| Updated: 21 January 1999 |
OpenVMS Connectivity Developer Guide
| Previous | Contents | Index |
A quota mechanism limits the size of the OpenVMS Registry database. The system assigns a quota to the root key datafile for every OpenVMS Registry file. By default, these root keys are the USERS key (REGISTRY$USERS.REG) and the LOCAL_MACHINE key) (REGISTRY$LOCAL_MACHINE.REG).
The quota limits the size of the information contained within the file but does not include the size of information stored in other files, even if the files are part of the subtree.
The default quota and file-specific quotas are stored in the
OpenVMS Registry under the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\Registry
key. For more information about these keys, see Section 7.3.
8.8 OpenVMS Registry Security
A user can access (read and modify) the OpenVMS Registry directly in the following ways:
For a discussion of what system privileges and right identifiers each
user needs, see Section 7.5.1. For a description of how to grant the
necessary system privileges and right identifiers, see Section 7.5.1.1.
8.9 Backing up and Restoring the OpenVMS Registry
The OpenVMS Registry includes a server management utility that allows you to back up and restore the entire OpenVMS Registry database to or from a file from the OpenVMS DCL prompt as long as you have the required system privileges.
For more information about backing up and restoring the OpenVMS Registry
database, see Section 9.2 and the REG$CP server management
utility CREATE SNAPSHOT command.
8.10 Using the OpenVMS Registry in an Alpha Mixed-Version Cluster
The OpenVMS Registry Server can run in an Alpha mixed-version cluster.
That is, the OpenVMS Registry can run in a cluster that includes OpenVMS
versions other than OpenVMS Version 7.2; but the OpenVMS Registry must be
running on the node that is running OpenVMS Version 7.2.
8.11 Internationalization and Unicode Support
To integrate with Windows NT, the OpenVMS Registry is Unicode compliant. For more information about Unicode, see the OpenVMS Version 7.2 New Features Manual.
The OpenVMS Registry includes a server management utility that allows you to update and display OpenVMS Registry information from the OpenVMS DCL prompt.
The utility also allows you to back up and restore the entire OpenVMS Registry database to or from a file, as long as you have the required system privileges. For more information about backing up and restoring the OpenVMS Registry database, see Section 9.2 and the CREATE SNAPSHOT function.
To start the OpenVMS Registry server management utility, enter one of the following commands:
$ RUN SYS$SYSTEM:REG$CP |
or
$ MCR REG$CP |
Before you can access the OpenVMS Registry database, the OpenVMS Registry server must be running either in the cluster or on the standalone system. |
Table 9-1 lists and describes OpenVMS Registry server management utility commands.
| Command | Identifier | Action |
|---|---|---|
| CREATE DATABASE | SYSPRV | Creates a new OpenVMS Registry database file. |
| CREATE KEY | REG$UPDATE | Creates one or more keys in the OpenVMS Registry database. |
| CREATE SNAPSHOT | SYSPRV | Makes an immediate backup of the OpenVMS Registry database files. |
| CREATE VALUE | REG$UPDATE | Specifies the data component for a given key. |
| DELETE KEY | REG$UPDATE | Removes one or more keys from the OpenVMS Registry database. |
| DELETE VALUE | REG$UPDATE | Removes one or more values from a specified given key. |
| LIST KEY | REG$LOOKUP | Displays all subkey information for a specified key. |
| LIST VALUE | REG$LOOKUP | Displays all values of a specified key. |
| MODIFY KEY | REG$UPDATE | Modifies the information of a specified key. |
| MODIFY VALUE | REG$UPDATE | Modifies the information of a specified value. |
| MODIFY TREE | REG$UPDATE | Modifies the information of a specified key and its subkeys. |
| SEARCH KEY | REG$LOOKUP | Displays the path name of all keys that match a specified key. |
| SEARCH VALUE | REG$LOOKUP | Displays the path name of all keys that match a specified value name. |
| SHOW COUNTERS | REG$PERFORMANCE | Displays counter information. |
| SHOW FILE | REG$PERFORMANCE | Displays OpenVMS Registry database file statistics. |
| SHOW INTERNAL | REG$PERFORMANCE | Displays internal values (used by shared libraries). |
| START MONITOR | REG$PERFORMANCE | Enables monitoring functions. |
| STOP MONITOR | REG$PERFORMANCE | Disables monitoring functions. |
| ZERO COUNTERS | REG$PERFORMANCE | Resets monitoring counters. |
A user who has the SYSPRV privilege can can execute all the commands listed in Table 9-1. You must specify an OpenVMS Registry identifier only if the user does not have SYSPRV privilege. If you grant a user the REG$UPDATE identifier, in addition to the commands listed in Table 9-1, the user can also execute the following commands:
|
The REG$CP server management utility includes the CREATE SNAPSHOT function that allows you to back up the OpenVMS Registry database files.
