![[Compaq]](../../images/hp.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/hp_ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 15 July 2002 | |
![[Compaq]](../../images/hp.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/hp_ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
If the command procedure report described in Section 15.6 shows AUTOGEN's calculations are different from the current values, correct the tuning by executing AUTOGEN with one of the two following commands:
$ @SYS$UPDATE:AUTOGEN GETDATA REBOOT FEEDBACK |
$ @SYS$UPDATE:AUTOGEN GETDATA SETPARAMS FEEDBACK |
Compaq recommends that you use AUTOGEN to modify system parameters. For more information, see Section 15.5. To view system parameters for a group of nodes or change parameters temporarily, use the System Management utility (SYSMAN). |
SYSMAN provides the ability to inspect and modify system parameters for an entire cluster or for any group of nodes, rather than just one system. The PARAMETERS commands available in SYSMAN duplicate the parameter functions of the System Generation utility (SYSGEN).
You can use SYSMAN to manage system parameters as follows:
| Task | For More Information |
|---|---|
| Show parameter values | Section 15.7.2 |
| Modify current values in the parameter file | Section 15.7.3 |
| Modify active values on a running system 1 | Section 15.7.4 |
SYSMAN provides the commands and functions shown in Table 15-3.
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| PARAMETERS SHOW | Displays parameter values. Requires the name of the parameter. |
| PARAMETERS USE | Reads a set of parameters from memory or disk into the work area for inspection or modification. Requires a file name or the additional parameters ACTIVE or CURRENT. |
| PARAMETERS SET | Changes parameter values only in the work area; more permanent modification requires the PARAMETERS WRITE command. Requires the name and value of the parameter. |
| PARAMETERS WRITE | Writes the content of the work area to memory or to disk. Requires a file name or the additional parameters ACTIVE or CURRENT. |
For more information about the temporary work area, see the next
section.
15.7.1 Understanding Parameter Values and SYSMAN
It helps to understand the different system parameter values explained in Section 15.1.1. Briefly, current values are stored in the default parameter file on disk. Active values are stored in memory and are used while the system is running. In addition to these values, SYSMAN writes a temporary copy into its own work area on disk. Figure 15-2 illustrates these different sets of values and how SYSMAN commands affect them. In this figure:
Figure 15-2 SYSMAN Temporary, Active, and Current Parameter Values
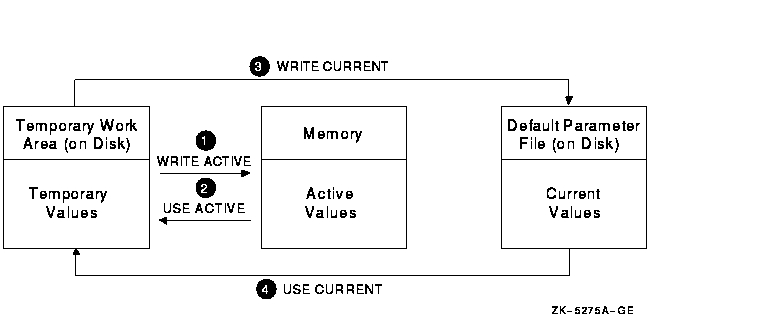
During a typical session, you can display and change values in the following sequence:
For a list of all the system parameters, refer to the OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.
15.7.2 Showing Parameter Values with SYSMAN
Use the SYSMAN command PARAMETERS SHOW to display parameter values for all the nodes in a cluster.
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:SYSMAN SYSMAN> PARAMETERS SHOW/LGI Parameters in use: Active Parameter Name Current Default Min. Max. Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TERM 0 1 0 1 Boolean D LGI_BRK_DISUSER 0 0 0 1 Boolean D LGI_PWD_TMO 30 30 0 255 Seconds D LGI_RETRY_LIM 3 3 0 255 Tries D LGI_RETRY_TMO 20 20 0 255 Seconds D LGI_BRK_LIM 5 5 0 255 Failures D LGI_BRK_TMO 300 300 0 -1 Seconds D LGI_HID_TIM 300 300 0 -1 Seconds D |
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:SYSMAN SYSMAN> SET ENVIRONMENT/CLUSTER %SYSMAN-I-ENV, Current command environment: Clusterwide on local cluster Username MORIN will be used on nonlocal nodes SYSMAN> PARAMETERS SHOW LGI_BRK_TMO Node NODE21: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 600 300 0 -1 Seconds D Node NODE22: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 600 300 0 -1 Seconds D |
Use the SYSMAN command PARAMETERS WRITE to write system parameter values and the name of the site-independent startup command procedure to your choice of parameter file or the current system parameter file on disk.
The PARAMETERS WRITE CURRENT command sends a message to OPCOM to record the event, unless you have changed the system message format with the DCL command SET MESSAGE.
The PARAMETERS WRITE CURRENT command writes all of the active or current parameter values---not just the one you may be working on---to disk. |
SYSMAN> PARAMETERS WRITE SYS$SYSTEM:NEWPARAM |
SYSMAN> PARAMETERS SET LGI_BRK_TMO 300 SYSMAN> PARAMETERS WRITE CURRENT |
Using the SYSMAN commands PARAMETERS SET, PARAMETERS WRITE, and PARAMETERS USE enables you to modify active parameter values.
Modifying active values immediately affects dynamic parameters by changing their values in memory. Appendix C of the OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual identifies dynamic parameters, as does the SYSMAN command PARAMETERS SHOW/DYNAMIC. Values for nondynamic parameters cannot be changed while the system is running.
Modifying active values does not affect current values in the system parameter file on disk, because the next time you boot the system, the values on disk are established as the active values.
If you set new active parameter values and you want to use the new values for subsequent boot operations, write the new values to the current parameter file with the PARAMETERS WRITE CURRENT command, as shown in the Examples section.
Parameter values modified with SYSMAN will be overridden by the AUTOGEN command procedure. To keep parameter modifications made with SYSMAN, edit the file SYS$SYSTEM:MODPARAMS.DAT as explained in Section 15.5.1 to specify the new parameter values. |
SYSMAN> PARAMETERS SET LGI_BRK_TMO 300 SYSMAN> PARAMETERS WRITE ACTIVE SYSMAN> PARAMETERS SHOW LGI_BRK_TMO Node NODE21: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 300 300 0 -1 Seconds D Node NODE22: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 300 300 0 -1 Seconds D |
SYSMAN> PARAMETERS USE CURRENT SYSMAN> PARAMETERS SHOW LGI_BRK_TMO Node NODE21: Parameters in use: CURRENT Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 600 300 0 -1 Seconds D Node NODE22: Parameters in use: CURRENT Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 600 300 0 -1 Seconds D |
SYSMAN> PARAMETERS WRITE ACTIVE SYSMAN> PARAMETERS USE ACTIVE SYSMAN> PARAMETERS SHOW LGI_BRK_TMO Node NODE21: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 600 300 0 -1 Seconds D Node NODE22: Parameters in use: ACTIVE Parameter Name Current Default Minimum Maximum Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- LGI_BRK_TMO 600 300 0 -1 Seconds D |
Compaq recommends that you use AUTOGEN to modify system parameters. For more information, see Section 15.5. If for some reason you cannot use AUTOGEN, Compaq recommends that you use SYSMAN. For more information, see Section 15.7. |
Although it is not the recommended method, you can also use the System Generation utility (SYSGEN) to manage system parameters as follows:
| Task | For More Information |
|---|---|
| Show parameter values | Section 15.8.2 |
| Modify current values in the default parameter file | Section 15.8.3 |
| Modify active values on a running system 1 | Section 15.8.4 |
| Create a new parameter file | Section 15.8.5 |
SYSGEN provides the commands shown in Table 15-4 for managing system parameters. Refer to the SYSGEN section of the OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual for detailed descriptions of SYSGEN commands.
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| SHOW | Displays parameter values. |
| USE | Reads a set of values from memory or disk into a temporary work area for inspection or modification. |
| SET | Changes parameter values only in the work area; more permanent modification requires the WRITE command. |
| WRITE | Writes the content of the work area to memory or to disk. |
For more information about the temporary work area, see the next
section.
15.8.1 Understanding Parameter Values and SYSGEN
You should understand the different system parameter values explained in Section 15.1.1. Briefly, current values are stored in the default parameter file on disk. Active values are stored in memory and are used while the system is running. In addition to these values, SYSGEN writes a temporary copy into its own work area on disk. Figure 15-3 illustrates these different sets of values and shows how SYSGEN commands affect them.
Figure 15-3 SYSGEN Temporary, Active, and Current Parameter Values

In a typical session, you might display and change values in the following sequence:
For a list of all the system parameters, refer to the OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.
15.8.2 Showing Parameter Values with SYSGEN
To display values for system parameters, perform the following steps:
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:SYSGEN |
| To Display | Enter |
|---|---|
| Active values | USE ACTIVE |
| Current values | USE CURRENT |
| Values from another parameter file | USE file-spec |
| For file-spec, specify the parameter file from which you want to display values; for example, USE SYS$SYSTEM:ALTPARAMS.DAT |
|
SHOW [/qualifier] [parameter-name] |
Specify qualifiers to display parameters grouped by type. For
example:
| To Display Values For | Enter |
|---|---|
| The WSMAX parameter | SHOW WSMAX |
| All dynamic parameters | SHOW/DYNAMIC |
| All parameters in the TTY category | SHOW/TTY |
| All parameters | SHOW/ALL |
For more information about the SYSGEN SHOW command and qualifiers, refer to the SYSGEN section of the OpenVMS System Management Utilities Reference Manual.
The following example uses SYSGEN to show the current values of all TTY system parameters:
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:SYSGEN SYSGEN> USE CURRENT SYSGEN> SHOW/TTY |
Parameters in use: Current(1) Parameter Name Current Default Min. Max. Unit Dynamic -------------- ------- ------- ------- ------- ---- ------- (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) TTY_SCANDELTA 10000000 10000000 100000 -1 100Ns TTY_DIALTYPE 0 0 0 255 Bit-Encode TTY_SPEED 15 15 1 16 Special TTY_RSPEED 0 0 0 16 Special TTY_PARITY 24 24 0 255 Special TTY_BUF 80 80 0 65535 Characters TTY_DEFCHAR 402657952 402657952 0 -1 Bit-Encode TTY_DEFCHAR2 135178 4098 0 -1 Bit-Encode TTY_TYPAHDSZ 78 78 0 -1 Bytes TTY_ALTYPAHD 2048 200 0 32767 Bytes TTY_ALTALARM 750 64 0 -1 Bytes TTY_DMASIZE 64 64 0 -1 Bytes D (8) TTY_CLASSNAME "TTY" "TTY" "AA" "ZZ" Ascii TTY_SILOTIME 8 8 0 255 Ms TTY_TIMEOUT 3600 900 0 -1 Seconds D TTY_AUTOCHAR 7 7 0 255 Character D SYSGEN> |
SYSGEN displays the following information:
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_comments.gif)
|
| privacy and legal statement | ||
| 6017PRO_070.HTML | ||