![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 30 March 2001 | |
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
The following table describes the significant bits:
| Bit | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | Do not format sensitive information. |
| 0 | Format sensitive information. | |
| 1 | 1 | Build a column title for messages in brief format. (You must specify a fmttyp of brief and a routin argument.) |
| 0 | Do not build column titles. |
The Format Security Audit Event Message service converts a security auditing event message from binary format to ASCII text and can filter sensitive information. $FORMAT_AUDIT allows the caller to format a message in a multiple-line format or a single-line format and tailor the information for a display device of a specific width.$FORMAT_AUDIT is intended for utilities that need to format the security auditing event messages received from the audit server listener mailbox or the system security audit log file.
None
$FORMAT_AUDIT can cause a process to exceed its page-file quota (PGFLQUOTA) if it has to format a long auditing event message. The caller of $FORMAT_AUDIT can also receive quota violations from services that $FORMAT_AUDIT uses, such as $IDTOASC, $FAO, and $GETMSG.
$AUDIT_EVENT
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_MSGNOTFND The service completed successfully; however, the message code cannot be found and a default message has been returned. SS$_ACCVIO The item list cannot be read by the caller, or the buffer length or buffer cannot be written by the caller. SS$_BADPARAM The item list contains an invalid identifier. SS$_BUFFEROVF The service completed successfully; however, the formatted output string overflowed the output buffer and has been truncated. SS$_INSFMEM The process dynamic memory is insufficient for opening the rights database. SS$_IVCHAN The format of the specified identifier is not valid. This condition value returned is not directly returned by $FORMAT_AUDIT. It is indirectly returned when $FORMAT_AUDIT in turn calls another service, such as an identifier translation or binary time translation service. SS$_IVIDENT The format of the specified identifier is invalid. SS$_NOSUCHID The specified identifier name does not exist in the rights database. This condition value returned is not directly returned by $FORMAT_AUDIT. It is indirectly returned when $FORMAT_AUDIT in turn calls another service, such as an identifier translation or binary time translation service.
On Alpha systems, releases a user capability, indicating to other processes that the resource is now available.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$FREE_USER_CAPABILITY cap_num [,prev_num] [,flags]
int sys$free_user_capability (int *cap_num, struct _generic_64 *prev_mask, struct _generic_64 *flags);
cap_num
OpenVMS usage: longword type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Capability number to be released by the calling Kernel thread. This number can range from 1 to 16. The cap_num argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of the longword containing the user capability number.prev_mask
OpenVMS usage: mask_quadword type: quadword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
The previous user capability reservation mask before execution of this service call. The prev_mask argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword into which the service writes a quadword bit mask specifying the previously reserved user capabilities.flags
OpenVMS usage: mask_quadword type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Options selected for the user capability reservation. The flags argument is a quadword bit vector wherein a bit corresponds to an option.Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, which the $CAPDEF macro defines. The flags argument is constructed by performing a logical OR operation using the symbolic names of each desired option.
At this time, all bits are reserved to Compaq and must be 0.
The Release a Reserved User Capability service releases a user capability back to the global pool, making it available for subsequent calls to $GET_USER_CAPABILITY. The state of all user capabilities in the system are kept in SCH$GQ_RESERVED_USER_CAPS; this service clears the bit position in that cell reflecting the capability number specified in cap_num.This service can also return the state of the global reservation bit mask prior to a release operation.
The caller must have both ALTPRI and WORLD privileges to call $FREE_USER_CAPABILITY to release a user capability. No privileges are required if $FREE_USER_CAPABILITY is called only to retrieve the current user capability reservation mask.
None
$GET_USER_CAPABILITY, $CPU_CAPABILITIES, $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_ACCVIO The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more arguments. SS$_INSFARG Fewer than the required number of arguments were specified, or no operation was specified. SS$_NOPRIV Insufficient privilege for the attempted operation. SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS Too many arguments were presented to the system service. SS$_WASCLR The requested user capability was already released.
Returns information related to the primary and secondary device characteristics of an I/O device.For synchronous completion, use the Get Device/Volume Information and Wait ($GETDVIW) service. The $GETDVIW service is identical to the $GETDVI service in every way except that $GETDVIW returns to the caller with the requested information.
