| Previous | Contents | Index |
It is useful to keep track of domains, groups, user accounts, and trust relationships you create as you build and modify your network. The information you record can help you manage your network and solve problems as they arise.
To record the way you build and modify your network, photocopy the worksheet templates provided in this chapter and fill them in as you plan your network; update the worksheets as you modify your network in the future.
The following is a list of worksheet templates provided.
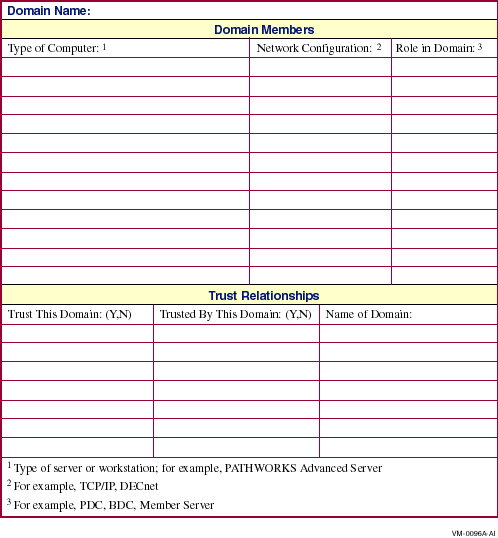
B.1 The Domain Worksheet
Use this worksheet to list all the servers in the domain with their
configurations and roles and to record the domain's trust relationships
with other domains.
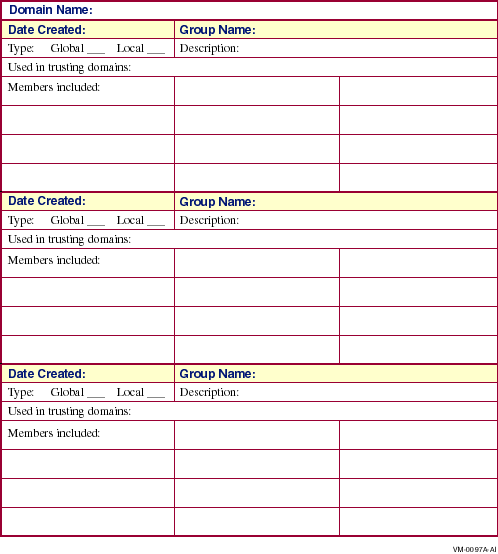
B.2 The Groups Worksheet
Use this worksheet to track the user groups created in the domain.
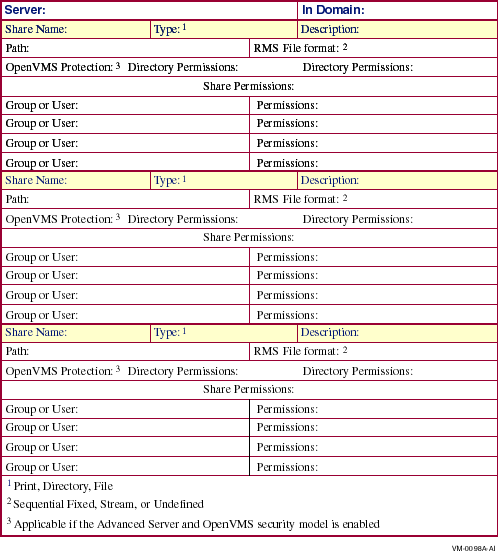
B.3 The Shares Worksheet
Use this worksheet to list the shares defined on the local server. Fill
out a separate worksheet for each server.
access control: The mechanism for validating the right
to use a resource or service, such as a connection, logon, or file
access, that is stored on or connected to a server. A user name and
password combination is the most common means of access control.
access control entry (ACE): An entry in an access
control list (ACL). Each access control entry defines the protection or
auditing to be applied to a file or other object for a specific user or
group.
access control list (ACL): The part of a security
descriptor that restricts and audits access to an object. The owner of
an object has discretionary access control of the object and can change
the object's ACL to allow or disallow other users access to the object.
Access control lists are ordered lists of access control entries (ACEs).
access permissions: See
permissions.
access right: A permission that controls the way in
which an object may be manipulated by a user or by members of a group.
Different object types support different access rights; these are
stored in an object's access control list (ACL).
access token (or security token): An object that
uniquely identifies a user who has logged on. An access token is
attached to all of the user's processes. The token contains the user's
security ID (SID), the SIDs of any groups to which the user belongs,
the user's privileges, and information describing the ownership and
access control list (ACL) to be applied to any objects that the user's
processes create. See also access control list,
security ID, and user privilege.
account: See user account.
account policy: Defines the way passwords are
implemented by all user accounts.
ACE: See access control
entry.
ACL: See access control list.
ADMIN$: An administrative resource that enables remote
administration of servers. A server's ADMIN$ resource is automatically
shared and the share cannot be deleted. See also
C$ and IPC$.
ADMINISTER commands: Commands used to manage an
Advanced Server locally or remotely. The ADMINISTER commands are the
Advanced Server command line interface and they conform to standard
OpenVMS DCL command syntax.
administrative alert: A message from the Advanced Server
concerning server and resource use, or problems relating to security
and access, user sessions, directory replication, and printing. See
also Alerter service.
administrative resource: A resource used when network
users and administrators perform certain tasks on the server, including
viewing the resources the server is sharing, administering the server
remotely, and running shared applications. Administrative resources
include ADMIN$ and IPC$.
administrator: The individual responsible for managing
the network. Typically, this person configures the network, maintains
the network's shared resources and security, assigns passwords and
privileges, and helps users.
Advanced Server: A network operating system compatible
with Microsoft Windows NT technology that provides domain, file, and
print services.
alert: A message that the server sends under certain
conditions. See also administrative alert and
error alert.
alert level: A value that users can specify so that
the software notifies them when licenses are getting used up. For more
information, see the Advanced Server for OpenVMS Guide to Managing Advanced Server Licenses.
Alerter service: A server component that notifies
selected users and computers of administrative alerts that occur on a
computer. It is used by the Server service and other services. See
also administrative alert.
alias: A name through which a user or computer can
receive messages. Each client's computer name is added automatically to
its list of aliases.
application programming interface (API): A set of
routines that an application program uses to request and carry out
lower-level services performed by the operating system.
archive bit: An attribute of any file: a bit that
backup programs use to mark files after backing them up with either the
normal or incremental backup types.
audit policy: The policy that defines the types of
events that are logged.
audit trail: The event and error messages that are
saved in the event log file, as defined by the audit policy.
auditing: The process by which Advanced Server records
an entry in the event log file whenever a user accesses a resource in a
certain way or logs on to the network.
authentication: Validation of a user's logon
information.
backup domain controller (BDC): In a domain, a server
that keeps and uses a copy of the user accounts database to validate
logon requests and that can take over the function of the primary
domain controller if the primary domain controller fails. Contrast
with primary domain controller.
batch command file: A file that contains one or more
commands to be processed sequentially. When a user types the file name
at the command prompt, the commands contained in the file are executed.
boot (or bootstrap): To run or initiate a program that
loads the operating system into memory and starts or restarts the
computer.
broadcast message: A message sent to client
workstations on the network. Users cannot respond to this type of
message.
browse: To look through lists of servers and
workstations in a domain.
built-in groups: The default groups provided with the
Advanced Server. These groups cannot be deleted. See also
group.
C$: The administrative resource that represents a
server's disk drive. The Advanced Server points C$ to
PWRK$LMROOT:[LANMAN].
cache memory: High-speed memory that contains copies
of data recently used by the processor. Cache memory avoids frequent
disk input/output, thus providing faster operation.
check box: In a dialog box, an indicator that a user
can select or clear to turn one or more options on or off. Used, for
example, in the Configuration Manager to select transports.
Contrast with radio button.
client: A personal computer or workstation, connected
to the network, that can access resources on a server. Contrast
with server.
Client License Requester: A client-based PATHWORKS
utility that is responsible for requesting client-based licenses for
clients so that they can access resources on the server.
Client License Transponder: A client-based
PATHWORKS utility that responds to license authentication requests.
client-based license: A license that is assigned on a
per-workstation basis and allows a client to access multiple file
servers. Contrast with server-based license.
computer name: A unique name that identifies a server,
personal computer, or workstation to the network.
configuration: The set of hardware, hardware options,
software, and software options on a computer or network.
Configuration Manager: An Advanced Server tool for
modifying server configuration parameters.
connection: The software link between a workstation
and a shared resource on a server. A connection is made by assigning a
local device name on the workstation to a shared resource on a server,
or by accessing the resource through a network path name with a command
or from an application. Contrast with session.
country code: A code in a user account that specifies
the language in which the server sends messages to the user.
DECnet-Plus: The Compaq family of peer-to-peer,
Ethernet-based network products.
default: The value assigned by a program if a value is
not supplied by the user.
default permissions: The permissions assigned to a
share if no permissions are specified.
destination directory: The directory to which one or
more files are to be moved or copied. Contrast with
source directory.
device driver: A program that enables a specific
device, such as a printer, to communicate with the operating system.
device name: The name by which a computer identifies a
printer, disk, or other device.
dialog box: A window displayed in response to user
action that allows users to enter information and presents choices for
further action.
directory: Part of a structure for organizing files on
a disk. A directory can contain files and other directories (called
subdirectories). See also directory tree.
directory access permissions: The type of access that
a group or user is granted to a particular directory, such as
read-only. See also share permissions and
special access permissions.
directory replication: The copying of a master set of
directories from a server (called an export server) to specified
servers or workstations (called import computers) in the same or other
domains.
Directory Replicator service: Replicates directories,
and the files in those directories, between computers.
directory tree: A conceptual representation of a
disk's directory structure. The directories on the disk are organized
in a hierarchy. The top-level directory is the root directory. See
also path.
disabled user account: A user account that does not
permit logons. The account can be restored to enabled status at any
time. See also user account.
disk resource: A disk device that can be shared.
distributed computing: An application design and
implementation strategy that divides the user interface, processing,
and database storage components of an application into units that can
execute on multiple networked computer systems.
DNS: Domain Name System. Provides name resolution
based on static configuration files, supplying computer names in place
of IP addresses to locate resources.
domain: A collection of computers that share a common
security database and policy. Each domain has a unique name. A network
can have many domains. See also workgroup and
logon security.
domain synchronization: The replication of the domain
database from the primary domain controller to one or more servers of
the domain. Domain synchronization is usually performed automatically
by the system, but can also be invoked manually by an administrator.
downlevel: A term that refers to earlier network
operating systems, such as LAN Manager, that can interoperate with the
Advanced Server.
driver: See device driver.
dynamic data exchange (DDE): A form of interprocess
communications (IPC) in which two or more programs that support dynamic
data exchange can exchange information and commands.
edit box: In a dialog box, a field for entering
information. Used, for example, in the Upgrade utility to enter the
domain name.
encapsulated PostScript (EPS): A file format optimized
for moving PostScript files between applications.
equivalence-name: The node name portion of a file
server name.
error alert: A message from the Advanced Server about
local area network or system errors. Error alerts are stored in the
error log.
Ethernet address: An alphanumeric string, six bytes in
length, that identifies a node on the Ethernet. The string is six pairs
of hexadecimal digits, separated by hyphens (for example,
AA-00-04-00-91-27).
event: Any significant occurrence in the system or in
an application that requires users, operators, or administrators to be
notified, or an entry to be added to a log.
EventLog service: The Advanced Server service that
records events in the system, security, and application event log files.
export path: In directory replication, a path from
which subdirectories, and the files in those subdirectories, are
automatically copied from an export server. See also
directory replication.
export server: In directory replication, a server from
which a master set of directories is copied to specified servers or
workstations (called import computers) in the same or other domains.
See also directory replication.
Extended File Specifications: On OpenVMS Alpha
systems, provides deep directories and extended file names support.
Deep directories support allows network clients to use hierarchical
storage of directories and files on the OpenVMS disk similar to the
client-based disk. Extended file names support uses the Online Disk
Structure (ODS-5), extending OpenVMS file name restrictions to support
longer file names and adding ISO Latin-1 characters to the supported
character set. See also ODS-5.
FAT: File allocation table. File system structure used
by the MS-DOS operating system.
file extension: Any characters that follow a period at
the end of a file name. A file extension usually identifies the file's
type.
File Index Table (FIT): A file name lookup table (with
the .FIT extension) that consists of file translation pairs. FIT files
map path names entered on a client workstation to the actual files on
the server.
file name: The unique name that identifies a file.
See also file extension.
file server: A system that enables a server to allow
access to its local resources.
frame: A packet of information transmitted as a single
unit. Every frame has the same basic organization and contains control
information, such as synchronizing characters, station address, and an
error-checking value, as well as a variable amount of data.
full name: A user's complete name, usually consisting
of the last name, first name, and middle initial. Under the Advanced
Server, the full name can be maintained as part of the information that
identifies and defines a user account. See also user
account.
global account: A normal user account in a user's home
domain. Most user accounts are global accounts. See also
local account and user account.
global group: A user group that can be employed to
define permissions and rights for accessing resources in its own domain
and in trusting domains. A global group can contain user accounts only
from its own domain. Global groups can become members of local groups.
Global groups are a mechanism for creating sets of users that are
available for use both in the domain where they are created and in
other domains. See also group and
local group.
group: A collection of user accounts that are called
members. The permissions and rights granted to a group are also granted
to its members, making groups a convenient way to grant common
capabilities to collections of user accounts. See also
global group and local group.
group memberships: The groups to which a user account
belongs. Permissions and rights granted to a group are also granted to
its members. In most cases, the actions a user can perform are
determined by the group memberships of the user account through which
the user logs on.
group name: A unique name identifying a local or
global group to the Advanced Server. A group's name cannot be identical
to any other group name or user name of its own domain or workstation.
See also group.
guest account: An account on a server that a user
without an individual user account can use to access the server's
resources.
hidden server: A server that is part of a domain, but
that does not appear in the list of servers.
home directory: A directory that is accessible to a
user and that contains files and programs for the user. A home
directory can be assigned to an individual user or can be shared by
many users.
host system: A computer, such as an OpenVMS system,
that runs the server services.
import computers: In directory replication, the
servers or workstations that receive copies of the master set of
directories from an export server. See also directory
replication.
import path: In directory replication, the path to
which imported subdirectories, and the files in those subdirectories,
are stored on an import computer. See also directory
replication.
inherited permissions: Implicit permissions based on
permissions assigned to a parent directory. See also
permissions.
Internet address: A 32-bit number identifying a host
connection on the Internet. An Internet address consists of a network
number and host number.
interprocess communications (IPC): Communication among
the component processes of a program, between different computers
running parts of a single program, or between two programs working
together.
IPC$: An administrative resource that controls how
interprocess communications operate on servers. A server's IPC$ is
automatically shared and cannot be deleted. See also
ADMIN$ and C$.
keyword: On PATHWORKS V6 for OpenVMS (Advanced Server) only, a parameter name in
the LANMAN.INI file that, with an associated value, establishes some
aspect of server configuration.
LAN: Local area network. A self-contained network that
offers a high-speed, reliable communications channel. LANs span a
limited distance, such as a building or cluster of buildings, but can
be connected to WANs with bridge devices. Contrast with
WAN.
LAN Manager: A Network Operating System (NOS) from
Microsoft that manages network tasks and coordinates communications
between clients and servers.
LANMAN.INI file: On PATHWORKS V6 for OpenVMS (Advanced Server) only, an
initialization file on each server and client. The values of the
keywords in this file determine the option settings for computers on
the network.
License Manager: The interface used to manage the
Advanced Server license server. The License Manager provides the ability
to manage license groups, set alert levels, set logging levels for
licensing events, enable or disable the license server, and revoke
assigned licenses.
License Manager Facility (LMF): The OpenVMS facility
that manages the product license database through a callable interface.
License Registrar: A component of the Advanced Server
licensing subsystem that runs on the same node as the file server and
validates whether a client is licensed to connect to the file server.
license server: A Advanced Server software program that
performs license-related services, such as assigning and verifying
licenses.
license server state file: The database on the system
running the license server. Includes client names, information about
the types and quantities of licenses available, and license group
information.
list box: In a dialog box, a box that lists available
choices such as all the files in a directory. If the available choices
do not fit in the viewable portion of the list box, a scroll bar allows
users to move up and down the list.
local account: A user account provided in a domain for
a user whose global account is in a non-trusted domain. Not required
where trust relationships exist between domains. See also
global account and user account.
local area network: See LAN.
local boot: A process in which a client operating
system is loaded and started locally from disk. Contrast with
remote boot.
local computer: The workstation or server at which the
user or administrator is currently working. Contrast with
remote computer.
local group: A user group that can be used to grant
permissions and rights only for the servers of its own domain. A local
group can contain user account names and global group names both from
its own domain and from trusted domains. Local groups are a device for
creating sets of users from both inside and outside the domain, to be
used at servers of the domain. See also global
group and group.
local printer: A printer that is directly connected to
one of the ports on a computer.
local user: The user or administrator working at the
local computer.
lockout: A security feature that disables a user
account if failed logon attempts exceed a specified limit.
log file: A history file. Advanced Server maintains a
system log and optionally enabled security and application logs.
log on: To provide a user name and password to gain
access to the network.
logical drive: On a PC, anything given a drive
designation (for example, D:) that is not physically located on the
system.
logon domain: The domain specified when a user logs on
to the local area network.
logon hours: The days and times during which a user
can access a server's resources.
logon restrictions: The logon hours during which a
user can access a server's resources, and the workstations from which
the user can access those resources.
logon script: A batch program containing Advanced
Server and operating system commands used to configure workstations.
Logon scripts can be written for one or more users. When the user logs
on, the logon script is run.
logon script path: The path or location where the
logon script is stored, if a logon script is assigned to the user's
account.
logon security: A means of verifying the identity of
users when they log on to the local area network or wide area network.
See also NetLogon service.
logon server: For a domain, the primary domain
controller and backup domain controllers. For a user, the server that
processes the user's logon request --- typically the server with the
lightest load. See also NetLogon service.
logon validation: A process of verifying the
identities of users when they log on to the network.
logon workstations: The workstations from which a user
is allowed to log on.
maximum password age: The period of time a password
can be used before the system requires the user to change it. Set in
the account policy.
member server: A server in a domain that keeps and
uses a copy of the domain's user accounts database but does not
validate logon requests. See also backup domain
controller and primary domain controller.
message forwarding: The method used to reroute
messages from one client or server to another.
minimum password age: The period of time a password
must be used before the user can change it. Set in the account policy.
mount: To make a disk available as a shared disk to
users on a network.
named pipe: An interprocess communication mechanism
that allows one process to communicate with another local or remote
process.
NetLogon service: Performs authentication of domain
logons, and keeps the domain's database synchronized between the domain
controller and the other Advanced Servers of the domain.
NetBEUI: A network transport on the Advanced Server. The
term NetBEUI is derived from NETBIOS Extended User Interface.
NETBIOS: Network Basic I/O System interface device
driver and transport interface developed by Microsoft and IBM.
network: A group of servers, clients, and devices
connected to each other by communications lines in order to share
information and resources.
network adapter (or network controller or network interface
card): A combination of hardware, firmware, and software that
controls the transmission and reception of data between a workstation
or server and the network.
network controller: See network
adapter.
network directory: See shared
directory.
network path: The computer name of a server followed
by the share name of a shared resource and, optionally, a relative
path. See also Universal Naming Convention.
node: An individual computer, such as a server or
client, that can communicate with other computers in a network.
NOS: Network Operating System. See
Advanced Server.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |