![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 10 November 2000 | |
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
Sometimes a Bookreader search generates error messages. When Bookreader encounters errors during a search, it displays all the error messages in the Search Messages Box at the conclusion of the search.
This feature is not available on all operating systems. If your version of Bookreader has an active Link menu in each window, then you can use the features described in this section. |
Bookreader supports LinkWorks features. Through the Link menu, you can make and follow links between pieces of information (linkable objects). The linked information can be another Bookreader object or an object accessed by any other application that supports LinkWorks.
Bookreader's linkable objects are:
For example, you can link the title of a book to a section of the same book or another book. You can link a section of a book to a Cardfiler card or a Calendar timeslot. However, you cannot link a sentence or word within a paragraph to anything.
For information about linking Bookreader objects, choose Help Mode from the Help menu. When the pointer changes to a question mark, click on the Link menu.
To exit Bookreader, choose Exit from the Library window's File menu.
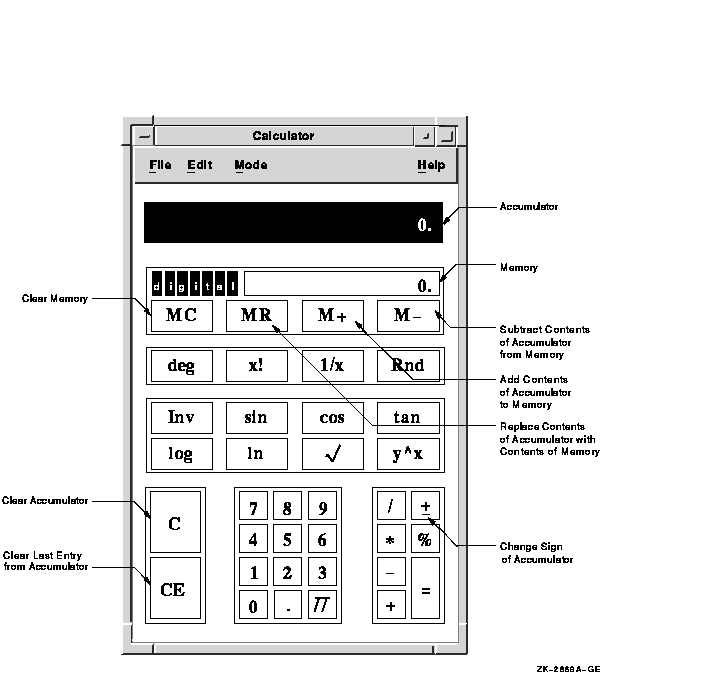
Calculator performs simple arithmetic functions---addition, subtraction, multiplication, division---and computes percentages and square roots. In addition, Calculator also performs trigonometric and inverse trigonometric functions, generates random numbers, and performs other more advanced operations.
Unlike a handheld calculator, DECwindows Motif Calculator has two displays. The top display is the accumulator, which shows the number being entered or the current result, and the bottom display is the memory.
This chapter describes how to
To start Calculator, choose Calculator from the Session Manager's Applications menu. Calculator, in decimal mode, appears on your screen. You can move and change the size of the calculator window.
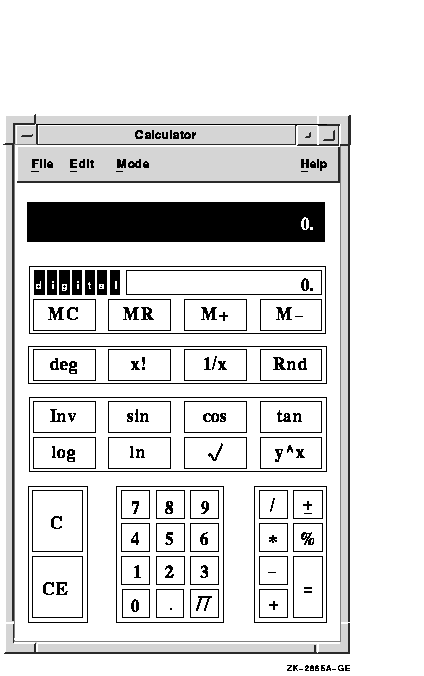
To change Calculator to hexadecimal mode, choose Hexadecimal from the Mode menu. Calculator, in hexadecimal mode, appears on your screen.
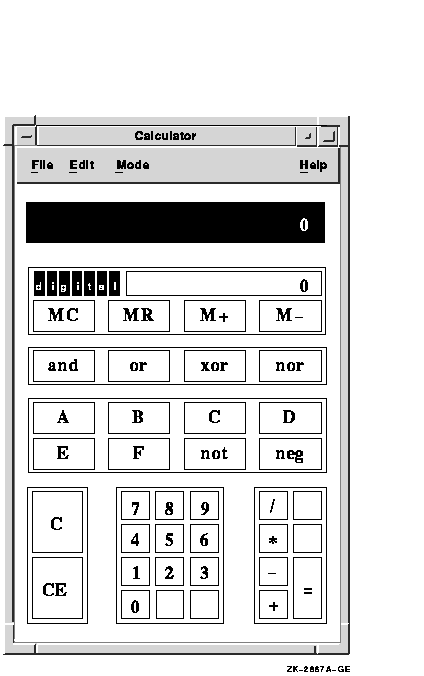
To change Calculator to octal mode, choose Octal from the Mode menu. Calculator, in octal mode, appears on your screen.
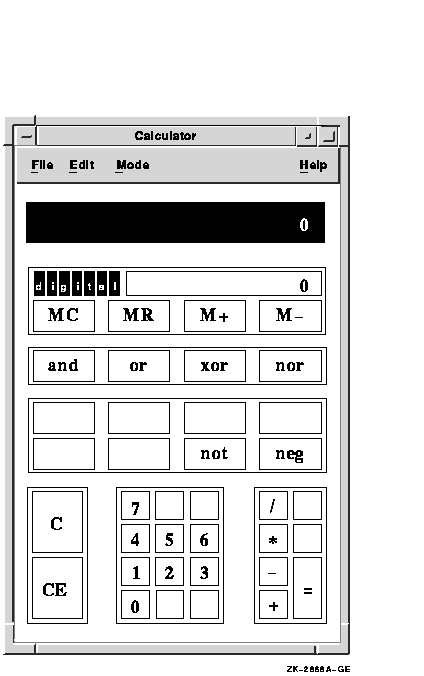
You can use Calculator with either the mouse or the keyboard.
| Keyboard Key | Keypad or Special-Function Key |
Produces |
|---|---|---|
| All Modes | ||
| 0--9 | 0--9 |
Numbers 0--9
(0--7 in octal mode) |
| / | PF2 | / |
| * | PF1 | * |
| -- | -- | -- |
| + | , | + |
| = | Enter | = |
| MC | Ctrl+F4 | MC |
| MR | Ctrl+F5 | MR |
| M+ | Ctrl+F6 | M+ |
| M-- | Ctrl+F7 | M-- |
| Decimal Mode | ||
| . | . | . |
| P | Pi sign | |
| N | PF3 | +/- |
| % | PF4 | % |
| C | Shift+F1 | Clear |
| E | Shift+F2 | Clear Entry |
| D | Ctrl+F8 | deg (switches the trigonometric argument type: deg, rad, or grad) |
| ! | Ctrl+F9 | x! (x factorial) |
| ~ | Ctrl+F10 | 1/x |
| R | Ctrl+F11 | Rnd |
| I | Shift+F3 | Inv (switches sin, cos, and tan to the inverse) |
| S | Shift+F4 | sin (sine) |
| O | Shift+F5 | cos (cosine, or arccosine if Inv is on) |
| T | Shift+F6 | tan (tangent, or arctangent if Inv is on) |
| LO | Shift+F7 | log (or 10 to x if Inv is on) |
| LN | Shift+F8 | ln (or e to x if Inv is on) |
| Q | Shift+F9 | <surd symbol> |
| ^ | Shift+F10 | y^x (or y to the 1/x if Inv is on) |
| Hexadecimal and Octal Modes | ||
| & | Ctrl+F8 | and |
| | | Ctrl+F9 | or |
| ^ | Ctrl+F10 | xor |
| Ctrl+F11 | nor | |
| ~ | Shift+F9 | not |
| ! | Shift+F10 | neg |
| C | Shift+F1 | Clear. Octal key. |
| E | Shift+F2 | Clear Entry. Octal key. |
| Hexadecimal Mode | ||
| A | Shift+F3 | A |
| B | Shift+F4 | B |
| C | Shift+F5 | C |
| D | Shift+F6 | D |
| E | Shift+F7 | E |
| F | Shift+F8 | F |
| Ctrl+C | Shift+F1 | Clear |
| Ctrl+E | Shift+F2 | Clear Entry |
When you enter data into the accumulator, notice that Calculator uses a radix separator (. or ,) to distinguish between entered digits and an operand. See what happens as you enter the following data:
Depending on the contents of the accumulator, you can use one of the following methods to correct mistakes in computation:
Calculator displays numbers in the range of plus or minus 99,999,999,999,999. Calculator performs all calculations in left-to-right order and treats operators with equal importance.
For example, to evaluate the equation 6 + 5 * 3:
Also note the way Calculator computes percentages. For example, to determine 6 percent of 195:
Use the memory display to store results and values for later computation. The figure in memory starts as zero. You can add the contents of the accumulator to memory or subtract the contents of the accumulator from memory, using the M+ and M-- buttons, respectively. To enter the contents of memory into the accumulator, click on the MR button. Clear the contents of memory with the MC button.
Calculator performs trigonometric and inverse trigonometric functions as well as other special functions.
