| Previous | Contents | Index |
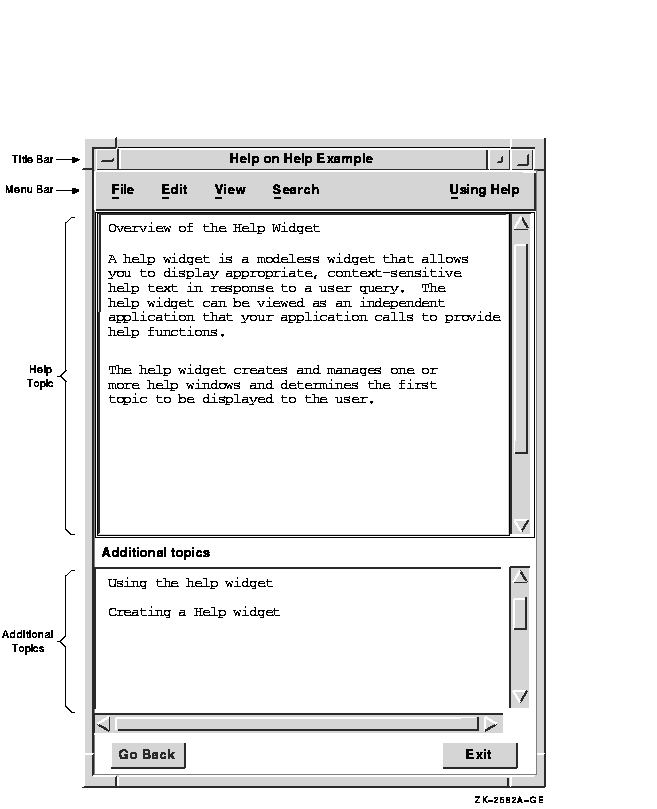
The help widget is a pop-up dialog box that is preconfigured to contain the child widgets, called subwidgets, it needs to implement its functions. Figure 4-2 shows a help widget with its component parts.
Figure 4-2 Help Widget Components
You can use the following help widget resources to modify the appearance of the help widget:
For example, the DXmNcols resource specifies the width, in characters, of the help text displayed by the help widget. The default is language dependent; the American English default is 55 characters.
The following UIL code fragment reduces the value of the DXmNcols resource to 50 columns.
object main_help : DXmHelpDialog
{
arguments
{
DXmNapplicationName = compound_string("Help Example");
DXmNglossaryTopic = compound_string("glossary");
DXmNoverviewTopic = compound_string("overview");
DXmNcols = 50;
};
};
|
The help widget appearance resources are described in the DECwindows Extensions to Motif
manual.
4.4.1 Modifying Help Widget Labels and Mnemonics
You can use the help widget label resources, described in the DECwindows Extensions to Motif manual, to modify the help widget labels.
For example, the DXmNapplicationName resource specifies the application name to be used in the help widget Help on... title bar. The default is null.
The following UIL code fragment sets the DXmNapplicationName resource to "Help Example":
object main_help : DXmHelpDialog
{
arguments
{
DXmNapplicationName = compound_string("Help Example");
DXmNglossaryTopic = compound_string("glossary");
DXmNoverviewTopic = compound_string("overview");
};
};
|
The mnemonics resources allow you to change the key a user presses to activate a help widget menu item. For example, the DXmNhelpLabelMnem resource specifies which key the user can press (instead of clicking MB1) to activate the Help pull-down menu. The default is the letter U.
The following UIL code fragment sets the DXmNhelpLabelMnem resource to "H":
object main_help : DXmHelpDialog
{
arguments
{
DXmNapplicationName = compound_string("Help Example");
DXmNglossaryTopic = compound_string("glossary");
DXmNoverviewTopic = compound_string("overview");
DXmNhelpLabelMnem = keysym("H");
};
};
|
The help widget mnemonics resources are described in DECwindows Extensions to Motif.
The most common reason to modify the help widget label and mnemonics
resources is for internationalization purposes.
4.4.2 Help Widget Messages
The help widget uses messages to provide status information to the user. You can use help widget resources to modify the text of these messages. The help widget message resources are described in DECwindows Extensions to Motif. Note that for OpenVMS applications, the !CS variable is replaced by the relevant compound string in the actual messages.
