
As well as receiving requests from the client and getting information from scanning modules, a server can act as a relay, and simply pass information through to another server or client. This has implications for what you need to plan if you have a Windows or a Motif client.
The MAILbus Monitor V2.1 client and server both used only the transport service that the user had specified during setup. Possible services were:
The Mail Monitor Motif client maintains this behaviour for V3.0.
The Windows NT server, however, uses only TCP/IP or Windows Socket 1.1 or later, so scanning information about Microsoft Exchange can only be sent directly to a Motif client over a TCP/IP connection. A V2.1 server can also receive scanning information using a TCP/IP link and relay the information to the Motif client using either DECnet Phase IV or DECnet-Plus.
Figure 1-2 and Figure 1-3 show possible configurations using the Motif client.


The Windows NT client, and the V3.0 server, uses any available transport service (whichever is the most efficient). Possible services are:
Figure 1-4 shows a DIGITAL UNIX or OpenVMS server receiving scanning information from a DIGITAL UNIX or OpenVMS server using a DECnet link, and relaying the information to the Windows NT client (which can only use TCP/IP to communicate with a DIGITAL UNIX or OpenVMS server).
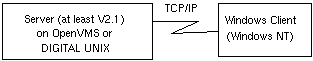
Figure 1-5 shows a DIGITAL UNIX or OpenVMS server receiving scanning information over a DECnet link from a V2.0 or earlier POLYCENTER Network Application Monitor server (running on a DIGITAL UNIX or OpenVMS system), and relaying the information to the Windows NT client.