The special-function keys in decimal mode are as follows:
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| deg | Degree key. Selects the units for angular measurement. By default, Calculator is in degree mode. Clicking on the deg key places Calculator in the radian mode, which is indicated by the key label changing to "rad." Clicking on the key again places Calculator in gradient mode, which is indicated by the key label changing to "grad." The angular mode has no effect on Calculator unless the trigonometric functions are being used. |
| x! | Factorial key. Calculates the factorial (x)(x-1)(x-2)...(2)(1) of the displayed integer x, 0 <=x <=16.0!=1 by definition. |
| 1/x | Reciprocal key. Divides the displayed value x into 1, if x is not 0. |
| Rnd | Random number generator key. Generates a random number between 1 and the integer of the display. It does not generate negative numbers or numbers less than 1. |
| Inv | Inversion key. By default, Calculator performs noninverted trigonometric functions. When you activate the inversion key by clicking on it (which is indicated by the key becoming darkened), Calculator performs inverted trigonometric, log, and exponent functions. |
| sin | Sine key. Instructs Calculator to find the sine (or arcsine if Inverse is on) of the displayed value. |
| cos | Cosine key. Instructs Calculator to find the cosine (or arccosine if Inverse is on) of the displayed value. |
| tan | Tangent key. Instructs Calculator to find the tangent (or arctangent if Inverse is on) of the displayed value. |
| log | Common logarithm key. Calculates the common logarithm (base 10) of the number x in the display, if x is greater than 0. If Inverse is on, calculates 10 to x. |
| ln | Natural logarithm key. Calculates the natural logarithm (base e) of the number x in the display, if x is greater than 0. If Inverse is on, calculates e to x. |
| <surd symbol> | Square root key. Calculates the square root of the number x in the display. The x value cannot be negative. |
| y^x | y to the xth power key. Raises the displayed value y to the xth power (or y to the 1/x power if Inverse is on). Order of entry is y y^x x. The y value cannot be negative, but both x and y can be fractionals. |
The special-function keys in hexadecimal and octal modes are as follows:
| Key | Description |
|---|---|
| Hexadecimal Mode | |
| A | Enter hexadecimal number A (decimal 10). |
| B | Enter hexadecimal number B (decimal 11). |
| C | Enter hexadecimal number C (decimal 12). |
| D | Enter hexadecimal number D (decimal 13). |
| E | Enter hexadecimal number E (decimal 14). |
| F | Enter hexadecimal number F (decimal 15). |
| Hexadecimal and Octal Modes | |
| and | In Boolean algebra, calculates logic AND (both propositions are true). |
| or | In Boolean algebra, calculates logic OR (either proposition is true or both propositions are true). |
| xor | In Boolean algebra, calculates logic XOR (either of the propositions is true). |
| nor | In Boolean algebra, calculates logic NOR (both propositions are false). |
| not | In Boolean algebra, calculates logic NOT (negation). |
| neg | In Boolean algebra, calculates NEG (the complement of x). |
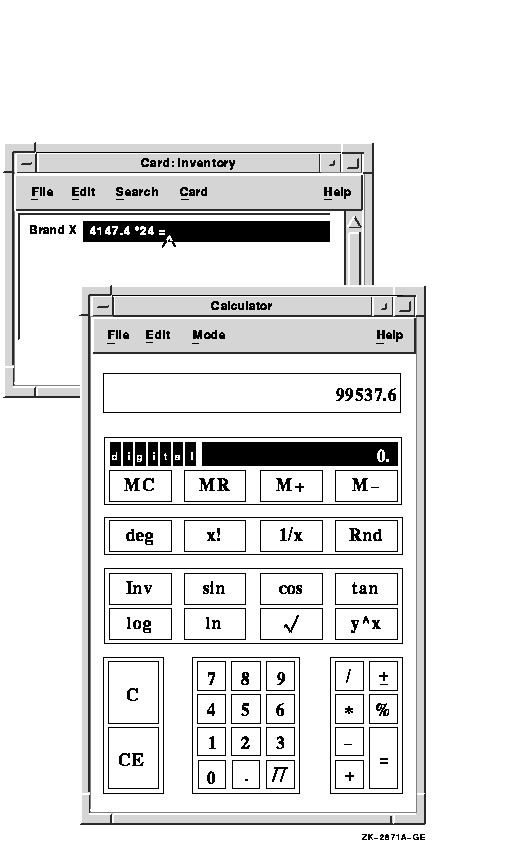
You can copy numbers from other applications into Calculator's accumulator and from Calculator's accumulator or memory into another application.
To transfer data from the active display in the calculator window to another application window, choose Copy from the Edit menu. For example:
Now you can paste the data to another application's window.
To copy data from another application, choose Paste from the Edit menu. The data can be copied directly from another window, or it can be the result of an equation copied from another window. Calculator treats the contents of a paste operation just as if you typed in the data from the keyboard.
If you change the screen placement and size of Calculator during a session and want to save those settings, choose Save Geometry from the File menu. The next time you start Calculator, the display reflects the new settings.
To restore the default size and placement of Calculator, choose Restore System Settings from the File menu.
To exit Calculator, choose Exit from the File menu.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
| privacy and legal statement | ||
| 5634PRO_001.HTML | ||