For example, the following UIL code fragment from an OpenVMS application changes the value of the DXmNbadlibMessage resource from "Couldn't open library !CS" to "TEST_HELP.HLB is missing":
object main_help : DXmHelpDialog
{
arguments
{
DXmNapplicationName = compound_string("Help Example");
DXmNglossaryTopic = compound_string("glossary");
DXmNoverviewTopic = compound_string("overview");
DXmNlibrarySpec = compound_string("test_help.hlb");
DXmNbadlibMessage = compound_string("TEST_HELP.HLB is missing");
};
};
|
The help widget supports the callbacks described in Table 4-3.
| Callback | Description |
|---|---|
| DXmNunmapCallback | The callback routine or routines called when the help widget is unmapped. For this callback routine, the reason is Unmap. The default is null. The help widget automatically unmanages itself when a user exits the help session, so the DXmNunmapCallback callback need not do this. You can use the DXmNunmapCallback callback to perform other functions when a user exits the help session. |
| DXmNmapCallback | The callback routine or routines called when the help widget is mapped. The default is null. |
You can use the help widget resources described in Table 4-4 to specify the topics of the help widget.
If you specify a help topic identified by a subkey name, you must also specify the key names that form the path to the subkey name. The key names must be separated by at least one space.
For example, suppose you have the following module:
1 programming
2 creating
3 create_help_widget
If you want to display the create_help_widget key-3 help text as the first topic in the help widget, pass the compound string "programming creating create_help_widget".
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| DXmNfirstTopic |
Specifies the
first help topic to be displayed.
If the DXmNfirstTopic resource is not specified (set to null), the help widget displays an empty window with a list of level 1 topics in the additional topic list box. See Section 4.7.1 for information about using DXmNfirstTopic to specify context-sensitive help. |
| DXmNoverviewTopic |
Specifies the Overview topic to be displayed. The Overview topic is
displayed when you select the Go To Overview menu item from the View
menu.
As described in Section 4.2, your application uses the DXmNoverviewTopic resource to pass to the help widget a string that identifies the key name of the Overview module. Overview is generally a key-1 name. |
| DXmNglossaryTopic |
Specifies the Glossary topic to be displayed. Your application uses
the
DXmNglossaryTopic resource to pass to the help widget
a string that identifies the key name of the Glossary module. Glossary
is generally a key-1 name.
If you pass a null string (the default), the Visit Glossary menu item does not appear in the View pull-down menu. Set DXmNglossaryTopic to null if your application does not support glossary help. |
This section describes general programming considerations for using the help widget.
The most basic approach to using the help widget is to create it, manage it to cause the help window to appear, and destroy it using the unmap callback routine when the user is finished. However, any changes to the help window, such as resizing, are lost when the widget is destroyed.
If your application destroys a help widget and then re-creates it, your application assumes the help widget creation overhead. On OpenVMS systems, an OpenVMS help library is initialized when it is first opened by the help widget and is cached in memory until the application closes down. Once a help widget initializes an OpenVMS help library on behalf of your application, the library is not reinitialized unless your application is restarted.
The recommended approach is to create the help widget once and use the same help widget each time the user requests help by specifying a new first topic in the DXmNfirstTopic resource (using the XtSetValues routine) and managing the widget (using the XtManageChild routine) to cause the help window to appear.
To use the help widget, perform the following steps:
| UIL object type | Use the DXmHelpDialog object type identifier to create a help widget in a UIL module. |
| Toolkit routine | Use the DXmCreateHelpDialog routine to create a help widget. |
In context-sensitive help, the application presents direct help on the current topic rather than starting at a higher level and working down through a help hierarchy. Users do not have to navigate through several layers of help to find the information they need.
All widgets that are a subclass of the XmPrimitive or XmManager widget class support a help callback with a reason of XmCR_HELP. (Other widgets can also support the help callback, but there is no requirement to do so.) Your application uses this help callback to implement context-sensitive help by associating a help callback routine with the widgets for which you want to provide help.
The Toolkit includes a routine, DXmHelpOnContext, that applications can use to enter context-sensitive help mode.
The OSF/Motif Style Guide recommends that, within dialog boxes, context-sensitive help should be provided for the dialog box as a whole. The first help frame should be an overview of the dialog box, with additional topics about each object in the dialog box. To be consistent with the recommendations of the OSF/Motif Style Guide, you need to provide a help callback only for the dialog box itself and not for the objects within the dialog box. Because the DXmHelpOnContext routine checks a widget's nearest ancestors until it finds a widget with an associated help callback routine, a user should be able to get context-sensitive help on a dialog box by clicking anywhere within that dialog box. |
An example of a help callback routine (sens_help_proc) is described in Example 4-5.
