![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 19 July 1999 | |
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
Allows a process to associate (map) a section of its address space with either a specified section of a file (a disk file section) or specified physical addresses represented by page frame numbers (a page frame section). This service also allows the process to create either type of section and to specify that the section be available only to the creating process (private section) or to all processes that map to it (global section).
SYS$CRMPSC [inadr] ,[retadr] ,[acmode] ,[flags] ,[gsdnam] ,[ident] ,[relpag] ,[chan] ,[pagcnt] ,[vbn] ,[prot] ,[pfc]
int sys$crmpsc (struct _va_range *inadr, struct _va_range *retadr, unsigned int acmode, unsigned int flags, void *gsdnam, unsigned int relpag, unsigned short int chan, unsigned int pagcnt, unsigned int vbn, unsigned int prot,unsigned int pfc);
inadr
OpenVMS usage: address_range type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Starting and ending virtual addresses into which the section is to be mapped. The inadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses. Only the virtual page number portion of each virtual address is used to specify which pages are to be mapped; the low-order byte-within-page bits are ignored for this purpose.The interpretation of the inadr argument depends on the setting of SEC$M_EXPREG in the flags argument and on whether you are using an Alpha or a VAX system. The two system types are discussed separately in this section.
On Alpha systems, if you do not set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag, the inadr argument specifies the starting and ending virtual addresses of the region to be mapped. Addresses in system space are not allowed. The addresses must be aligned on CPU-specific pages; no rounding to CPU-specific pages occurs. The lower address of the inadr argument must be on a CPU-specific page boundary and the higher address of the inadr argument must be 1 less than a CPU-specific boundary, thus forming a range, from lowest to highest, of address bytes. You can use the SYI$_PAGE_SIZE item code in the $GETSYI system service to set the inadr argument to the proper values. You do this to avoid programming errors that might arise because of incorrect programming assumptions about page sizes.
If, on the other hand, you do set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag, indicating that the mapping should take place using the first available space in a particular region, the inadr argument is used only to indicate the desired region: the program region (P0) or the control region (P1).
Caution
Mapping into the P1 region is generally discouraged, but, if done, must be executed with extreme care. Since the user stack is mapped in P1, it is possible that references to the user stack might inadvertently read or write the pages mapped with $CRMPSC.When the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is set, the second inadr longword is ignored, while bit 30 (the second most significant bit) of the first inadr longword is used to determine the region of choice. If the bit is clear, P0 is chosen; if the bit is set, P1 is chosen. On Alpha systems, bit 31 (the most significant bit) of the first inadr longword must be 0. To ensure compatibility between VAX and Alpha systems when you choose a region, Compaq recommends that you specify, for the first inadr longword, any virtual address in the desired region.
In general, the inadr argument should be specified. However, it can be omitted to request a special feature: for permanent global sections, you can omit the inadr argument, or specify it as 0, to request that the section be created but not mapped. Such a request will be granted regardless of the setting of the SEC$M_EXPREG flag. However, to ensure compatibility between VAX and Alpha systems, Compaq recommends that the SEC$M_EXPREG flag be clear when the inadr argument is omitted.
On VAX systems, if you do not set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag, the inadr argument specifies the starting and ending virtual addresses of the region to be mapped. Addresses in system space are not allowed. If the starting and ending virtual addresses are the same, a single page is mapped.
Note
If the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is not set, Compaq recommends that the inadr argument always specify the entire virtual address range, from starting byte address to ending byte address. This ensures compatibility between VAX and Alpha systems.If, on the other hand, you do set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag, indicating that the mapping should take place using the first available space in a particular region, the inadr argument is used only to indicate the desired region: the program region (P0) or the control region (P1).
Caution
Mapping into the P1 region is generally discouraged, but, if done, must be executed with extreme care. Since the user stack is mapped in P1, it is possible that references to the user stack might inadvertently read or write the pages mapped with $CRMPSC.When the SEC$M_EXPREG flag is set, the second inadr longword is ignored, while bit 30 (the second most significant bit) of the first inadr longword is used to determine the region of choice. If the bit is clear, P0 is chosen; if the bit is set, P1 is chosen. On VAX systems, bit 31 (the most significant bit) of the first inadr longword is ignored. To ensure compatibility between VAX and Alpha systems when you choose a region, Compaq recommends that you specify, for the first inadr longword, any virtual address in the desired region.
In general, the inadr argument should be specified. However, it can be omitted to request a special feature: for permanent global sections, you can omit the inadr argument, or specify it as 0, to request that the section be created but not mapped. You must also ensure that SEC$M_EXPREG is not set in the flags argument. Omitting the inadr argument with SEC$M_EXPREG set is interpreted by VAX systems as a request to map with no region preference. This latter combination of argument settings is strongly discouraged, as the chosen region is indeterminate. To ensure compatibility between VAX and Alpha systems, Compaq recommends that the SEC$M_EXPREG flag be clear when the inadr argument is omitted.
retadr
OpenVMS usage: address_range type: longword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by reference--array reference
Starting and ending process virtual addresses into which the section was actually mapped by $CRMPSC. The retadr argument is the address of a 2-longword array containing, in order, the starting and ending process virtual addresses.On Alpha systems, the retadr argument returns starting and ending addresses of the usable range of addresses. This might differ from the total amount mapped. The retadr argument is required when the relpag argument is specified. If the section being mapped does not completely fill the last page used to map the section, the retadr argument indicates the highest address that actually maps the section. If the relpag argument is used to specify an offset into the section, the retadr argument reflects the offset.
acmode
OpenVMS usage: access_mode type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Access mode that is to be the owner of the pages created during the mapping. The acmode argument is a longword containing the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the four access modes.
Symbol Access Mode PSL$C_KERNEL Kernel PSL$C_EXEC Executive PSL$C_SUPER Supervisor PSL$C_USER User The most privileged access mode used is the access mode of the caller.
flags
OpenVMS usage: mask_longword type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Flag mask specifying the type of section to be created or mapped to, as well as its characteristics. The flags argument is a longword bit vector wherein each bit corresponds to a flag. The $SECDEF macro defines a symbolic name for each flag. You construct the flags argument by performing a logical OR operation on the symbol names for all desired flags. The following table describes each flag and the default value that it supersedes.
Flag Description SEC$M_GBL Pages form a global section. The default is private section. SEC$M_CRF Pages are copy-on-reference. By default, pages are shared. SEC$M_DZRO Pages are demand-zero pages. By default, they are not zeroed when copied. For page file sections, the default is demand zero. SEC$M_EXPREG Pages are mapped into the first available space. By default, pages are mapped into the range specified by the inadr argument. See the inadr argument description for a complete explanation of how to set the SEC$M_EXPREG flag.
SEC$M_WRT Pages form a read/write section. By default, pages form a read-only section. For page file sections, the default is writeable. SEC$M_PERM Global section is permanent. By default, global sections are temporary. SEC$M_PFNMAP Pages form a page frame section. By default, pages form a disk file section. Pages mapped by SEC$M_PFNMAP are not included in or charged against the process's working set; they are always valid. Do not lock these pages in the working set by using $LKWSET; this can result in a machine check if they are in I/O space. ++On Alpha systems, when the SEC$M_PFNMAP flag is set, the pagcnt and relpag arguments are interpreted in CPU-specific pages, not as pagelets.
SEC$M_SYSGBL Pages form a system global section. By default, pages form a group global section. SEC$M_PAGFIL Pages form a global page file section. By default, pages form a disk file section. SEC$M_PAGFIL also implies SEC$M_WRT and SEC$M_DZRO. SEC$M_EXECUTE Pages are mapped if the caller has execute access. This flag takes effect only (1) when specified from executive or kernel mode, (2) when the SEC$M_GBL flag is also specified, and (3) when SEC$M_WRT is not specified. By default $CRMPSC performs a read access check against the section. SEC$M_NO_OVERMAP Pages cannot overmap existing address space. Note that, by default, pages can overmap existing address space.
| OpenVMS usage: | section_name |
| type: | character-coded text string |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor |
For group global sections, the operating system interprets the UIC group as part of the global section name; thus, the names of global sections are unique to UIC groups.
| OpenVMS usage: | section_id |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The version number is in the second longword. The version number contains two fields: a minor identification in the low-order 24 bits and a major identification in the high-order 8 bits. You can assign values for these fields by installation convention to differentiate versions of global sections. If no version number is specified when a section is created, processes that specify a version number when mapping cannot access the global section.
The first longword specifies, in its low-order two bits, the matching criteria. The valid values, symbolic names by which they can be specified, and their meanings are as follows.
| Value/Name | Match Criteria |
|---|---|
| 0 SEC$K_MATALL | Match all versions of the section. |
| 1 SEC$K_MATEQU | Match only if major and minor identifications match. |
| 2 SEC$K_MATLEQ | Match if the major identifications are equal and the minor identification of the mapper is less than or equal to the minor identification of the global section. |
When a section is mapped at creation time, the match control field is ignored.
If you do not specify the ident argument or specify it as 0 (the default), the version number and match control fields default to 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
On Alpha systems, the relpag argument is interpreted as an index into the section file, measured in pagelets for a file-backed section or in CPU-specific pages for a PFN-mapped section.
On Alpha and VAX systems, you use this argument only for global sections. If you do not specify the relpag argument or specify it as 0 (the default), the global section is mapped beginning with the first virtual block in the file.
| OpenVMS usage: | channel |
| type: | word (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The file must have been accessed with the OpenVMS RMS macro $OPEN; the file options parameter (FOP) in the FAB must indicate a user file open (UFO keyword). The access mode at which the channel was opened must be equal to or less privileged than the access mode of the caller.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
On Alpha systems, the smallest allocation is an Alpha page, which is 8192 bytes. When requesting pagelets, the size requested is a multiple of 512 bytes, but the actual allocation is rounded to 8192. For example, when requesting 17 pagelets, the allocation is for two Alpha pages, 16384 bytes.
On Alpha systems, if the SEC$M_PFNMAP flag bit is set, the pagcnt argument is interpreted as CPU-specific pages, not as pagelets.
On Alpha and VAX systems, the specified page count is compared with the number of blocks in the section file; if they are different, the lower value is used. If you do not specify the page count or specify it as 0 (the default), the size of the section file is used. However, for physical page frame sections, this argument must not be 0.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
If you specified page frame number mapping (by setting the SEC$M_PFNMAP flag), the vbn argument specifies the CPU-specific page frame number where the section begins in memory.
Table SYS-6 shows which arguments are required and which are optional for three different uses of the $CRMPSC service.
| Argument | Create/Map Global Section |
Map Global1 Section |
Create/Map Private Section |
|---|---|---|---|
| inadr | Optional 2 | Required | Required |
| retadr | Optional | Optional | Optional |
| acmode | Optional | Optional | Optional |
| flags | |||
| SEC$M_GBL | Required | Ignored | Not used |
| SEC$M_CRF 3 | Optional | Not used | Optional |
| SEC$M_DZRO 3 | Optional | Not used | Optional |
| SEC$M_EXPREG | Optional | Optional | Optional |
| SEC$M_PERM | Optional 2 | Not used | Not used |
| SEC$M_PFNMAP | Optional | Not used | Optional |
| SEC$M_SYSGBL | Optional | Optional | Not used |
| SEC$M_WRT | Optional | Optional | Optional |
| SEC$M_PAGFIL | Optional | Not used | Not used |
| gsdnam | Required | Required | Not used |
| ident | Optional | Optional | Not used |
| relpag 3 | Optional | Optional | Not used |
| chan 3 | Required | Required | |
| pagcnt | Required | Required | |
| vbn 3 | Optional | Optional | |
| prot | Optional | Not used | |
| pfc 3 | Optional | Optional |
| OpenVMS usage: | file_protection |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The mask contains four 4-bit fields. Bits are read from right to left in each field. The following diagram depicts the mask.
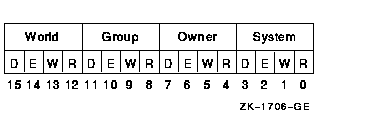
Cleared bits indicate that read, write, execute, and delete access, in that order, are granted to the particular category of user.
Only read, write, and execute access are meaningful for section protection. Delete access bits are ignored. Read access also grants execute access for those situations where execute access applies.
Protection is taken from the system or group global section template for page file or PFN global sections if the prot argument is not specified.
| OpenVMS usage: | longword_unsigned |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
On Alpha systems, this argument is not used for page file sections or physical page frame sections. The pfc argument is rounded up to CPU-specific pages. That is, at least 16 pagelets (on an Alpha system with an 8KB page size) will be mapped for each physical page. The system cannot map less than one physical page.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
| privacy and legal statement | ||
| 4527PRO_019.HTML | ||