| Previous | Contents | Index |
The Configuration Manager lets you specify the security model that the server imposes at file access level, as follows:
| If you choose... | The server uses... |
|---|---|
| Advanced Server Only | A security model in which only network permissions are checked. This is the default. |
| Advanced Server and OpenVMS | A security model in which both network permissions and OpenVMS protections are checked. |
For more information about the security models, see Section 4.1.2,Advanced Server Security Models.
To select the server security model, on the Advanced Configuration
Parameters screen, select either Advanced Server Only or Advanced
Server and OpenVMS.
7.1.5.7 Saving Advanced Configuration Parameter Changes
You can save the Advanced Configuration Parameters you have modified, or you can quit without saving your changes.
To save advanced configuration parameters changes, on the Advanced Configuration Parameters screen, select the OK button. If any setting is not appropriate, the Configuration Manager displays an Information screen (as shown in Figure 7-5, Information Screen. If all the settings are appropriate, the Basic Configuration Parameters screen reappears.
To ignore advanced configuration parameters changes, on the Advanced
Configuration Parameters screen, select the Cancel
button or press [Ctrl/Z]. The Basic Configuration Parameters
screen reappears.
7.1.6 Configuring Transports
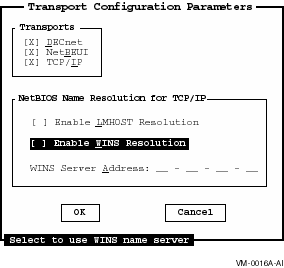
The Transport Configuration Parameters screen allows you to specify the types of transports that are enabled on the server, and the type of wide-area network capabilities, if any. To change the transport parameters, select the Tranports command button on the Basic Configuration Parameters screen. The Transport Configuration Parameters screen appears, as shown in Figure 7-3, Transport Configuration Parameters Screen.
Figure 7-3 Transport Configuration Parameters Screen
The transport configuration parameters are described in the the
following sections.
7.1.6.1 Enabling and Disabling Transports
The Configuration Manager lets you enable or disable one or more of the following transports: DECnet, NetBEUI, TCP/IP. For more information on transports and the protocols they support, see Appendix B, Network Protocols.
To enable and disable a transport, on the Transport Configuration
Parameters screen, select the transport names. The transport is enabled
if the check box contains an X.
7.1.6.2 Selecting NetBIOS Name Resolution
The Configuration Manager lets you select name resolution for wide-area network support with LMHOSTS and WINS name resolution.
For additional procedures required in order to set up wide-area networking, refer to the Advanced Server for OpenVMS Server Installation and Configuration Guide.
To enable or disable LMHOSTS, on the Transport Configuration Parameters screen, select Enable LMHOSTS Resolution. The checkbox contains an X when LMHOSTS Resolution is enabled.
To enable or disable WINS name resolution, on the Transport Configuration Parameters screen, select Enable WINS Resolution. The check box contains an X when WINS name resolution is enabled.
When WINS name resolution is enabled, you must supply the TCP/IP address for the WINS server.
To supply the TCP/IP address for the WINS server, on the Transport Configuration Parameters screen:
You can save the changes you have made to the transport configuration, or you can quit without saving your changes.
To save transport configuration parameter changes, on the Transport Configuration Parameters screen, choose the OK command button. If any setting is not appropriate, the Configuration Manager displays an Information screen, as shown in Figure 7-5, Information Screen. If all the settings are appropriate, the Basic Configuration Parameter screen reappears.
To ignore transport configuration parameter changes, on the Transport
Configuration Parameters screen, choose the Cancel
command button, or press [Ctrl/Z]. The Basic Configuration
Parameters screen reappears.
7.1.7 Verifying and Saving the New Configuration
When you verify the configuration, the Configuration Manager determines whether the new configuration can be supported.
To verify the new configuration, on the Basic Configuration Parameters screen, select the Verify command button.
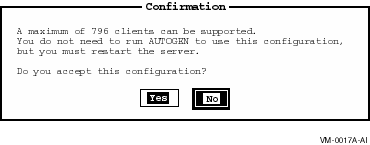
If the configuration can be supported, the Configuration Manager displays a Confirmation screen that allows you to accept or reject the new configuration. The Confirmation screen also tells you whether the server must be restarted for the new settings to take effect, or if AUTOGEN or reboot will be necessary to use the new configuration.
Figure 7-4 Confirmation Screen
If the configuration cannot be supported, or requires AUTOGEN or reboot, the Configuration Manager displays an Information screen, as shown in Figure 7-5, Information Screen, which allows you to view the configuration log file for details.
Figure 7-5 Information Screen

To view the log file, select the View Log File button. The log file shows the OpenVMS SYSGEN parameter changes required to support the new configuration, or why the configuration cannot be supported at all.
To dismiss the Information screen, select the OK
button.