By default, the REGISTRY_SERVER process creates a snapshot of the OpenVMS Registry database every 24 hours. You can change this interval by modifying the Snapshot Interval setting in the OpenVMS Registry server operations. (For more information about these operations, see Section 7.6.)
The following example shows how to modify the interval between automatic snapshots of the OpenVMS Registry database from the default of once every 24 hours to once every hour.
$ MCR REG$CP REG> MODIFY VALUE HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\REGISTRY - _REG> /NAME="Snapshot Interval"/DATA=3600/TYPE=DWORD |
Use the following procedure to create a snapshot of the OpenVMS Registry database:
$ MCR REG$CP REG> CREATE SNAPSHOT |
REGISTRY$LOCAL_MACHINE.RSS REGISTRY$USERS.RSS |
Use the following procedure to restore a snapshot of the OpenVMS Registry database:
$ RENAME REGISTRY$LOCAL_MACHINE.RSS REGISTRY$LOCAL_MACHINE.REG $ RENAME REGISTRY$USERS.RSS REGISTRY$USERS.REG |
Any information that the system has written to the OpenVMS Registry database between the time of the last snapshot and this restore process will be lost. |
The following command section describes each OpenVMS Registry command in alphabetical order.
In all the commands in this section, the key-name parameter is a string that specifies the full path of the key, beginning from one of following entry points:
You can also specify the strings REG$_HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, REG$_HKEY_USERS, and REG$_HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT. For all server management commands, links are not followed. (For more information about links, see Section 7.2.1.3.) To make key and values names case sensitive, enclose the keys and values in quotation marks (for example: "value"). |
Creates the basic OpenVMS Registry database files in the location specified by the SYS$REGISTRY logical. The command creates an empty database and loads the predefined keys.If you enter this command and the database files already exist, the utility does not overwrite the existing files. The system displays a warning that the files already exist. If you want to create a new OpenVMS Registry database, you must first delete all previous versions of the database files. If you delete the OpenVMS Registry database files, you will lose all keys, subkeys, and values stored in the OpenVMS Registry.
This command requires the SYSPRV privilege.
The following table lists and describes the OpenVMS Registry database files.
File Description REGISTRY$ROOT.DAT Root of the database REGISTRY$USERS.REG HKEY_USERS tree REGISTRY$LOCAL_MACHINE.REG HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE tree REGISTRY$MASTER.RLG The master commit log file REGISTRY$REPLY.RLG Log file that tracks modification requests to the OpenVMS Registry database
CREATE DATABASE
None
None
REG> CREATE DATABASERegenerates the basic OpenVMS Registry database files if the database files are lost or deleted.
Creates one or more keys in the OpenVMS Registry database.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$UPDATE rights identifier.
CREATE KEY key-name [,...]
key-name[,...]
Specifies the name of the key to create. You can create multiple keys by separating the keys with commas
/WRITEBEHIND
Specifies that the key information must be written to disk immediately. /NOWRITEBEHIND specifies a write-through operation.
/NOWRITEBEHIND (default)/VOLATILE=level
Specifies whether or not the new key is volatile. If you are running the OpenVMS Registry on a standalone OpenVMS system, volatile keys are lost when the system reboots. If you are running the OpenVMS Registry in an OpenVMS cluster, volatile keys are lost when all notes in the cluster are rebooted.
/NONVOLATILE (default)The values for level are as follows:
- NONE (same as /NONVOLATILE)
- CLUSTER
/CACHE_ACTION=value
Specifies the cache attribute for the new key. The value can be WRITEBEHIND (default) or WRITETHRU (write to disk immediately)./CLASS_NAME=string
Specifies the class name of the key./SECPOLICY=policy
Defines the security policy for the key. Currently the only valid policy is NT_40./LINK=(TYPE=value, NAME=key-name)
Defines the key as a link to another key. The link value must be one of the following:
- SYMBOLICLINK
- NONE
To remove a link, enter the following:
/LINK=(TYPE=NONE,NAME="")
REG> CREATE KEY/CACHE_ACTION=WRITEBEHIND HKEY_USERS\GUEST, HKEY_USERS\SYSTEMCreates the GUEST and SYSTEM keys under the HKEY_USERS entry point. The keys are created with the write-behind attribute.
Creates a snapshot of the OpenVMS Registry database. That is, the system writes all cached OpenVMS Registry keys or values and makes a copy of the OpenVMS Registry database files.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege.
CREATE SNAPSHOT
None
/DESTINATION=file-spec
Controls where the system will write the snapshot files. By default, the system creates the snapshot in the location specified by the SYS$REGISTRY logical.If you specify the /DESTINATION qualifier but do not provide a valid directory, the system creates the snapshot files in the directory in which you started the OpenVMS Registry server.
/VERSIONS=number
Specifies how many previous versions of the snapshot files to keep.
REG> CREATE SNAPSHOT/DESTINATION=SYS$REGISTRY/VERSION=3Creates a snapshot of the OpenVMS Registry database in the SYS$REGISTRY directory. If more than three versions of the OpenVMS Registry database snapshot files exist, the system deletes the oldest version (the same as purge/keep=3 command).
Specifies the data component for the specified key. If the value does not exist, the command creates the value.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$UPDATE rights identifier.
CREATE VALUE key-name
key-name
Specifies the name of the key for which you will set the value.
/FLAGS=flag
Specifies the data flags value. This is an application-dependent 64-bit flag specified as a decimal number or as a hexadecimal number preceded by 0x or %X./WRITEBEHIND
Specifies that the value must be written to disk immediately. /NOWRITEBEHIND specifies a write-through operation.
/NOWRITEBEHIND (default)/DATA=value
The value can be one of the following:
- String (for example, /DATA=COSMOS)
- An array of strings separated by a comma and enclosed in parentheses (for example, /DATA=(COSMOS,Noidea)
- A longword in octal (%O), decimal, or hexadecimal (%X) format (for example, /DATA=%X1A0FCB or /DATA=1234)
/NAME=string
Specifies the name of the new value./TYPE_CODE=type
Specifies the type of the new value. The type value must be one of the following:
- SZ: a null-terminated Unicode string
- EXPAND_SZ: a string of Unicode characters
- MULTI_SZ: a concatenated array of SZ strings
- DWORD: a 32-bit number
/LINK=(TYPE=value, NAME=key-name)
Defines the key as a link to another key. The link value must be one of the following:
- SYMBOLICLINK
- NONE
To remove a link, enter the following:
/LINK=(TYPE=NONE,NAME="")
REG> CREATE VALUE/DATA=COSMOS/TYPE=SZ/NAME=COMPUTERNAME HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\NODECreates the COMPUTERNAME value for the key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\NODE and sets its type to SZ and its data value to COSMOS.
Removes a specified key from the OpenVMS Registry database. The system does not delete a key if the key has subkeys.
Caution
Deleting a key results in symbolic links not being followed. This is because the system deletes the key you specified, even if it has symbolic links.
Note
The OpenVMS Registry database predefined keys are reserved keys and cannot be deleted. These keys are HKEY_USER, HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, and HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$UPDATE rights identifier.
DELETE KEY key-path key-name
key-path
Specifies the key path.key-name
Specifies the name of the key to delete.
/WRITEBEHIND
Specifies that the key information must be written to disk immediately. /NOWRITEBEHIND specifies a write-through operation.
/NOWRITEBEHIND (default)
REG> DELETE KEY HKEY_USERS\NODE GUESTDeletes the GUEST key from the OpenVMS Registry database.
Removes a value from a specified key.
Caution
Deleting a value results in symbolic links not being followed. This is because the system deletes the value you specified, even if it has symbolic links.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$UPDATE rights identifier.
DELETE VALUE key-name value-name
key-name
Specifies the key name whose value should be removed.value-name
Specifies the value to remove.
/WRITEBEHIND
Specifies that the information must be written to disk immediately. /NOWRITEBEHIND specifies a write-through operation.
/NOWRITEBEHIND (default)
REG> DELETE VALUE HKEY_USERS\GUEST PASSWORDDeletes the PASSWORD value from the GUEST key.
Displays the attributes for the specified key.
Note
Symbolic links are not followed.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$LOOKUP rights identifier.
LIST KEY key-name
key-name
Specifies the name of the key to list.
/FULL
Displays all available information---that is, information displayed by the /LAST_WRITE, /CACHE_ACTION, /INFORMATION, /LINK_PATH, and /CLASS_NAME qualifiers./CACHE_ACTION=value
Specifies the cache attribute for the subkey. The value can be WRITEBEHIND (default) or WRITETHRU (write to disk immediately)./CLASS_NAME
Displays the class name of the subkey./INFORMATION
Displays the information (subkey number, value number, subkey name max, and so on) about the specified key./LAST_WRITE
Displays the time when the subkey was last updated./LINK_PATH
Displays the key path to which the subkey is linked./OUTPUT=file-spec
Controls where the output of the command is sent. If you do not specify a file name, the system uses the default name REGISTRY.LIS.
REG> LIST KEY/FULL HKEY_USERS\GUEST Key name: HKEY_USERS\GUEST Security policy: REG$K_POLICY_NT_40 Volatile: REG$K_NONE Cache: REG$K_WRITEBEHIND Class: System Authorization Link Type: REG$K_NONE Last written: 7-AUG-1998 12:42:08.55 Key information: Number of subkeys: 2 Number of values: 0 Max size of subkey name: 40 Max size of class name: 40 Max size of value name: 0 Max size of value data: 0 Subkey(s): Key name: QUOTAS Security policy: REG$K_POLICY_NT_40 Volatile: REG$K_NONE Cache: REG$K_WRITEBEHIND Class: Disk quota Link Type: REG$K_NONE Last written: 7-AUG-1998 12:41:19.21 Key information: Number of subkeys: 0 Number of values: 0 Max size of subkey name: 0 Max size of class name: 0 Max size of value name: 0 Max size of value data: 0 Key name: IDENTIFIER Security policy: REG$K_POLICY_NT_40 Volatile: REG$K_NONE Cache: REG$K_WRITETHRU Class: Disk quota Link Type: REG$K_SYMBOLICLINK Link Path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\IDENTIFIER\GUEST Last written: 7-AUG-1998 12:42:08.55 Key information: Number of subkeys: 0 Number of values: 0 Max size of subkey name: 0 Max size of class name: 0 Max size of value name: 0 Max size of value data: 0The LIST KEY/FULL command in this example displays the GUEST key attributes as well as the name and attributes of the subkeys of GUEST.
Note
The Max sizes information shows the number of bytes, not characters. (Each character is 4 bytes long.)
Displays all values and value attributes of the specified key.
Note
Symbolic links are not followed.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$LOOKUP rights identifier.
LIST VALUE key-name
key-name
Specifies the name of the key to enumerate.
/FULL
Displays all available information---that is, information displayed by the /TYPE_CODE, /LINK_PATH, /DATA_FLAGS, and /VALUE_DATA qualifiers./TYPE_CODE
Display the type code of the value./FLAGS
Displays an ASCII representation of the data flag of the value in hex format./LINK_PATH
Displays the key path to which the subkey is linked./DATA
Displays an ASCII representation of the value in hex format./OUTPUT=file-spec
Controls where the output of the command is sent. If you do not specify a file name, the system uses the default name REGISTRY.LIS.
REG> LIST VALUE/TYPE_CODE/DATA HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\FORTRAN Key name: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\FORTRAN Security policy: REG$K_POLICY_NT_40 Volatile: REG$K_NONE Last written: 11-AUG-1998 16:27:55.81 Value(s): Value name: Version Volatile: REG$K_NONE Type: REG$K_SZ Data: 5.3-50 Value name: Date Installed Volatile: REG$K_NONE Type: REG$K_SZ Data: 04-Jan-1998The LIST VALUE/TYPE_CODE/DATA command in this example displays the FORTRAN key and its value names, types, and data.
Modifies the attributes of the specified key.
Caution
Modifying a key results in symbolic links not being followed. This is because the system modifies the key you specified, not the key pointed to by the symbolic link.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$UPDATE rights identifier.
MODIFY KEY key-name
key-name
Specifies the name of the key to modify.
/CACHE_ACTION=value
Specifies the cache attribute for the new key. The value can be WRITEBEHIND (default) or WRITETHRU (write to disk immediately)./CLASS_NAME=string
Specifies the new class name of the key./WRITEBEHIND
Specifies that the key information must be written to disk immediately. /NOWRITEBEHIND specifies a write-through operation.
/NOWRITEBEHIND (default)/NEW_NAME=new-key-name
Specifies the new name of the key./SECPOLICY=policy
Defines the security policy for the key. Currently the only valid policy is NT_40./LINK=(TYPE=value, NAME=key-name)
Defines the key as a link to another key. The link value must be one of the following:
- SYMBOLICLINK
- NONE
To remove a link, enter the following:
/LINK=(TYPE=NONE,NAME="")
REG> MODIFY KEY/CACHE_ACTION=WRITEBEHIND HKEY_USERS\GUESTModifies the cache attribute of the GUEST key.
Specifies the data component for the specified value. This command will modify an existing value.
Caution
Modifying a value results in symbolic links not being followed. This is because the system modifies the value you specified, not the value pointed to by the symbolic link.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$UPDATE rights identifier.
MODIFY VALUE /NAME=string key-name
key-name
Specifies the name of the key for which to set the value.
/FLAGS=flag
Specifies the data flags value. This is an application-dependent 64-bit flag specified as a decimal number or as a hexadecimal number preceded by 0x or %X./WRITEBEHIND
Specifies that the value information must be written to disk immediately. /NOWRITEBEHIND specifies a write-through operation.
/NOWRITEBEHIND (default)/DATA=value
Specifies the data for the value. The value can be:
- A string (for example, /DATA=COSMOS)
- An array of strings separated by a comma and enclosed in parentheses (for example, /DATA=(COSMOS,Noidea)
- A longword in octal (%O), decimal, or hexadecimal (%X) format (for example, /DATA=%X1A0FCB or /DATA=1234)
/NAME=string
Specifies the name of the value./TYPE_CODE=type
Specifies the type of the new value. The type value must be one of the following:
- SZ: a null-terminated Unicode string
- EXPAND_SZ: a string of Unicode characters
- MULTI_SZ: a concatenated array of SZ strings
- DWORD: a 32-bit number
/LINK=(TYPE=value, NAME=key-name)
Defines the key as a link to another key. The link value must be one of the following:
- SYMBOLICLINK
- NONE
To remove a link, enter the following:
/LINK=(TYPE=NONE,NAME="")
REG> MODIFY VALUE/DATA=COSMOS/TYPE=SZ/NAME=COMPUTERNAME HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\NODECreates COMPUTERNAME value for the key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\NODE, and sets its type code to SZ and its data value to COSMOS.
Modifies the information for the specified key and its subkeys.
Caution
Modifying a tree results in symbolic links not being followed. This is because the key and subkeys you specify are modified, not the key pointed to by the symbolic link.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$UPDATE rights identifier.
MODIFY TREE key-name
key-name
Specifies the name of key to modify.
/CACHE_ACTION=value
Specifies the cache attribute for the key and its subkeys. The value can be WRITEBEHIND (default) or WRITETHRU (write to disk immediately)./CLASS_NAME=string
Specifies the new class name for the given key and all its subkeys./WRITEBEHIND
Specifies that the key information must be written to disk immediately. /NOWRITEBEHIND specifies a write-through operation.
/NOWRITEBEHIND (default)/SECPOLICY=policy
Defines the security policy for the key. Currently the only valid policy is NT_40.
REG> MODIFY TREE/CACHE_ACTION=WRITEBEHIND HKEY_USERS\GUESTModifies the cache attribute of the GUEST key and all its subkeys.
Displays the path name of all the keys that match the specified key.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$LOOKUP rights identifier.
SEARCH KEY key-search
key-search
Specifies the key name for which to search.
/OUTPUT=file-spec
Controls where the output of the command is sent. If you do not specify a file name, the system uses the default name REGISTRY.LIS.
REG> SEARCH KEY HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\...\NODE HARDWARE\CLUSTER\NODE HARDWARE\LOCAL\NODE NODEDisplays all the key paths that match the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\...\NODE selection. The ellipsis (...) wildcard specifies that there can be any number of subkeys between the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE entry point and the NODE subkey. Note that the search is not case sensitive.
Displays the path name of all the values that match the specified value name.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$LOOKUP rights identifier.
SEARCH VALUE key-name value-name
key-name
Specifies the name of the key path to search.value-name
Specifies the value name for which to search.
/OUTPUT=file-spec
Controls where the output of the command is sent. If you do not specify a file name, the system uses the default name REGISTRY.LIS.
REG> SEARCH VALUE HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\... *AM% HARDWARE\CLUSTER\Name HARDWARE\CLUSTER\NODE\Name HARDWARE\LOCAL\NODE\Name NODE\COMPUTERNAMEDisplays all the value names that match the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\...\*am% selection. The ellipsis (...) wildcard specifies that there can be any number of subkeys between the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE entry point and the *am% value name. Note that the search is not case sensitive.
Displays OpenVMS Registry server internal statistics and information.
- SHOW COUNTERS
Displays monitoring information from the OpenVMS Registry server.- SHOW FILE
Displays status information on files loaded into the OpenVMS Registry server.- SHOW INTERNAL_VALUES
Displays library internal values.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$PERFORMANCE rights identifier.
SHOW COUNTERS/FILE [name]
SHOW FILE [name]
SHOW INTERNAL_VALUES key
name
Identifies the file (used with the /FILE qualifier only).
/FILE
Displays counters for the specified file or for all files./PERFORMANCE
Displays performance counters./OUTPUT=file-spec
Controls where the output of the command is sent. If you do not specify a file name, the system uses the default name REGISTRY.LIS.
REG> SHOW COUNTERS/FILEDisplays monitoring information from the OpenVMS Registry server.
Starts a monitoring component within the OpenVMS Registry server.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$PERFORMANCE rights identifier.
START MONITORING/FILE [name]
START MONITORING/PERFORMANCE
name
Identifies the file (used with the /FILE qualifier only).
/FILE
Start gathering counters for the specified file or for all files./PERFORMANCE
Start gathering performance counters.
REG> START MONITORING/PERFORMANCEEnables a monitoring component of the OpenVMS Registry.
Stops a monitoring component within the OpenVMS Registry server.This command is used to stop a monitoring component within the OpenVMS Registry server.
This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$PERFORMANCE rights identifier.
STOP MONITORING/FILE [name]
STOP MONITORING/PERFORMANCE
name
Identifies the file (used with the /FILE qualifier only).
/FILE
Stop gathering counters for the specified file or for all files./PERFORMANCE
Stop gathering performance counters.
REG> STOP MONITORING/PERFORMANCEDisables a monitoring component of the OpenVMS Registry.
Initializes counters within the OpenVMS Registry server.This command requires the SYSPRV privilege or the REG$PERFORMANCE rights identifier.
ZERO COUNTERS/FILE [name]
ZERO COUNTERS/PERFORMANCE
name
Identifies the file (used with the /FILE qualifier only).
/FILE
Initializes the file counters for the specified file or for all files./PERFORMANCE
Initializes all performance counters.
REG> ZERO COUNTERS/PERFORMANCEResets the performance counters.
This chapter lists and describes the OpenVMS Registry $REGISTRY and $REGISTRYW system services.
The $REGISTRY and $REGISTRYW system services are the interface to the OpenVMS Registry database server. The $REGISTRY service allows you to query, update, and set keys, subkeys, and values in the OpenVMS Registry database.The $REGISTRY service completes most operations asynchronously. For synchronous completion, use the Registry and Wait ($REGISTRYW) system service. The $REGISTRYW system service is identical to the $REGISTRY system service, except that $REGISTRYW returns to the caller after the system completes the requested operation. For additional information about system service completion, see the Synchronize ($SYNCH) system service.
This system service is 64-bit compatible.
SYS$REGISTRY [efn], func, 0, itmlst, [iosb or iosa_64], [astadr or astadr_64], [astprm or astprm_64]
SYS$REGISTRYW [efn], func, 0, itmlst, [iosb or iosa_64], [astadr or astadr_64], [astprm or astprm_64]
efn
OpenVMS usage: ef_number type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Number of the event flag to be used by $REGISTRY. If you do not specify the event flag, the system defaults to EFN$C_ENF. The event flag is initially cleared by $REGISTRY and then set when the operation completes.func
OpenVMS usage: function_code type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Function code specifying the action that $REGISTRY is to perform. The func argument is a longword containing this function code. The function code can contain function modifiers. For more information on function modifiers, see the Function Modifiers section in this chapter.A single call to $REGISTRY can specify only one function code. All function codes require additional information to be passed in the call with the itmlst argument.
itmlst
OpenVMS usage: item_list3 or item_list_64b type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Item list supplying information that the system will use to perform the function specified by the func argument. The itmlst argument is the address of the item list. The item list consists of one or more sets of item descriptors. Each descriptor is either an item-list-3 or item-list-64b format.Some function codes allow you specify multiple operations in a single call. In this case, you must place the REG$_SEPARATOR item code between each set of item codes. Each request, separated by a REG$_SEPARATOR item code, can contain the item codes in any order.
You can specify item codes as either input or output parameters. Input parameters modify functions, set context, or describe the information to be returned. Output parameters return the requested information. For item-list-3 lists, you must terminate the list with a longword of 0. For item-list-64b lists, you must terminate the list with a quadword of 0.
Figure 10-1 shows the structure of an item-list-3 descriptor.
Figure 10-1 Item-list-3 Structure
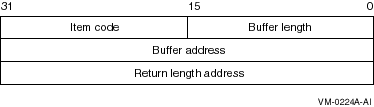
Figure 10-2 shows the structure of an item-list-64b descriptor.
Figure 10-2 Item-list-64b Structure

Table 10-1 defines the item descriptor fields.
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| Buffer length | A word that specifies the length of the buffer. The buffer either supplies information to be used by $REGISTRY, or receives information from $REGISTRY. The required length of the buffer varies, depending on the item code specified. Each item code description specifies the required length. |
| Item code | A word containing a symbolic code that describes the type of information currently in the buffer or that is returned in the buffer. The buffer address field points to the location of the buffer. |
| Buffer address | A longword that contains the address of the buffer that specifies or receives the information. |
| Return length address | A longword that contains the address of a word that specifies the actual length in bytes of the information returned by $REGISTRY. The information resides in a buffer identified by the buffer address field. The field applies to output item list entries only, and must be 0 (zero) for input entries. If the return length address is 0, it is ignored. |
| OpenVMS usage: | status_block |
| type: | buffer |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
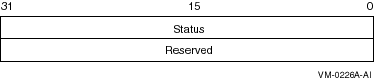
When $REGISTRY begins execution, it clears the quadword I/O status block if you specify the iosb argument.
Although the iosb argument is optional, Compaq strongly recommends that you specify it for the following reasons:
The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of the call to the $REGISTRY service. The condition value returned in R0 provides information about the success or failure of the service call itself; the condition value returned in the I/O status block provides information about the success or failure of the service operation.
To assess the success or failure of the call to $REGISTRY accurately, you must first check the condition value returned in R0. If R0 contains a successful value, you must check the condition value in the I/O status block.
Table 10-2 defines the item descriptor fields.
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| Status | A longword specifying the final status of the $REGISTRY service. If you request multiple operations for a function code, the system returns either SS$_NORMAL or SS$_REGERROR to iosb. This field is set to 0 (zero) when the operation begins. |
| Reserved | A reserved longword. |
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
If the $REGISTRY service is not called successfully (that is, if it returns an error immediately), the AST routine is not executed.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
The $REGISTRY service provides the means to create, delete and modify registry keys, key values, and key attributes.The $REGISTRY service uses process P1 space to store handles to keys. The $REGISTRY service must be called at IPL 0, and requires system dynamic memory to deliver AST requests.
- $REGISTRYW
Function Codes Table 10-3 provides a summary of valid function codes, a brief description of their function, and the OpenVMS Registry rights identifier required to perform the function. You can find a detailed description of each item code in the Item Codes section of this chapter.
SS$_ACCVIO One of the arguments cannot be read/written SS$_BADPARAM Function code or one of the item list code is invalid SS$_EXASTLM Exceeded AST limit SS$_EXBYTLM Exceeded byte count quota SS$_ILLEFC Illegal event flag number SS$_INSFARG Insufficient number of argument supplied SS$_INSFMEM Insufficient dynamic memory SS$_NORMAL Normal successful completion SS$_TOO_MANY_ARGS Too many arguments REG$ACCESS_DENIED Requested access is denied REG$_ACCESSDENIED Requested access to key is denied REG$_BADFILEVER Bad file version number REG$_BUFFEROVF Buffer overflow REG$_CANTCLEANVOLSEG Cannot clean the registry volatile segments REG$_CANTCONVCS Code set conversion error REG$_CANTOPENOUTFILE Cannot open the specified output file REG$_DBACCESS Cannot access registry database object REG$_DBALREADYLOADED Database is already loaded REG$_DBCREATE Cannot create registry database REG$_DBCSMISMATCH Database checksum mismatch: Stored=!XL Calculated=!XL REG$_DBFIND Cannot locate registry database REG$_DBFULL Registry database is full REG$_DBLOAD Cannot load registry database REG$_DBNOTYETLOADED Database is not yet loaded REG$_DBVERMISMATCH Database version mismatch: Current=V!UW.!UW Database=V!UW.!UW REG$_DELROOTKEY Root key was deleted REG$_DOUBLEDEALLOC Structure is already on the free list REG$_DTMUTEXERROR DECthreads mutex lock/unlock error REG$_DTMUTEXINIT DECthreads mutex init error !UL REG$_DTMUTEXLOCK DECthreads mutex lock error !UL REG$_DTMUTEXLOCKED DECthreads mutex is already held by another thread REG$_DTMUTEXUNLOCK DECthreads mutex unlock error !UL REG$_DTRWLOCKINIT DECthreads read/write lock init error !UL REG$_DTRWLOCKLOCK DECthreads read/write lock error !UL REG$_DTRWLOCKUNLOCK DECthreads read/write unlock error !UL REG$_DUPLREQUEST Work-in-progress hash table insert found duplicate request REG$_EXQUOTA Registry file quota or page file quota exceeded REG$_FILECREATE Error creating !AZ!AZ REG$_FILENAMEINVAL Invalid file name REG$_FILEOPEN Error opening !AZ!AZ REG$_FILEREADEOF Attempt to read past end of file; FTE !XL REG$_FNAMMISMATCH Physical/logical file name mismatch; FTE=!AZ LTE=!AZ REG$_FSOCORRUPT File was previously flagged as corrupt; FSO: !XL !XL REG$_FSOFILEINDEX Invalid file index in FSO: !XL !XL REG$_FSOOFFSET Invalid offset in FSO: !XL !XL REG$_FSOSEGNUMBER Invalid segment number in FSO: !XL !XL REG$_FSOSEGREADERR Error reading segment in FSO: !XL !XL REG$_FTEALLOC Error allocating file table entry !XL for !AZ REG$_FTEALREADYEXIST Cannot create file !AZ!AZ; file already exists REG$_FTEALREADYOPEN File is already open REG$_FTEDUPNAME Error allocating file table entry; duplicate file name REG$_FTEINSUFFINFO Specified file table entry is not allocated REG$_FTEINUSE Error allocating file table entry; entry in use REG$_FTENOTEXIST Specified file table entry does not exist REG$_FTENOTOPEN Specified file is not open REG$_FTIMISMATCH Physical file index mismatch; LTE = !XL, FTE = !XL REG$_HASLINK Key has a link to another key REG$_HAVESUBKEYS Cannot delete a key with subkeys REG$_INTERNERR Registry internal error REG$_INVCACHEACTION Invalid cache action parameter REG$_INVCREDENTIALS NT credentials are not valid REG$_INVDATA Invalid data value REG$_INVDATATYPE Invalid data type parameter REG$_INVFUNCCODE Invalid function code REG$_INVKEYFLAGS Invalid key flags REG$_INVKEYID Key does not exist or invalid key ID was specified REG$_INVKEYNAME Invalid key name REG$_INVLINK Invalid link or link type REG$_INVLINKPATH Invalid link path REG$_INVLOG Invalid log file REG$_INVLOGREC Invalid log record REG$_INVPARAM Invalid parameter REG$_INVPATH Invalid key path REG$_INVSECDESCRIPTOR Invalid security descriptor REG$_INVSECPOLICY Invalid security policy parameter REG$_INVSEGNUM Invalid segment number REG$_INVVOLROOTKEY Cannot create a new file with a volatile root key REG$_IOREADERR Disk read error at block !UL for length !UL REG$_IOWRITERR Disk write error at block !UL for length !UL REG$_IPCCONACC IPC connect accept failure: !XL REG$_IPCCONREJ IPC connect reject failure: !XL REG$_IPCDCLAST IPC cannot declare AST for synch completion: !XL REG$_IPCOPEASS IPC open association failure: !XL REG$_IPLTOOHIGH Callers above IPL 0 cannot call this service REG$_KEYCHANGED Key or subkey has changed REG$_KEYEXIST Key already exists REG$_KEYLOCKED Key locked by another thread REG$_KEYNAMEEXIST Key name already exists REG$_LOGFILETABFULL Logical file table is full REG$_LTENOTEXIST Specified logical file table entry does not exist REG$_MOREDATA Buffer provided is too small for requested data REG$_NOBLOCKFOUND Registry database has no available blocks REG$_NOKEY Specified key does not exist REG$_NOMEMORY Insufficient memory REG$_NOMOREITEMS No more items for specified key REG$_NOMORESEG No more segments available REG$_NOMORESUBSTRING No substring found REG$_NOPATHFOUND Path not found REG$_NOSUCHFILE No such file REG$_NOTROOTKEY Invalid root key index REG$_NOTSUPPORTED Function code, item code, or item value is not supported REG$_NOVALUE Specified value does not exist REG$_OBJWITHLINK Deleted key or value had link(s)pointing to it REG$_REQRECEIVED Received request for key change notification REG$_RESERVED Cannot delete or modify a reserved key or value REG$_ROOTINSFILE Insufficient file list in root file REG$_RUIDMISMATCH Root key UID mismatch; LTE = !@XQ !@XQ; Root key = !@XQ !@XQ REG$_SECVIO Violates the security access method specified when this key was last opened REG$_SEGREADERR Error reading segment !UL of file !AZ REG$_STRINGTOOLONG Input string too long REG$_STRINGTRUNC Output buffer is not large enough to contain the converted string REG$_SVRVERMISMATCH Version mismatch: Server=V!UL.!UL Database=V!UL.!UL REG$_SVRSHUTDOWN Server shutdown in progress REG$_TOOMANYOPENKEY Number of opened keys exceeds the limit; close some opened key REG$_UNKTHRREQ Unknown thread request code REG$_VALUEEXIST Value already exists REG$_VOLMISMATCH Cannot create nonvolatile subkey for a volatile key
The OpenVMS Registry identifier is required only if you do not provide a valid NT access token and you do not have the SYSPRV privilege. If you have a granted REG$UPDATE identifier, you can perform all the functions in Table 10-3.
| Function Code | Identifier | Description |
|---|---|---|
| REG$FC_CLOSE_KEY | REG$LOOKUP | Closes an open key or subkey. |
| REG$FC_CREATE_KEY | REG$UPDATE | Creates (and opens) a subkey. |
| REG$FC_DELETE_KEY | REG$UPDATE | Removes a subkey from a key. |
| REG$FC_DELETE_VALUE | REG$UPDATE | Removes a value from a key. |
| REG$FC_ENUM_KEY | REG$LOOKUP | Lists (enumerates) the subkeys of a key. |
| REG$FC_ENUM_VALUE | REG$LOOKUP | Lists (enumerates) the values of a key. |
| REG$FC_FLUSH_KEY | REG$UPDATE | Ensures that all information for the key is backed to disk. |
| REG$FC_MODIFY_KEY | REG$UPDATE | Modifies a key. |
| REG$FC_MODIFY_TREE_KEY | REG$UPDATE | Modifies a key and all its subkeys. |
| REG$FC_NOTIFY_CHANGE_KEY_VALUE | REG$UPDATE | Notifies when a key or value has changed. |
| REG$FC_OPEN_KEY | REG$LOOKUP | Opens a key or subkey. |
| REG$FC_QUERY_KEY | REG$LOOKUP | Fetches information about a key. |
| REG$FC_QUERY_VALUE | REG$LOOKUP | Fetches information about a value. |
| REG$FC_SEARCH_TREE_DATA | REG$LOOKUP | Searches the value data of key and its subkeys. |
| REG$FC_SEARCH_TREE_KEY | REG$LOOKUP | Searches the names of a key and its subkeys. |
| REG$FC_SEARCH_TREE_VALUE | REG$LOOKUP | Searches the values of a key and its subkeys. |
| REG$FC_SET_VALUE | REG$UPDATE | Changes the data associated with a value name. |
REG$FC_CLOSE_KEY
This request releases the open resources of the specified key. If REG$_KEYID indicates a predefined key, the system ignores the action and returns success.
Previous Next Contents Index
Copyright © Compaq Computer Corporation 1999. All rights reserved.
6539P003.HTM