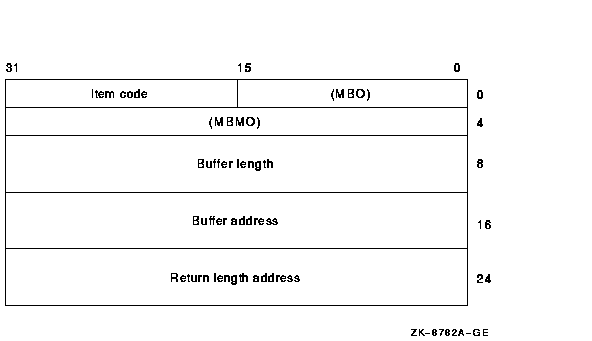
The following table defines the item descriptor fields for 64-bit item list entries.
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| MBO | The field must contain a 1. The MBO and MBMO fields are used to distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries. |
| Item code | A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of information that $GETSYI is to return. The $SYIDEF macro defines these codes. A description of each item code is given in the Item Codes section. |
| MBMO | The field must contain a --1. The MBMO and MBO fields are used to distinguish 32-bit and 64-bit item list entries. |
| Buffer length | A quadword containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer in which $GETSYI is to write the information. The length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of the buffer length is too small, $GETSYI truncates the data. |
| Buffer address | A quadword containing the user-supplied 64-bit address of the buffer into which $GETSYI is to write the information. |
| Return length address | A quadword containing the user-supplied 64-bit address of a word in which $GETSYI writes the length in bytes of the information it actually returned. |
See the Item Codes section for a description of the various $GETSYI item codes.
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
When you specify the iosb argument, $GETSYI sets the quadword to 0 upon request initiation. Upon request completion, a condition value is returned to the first longword; the second longword is reserved for future use.
Though this argument is optional, Compaq strongly recommends that you specify it, for the following reasons:
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) |
| mechanism: | by 32-bit reference (VAX) |
If you specify astadr, the AST routine executes at the same access mode as the caller of the $GETSYI service.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
SYI$_ACTIVECPU_CNT
When you specify SYI$_ACTIVECPU_CNT, $GETSYI returns a count of the CPUs actively participating in the current boot of the symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) system.Because this number is a longword, the buffer length field in the item descriptor should specify 4 (bytes).
SYI$_ACTIVE_CPU_MASK
On Alpha systems, when you specify SYI$_ACTIVE_CPU_MASK, $GETSYI returns a mask of the CPUs actively participating in the current boot of the symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) system.SYI$_ARCHFLAG
When you specify SYI$_ARCHFLAG, $GETSYI returns the architecture flags for the system.
Previous Next Contents Index
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
privacy and legal statement 4527PRO_050.HTML