For additional information about system service completion, refer to the Synchronize ($SYNCH) service.
SYS$GETDVI [efn] ,[chan] ,[devnam] ,itmlst [,iosb] [,astadr] [,astprm] [,nullarg]
int sys$getdvi (unsigned int efn, unsigned short int chan, void *devnam, void *itmlst, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm, struct _generic_64 *nullarg);
efn
OpenVMS usage: ef_number type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Number of the event flag to be set when $GETDVI returns the requested information. The efn argument is a longword containing this number; however, $GETDVI uses only the low-order byte.Upon request initiation, $GETDVI clears the specified event flag (or event flag 0 if efn was not specified). Then, when $GETDVI returns the requested information, it sets the specified event flag (or event flag 0).
chan
OpenVMS usage: channel type: word (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Number of the I/O channel assigned to the device about which information is desired. The chan argument is a word containing this number.To identify a device to $GETDVI, you can specify either the chan or devnam argument, but you should not specify both. If you specify both arguments, the chan argument is used.
If you specify neither chan nor devnam, $GETDVI uses a default value of 0 for chan.
devnam
OpenVMS usage: device_name type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
The name of the device about which $GETDVI is to return information. The devnam argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to this name string.The device name string can be either a physical device name or a logical name. If the first character in the string is an underscore (_), the string is considered a physical device name; otherwise, the string is considered a logical name and logical name translation is performed until either a physical device name is found or the system default number of translations has been performed.
If the device name string contains a colon (:), the colon and the characters that follow it are ignored.
To identify a device to $GETDVI, you can specify either the chan or devnam argument, but you should not specify both. If both arguments are specified, the chan argument is used.
If you specify neither chan nor devnam, $GETDVI uses a default value of 0 for chan.
itmlst
OpenVMS usage: item_list_3 type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Item list specifying which information about the device is to be returned. The itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of information. The list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0. The following diagram depicts the format of a single item descriptor:
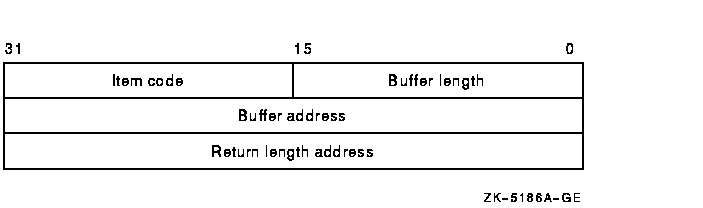
The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| Buffer length | A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer in which $GETDVI is to write the information. The length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer length is too long, $GETDVI truncates the data. |
| Item code | A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code specifying the item of information that $GETDVI is to return. The $DVIDEF macro defines these codes. Each item code is described in the Item Codes section. |
| Buffer address | A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer in which $GETDVI is to write the information. |
| Return length address | A longword containing the user-supplied address of a word in which $GETDVI is to write the information. |
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
When you specify the iosb argument, $GETDVI sets the quadword to 0 upon request initiation. Upon request completion, a condition value is returned to the first longword; the second longword is reserved to Compaq.
Though this argument is optional, Compaq strongly recommends that you specify it, for the following reasons:
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
If you specify astadr, the AST routine executes at the same access mode as the caller of the $GETDVI service.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
| OpenVMS usage: | null_arg |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
DVI$_ACPPID
Returns the ACP process ID as an unsigned integer longword.DVI$_ACPTYPE
Returns the ACP type code as an unsigned integer longword. The following symbols define each of the ACP type codes that $GETDVI can return:
Symbol Description DVI$C_ACP_F11V1 Files-11 Level 1 DVI$C_ACP_F11V2 Files-11 Level 2 DVI$C_ACP_F11V5 Files-11 Level 5 DVI$C_ACP_MTA Magnetic tape DVI$C_ACP_NET Networks DVI$C_ACP_REM Remote I/O DVI$_ALL
Returns a string that is either TRUE or FALSE to indicate whether the device is allocated or not allocated.DVI$_ALLDEVNAM
Returns the allocation-class device name, which is a 64-byte string. The allocation-class device name uniquely identifies each device that is currently connected to any node in an OpenVMS Cluster system or to a single-node system. This item code generates a single unique name for a device even if the device is dual ported.One use for the allocation-class device name might be in an application wherein processes need to coordinate their access to devices (not volumes) using the lock manager. In this case, the program would make the device a resource to be locked by the lock manager, specifying as the resource name the following concatenated components: (1) a user facility prefix followed by an underscore character and (2) the allocation-class device name of the device.
Note that the name returned by the DVI$_DEVLOCKNAM item code should be used to coordinate access to volumes.
DVI$_ALLOCLASS
Returns the allocation class of the host as a longword integer between 0 and 32767. An allocation class is a unique number between 0 and 32767 that the system manager assigns to a pair of hosts and the dual-pathed devices that the hosts make available to other nodes in the cluster.The allocation class provides a way for you to access dual-pathed devices through either of the hosts that act as servers to the cluster. In this way, if one host of an allocation class set is not available, you can gain access to a device specified by that allocation class through the other host of the allocation class. You do not have to be concerned about which host of the allocation class provides access to the device. Specifically, the device name string has the following format:
$allocation_class$device_name
For a detailed discussion of allocation classes, refer to OpenVMS Cluster Systems.
DVI$_ALT_HOST_AVAIL
Returns a longword that is interpreted as Boolean. A value of 1 indicates that the host serving the alternate path is available; a value of 0 indicates that it is not available.The host is the node that makes the device available to other nodes in the OpenVMS Cluster system. A host node can be either a VAX system with an MSCP server or an HSC50 controller.
A dual-pathed device is one that is made available to the cluster by two hosts. Each of the hosts provides access (serves a path) to the device for users. One host serves the primary path; the other host serves the alternate path. The primary path is the path that the system creates through the first available host.
You should not be concerned with which host provides access to the device. When accessing a device, you specify the allocation class of the desired device, not the name of the host that serves it.
If the host serving the primary path fails, the system automatically creates a path to the device through the alternate host.
DVI$_ALT_HOST_NAME
Returns the name of the host serving the alternate path as a 64-byte zero-filled string.For more information about hosts, dual-pathed devices, and primary and alternate paths, refer to the description of the DVI$_ALT_HOST_AVAIL item code.
DVI$_ALT_HOST_TYPE
Returns a four-byte string containing an arbitrary text description of the OpenVMS host or cluster storage controller that is serving this storage device. The particular text string displayed was provided to the local OpenVMS system by the remote System Communications Services (SCS) server.Storage devices are served within an OpenVMS Cluster utilizing the SCS protocol, with the server running on a remote OpenVMS system or on an SCS-capable storage controller. The alternate host type value displayed is determined from the local cluster storage hardware configuration, and indicates the type of devices serving the storage for the available SCS path or paths to the particular storage device.
Item codes in this group include: DVI$_HOST_TYPE, DVI$_ALT_HOST_TYPE, DVI$_HOST_AVAIL, and DVI$_ALT_HOST_AVAIL. Also related is DVI$_HOST_NAME.
Compaq suggests this item code be used solely for display purposes, and should not be used during an attempt to determine the particular cluster hardware configuration.
DVI$_CLUSTER
Returns the volume cluster size as an unsigned integer longword. This item code is applicable only to disks.DVI$_CYLINDERS
Returns the number of cylinders on the volume as an unsigned integer longword. This item code is applicable only to disks.DVI$_DEVBUFSIZ
Returns the device buffer size (for example, the width of a terminal or the block size of a tape) as an unsigned integer longword.DVI$_DEVCHAR
Returns device-independent characteristics as a 4-byte bit vector. Each characteristic is represented by a bit. When $GETDVI sets a bit, the device has the corresponding characteristic. Each bit in the vector has a symbolic name. The $DEVDEF macro defines the following symbolic names:
Symbol Description DEV$V_REC Device is record oriented. DEV$V_CCL Device is a carriage control device. DEV$V_TRM Device is a terminal. DEV$V_DIR Device is directory structured. DEV$V_SDI Device is single-directory structured. DEV$V_SQD Device is sequential and block oriented. DEV$V_SPL Device is being spooled. DEV$V_OPR Device is an operator. DEV$V_RCT Disk contains Revector Cache Table (RCT). This bit is set for every DAA disk. DEV$V_NET Device is a network device. DEV$V_FOD Device is files oriented. DEV$V_DUA Device is dual ported. DEV$V_SHR Device is shareable. DEV$V_GEN Device is a generic device. DEV$V_AVL Device is available for use. DEV$V_MNT Device is mounted. DEV$V_MBX Device is a mailbox. DEV$V_DMT Device is marked for dismount. DEV$V_ELG Device has error logging enabled. DEV$V_ALL Device is allocated. DEV$V_FOR Device is mounted foreign. DEV$V_SWL Device is software write locked. DEV$V_IDV Device can provide input. DEV$V_ODV Device can provide output. DEV$V_RND Device allows random access. DEV$V_RTM Device is a real-time device. DEV$V_RCK Device has read-checking enabled. DEV$V_WCK Device has write-checking enabled. Note that each device characteristic has its own individual $GETDVI item code with the format DVI$_xxxx, where xxxx are the characters following the underscore character in the symbolic name for that device characteristic.
For example, when you specify the item code DVI$_REC, $GETDVI returns a longword value that is interpreted as Boolean. If the value is 0, the device is not record oriented; if the value is 1, it is record oriented. This information is identical to that returned in the DEV$V_REC bit of the longword vector specified by the DVI$_DEVCHAR item code.
The buffer must specify a longword for all of these device-characteristic item codes.
DVI$_DEVCHAR2
Returns additional device-independent characteristics as a 4-byte bit vector. Each bit in the vector, when set, corresponds to a symbolic name. The $DEVDEF macro defines the following symbolic names:
Symbol Description DEV$V_CLU Device is available clusterwide. DEV$V_DET Device is detached terminal. DEV$V_RTT Device has remote terminal UCB extension. DEV$V_CDP Dual-pathed device with two UCBs. DEV$V_2P Two paths are known to this device. DEV$V_MSCP Device accessed using MSCP (disk or tape). Before using this bit to differentiate between types of disk and tape devices, be sure that no other more appropriate differentiation mechanism exists. DEV$V_SSM Device is a shadow set member. DEV$V_SRV Device is served by the MSCP server. DEV$V_RED Device is redirected terminal. DEV$V_NNM Device has node$ prefix. DEV$V_WBC Device supports write-back caching. DEV$V_WTC Device supports write-through caching. DEV$V_HOC Device supports host caching. DEV$V_LOC Device accessible by local (non-emulated) controller. DEV$V_DFS Device is DFS-served. DEV$V_DAP Device is DAP accessed. DEV$V_NLT Device is not-last-track; that is, it has no bad block. Information is on its last track. DEV$V_SEX Device (tape) supports serious exception handling. DEV$V_SHD Device is a member of a host-based shadow set. DEV$V_VRT Device is a shadow set virtual unit. DEV$V_LDR Loader present (tapes). DEV$V_NOLB Device ignores server load balancing requests. DEV$V_NOCLU Device will never be available clusterwide. DEV$V_VMEM Virtual member of a constituent set. DEV$V_SCSI Device is an SCSI device. DEV$V_WLG Device has write-logging capability. DEV$V_NOFE Device does not support forced error. DVI$_DEVCLASS
Returns the device class as an unsigned integer longword. Each class has a corresponding symbol. The $DCDEF macro defines these symbols. The following table describes each device class symbol:
Symbol Description DC$_DISK Disk device DC$_TAPE Tape device DC$_SCOM Synchronous communications device DC$_CARD Card reader DC$_TERM Terminal DC$_LP Line printer DC$_REALTIME Real-time DC$_MAILBOX Mailbox DC$_MISC Miscellaneous device DVI$_DEVDEPEND
Returns device-dependent characteristics as a 4-byte bit vector. To determine what information is returned for a particular device, refer to the OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
Previous Next Contents Index
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
privacy and legal statement 4527PRO_043.HTML