.title Dassign
.ident /01/
$inetsymdef ; INET symbols
exit
purge
: .ascid /tcpip$device:/ ; INET device name
channel: .word 0 ; INET channel
.entry start,^m<>
.
.
.
;
; Deassign an INET device
;
$Dassgn_s chan=channel
.
.
.
.end start
|
| Example 4-6 $DASSGN System Service (C Programming) |
|---|
#module dassgn_chan
/*
**++
**
** This example deassigns the specified channel
** using system service SYS$DASSNG
**
**--
*/
/*
** INCLUDE FILES
*/
dassgn_chan(chan)
short chan ; /* INET channel which is to be deassigned */
{
int status ; /* For return status */
/*
** Deassign the channel
*/
status = SYS$DASSGN(chan) ;
if ((status & 1) == 0) {
printf("Failed to deassign the channel\n") ;
return(status) ;
}
return(status) ;
}
|
$GETDVI
This service returns information about primary and secondary device characteristics of the internet pseudodevice.The $GETDVI service is completed asynchronously. It returns to the caller after queuing the information request without waiting for the requested information to be returned.
For synchronous completion, use the Get Device/Volume Information and Wait ($GETDVIW) service. The $GETDVIW service is identical to the $GETDVI service except that $GETDVIW returns to the caller with the requested information.
The equivalent C Socket calls are the getpeername(), getsockname(), and getsockopt() routines.
Format
SYS$GETDVI [efn],[chan], [devnam],itmlst,[iosb],[astadr], [astprm],[nullarg]
Returns
OpenVMS usage: longword (unsigned) type: write only access: by value
Longword condition value. All system services return (by immediate value) a condition value in R0. Condition values that can be returned by this service are listed under Condition Values Returned.
Arguments
efn
OpenVMS usage: ef_number type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Number of the event flag to be set when $GETDVI returns the requested information. The efn argument is a longword containing this number.When the request is initiated, $GETDVI clears the specified event flag (or event flag 0 if efn was not specified). When $GETDVI returns the requested information, it sets the specified event flag (or event flag 0).
chan
OpenVMS usage: channel type: word (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Number of the I/O channel assigned to the device about which information is desired. The chan argument is a word containing this number.devnam
OpenVMS usage: device_name type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by descriptor---fixed-length string descriptor
The name of the device for which $GETDVI returns information. The devnam argument is the address of a character string descriptor pointing to the name string.The device name string can be either a physical device name or a logical name. If the first character in the string is an underscore (_), the string is considered a physical device name. Otherwise, the string is considered to be a logical name. In that case, logical name translation is done until either a physical device name is found or the system default for number of translations has been reached.
If the device name string contains a colon, the colon and the characters that follow it are ignored.
To identify a device to $GETDVI, specify either the chan argument or the devnam argument, but not both. If both arguments are specified, the chan argument is used.
If neither chan nor devnam is specified, $GETDVI uses a default value of zero for chan.
itmlst
OpenVMS usage: item_list type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Item list specifying which information about the device is to be returned. The itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors, each of which describes an item of information. The list of item descriptors is terminated by a length and item code of zero. Figure 4-1 depicts the format of an item descriptor.Figure 4-1 Single Item Descriptor
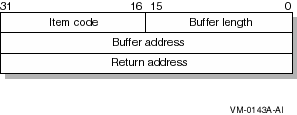
$GETDVI Item Descriptor Fields
- buffer-length
A word containing a user-supplied integer specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer for which the $GETDVI returns information. The length of the buffer needed depends on the item code specified in the item code field of the item descriptor. If the value of buffer-length is too small, $GETDVI truncates the data. -
item-code
A word containing a user-supplied symbolic code that specifies the information that $GETDVI returns. These codes are defined by the $DVIDEF macro, which is defined in SYS$LIBRARY:STARLET.MLB for the MACRO-32 language and SYS$LIBRARY:DVIDEF.H for the C language. Each item code is listed in the Table 4-2. -
buffer-address
A longword containing the user-supplied address of a word in which the length of the information (in bytes) is returned. -
return-length-address
A longword containing the user-supplied address of a word in which $GETDVI writes the length of the information it returned (in bytes).
$GETDVI Item Codes
| Item Code | Description |
|---|---|
| DVI$_ACPTYPE | A 4-byte hexadecimal number. The DVI$_ACP_TCP symbol defines the ACP type code that $GETDVI can return. This symbol is defined in the TCPIP$INETDEF symbol definition file. |
| DVI$_DEVCHAR | Returns device-independent characteristics as a 4-byte vector. Each characteristic is represented by a bit. When $GETDVI sets a bit, the device has the corresponding characteristic. Each bit in the vector has a symbolic name. These symbolic names are defined by the $DEVDEF macro, and are listed in Table 4-3. |
| Symbol | Device Type |
|---|---|
| DVI$_NET | Network device |
| DVI$_AVL | Available |
| DVI$_MNT | Mounted |
| DVI$_IDV | Input device |
| DVI$_ODV | Output device |
When DVI$_STS is specified, $GETDVI returns the device unit status as a 4-byte vector. Each bit in the vector, when set, corresponds to a symbolic name that is defined by the $UCBDEF macro. These symbols are defined in Table 4-4.
| Symbol | Device Type |
|---|---|
| UCB$M_ONLINE | Online |
| UCB$M_TEMPLATE | Template |
iosb
| OpenVMS usage: | io_status_block |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The iosb argument signifies the I/O status block that receives the final completion status code. The iosb is the address of the quadword I/O status block.
When the iosb argument is specified, $GETDVI sets the quadword to zero when the request is initiated. When the request is completed, a condition value is returned to the first longword. The second longword is reserved for Compaq.
Although the iosb argument is optional, Compaq strongly recommends that you specify it for the following reasons:
- If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value. This allows you to be sure that the event flag was not set by an event other than service completion.
- If you are using the $SYNCH system service to synchronize the completion of the service, you must use iosb as an argument. The iosb argument is required for $SYNCH.
- The condition value returned in R0 and the condition value returned in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of the call to the $GETDVI service. The condition value returned in R0 gives you information about the success or failure of the service call itself. The condition value returned in the I/O status block gives you information about the success or failure of the service operation. Therefore, to accurately assess the success or failure of the call to $GETDVI, you must check the condition values returned in both R0 and the I/O status block.
astadr
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure entry mask |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
AST service routine to be executed when $GETDVI is completed. The astadr argument is the address of the entry mask of this routine.
If astadr is specified, the AST routine executes at the same access mode as the caller of the $GETDVI service.
astprm
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine specified by the astadr argument. The astprm argument contains a longword parameter value.
nullarg
| OpenVMS usage: | null_arg |
| type: | quadword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
Place-holding argument. This argument is reserved for Compaq.
Description
The chan argument can be used only if the channel has already been assigned and the caller's access mode is equal to or more privileged than the access mode from which the original channel assignment was made.The $GETDVI system service does not need to have a channel assigned to the device about which information is desired.
The $GETDVI system service returns information about both primary and secondary characteristics of the device. By default, $GETDVI returns information about the primary characteristics only.
To obtain information about secondary device characteristics, the item code specifying the information desired must be merged (ORed) with the code DVI$M_SECONDARY.
Information about primary and secondary devices can be obtained in a single call to $GETDVI.
In most cases, the two sets of characteristics (primary and secondary) returned by $GETDVI are identical. However, the two sets provide different information in the following cases:
- If the device has an associated mailbox, the primary characteristics are those of the assigned device and the secondary characteristics are those of the associated mailbox.
- If the device represents a logical link on the network, the secondary characteristics contain information about the link.
Unless otherwise stated in the item code description, $GETDVI returns information about the local node only.
Condition Values Returned
SS$_NORMAL Service successfully completed. SS$_ACCVIO The device name string descriptor, device name string, or itmlst argument cannot be read or the buffer or return length longword cannot be written by the caller. SS$_BADPARAM The item list contains an invalid item code, or the return length address field in an item descriptor specifies less than 4 bytes for the return length information. SS$_EXASTLM The process has exceeded its AST limit quota. SS$_IVCHAN An invalid channel number was specified (that is, a channel number of zero or a number greater than the number of channels). SS$_IVDEVNAM The device name string contains invalid characters or neither the devnam nor the chan arguments was specified. SS$_IVLOGNAM The device name string has either a length of zero or more than 63 characters. SS$_NONLOCAL This warning code indicates that the device is on a remote system. SS$_NOPRIV The specified channel is not assigned or was assigned from a more privileged access mode. SS$_NOSUCHDEV This warning code indicates that the specified device does not exist on the host system.
$QIO
This service queues an I/O request to a channel associated with an internet pseudodevice.The $QIO service is completed asynchronously, which means it returns to the caller immediately after queuing the I/O request, without waiting for the I/O operation to be completed.
For synchronous completion, use the Queue I/O Request and Wait ($QIOW) service. The $QIOW service is identical to the $QIO service, except the $QIOW returns to the caller after the I/O operation has been completed.
On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
The equivalent C Socket calls are the bind() and listen() routines.
Format
SYS$QIO [efn],chan,func, [iosb],[astadr],[astprm],[p1], [p2],[p3],[p4],[p5], [p6]
C Prototype
int sys$qio unsigned int efn, unsigned short int chan, unsigned int func, struct _iosb *iosb, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), __int64 astprm, void *p1, __int64 p2, __int64 p3, __int64 p4, __int64 p5, __int64 p6
;)
Returns
OpenVMS usage: longword (unsigned) type: write only access: by value
Longword condition value. All system services return (by immediate value) a condition value in R0.
Arguments
efn
OpenVMS usage: ef_number type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Event flag that $QIO sets when the I/O operation is completed. The efn argument is a longword value containing the number of the event flag.If efn is not specified, event flag 0 is set.
The specified event flag is set if the service terminates without queuing an I/O request.
chan
OpenVMS usage: channel type: word (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
I/O channel that is assigned to the device to which the request is directed. The chan argument is a word value containing the number of the I/O channel.func
OpenVMS usage: function_code type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Function codes and function modifiers specify the operation of the software. The func argument is a longword value containing the function code.For more information about the function codes and modifiers, see Section 4.2.
iosb
OpenVMS usage: io_status_block type: quadword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by 32-reference or 64-bit reference (Alpha only)
I/O status block to receive the final completion status of the I/O operation. The iosb is the address of the quadword I/O status block. See Figure 3-1 for a description of the general structure of the I/O status block.When the $QIO begins executing, the event flag clears. The $QIO also clears the quadword I/O status block if the iosb argument is specified.
Although the iosb argument is optional, Compaq strongly recommends that you specify it for the following reasons:
- If you are using an event flag to signal the completion of the service, you can test the I/O status block for a condition value. This assures that the event flag was not set by an event other than service completion.
- If you are using the OpenVMS $SYNCH service to synchronize service completion, the I/O status block is a required argument for $SYNCH.
- The condition values returned in the R0 and those returned in the I/O status block provide information about different aspects of the call to the $QIO service. The condition value returned in R0 gives you information about the success or failure of the service call itself. The condition values returned in the I/O status block report the success or failure of the service operation. Therefore, to access the success or failure of the $QIO call, check the condition values returned in both the R0 and the I/O status block.
astadr
OpenVMS usage: ast_procedure type: procedure entry mask access: call without stack unwinding mechanism: by 32-reference or 64-bit reference (Alpha only)
AST service routine to be executed when the I/O is completed. The astadr argument is the address of the entry mask to the AST routine.The AST routine executes at the access mode of the caller of $QIO.
astprm
OpenVMS usage: user_arg type: quadword unsigned (Alpha); longword unsigned (VAX) access: read only mechanism: by 32-bit value or 64-bit value (Alpha only)
AST parameter to be passed to the AST service routine. The astprm argument is a longword value of the AST parameter.p1 to p6
OpenVMS usage: varying_arg type: quadword unsigned (Alpha); longword unsigned (VAX) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit (Alpha only) reference, value, or descriptor
Optional device- and function-specific I/O request arguments. The parameter values contained in these arguments vary according to the function for which they are used. See Table 4-5 for the descriptions of internet I/O function codes.
Description
$QIO operates only on assigned I/O channels and only from access modes that are equal to or more privileged than the access mode from which the original channel assignment was made.
Previous Next Contents Index