The remainder of this section describes how to implement
context-sensitive help.
4.7.1.1 Creating the On Context Push Button in UIL
Example 4-2 shows how to create an On Context push button in the Help pull-down menu.
| Example 4-2 The On Context Push Button in UIL |
|---|
.
.
.
object help_menu_entry : XmCascadeButton {
arguments {
XmNlabelString = k_help_label_text;
XmNmnemonic = keysym("H");
};
controls {
XmPulldownMenu help_menu;
};
callbacks
{
XmNhelpCallback = procedure sens_help_proc(k_help_help);
};
};
object help_menu : XmPulldownMenu
{
controls
{
XmPushButton help_sensitive;
XmPushButton help_window;
XmPushButton help_version;
XmPushButton help_onhelp;
};
callbacks
{
XmNhelpCallback = procedure sens_help_proc(k_help_help);
};
};
object help_sensitive : XmPushButton
{
arguments
{
XmNlabelString = k_sensitive_label_text;
XmNmnemonic = keysym("C");
};
callbacks
{
(1)XmNactivateCallback = procedure activate_proc (k_help_sensitive);
XmNhelpCallback = procedure sens_help_proc(k_sensitive_help);
};
};
.
.
.
|
The activate callback for the On Context push button calls a routine to enter context-sensitive help mode, as shown in Example 4-3. Note that all of the push buttons in OpenVMS DECburger call back to the activate_proc routine. However, your application could directly invoke the context-sensitive help callback from the On Context push button.
| Example 4-3 Calling the DXmHelpOnContext Routine |
|---|
.
.
.
static void activate_proc(w, tag, reason)
Widget w;
int *tag;
XmAnyCallbackStruct *reason;
{
int widget_num = *tag; /* Convert tag to widget number. */
int i, value;
XmString topic;
switch (widget_num) {
.
.
.
(1)case k_help_sensitive:
tracking_help();
break;
.
.
.
static void tracking_help()
{
(2)DXmHelpOnContext(toplevel_widget, FALSE);
}
.
.
.
|
Your application uses the XmNhelpCallback resource to associate a help callback routine with the widgets for which you want to provide help.
Your application can use the callback's tag argument to supply application-specific data. For example, the widgets in the OpenVMS DECburger application supply the help callback routine with a compound string value that specifies the help topic, as shown in Example 4-4.
The string value for the Help System callback is described in Chapter 5.
| Example 4-4 Specifying a Help Callback---UIL Module |
|---|
.
.
.
!Compound strings to use for context-sensitive help callbacks
value
k_order_help : compound_string ("order");
k_print_help : compound_string ("print");
k_options_help : compound_string ("options");
k_menu_bar_help : compound_string ("menu_bar");
k_file_help : compound_string ("file_menu");
k_edit_help : compound_string ("edit_menu");
k_order_menu_help : compound_string ("order_menu");
k_help_help : compound_string ("help");
k_sensitive_help : compound_string ("sensitive");
k_onhelp_help : compound_string ("onhelp");
k_about_help : compound_string ("about");
k_overview_help : compound_string ("overview");
k_nyi_help : compound_string ("not_implemented");
!String value to use for the Help System callback
value
helpsys_order_help : 'order';
.
.
.
object
s_menu_bar : XmMenuBar {
arguments {
XmNorientation = XmHORIZONTAL;
XmNmenuHelpWidget = XmCascadeButton help_menu_entry;
};
controls {
XmCascadeButton file_menu_entry;
XmCascadeButton edit_menu_entry;
XmCascadeButton order_menu_entry;
XmCascadeButton options_menu_entry;
XmCascadeButton help_menu_entry;
};
callbacks {
MrmNcreateCallback = procedure create_proc (k_menu_bar);
(1)XmNhelpCallback = procedure sens_help_proc(k_menu_bar_help);
};
};
.
.
.
|
Example 4-5 shows how the OpenVMS DECburger application help callback routine calls a creation routine (create_help) to set the DXmNfirstTopic resource. See Example 4-7 for a complete description of create_help.
| Example 4-5 Specifying a Help Callback---C Module |
|---|
.
.
.
static void sens_help_proc(w, tag, reason)
Widget w;
XmString *tag;
XmAnyCallbackStruct *reason;
{
create_help(tag);
}
.
.
.
|
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |