|
Document revision date: 19 July 1999
|
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
OpenVMS RTL Library (LIB$) Manual
LIB$CRF_OUTPUT
The Output Cross-Reference Table Information routine extracts the
information from the cross-reference tables and formats the output
pages.
Note
No support for arguments passed by 64-bit address reference or for use
of 64-bit descriptors, if applicable, is planned for this routine.
|
Format
LIB$CRF_OUTPUT control-table ,output-line-width ,page1 ,page2
,mode-indicator ,delete-save-indicator
RETURNS
None.
Arguments
control-table
| OpenVMS usage: |
vector_longword_signed |
| type: |
longword integer (signed) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference, array reference |
Control table associated with the cross-reference. The
control-table argument is the address of an array
containing the control table. The table contains the address of the
user-supplied routine that prints the lines formatted by LIB$CRF_OUTPUT.
output-line-width
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_signed |
| type: |
longword integer (signed) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Width of the output line. The output-line-width
argument is the address of a signed longword integer containing the
width.
page1
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_signed |
| type: |
longword integer (signed) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Number of lines on the first page of the output. The
page1 argument is the address of a signed longword
integer containing this number. This allows the user to reserve space
to print header information on the first page of the cross-reference.
page2
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_signed |
| type: |
longword integer (signed) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Number of lines per page for the other pages. The
page2 argument is the address of a signed longword
integer containing this number.
mode-indicator
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_signed |
| type: |
longword integer (signed) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Output mode indicator. The mode-indicator argument is
the address of a signed longword integer containing the mode indicator.
This indicator allows the user to select which of three output modes is
desired.
| Output Mode |
Description |
|
CRF$K_VALUES
|
Only the value and key fields are to be printed. LIB$CRF_OUTPUT creates
multiple columns across the page. Each column consists of the KEY1,
KEY2, VAL1, and VAL2 fields. A minimum of one space between each column
is guaranteed.
|
|
CRF$K_VALS_REFS
|
Requests a cross-reference summary that has no column space saved for a
defining reference. If the user inserted a reference with the CRF$K_DEF
indicator, the entry is ignored.
|
|
CRF$K_DEFS_REFS
|
Requests a cross-reference summary with the first REF1 and REF2 fields
used only for definition references. If no definition reference is
provided, the fields are filled with spaces.
|
delete-save-indicator
| OpenVMS usage: |
longword_signed |
| type: |
longword integer (signed) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Delete/save indicator, which LIB$CRF_OUTPUT uses to determine whether
the table's built-in accumulating symbol information is to be saved or
deleted once the cross-reference is produced. The
delete-save-indicator argument is the address of a
signed longword integer containing the delete/save indicator.
The indicator can be either of the following:
|
CRF$K_SAVE
|
To preserve the tables for subsequent processing
|
|
CRF$K_DELETE
|
To delete the tables
|
Description
LIB$CRF_OUTPUT can format output lines for three types of
cross-reference listings:
- A summary of symbol names and their values, as shown in
Figure lib-2.
- A summary of symbol names, their values, and the names of modules
that refer to each symbol, as shown in Figure lib-3.
- A summary of symbol names, their values, the names of the defining
modules, and the names of those modules that refer to each symbol, as
shown in Figure lib-4.
Figure lib-2 Summary of Symbol Names and Values
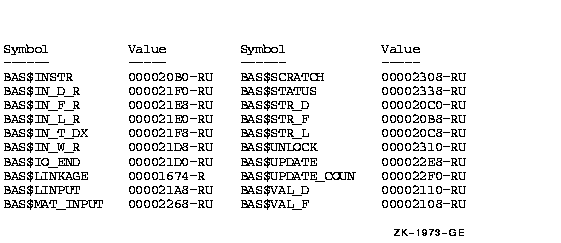
Figure lib-3 Summary of Symbol Names, Values, and Names of
Referring Modules
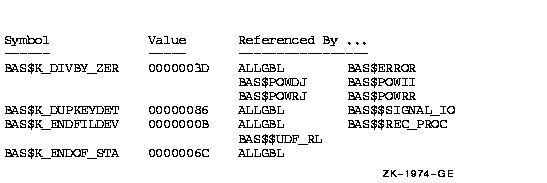
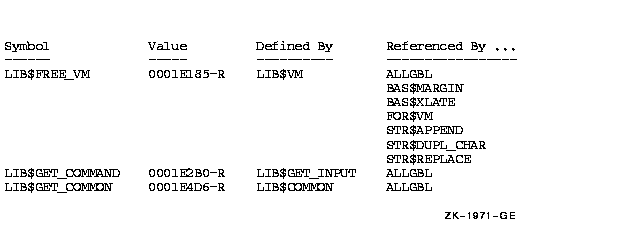
Figure lib-4 Summary Indicating Defining Modules
Regardless of the format of the output, LIB$CRF_OUTPUT considers the
output line as consisting of six different field types:
|
KEY1
|
Is the first field in the line. It contains a symbol name.
|
|
KEY2
|
Is the second field in the line. It contains a set of flags (for
example, -R) that provide information about the symbol.
|
|
VAL1
|
Is the third field in the line. It contains the value of the symbol.
|
|
VAL2
|
Is the fourth field in the line. It contains a set of flags describing
VAL1.
|
|
REF1 and REF2 fields
|
Within each REF1 and REF2 pair, REF1 provides a set of flags, and REF2
provides the name of a module that references the symbol.
|
Any of these fields can be omitted from the output.
For example:
Symbol Value Symbol Value
------ ----- ------ -----
BAS$INSTR 000020B0-RU BAS$SCRATCH 00002308-RU
KEY1 VAL1 VAL2 KEY1 VAL1 VAL2
Symbol Value Defined By Referenced By ...
------ ----- ---------- -----------------
LIB$FREE_VM 0001E185-R LIB$VM ALLGBL
KEY1 VAL1 VAL2 REF2 REF2
(CRF$K_DEF) (CRF$K_REF)
|
Condition Values Returned
None.
LIB$CURRENCY
The Get System Currency Symbol routine returns the system's currency
symbol.
Format
LIB$CURRENCY currency-string [,resultant-length]
RETURNS
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Arguments
currency-string
| OpenVMS usage: |
char_string |
| type: |
character string |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Currency symbol. The currency-string argument is the
address of a descriptor pointing to the currency symbol.
resultant-length
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Number of characters that LIB$CURRENCY has written into the
currency-string argument, not counting padding in the
case of a fixed-length string. The resultant-length
argument is the address of an unsigned word containing the length of
the currency symbol. If the input string is truncated to the size
specified in the currency-string argument,
resultant-length is set to this size. Therefore,
resultant-length can always be used by the calling
program to access a valid substring of currency-string.
Description
LIB$CURRENCY attempts to translate the logical name SYS$CURRENCY as a
process, group, or system logical name, in that order. If the
translation fails, the routine returns the United States currency
symbol ($). If the translation succeeds, the text produced is returned.
Thus, a system manager can define SYS$CURRENCY as a systemwide logical
name to provide a default for all users, and an individual user with a
special need can define SYS$CURRENCY as a process logical name to
override the system default.
For example, if you want to use the British pound sign (£) as the
currency symbol within your process but you want to leave the dollar
sign as the system's default, define SYS$CURRENCY to be the pound sign
in your process logical name table. After this, any call to
LIB$CURRENCY within your process returns the pound sign (£),
while any call outside your process returns the dollar sign ($).
Condition Values Returned
|
SS$_NORMAL
|
Routine successfully completed.
|
|
LIB$_FATERRLIB
|
Fatal internal error. An internal consistency check has failed. This
usually indicates an internal error in the Run-Time Library and should
be reported to your Digital support representative.
|
|
LIB$_INSVIRMEM
|
Insufficient virtual memory. Your program has exceeded the image quota
for virtual memory.
|
|
LIB$_INVSTRDES
|
Invalid string descriptor. A string descriptor has an invalid value in
its CLASS field.
|
|
LIB$_STRTRU
|
Successfully completed, but the currency string was truncated.
|
Example
|
10 !+
! This BASIC program uses LIB$CURRENCY to
! return the default system currency symbol.
!-
OUTLEN = 1
CALL LIB$CURRENCY (CURR$, OUTLEN)
PRINT CURR$
99 END
|
This BASIC program uses LIB$CURRENCY to display the system currency
symbol default. The output generated by the program is a dollar sign
($).
LIB$CVTF_FROM_INTERNAL_TIME
The Convert Internal Time to External Time (F-Floating-Point Value)
routine converts a delta internal OpenVMS system time into an external
F-floating time.
Format
LIB$CVTF_FROM_INTERNAL_TIME operation ,resultant-time ,input-time
RETURNS
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Arguments
operation
| OpenVMS usage: |
function_code |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The conversion to be performed. The operation argument
is the address of an unsigned longword specifying the operation. Valid
values for operation are the following:
| Operation |
Interpretation |
|
LIB$K_DELTA_WEEKS_F
|
Fractional weeks
|
|
LIB$K_DELTA_DAYS_F
|
Fractional days
|
|
LIB$K_DELTA_HOURS_F
|
Fractional hours
|
|
LIB$K_DELTA_MINUTES_F
|
Fractional minutes
|
|
LIB$K_DELTA_SECONDS_F
|
Fractional seconds
|
resultant-time
| OpenVMS usage: |
floating_point |
| type: |
F_floating |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The external time that results from the conversion. The
resultant-time argument is the address of an
F-floating-point value containing the result.
input-time
| OpenVMS usage: |
date_time |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Delta time to be converted. The input-time argument is
the address of an unsigned quadword containing the time.
Description
LIB$CVTF_FROM_INTERNAL_TIME converts a delta internal OpenVMS system
time into an external F-floating-point time. The
operation argument specifies the conversion.
LIB$_CVTF_FROM_INTERNAL_TIME converts the value of
input-time into one of the external formats listed in
the operation argument description.
LIB$_CVTF_FROM_INTERNAL_TIME then places the result into
resultant-time.
Condition Values Returned
|
LIB$_NORMAL
|
Routine successfully completed.
|
|
LIB$_DELTIMREQ
|
Delta time required but absolute time supplied.
|
|
LIB$_INVOPER
|
Invalid operation.
|
|
LIB$_IVTIME
|
Invalid time.
|
|
LIB$_WRONUMARG
|
Incorrect number of arguments.
|
LIB$CVTF_TO_INTERNAL_TIME
The Convert External Time to Internal Time (F-Floating-Point Value)
routine converts an external time interval into an OpenVMS internal
format F-floating delta time.
Format
LIB$CVTF_TO_INTERNAL_TIME operation ,input-time ,resultant-time
RETURNS
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Arguments
operation
| OpenVMS usage: |
function_code |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The conversion to be performed. The operation argument
is the address of an unsigned longword specifying the operation. Valid
values for operation are the following:
| Operation |
Interpretation |
|
LIB$K_DELTA_WEEKS_F
|
Fractional weeks
|
|
LIB$K_DELTA_DAYS_F
|
Fractional days
|
|
LIB$K_DELTA_HOURS_F
|
Fractional hours
|
|
LIB$K_DELTA_MINUTES_F
|
Fractional minutes
|
|
LIB$K_DELTA_SECONDS_F
|
Fractional seconds
|
input-time
| OpenVMS usage: |
varying_arg |
| type: |
F_floating |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Delta time to be converted. The input-time argument is
the address of this input time. The value you supply for
input-time must be greater than 0.
resultant-time
| OpenVMS usage: |
date_time |
| type: |
quadword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
The OpenVMS internal format delta time that results from the
conversion. The resultant-time argument is the address
of an unsigned quadword containing the result.
Description
LIB$CVTF_TO_INTERNAL_TIME converts an external time interval, such as
3.5 weeks, into an OpenVMS internal format F-floating delta time. The
operation argument specifies the conversion.
LIB$_CVTF_TO_INTERNAL_TIME converts the value of
input-time into one of the internal format delta times
listed in the operation argument description.
LIB$_CVTF_TO_INTERNAL_TIME then places the result into
resultant-time.
Condition Values Returned
|
LIB$_NORMAL
|
Routine successfully completed.
|
|
LIB$_INVOPER
|
Invalid operation.
|
|
LIB$_IVTIME
|
Invalid time.
|
|
LIB$_WRONUMARG
|
Incorrect number of arguments.
|
LIB$CVT_DX_DX
The General Data Type Conversion routine converts OpenVMS standard
atomic or string data described by a source descriptor to OpenVMS
standard atomic or string data described by a destination descriptor.
This conversion is supported over a subset of the OpenVMS standard data
types.
Format
LIB$CVT_DX_DX source-item ,destination-item
[,word-integer-dest-length]
RETURNS
| OpenVMS usage: |
cond_value |
| type: |
longword (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by value |
Arguments
source-item
| OpenVMS usage: |
unspecified |
| type: |
unspecified |
| access: |
read only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Source item to be converted by LIB$CVT_DX_DX. The
source-item argument is the address of a descriptor
pointing to the source item to be converted. The type of the item to be
converted is contained in the descriptor.
The combination of source descriptor class and data type is restricted
as described in Table lib-1 and Table lib-2.
destination-item
| OpenVMS usage: |
unspecified |
| type: |
unspecified |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by descriptor |
Destination of the conversion. The destination-item
argument is the address of a descriptor pointing to the destination
item. The destination descriptor specifies the data type to which the
source item is converted.
The combination of destination descriptor class and data type is
restricted as described in Table lib-1 and Table lib-2.
word-integer-dest-length
| OpenVMS usage: |
word_unsigned |
| type: |
word (unsigned) |
| access: |
write only |
| mechanism: |
by reference |
Length in bytes of the destination item (when that item is a string)
that has been converted by LIB$CVT_DX_DX, not including any space
filling. The word-integer-dest-length argument
contains the address of an unsigned word containing this length.
If the destination string is truncated, the returned length reflects
the truncation. This word can be used by the calling program to
determine if truncation has occurred or to extract the exact length of
the string when the string contains space filling.
Description
LIB$CVT_DX_DX is a universal conversion utility routine. Table lib-1
shows the complete matrix of data type and descriptor class
combinations (as specified in the fields of the descriptor) supported
by LIB$CVT_DX_DX.
Conversion is defined over three sets of data types: atomic, string,
and numeric byte data strings.
Although some of the functions of this routine may be found in other
Run-Time Library routines, LIB$CVT_DX_DX packages the conversion
functions with a general interface. Because of this general interface,
the calling program does not have to specify what conversion should be
done for which data type.
Refer to LIB$CVT_xTB if you want to convert the ASCII text
string representation of a decimal, hexadecimal, or octal number into a
binary representation.
The description of this routine has been divided into the following
parts:
For more information about numeric byte data strings, see the section
called Use of Numeric Byte Data Strings (NBDS). Although the set of data types in NBDS is actually
a subset of the atomic and string data types, the three sets are
mutually exclusive in this routine. For more information on the OpenVMS
atomic and string data types and the argument descriptor classes
supported by this routine, see the OpenVMS Calling Standard manual.
Table lib-1 OpenVMS Descriptor Class and Data Type Combinations Accepted by LIB$CVT_DX_DX
| |
Descriptor Class |
| DSC$K_DTYPE_yyy |
A |
D |
NCA |
S |
SD |
VS |
|
B
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
BU
|
NBDS
|
|
NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
|
D
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
F
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
FS
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
FT
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
G
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
H
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
L
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
LU
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
|
NL
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
NLO
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
NR
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
NRO
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
NU
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
NZ
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
P
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
Q
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
T
|
NBDS
|
NBDS
|
NBDS
|
NBDS
|
NBDS
|
|
|
VT
|
|
|
|
|
|
NBDS
|
|
W
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
WU
|
|
|
|
Non-NBDS
|
|
|
Invalid combinations are blank. Any source data can be converted into
any
other destination data as long as they are both represented by one of
the
valid combinations.
Note:
LIB
$CVT
_DX
_DX treats an array, described by a CLASS
_A
or CLASS
_NCA descriptor, as a character string. NBDS must have the format
defined in
Table lib-2
.
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)



![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)