![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 19 July 1999 | |
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
This chapter contains release notes pertaining to OpenVMS device
support on Alpha and VAX systems. Where appropriate, section headings
indicate whether specific notes contain Alpha-specific or VAX-specific
information.
6.1 Recompiling and Relinking OpenVMS Device Drivers
The following sections contain release notes pertaining to recompiling
and relinking OpenVMS device drivers.
6.1.1 Possible Per-Threads Security Impacts on Alpha Device Drivers
V7.2
Refer to Section 5.19.2.1 for information about possible per-thread
security impacts on OpenVMS Alpha device drivers.
6.1.2 Alpha and VAX SCSI Device Drivers
V7.2
All OpenVMS Alpha SCSI device drivers from previous versions of OpenVMS must be recompiled and relinked to run correctly on OpenVMS Version 7.2.
You must recompile and relink these drivers because OpenVMS Version 7.2 includes significant changes to SCSI data structures. These changes are needed in preparation for support of Fibre Channel as a SCSI interconnect. No source changes are required by these data structure changes.
If you have an OpenVMS Alpha SCSI driver that you are upgrading from a version prior to OpenVMS Alpha 7.0, see Section 6.1.3.
Note that for OpenVMS Version 7.1 all OpenVMS Alpha and VAX SCSI device
drivers required recompiling and relinking. OpenVMS VAX device drivers
that were recompiled and relinked to run on OpenVMS Version 7.1 will
run correctly on OpenVMS Version 7.2.
6.1.3 OpenVMS Alpha Device Drivers
V7.1
Device drivers that were recompiled and relinked to run on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 do not require source-code changes and do not have to be recompiled and relinked to run on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1 and later. (Note that Alpha SCSI drivers, however, must be recompiled and relinked as described in Section 6.1.2.)
Device drivers from releases prior to OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 that were not recompiled and relinked for OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 must be recompiled and relinked to run on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1 and later.
OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 included significant changes to OpenVMS Alpha
privileged interfaces and data structures. As a result of these
changes, device drivers from releases prior to OpenVMS Alpha Version
7.0 might also require source-code changes to run correctly on OpenVMS
Alpha Version 7.0 and later. For more details about OpenVMS Alpha
Version 7.0 changes that may require source changes to customer-written
drivers, see the OpenVMS Alpha Guide to Upgrading Privileged-Code Applications.
6.2 Restriction: Parallel SCSI Support for Logical Unit Numbers
V7.2
OpenVMS supports up to eight Logical Unit Numbers (LUNs) LUNs per target ID on a parallel SCSI bus.
The SCSI-2 standard is limited to eight LUNs, but the SCSI-3 standard recently increased to 64 LUNs. The HSZ80 is the only supported device that implements more than eight LUNs (it supports 32 LUNs per target ID). This feature cannot be used in the current release of OpenVMS. LUN values on OpenVMS must be in the range 0-7.
This restriction may be removed in a future release of the operating
system. This restriction does not apply to Fibre Channel.
6.3 Selective Autoconfiguration Unsupported in Some SCSI Configurations
V7.2
OpenVMS Alpha provides SYSMAN commands that allow system managers to specify which devices will be autoconfigured. This can be specified permanently, so that it is applied at each system boot or for the duration of a manual autoconfiguration command, using the following qualifiers:
SYSMAN> IO SET/EXCLUDE=(device_name) SYSMAN> IO AUTOCONFIGURE/EXCLUDE=(device_name) and/or /SELECT=(device_name) |
These commands cannot be used selectively to autoconfigure SCSI device names that include a port allocation class or device names that have an HSZ allocation class. The commands also cannot be used for Fibre Channel devices. This restriction applies to class-driver devices only (DK, MK, DG). Selective autoconfiguration can be used for all SCSI and Fibre Channel port-driver devices (PK, PG, and FG).
This restriction also applies to OpenVMS Version 7.1 systems that use
port allocation classes.
6.4 Changed Behavior of IO$_SKIPFILE Function
V7.2
The performance of the IO$_SKIPFILE function was significantly improved in OpenVMS Version 7.1 for certain SCSI tape drives. The new IO$_SKIPFILE implementation functions correctly with all built-in OpenVMS tape functions such as INIT, MOUNT, BACKUP, and COPY when tapes are formatted according to the ANSI Standard X3.27-1987. This is the default tape standard for OpenVMS.
Higher performance for the IO$_SKIPFILE function is requested with the modifier (IO$M_ALLOWFAST). When the IO$M_ALLOWFAST modifier is used, IO$_SKIPFILE stops at the end of data rather than at double filemarks. For more information about the IO$M_ALLOWFAST modifier, refer to the OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
In OpenVMS Version 7.2, SKIPFILE support is implemented through a
standard DCL interface, making the old SYS$ETC:MKSET.TXT and
SYS$ETC:MKSET.EXE files obsolete. Refer to the OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual for
details about using the DCL interface.
6.5 CRCTX Routines Enhanced (Alpha Only)
V7.1-2
The system routines that can be used to manage the Counted Resource Context Block (CRCTX) data structure have been improved. The following routines now set and check the status (CRCTX$V_ITEM_VALID) of the CRCTX data structure:
These routines have changed as follows:
If you call IOC$DEALLOC_CRCTX with a valid CRCTX status (CRCTX$V_ITEM_VALID set to 1), the service returns a bad status. If the SYSBOOT parameter SYSTEM_CHECK is set, the system will crash. This prevents users from deallocating a CRCTX when they have valid resources that have not been deallocated.
You must call IOC$ALLOC_CNT_RES with an invalid CRCTX status (CRCTX$V_ITEM_VALID set to 0). If you call this routine with a valid status, OpenVMS assumes that you will lose the resources mapped by this CRCTX. OpenVMS does not allocate new resources and returns a bad status. If SYSTEM_CHECK is set, the system will crash. IOC$ALLOC_CNT_RES sets the valid bit before it returns.
IOC$DEALLOC_CNT_RES must be called with a valid CRCTX (CRCTX$V_ITEM_VALID set to 1). If you call IOC$DEALLOC_CNT_RES with an invalid CRCTX, OpenVMS assumes that the other parameters are not valid, and returns a bad status. If SYSTEM_CHECK is set, the system will crash. IOC$DEALLOC_CNT_RES clears the valid bit before it returns.
IOC$LOAD_MAP must be called with a valid CRCTX. If it is called with an invalid CRCTX (CRCTX$V_ITEM_VALID set to 0), it assumes that the other parameters are also invalid, and returns a bad status. If the SYSBOOT parameter SYSTEM_CHECK is set, the system will crash.
These improvements indicate to device support and privileged-code
application developers whether they need to deallocate scatter gather
registers, which are treated by OpenVMS as generic resources. If the
CRCTX$V_ITEM_VALID bit is set, IOC$DEALLOC_CNT_RES still needs to be
called.
6.6 New Values for Length Parameter in System Routines (Alpha Only)
V7.1-2
The following system routines called by OpenVMS Alpha device drivers have new values for the length parameter:
The two new length values (IOC$K_BYTE and IOC$K_WORD) allow byte and word data to be passed in right-aligned fashion. Table 6-1 shows the accepted values for the length parameter.
| Value (hex) | Keyword |
|---|---|
| 1 | IOC$K_BYTE_LANED |
| 2 | IOC$K_WORD_LANED |
| 4 | IOC$K_LONGWORD |
| 8 | IOC$K_QUADWORD |
| 100 | IOC$K_BYTE |
| 200 | IOC$K_WORD |
IOC$K_BYTE_LANED and IOC$K_WORD_LANED lane bytes in the following way:
IOC$K_BYTE_LANED (1) byte-laned byte
Depending on bits <1:0> of the address, the byte resides in a longword in one of the following lanes:
+---+---+---+---+ | | | | X | bits <1:0> = 0 +---+---+---+---+ +---+---+---+---+ | | | X | | bits <1:0> = 1 +---+---+---+---+ +---+---+---+---+ | | X | | | bits <1:0> = 2 +---+---+---+---+ +---+---+---+---+ | X | | | | bits <1:0> = 3 +---+---+---+---+ |
The driver must use the low 2 bits of the address to select the correct byte.
IOC$K_WORD_LANED (2) byte-laned word
Depending on bits <1:0> of the address, the word resides in a longword in one of the following locations.
+---+---+---+---+ | | | XXXXX | bits <1:0> = 0 +---+---+---+---+ +---+---+---+---+ | | XXXXX | | bits <1:0> = 1 +---+---+---+---+ +---+---+---+---+ | XXXXX | | | bits <1:0> = 2 +---+---+---+---+ |
The driver must use the low 2 bits of the address to select the correct word.
However, if IOC$K_BYTE and IOC$K_WORD are used, the data is always right-aligned:
IOC$K_BYTE (hex 100) right-aligned byte
The byte is always in the right-most lane:
+---+---+---+---+ | | | | X | bits <1:0> = 0,1,2,3 +---+---+---+---+ |
Note that the high-order byte contains unpredictable data and must be masked to operate correctly.
IOC$K_WORD (hex 200) right-aligned word
The word is always in the right-most lane:
+---+---+---+---+ | | | XXXXX | bits <1:0> = 0,1,2 +---+---+---+---+ |
Note that the high-order word contains unpredictable data and must be masked to operate correctly.
By using the new values for the length parameter, programmers who write
device drivers no longer have to put data into the correct lanes before
writes and after reads.
6.7 Memory Barriers Required in Drivers for DMA (Alpha Only)
V7.1-2
The two ways that the architecture of 21264 processors improves performance is by executing instructions out of order and by executing code sequences ahead of the actual location of the code. This can affect any interprocess communications, including communications with DMA devices. Code that executed successfully on previous hardware implementations might fail on 21264 processors and on future Alpha processors.
The Alpha Architecture Reference Manual, Third Edition describes rules for communicating using shared memory between CPUs and devices. The rules have not changed for 21264 processors, but the possibility for ordering problems has increased.
The problem exists primarily in device drivers that perform DMA reads when both of the following conditions occur:
For example:
Device: Write DATA
Logical MB (logical memory barrier)
Write FLAG (perhaps memory queue pointer,
memory location, or CSR bit)
Driver: Read FLAG
If FLAG, Read/Use DATA
else exit Interrupt Service Routine
Loop to Read flag
|
In this example, the LOGICAL MB in the device may actually be a CSR read from the device. The problem in the driver is that a memory barrier instruction must exist in the code between the read of the flag and the use of the data. This has always been the case in interprocessor communications, but it may have been omitted by drivers that communicate with devices.
In previous releases, the driver probably would not have seen old DATA after seeing the flag due to the ordering rules for PCI and cache coherency.
With 21264 processors, speculative execution may have progressed past the Read FLAG and speculatively prefetched the DATA, while waiting for the FLAG to be loaded. If there was no explicit dependency between the DATA and the FLAG and if the FLAG was found to be set, then the potentially older DATA that was prefetched may be used. Decisions may have been already made based on the presumed contents.
A memory barrier between the read of the FLAG and the Read/Use of the DATA places an explicit barrier to speculation. Such a barrier also forces the ordering of the FLAG and DATA.
Using LOCK/DEVICELOCK will not ensure that a memory barrier is placed in the code. In addition, a memory barrier in a subroutine call between the Read FLAG and the Read/Use of the DATA will not prevent speculation. The memory barrier must be in line. The same issue can occur (but probably less frequently) in sending data to a device that uses shared memory. In this case, the code must place a memory barrier between the writing of the DATA and the writing of the FLAG. This rule is a requirement for correct ordering in device drivers that communicate with devices through shared memory. |
V7.1
Support for using the SYS$MANAGER:ISA_CONFIG.DAT file to configure ISA
devices will be discontinued in a future release of OpenVMS Alpha. If
you use this file, you should convert to using the ISACFG utility from
the console and using the new file-based autoconfiguration method for
loading device drivers (as described in Writing OpenVMS Alpha
Device Drivers in C).
6.9 Required Change in ISA_CONFIG.DAT on AlphaStation 200/400
V7.1
Customers configuring ISA devices on AlphaStation 200/400 Family systems must change their SYS$MANAGER:ISA_CONFIG.DAT file, so that the node information for each device appears at the end of each device description block.
For upgrades from OpenVMS Version 6.2 or 7.0 systems, this change must be made before starting the upgrade procedure. |
For example, prior to OpenVMS Version 7.1, the following device description block:
[AUA0]
NAME=AU
NODE=3
DRIVER=SYS$MSBDRIVER
IRQ=9
DMA=(0,1)
PORT=(388:4,530:8)
|
would be changed as follows:
[AUA0]
NAME=AU
DRIVER=SYS$MSBDRIVER
IRQ=9
DMA=(0,1)
PORT=(388:4,530:8)
NODE=3
|
Customers using SYS$MANAGER:ISA_CONFIG.DAT files should read
Section 6.8.
6.10 Naming Serial Line Devices on Alpha Systems
V7.1
OpenVMS has changed the way it handles the second serial port on the following Alpha systems:
If one of these systems is booted with the console environment variable set to graphics, the name of the serial line (COM1) will be different from that in previous releases. The COM1 device is called TTB0 instead of OPA1. In this case, the COM1 device is controlled by SYS$YSDRIVER instead of SYS$OPDRIVER.
If the console is set to serial, the COM1 device is called OPA0.
6.11 Memory Holes on AlphaServer 4100 Systems
V7.1
Physical memory holes might exist on AlphaServer 4100 systems. As illustrated in Figure 6-1, there are three different sizes of memory daughter card pairs: 512 MB, 256 MB, and 128 MB. In accordance with AlphaServer 4100 systems configuration rules, memory card pairs must be arranged in descending order of size.
The AlphaServer 4100 hardware reads the first set of memory daughter cards and assumes that any memory card pairs that follow are the same size. Memory holes occur because memory card pairs following the first set of cards read by the hardware might not be the same size. As shown in Figure 6-1, the hole at 3000.0000 must be dealt with by OpenVMS. The hole at 4800.0000 is at the top of the address space and can be ignored by OpenVMS.
Previous versions of OpenVMS Alpha did not efficiently support systems with physical memory holes and ultimately led to an inefficient use of system memory. The memory management data structures in OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1 and later have been slightly modified to recognize the memory holes. As a result, inefficiencies in previous versions of the OpenVMS Alpha operating system have been eliminated. |
Figure 6-1 Example Memory Diagram
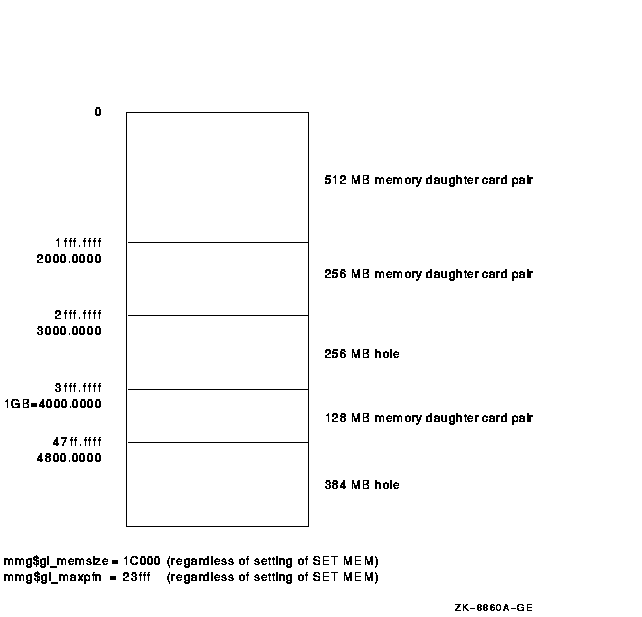
Note that this configuration impacts the algorithm used to determine whether a driver needs to use map registers. In releases prior to OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1, device drivers do the following:
The mmg$gl_memsize global cell does not contain the memory hole. As a result, the system has only 7/8 GB of memory, but according to the algorithm in releases prior to OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1, it appears that the device can use the direct DMA window. Yet there is 128 MB of memory beyond the 1 GB border, which requires that the drivers use map registers. To eliminate this problem, drivers using the algorithm in releases prior to OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1 must substitute it with the following algorithm:
int dma_size;
int pages;
status = IOC$NODE_DATA (crb, IOC$K_DIRECT_DMA_SIZE, &dma_size);
/* dma_size contains the number of megabytes.
* convert number of megabytes to bytes.
*/
dma_size = dma_size * (1024 * 1024);
/* Convert number of bytes to number of pages by
* dividing by number of bytes per page.
*/
pages = dma_size / MMG$GL_PAGE_SIZE;
|
The driver for the Microsoft Windows Sound System ISA sound card (MSB), SYS$MSBDRIVER, has been removed from the OpenVMS Alpha distribution as of Version 7.0. The following files have been removed:
An enhanced version of this driver, called MMOV$MSBDRIVER, is included in Multimedia Services Version 2.0 for OpenVMS Alpha. This layered product also includes support for video capture and playback, an enhanced version of DECsound, and other audio and video applications.
MMOV$MSBDRIVER provides the same $QIO programming interface as
SYS$MSBDRIVER. Compaq recommends that the WAVE Applications Programming
Interface provided by Multimedia Services for OpenVMS be used instead
because it is more flexible and is portable to other platforms.
(Multimedia Services Version 2.0 for OpenVMS is described in SPD
64.24.00.)
6.13 Device IPL Setup for OpenVMS Alpha Drivers
V6.2
Alpha hardware platforms that support PCI, EISA, and ISA buses deliver I/O device interrupts at different IPLs, either 20 or 21. The IPL at which device interrupts are delivered can change if you move the device from one platform to another. This is a problem if the driver declares its device IPL to be 20, and then that driver is executed on a machine that delivers I/O device interrupts at IPL 21.
The simplest solution to this problem is for PCI, EISA, and ISA device drivers to use IPL 21. This works correctly on platforms that deliver I/O device interrupts at IPL 20 and on platforms that deliver I/O device interrupts at IPL 21.
A future release of OpenVMS Alpha may provide a platform-independent
mechanism for drivers to determine the device IPL dynamically.
6.14 AlphaStation 255: PCI Configuration Restriction
V7.1
The OpenVMS Alpha operating system does not support PCI option cards configured in PCI slot 0 on any AlphaStation 255 series systems.
PCI slot 0 is the lowest physical PCI option slot on AlphaStation 255
series systems. The interrupt signal for this slot is shared with the
built-in Ethernet port. Because the OpenVMS Alpha operating system does
not currently permit PCI devices to share an interrupt line, a PCI
device installed in slot 0 will not function correctly or might cause
errors to occur with the built-in Ethernet port. As a result of this
restriction, AlphaStation 255 series systems support a maximum of two
PCI option cards, configured in slot 1 and slot 2.
6.15 Recommendation for RZ25M and RZ26N Disk Drives (Alpha)
V7.1
During the testing of Compaq supported SCSI disk drives on configurations with DWZZAs and long differential SCSI buses, two drives (RZ25M and RZ26N) were found to have bus phase problems. For this reason, these drives are not recommended for use in configurations where the differential bus length connecting DWZZAs equals or exceeds 20 meters.
This recommendation applies only to the RZ25M and RZ26N drives. All
other disk drives, listed as supported in the OpenVMS SPD, may be used
in configurations to the full bus lengths of the SCSI-2 specification.
6.16 SCSI Controller Restriction on AlphaServer 2100 Systems
The Adaptec 1740/1742 SCSI controller (PB2HA--SA) is not supported on AlphaServer 2100 systems having more than 1 gigabyte (GB) of memory. If the controller is connected to such a system, the following message appears on the operator's console:
%PKJDRVR-E- PKX0, Port is going OFFLINE. |
The following sections relate to SCSI firmware support.
6.17.1 Recommended Firmware Support for RZ26N and RZ28M Disks
V6.2---1H3
The minimum firmware revision level recommended for RZ26N and RZ28M disks is Revision 0568.
If the latest firmware revision level is not used with these disks,
multiple problems may occur.
6.17.2 Required Firmware for Multihost Use of RZ26L and RZ28 Disks
V6.2
If you install RZ26L or RZ28 disks on a multihost SCSI bus in an OpenVMS Cluster, the disk's minimum firmware revision is 442.
The following sections describe a procedure that can be used to update the firmware on some RZ26L and RZ28 drives. This procedure can only be used with drives that are directly connected to a SCSI adapter on a host system. Drives that are attached through an intelligent controller (such as an HSZ40 or KZPSC) cannot be updated using this procedure. Refer to the intelligent controller's documentation to determine whether an alternative firmware update procedure exists.
Only certain RZ26L and RZ28 firmware revisions can be safely upgraded to firmware revision level 442. Refer to Section 6.17.2.1 to determine if your disks are capable of being upgraded to firmware revision level 442. If your disk is capable of supporting firmware revision level 442, use the RZTOOLS Utility that is described in Section 6.17.2.2 to update the disk's firmware. |
Only the combinations of disk drives and firmware revision levels listed in Table 6-2 are capable of being upgraded safely to firmware revision level 442. Performing the update procedure on any other combination can permanently damage the disk.
| Disk Drive | Firmware Revision | Disk File Name |
|---|---|---|
| RZ26L | 440C | RZ26L_442D_DEC.FUP |
| RZ28 |
441C or D41C
435 or 436 |
RZ28_442D_DEC2104.FUP
RZ28P4_442C_DEC.FUP |
If you determine that your disk requires revision level 442 firmware and it is capable of being upgraded safely, use the following procedure to update the firmware. (See Table 6-2 for the file name of the disk you are upgrading.)
$ MCR SYS$ETC:RZTOOLS_ALPHA DKB500 /LOAD=SYS$ETC:filename.FUP Read in 262144 bytes. Current FW version - X440C Upgrading to - DEC0 Loading code ...... New code has been sent to the drive. |
V6.2
The following sections describe OpenVMS Alpha SCSI class and port
device driver restrictions.
6.18.1 Add-On SCSI Adapters
V6.2
Version 6.2 and later of OpenVMS Alpha supports various add-on SCSI adapters. Compaq's AlphaGeneration platforms typically support one or more integral SCSI adapters, with the option of installing additional add-on SCSI adapters. Due to differences in device-naming conventions used between the Alpha console and OpenVMS, the OpenVMS device name may not match the name displayed by the console.
For example, the console designation for a SCSI device on the integral SCSI adapter may be DKA100. However, when two additional add-on SCSI adapters are added, the "A" designation becomes "C"; and DKA100 appears as DKC100 when OpenVMS is running.
Note that although the console and OpenVMS device names may be
different, the unique specification of a device name from the console
to the device name under OpenVMS stays consistent, provided add-on SCSI
adapters are not added or removed.
6.18.2 SCSI Disk I/O Performance Degradation for KZMSA XMI and Adaptec 1742A Adapters
V6.2
As a result of the SCSI-2 Tagged Command Queuing (TCQ) support in OpenVMS Alpha Version 6.2, Compaq has determined that customers with KZMSA XMI to SCSI and Adaptec 1742A adapters might experience a 20% SCSI disk I/O performance degradation because TCQ is not implemented for these adapters. The performance degradation is in the area of increased CPU cost per I/O. Customers running at less than maximum CPU utilization under OpenVMS Alpha Version 6.1 might not experience any degradation under OpenVMS Alpha Version 6.2.
Compaq does not expect this situation to significantly affect DEC 7000 customers planning to upgrade to DEC 8000 Family systems using KZMSA adapters because the speed of those processors should offset the performance degradation. However, DEC 7000 customers who upgrade to OpenVMS Alpha Version 6.2 will experience the SCSI I/O disk performance degradation.
Compaq expects that this will significantly affect existing DEC 2000
Model 300 systems customers that use the Adaptec 1742A SCSI adapter.
6.19 OpenVMS Alpha Device Support Documentation
As of OpenVMS Version 7.2, the Writing OpenVMS Alpha Device Drivers in C manual no longer ships with the OpenVMS documentation set. The latest revision of this manual will be available from Digital Press in February 1999.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
| privacy and legal statement | ||
| 6534PRO_015.HTML | ||