This chapter contains the following sections:
To check whether a Windows NT computer has lost its connection to a disk service, use the NTDS SHOW SERVICES command on all the OpenVMS Alpha nodes that are configured to provide the service. For example:
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:SYSMAN SYSMAN> SET ENVIRONMENT /NODE=(GREEN,BLUE,YELLOW) SYSMAN> SET PROFILE /PRIVILEGES=SYSPRV SYSMAN> DO NTDS SHOW SERVICES "Movies"
If the node on which the service is active has (none) in the Computer connected field, the Windows NT computer has lost its connection to the disk service.
Take immediate steps to correct the problem that caused the computer to lose the connection, for example, repair the network link.
You cannot tell if the Windows NT computer has lost a connection by looking at the NTDS Administrator's Main screen (Figure 2-1). This screen shows which services it is configured to connect to. The Connected status means:
To check whether the computer has lost its connection to a disk service, use the Windows NT Event Viewer. Follow these steps:
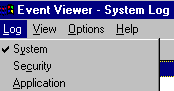
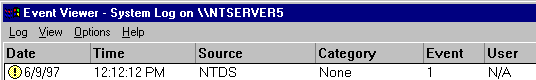
These warnings are logged:
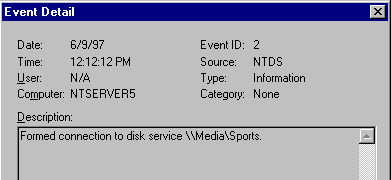
Double click the NTDS warning entry to display the description text which tells you the cluster name and service name, for example:
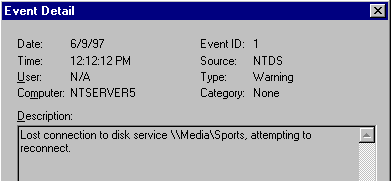
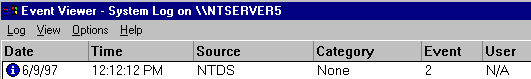
Its description text looks like this:
Take immediate steps to correct the problem that caused the computer to lose the connection, for example, repair the network link.
During its startup sequence, a Windows NT computer automatically tries to connect to all of the disk services that it was connected to (or was trying to reconnect to) when it was shut down.
If the Windows NT computer fails to connect to a service during startup, follow these steps:
For example, if the service has been stopped on the OpenVMS Cluster, use the NTDS START SERVICE command to restart it.
The screen shown in Figure 2-1 appears.
Running NTDS Administrator resets the status of the disk service to Disconnected.
If your Windows NT computer cannot connect to a disk service that is being provided by an OpenVMS Cluster on another subnet, it could be that your routers are not configured to allow messages to be broadcast to other subnets. In this case, follow these steps:
The screen shown in Figure 2-1 appears.
If necessary, use Add to add the appropriate entries to the list.
If NTDS Administrator takes a long time to disconnect a disk service, check whether the service has been stopped on the OpenVMS Cluster.
Use the NTDS SHOW SERVICES command on each node that is configured to provide the service, for example:
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:SYSMAN SYSMAN> SET ENVIRONMENT /NODE=(GREEN,BLUE,YELLOW) SYSMAN> SET PROFILE /PRIVILEGES=SYSPRV SYSMAN> DO NTDS SHOW SERVICES "Movies"
If the service is not available, restart it immediately, using the NTDS START SERVICE command.
Disconnecting a disk service automatically closes all open files in NTFS partitions on its virtual disk.
You cannot disconnect a disk service if its virtual disk has a partition formatted with a file system other than NTFS (for example, the FAT file system) and there are any open files in the partition.
If the virtual disk has multiple partitions, the failed attempt to disconnect the service may succeed in taking other partitions on the disk off line and making them inaccessible. These partitions no longer appear in the Drive column of NTDS Administrator's Main screen (Figure 2-1).
To get these partitions back on line again, use the Windows NT Disk Administrator to reassign drive letters to them.
If NTDS commands fail with the %SYSTEM-E-NOT_LOADED
error, follow these steps:
$ DIRECTORY SYS$LOADABLE_IMAGES:SYS$NTDS.EXE
If it does not exist, reinstall the server component of DIGITAL OpenVMS Disk Services for Windows NT, as described in Installing DIGITAL OpenVMS Disk Services for Windows NT.
Copyright © Digital Equipment Corporation 1997. All Rights Reserved.