![[Compaq]](../../images/hp.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/hp_ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 15 July 2002 | |
![[Compaq]](../../images/hp.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/hp_ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
Figure 1-5 shows the format of the record attributes area.
Figure 1-5 ACP-QIO Record Attributes Area
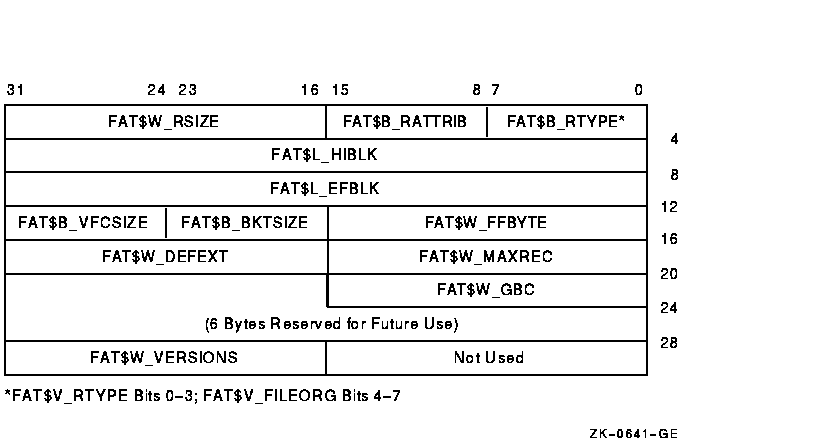
Table 1-9 lists the record attributes values and their meanings.
| Field Value | Meaning | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAT$B_RTYPE | Record type. Contains FAT$V_RTYPE and FAT$V_FILEORG. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$V_RTYPE |
Record type. The following bit values are defined:
|
||||||||||||||
| FAT$V_FILEORG |
File organization. The following bit values are defined:
|
||||||||||||||
| FAT$B_RATTRIB |
Record attributes. The following bit values are defined:
|
||||||||||||||
| FAT$W_RSIZE | Record size in bytes. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$L_HIBLK 2 |
Highest allocated VBN. The ACP maintains this field when the file is
extended or truncated. Attempts to modify this field in a write
attributes operation are ignored.
|
||||||||||||||
| FAT$L_EFBLK 2 3 |
End-of-file VBN
|
||||||||||||||
| FAT$W_FFBYTE 3 | First free byte in FAT$L_EFBLK. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$B_BKTSIZE | Bucket size in blocks. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$B_VFCSIZE | Size in bytes of fixed-length control for VFC records. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$W_MAXREC | Maximum record size in bytes. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$W_DEFEXT | Default extend quantity. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$W_GBC | Global buffer count. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$W_VERSIONS | Default version limit; valid only if the file is a directory. |
Figure 1-6 shows the format of the attributes statistics block. Table 1-10 lists the contents of this block.
Figure 1-6 ACP--QIO Attributes Statistics Block

| Field | Subfields | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| SBK$L_STLBN | Contains the starting LBN of the file if the file is contiguous. If the file is not contiguous, this field contains a value of 0. The LBN appears as an inverted longword (the high- and low-order 16 bits are transposed for PDP-11 compatibility). The following subfields are defined: | |
| SBK$W_STLBNH | Starting LBN (high-order 16 bits) | |
| SBK$W_STLBNL | Starting LBN (low-order 16 bits) | |
| SBK$L_FILESIZE | Contains the size of the file in blocks. The file size appears as an inverted longword (the high- and low-order 16 bits are transposed for PDP-11 compatibility). The following subfields are defined: | |
| SBK$W_FILESIZH | File size (high-order 16 bits) | |
| SBK$W_FILESIZL | File size (low-order 16 bits) | |
| SBK$B_ACNT 1 | Access count (low byte). Field is for PDP-11 compatibility. | |
| SBK$B_LCNT 1 | Lock count (low byte). Field is for PDP-11 compatibility. | |
| SBK$L_FCB | System pool address of the file's file control block. | |
| SBK$W_ACNT 1 | Access count (number of channels with file open currently). | |
| SBK$W_LCNT 1 | Lock count (the number of access operations that have locked the file against writers). | |
| SBK$W_WCNT 1 | Writer count (the number of channels that currently have the file open for write). | |
| SBK$W_TCNT 1 | Truncate lock count (the number of access operations that have locked the file against truncation). | |
| SBK$L_READS | Number of read operations executed for the file on this channel. | |
| SBK$L_WRITES | Number of write operations executed for the file on this channel. |
The following sections describe the operation of the major ACP
functions. Each section describes the required and optional parameters
for a particular function, as well as the sequence in which the
function is performed. For clarity, when a major function invokes a
subfunction, the input parameters used by the subfunction are omitted.
1.6.1 Create File
Create file is a virtual I/O function that creates a directory entry or a file on a disk device, or a file on a magnetic tape device.
The following is the function code:
The following are the function modifiers:
The following are the device- or function-dependent arguments for IO$_CREATE:
Table 1-11 lists fields in the FIB that are applicable to the IO$_CREATE operation.
| Field | Subfields | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| FIB$L_ACCTL | Specifies field values that control access to the file. The following bits are applicable to the IO$_CREATE function: | |
| FIB$V_REWIND | Set to rewind magnetic tape before creating the file. Any data currently on the tape is overwritten. | |
| FIB$V_CURPOS | Set to create magnetic tape file at the current tape position. (Note: a magnetic tape file is created at the end of the volume set if neither FIB$V_REWIND nor FIB$V_CURPOS is set.) If the tape is not positioned at the end of a file, FIB$V_CURPOS creates a file at the next file position. Any data currently on the tape past the current file position is overwritten. | |
| FIB$V_WRITETHRU | Specifies that the file header is to be written back to the disk. If not specified and the file is opened, writing of the file header can be deferred to some later time. | |
| FIB$W_CNTRLFUNC | Specifies the following value, which allows you to control actions subsequent to EOT detection on a magnetic tape file. | |
| FIB$W_FID | Contains the file ID of the file created or entered. | |
| FIB$W_DID | Contains the file identifier of the directory file. | |
| FIB$W_NMCTL | Controls the processing of the file name in a directory operation. The following bits are applicable to the IO$_CREATE function: | |
| FIB$V_NEWVER | Set to create a file of the same name with the next higher version number. Only for disk devices. | |
| FIB$V_SUPERSEDE | Set to supersede an existing file of the same name, type, and version. Only for disk devices. | |
| FIB$V_LOWVER | Set on return if a lower numbered version of the file exists. Only for disk devices. | |
| FIB$V_HIGHVER | Set on return if a higher numbered version of the file exists. Only for disk devices. | |
| FIB$W_VERLIMIT | Specifies the version limit for the directory entry created. Used only for disk devices and only when the first version of a new file is created. If 0, the directory default is used. If a directory operation was performed, FIB$W_VERLIMIT always contains the actual version limit of the file. | |
| FIB$L_ACL_STATUS | Status of the requested ACL attribute operation, if any. The ACL attributes are included in Table 1-7. If no ACL attributes are given, SS$_NORMAL is returned here. |
If the modifier IO$M_CREATE is specified, a file is created. The file ID of the file created is returned in FIB$W_FID. If the modifier IO$M_DELETE is specified, the file is marked for deletion.
If a nonzero directory ID is specified in FIB$W_DID, a directory entry is created. The file name specified by parameter P2 is entered in the directory, together with the file ID in FIB$W_FID. ( Section 1.3.1.1 describes the format for the file name string.) Wildcards are not permitted. Negative version numbers are treated as equivalent to a 0 version number. If a result string buffer and length are specified by P3 and P4, the actual file name entered, and its length, are returned.
The version number of the file receives the following treatment:
The file name string entered in the directory is returned using the P3 and P4 result string parameters, if present. The file name string is also written into the header. If no directory operation was requested (FIB$W_DID is 0), the file name string specified by P2, if any, is written into the file header.
If an attribute list is specified by P5, a write attributes subfunction is performed (see Section 1.3.5).
If the modifier IO$M_ACCESS is specified, the file is opened (see Section 1.3.2).
If the extend enable bit FIB$V_EXTEND is specified in the FIB, an extend subfunction is performed (see Section 1.3.3).
Finally, if a file was set aside for deletion (IO$M_DELETE is specified), that file is deleted. If the file is deleted because the FIB$V_SUPERSEDE bit was set, the alternate success status SS$_SUPERSEDE is returned in the I/O status block. If the file is deleted because the version limit was exceeded, the alternate success status SS$_FILEPURGED is returned.
If an error occurs in the operation of an IO$_CREATE function, all
actions performed to that point are reversed (the file is neither
created nor changed), and the error status is returned to the user in
the I/O status block.
1.6.1.3 Directory Entry Creation
Creating a new version of a file eliminates default access to the
previously highest version of the file. For example, creating
RESUME.TXT;4 masks RESUME.TXT;3 so the DCL command TYPE RESUME.TXT
yields the contents of version 4, not version 3. To protect the
contents of the earlier version of a file, the creator of a file must
have write access to the previous version of a file of the same name.
1.6.1.4 Magnetic Tape ACP Operation
No operation is performed unless the IO$M_CREATE modifier is specified. The magnetic tape is positioned as specified by FIB$V_REWIND and FIB$V_CURPOS, and the file is created. The name specified by the P2 parameter is written into the file header label.
If P5 specifies an attribute list, a write attributes subfunction is performed (see Section 1.3.5).
If the modifier IO$M_ACCESS is specified, the file is opened (see
Section 1.3.2).
1.6.2 Access File
This virtual I/O function searches a directory on a disk device or a magnetic tape for a specified file and accesses that file if found.
The following is the function code:
The following are the function modifiers:
The following are the device- or function-dependent arguments for IO$_ACCESS:
Table 1-12 lists FIB fields that are applicable to the IO$_ACCESS operation.
| Field | Subfields | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| FIB$W_CNTRLFUNC | Specifies the value that allows the user to control actions subsequent to EOT detection on a magnetic tape file. | |
| FIB$W_VERLIMIT | Receives the version limit for the file. Applicable only if FIB$W_DID is a nonzero number (if a directory lookup is done). Used only for disk devices. | |
| FIB$L_ACL_STATUS | Status of the requested ACL attribute operation, if any. The ACL attributes are included in Table 1-7. If no ACL attributes are given, SS$_NORMAL is returned here. (For Files-11 C/D, this field is always set to SS$_NORMAL.) | |
| FIB$L_STATUS | Alternate access status. The following bits are supported: | |
| FIB$V_ALT_REQ | Set to indicate whether the alternate access bit is required for the current operation. If not set, the alternate access bit is optional. | |
| FIB$V_ALT_GRANTED | If FIB$V_ALT_REQ = 0 and the alternate access check succeeded, the FIB bit returned from the file system is set. | |
| FIB$L_ALT_ACCESS | A 32-bit mask that represents an access mask to check against file protection; for example, to open a file for read and to check whether it can be deleted. The mask has the same configuration as the standard protection mask. |
If a nonzero directory file ID is specified in FIB$W_DID, a lookup subfunction is performed (see Section 1.3.1.) The version limit of the file found is returned in FIB$W_VERLIMIT.
If the directory search fails with a "file not found" condition and the IO$M_CREATE function modifier is specified, the function is reexecuted as a CREATE. In that case, the argument interpretations for IO$_CREATE, rather than those for IO$_ACCESS, apply.
If IO$M_ACCESS is specified, an access subfunction is performed to open the file (see Section 1.3.2).
If P5 specifies an attribute list, a read attributes subfunction is performed (see Section 1.3.5).
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_comments.gif)
|
| privacy and legal statement | ||
| 6136PRO_003.HTML | ||