7.1.8 Navigating the Configuration Manager Using a Keyboard
You can control the Configuration Manager using a mouse or using keys on the keyboard. Using the mouse, you can navigate through the Configuration Manager screens by pointing and clicking on the desired item to select (highlight) items in the menus, scroll boxes, or dialog boxes. (You must have a DECterm window or equivalent emulator.) Table 7-2, Keys for Controlling the Configuration Manager, lists the keys you use to control the action of the Configuration Manager.
| To... | Do the following... |
|---|---|
| Access the menu bar | Press F10, or press PF1 twice. Use the Tab key to select the first item on the menu bar. |
| Move from one menu to another | Use the left and right arrow keys. |
| Point to a menu item | Use the up and down arrow keys. |
| Select a menu item within a menu | Use the up and down arrow keys, then press the [Enter] or [Return] key. |
| Select a menu or an item within a menu | Move to the menu or menu item, then press the [Enter] or [Return] key. |
| Exit the menu bar | Press [Ctrl/Z]. |
| Point to buttons and items in a dialog box | Press the [Tab] key to advance, and [PF1] [Tab] to back up. |
| Move within a set of buttons or check boxes | Use the arrow keys. |
| Choose among a set of options (radio buttons) | Advance to the currently selected option button using [Tab] or [PF1] [Tab]. Then use the arrow keys to choose a new option within the set. |
| Change the state of a check box (on or off) | Advance to the check box, then press the space bar to toggle the state of the box. |
| Press a command button | Advance to the button and press the space bar or the [Return] key. This executes the button's command. |
| Enter new text | Advance to the edit box using [Tab] or [PF1] [Tab], and enter the new text. Any previous text is erased. |
| Edit text or edit text in a text box | Advance to the text box using [Tab] or [PF1] [Tab]. Use the arrow keys to move within existing text. |
| Refresh the display at any time | Press [Ctrl/W]. |
| Save any changes made in a dialog box, and return to the previous dialog box | Select the OK command button. |
| Discard any changes made in a dialog box and return to the Basic Configuration parameters screen. | Select the Cancel command button, or press [Ctrl/Z], or select Quit from the Options menu on the Basic Configuration Parameters screen. |
7.2 Managing Server Configuration Parameters
The Advanced Server software relies on the OpenVMS Registry to store and
reference server configuration parameters. (For information about
managing the OpenVMS Registry, refer to the OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.)
In previous versions of the server software (for example, PATHWORKS for OpenVMS servers), the LANMAN.INI file is used to store server parameters. Advanced Server stores these parameters in the OpenVMS Registry, which is similar to the Windows NT Registry. If you are upgrading a system from PATHWORKS V6 for OpenVMS (Advanced Server) to Advanced Server for OpenVMS, the parameters and settings in the existing LANMAN.INI file are migrated to registry parameters when you run the PWRK$CONFIG.COM initial configuration procedure, as described in the Advanced Server for OpenVMS Server Installation and Configuration Guide.
With Advanced Server for OpenVMS, server parameters are stored in the OpenVMS
Registry. The server parameters described in Appendix A, Server Configuration Parameters, are
available for modification.
7.2.1 OpenVMS Registry Overview
The OpenVMS Registry, like the Windows NT Registry, is a single
cluster-wide hierarchical database of configuration information about
hardware and software (including both the operating system and
applications). The OpenVMS Registry is accessible from Windows NT
applications as well as from OpenVMS utilities and Advanced Server
utilities.
7.2.1.1 Registry Architecture
Both the Windows NT and the OpenVMS Registry contain keys and values:
The OpenVMS Registry contains two predefined roots of keys:
Parameters defining the configuration of the Advanced Server are stored in the key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE. Each server parameter and the key under which it is defined is listed in Appendix A, Server Configuration Parameters.
Figure 7-6, Example Keys to Advanced Server Registry Parameters, shows the registry architecture on OpenVMS as displayed by the Windows NT registry editor.
Figure 7-6 Example Keys to Advanced Server Registry Parameters
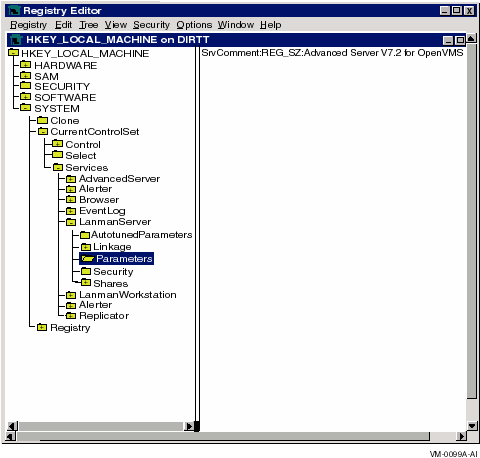
The selected key, Parameters, contains the SrvComment value, which defines a text string that is broadcast to identify the Advanced Server.
For more information about the server configuration parameters and data
that may be associated with them, see Appendix A, Server Configuration Parameters.
7.2.1.2 The Registry Server
The OpenVMS Registry Server starts automatically when the Advanced Server
is started. The Registry Server must be running in order for the
Advanced Server to run. If the Registry Server is not running when you
initially configure the Advanced Server or when the Advanced Server is
started, the Advanced Server attempts to start the Registry Server. For
more information about configuring and starting the Registry Server,
refer to the OpenVMS Alpha V7.2 Upgrade and Installation Guide.
7.2.2 Registry Parameters
Server parameters are stored in the OpenVMS Registry when you configure the Advanced Server. A parameter is stored in the registry only if the data associated with the parameter is changed from the supplied default setting. A server parameter is stored in the OpenVMS Registry when:
You can manage server parameters in the OpenVMS Registry using any one of a number of utilities and tools, depending on the way you manage the Advanced Server software.
Managing the Registry from a Windows NT Computer
You can manage Advanced Server software remotely, from a Window NT computer running Windows NT Server software. Windows NT provides two registry editor utilities: REGEDT32 and REGEDIT. Use the REGEDT32 application to display and modify server parameters. For more information about using REGEDT32, refer to the Window NT product documentation. (The REGEDIT utility does not provide security and cannot be used to modify the OpenVMS Registry. Refer to the Windows NT documentation for more information.)
When you access the OpenVMS Registry from a network client, the connection is based on network user authentication. Therefore, you must be logged on to the network in order to access the registry from a network client. If you are using Windows NT REGEDT32 to modify server parameters, you must be logged on as Administrator.
To access the server parameters in the OpenVMS Registry:
Figure 7-6, Example Keys to Advanced Server Registry Parameters, provides an example of the REGEDT32 display.
Managing the Registry from OpenVMS
If you are managing the Advanced Server from the OpenVMS system (using a workstation or terminal emulator), you can use either the the OpenVMS system registry control program (REG$CP) or the PWRK$REGUTL utility supplied with the Advanced Server.
Compaq recommends that you use PWKR$REGUTL to manage server
configuration parameters, because it has built-in knowledge of keys and
values used by the Advanced Server, including the attributes of the data,
such as minimum, maximum, and default values. The following sections
describe how to manage server configuration parameters using the
PWRK$REGUTL utility.
7.2.3 Using the PWRK$REGUTL Utility
The PWKR$REGUTL utility is available for you to use after you install the Advanced Server software. The program is found at:
SYS$SYSTEM:PWRK$REGUTL.EXE |
If your process has included the Advanced Server command definitions in the PWRK$DEFINE_COMMANDS.COM file, or if you have defined the REGUTL command, you can start the PWRK$REGUTL utility by entering the REGUTL command. To define the REGUTL command and start the utility, enter the following commands at the OpenVMS command prompt:
$ REGUTL :== $SYS$SYSTEM:PWRK$REGUTL.EXE $ REGUTL REGUTL> |
The PWRK$REGUTL utility responds by displaying the REGUTL> prompt.
To use PWRK$REGUTL to access the OpenVMS Registry, your process must have one of the following:
The PWRK$REGUTL utility has a command line user interface that is compatible with OpenVMS DCL command conventions.
When you use the PWRK$REGUTL utility, the Registry Server must be
running on the OpenVMS system. However, the Advanced Server need not be
running. This allows you to modify server configuration parameters
before the Advanced Server is started.
7.2.3.1 How to Exit PWRK$REGUTL
To exit the PWRK$REGUTL utility, enter the EXIT command in response to the REGUTL> prompt. For example:
REGUTL> EXIT $ |
The PWRK$REGUTL program includes complete online help, displaying the PWRK$REGUTL commands, qualifiers, and parameters. The following sections describe some common operations performed with PWRK$REGUTL. For example, display the online help as follows:
The PWRK$REGUTL utility is provided with Advanced Server for OpenVMS
for setting and modifying server configuration parameters. Refer to
the Advanced Server for OpenVMS Server Administrator's Guide for more
information about using this utility.
You can get more help by entering any of the following commands:
CREATE KEYS DELETE KEY
DELETE KNOWN KEYS DELETE KNOWN VALUES
DELETE VALUE EXIT
HELP SET MODE
SET VALUE SHOW MODE
SHOW VALUE
Topic?
REGUTL>
|
This example shows the top-level help, listing the possible commands.
The help file displays further information about specific commands when
you enter the command name after the Topic? prompt.
7.2.3.3 PWRK$REGUTL Commands
The PWRK$REGUTL commands and the purpose of each is described in Table 7-3.
| Command Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
| CREATE KEYS | Creates all the server parameter keys in the registry. For use by authorized software specialists only. |
| DELETE KEY | Deletes the specified key from the registry. The key will not be deleted if it contains any values or subkeys. |
| DELETE KNOWN KEYS | Deletes all known keys from the registry. A key will not be deleted if it contains any values or subkeys. |
| DELETE KNOWN VALUES | Deletes all known server parameter values from the registry. |
| DELETE VALUE | Deletes the specified value from the registry. |
| EXIT | Exits the PWRK$REGUTL utility. |
| HELP | Displays information about the PWRK$REGUTL commands. |
| SET MODE | Specifies the syntax mode to be used for displaying and specifying server parameter value names. |
| SET VALUE | Sets the data in the registry for the named value. |
| SHOW MODE | Displays information about the current syntax mode. |
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |