- <FROM_ADDRESS>
- <MEMO_TO>
DESCRIPTION
The <TO_ADDRESS> tag places the name and address of the receiver of a letter flush left on the left margin. The tag outputs one to five lines of text, based on the number of address line arguments specified. Each argument is placed flush left on a new line at the left margin.Alternatively, you can use the <MEMO_TO> tag to specify this same information, but in a different format. See the description of the <MEMO_TO> tag in this chapter for more information.
Example
The following example shows a typical beginning of a letter using the <TO_ADDRESS> tag.
<FROM_ADDRESS>(Bob Smith\Harvard University\Cambridge, MA) <TO_ADDRESS>(Carol Jones\World Wide Wicker Co.\Seattle, WA) <SUBJECT>(Ted and Alice) <SALUTATION>(Hi Carol,) <P> This is the text of the letter... |
Chapter 6
Using the MANUAL Doctype
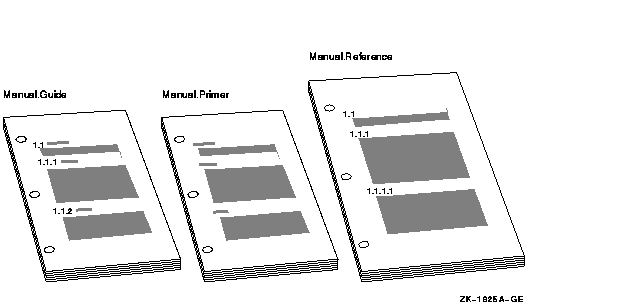
The MANUAL doctype has three designs for printed documentation, shown in Figure 6-1, and one design for online documentation:
- MANUAL.GUIDE
Creates a users' manual in a 7 x 9 -inch format with numbered headings. This design is intended for chapter-oriented tutorial material. - MANUAL.PRIMER
Creates a users' manual in a 7 x 9 inch format with unnumbered headings. This design is intended for chapter-oriented primer material. - MANUAL.REFERENCE
Creates a users' manual in an 8 1
2 x 11 inch format with numbered headings. This design is intended for reference material, and is the default design. - MANUAL.ONLINE
Creates an online users' manual in a 5.9 x 6.6 -inch format with numbered headings and ragged right margin. This design is solely for online display. Refer to Chapter 8 for information about online documentation.
Table 6-1, Table 6-2, and Table 6-3 list the page layout characteristics of the MANUAL doctype designs for printed documentation.
Figure 6-1 MANUAL Doctype Designs
| Page Layout Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Running heads | Chapter title text |
| Running feet | Chapter number and page number |
| Page numbering | Chapter-oriented |
| Trim size | 7 x 9 inches |
| Gutter width | 2.5 picas |
| Right margin | Justified |
| Text Element Characteristics | |
| Headings | Numbered |
| Paragraphs | Flush left at gutter width |
| Figures, tables, and examples | Numbered, table of contents entry |
| Page Layout Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Running heads | Chapter title text |
| Running feet | Page number |
| Page numbering | Chapter oriented |
| Trim size | 7 x 9 inches |
| Gutter width | 2.5 picas |
| Right margin | Justified |
| Text Element Characteristics | |
| Headings | Unnumbered |
| Paragraphs | Flush left at gutter width |
| Figures, tables, and examples | Numbered, table of contents entry |
| Page Layout Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Running heads | None |
| Running feet | Chapter title text and page number |
| Page numbering | Chapter oriented |
| Trim size | 8 1/2 x 11 inches |
| Gutter width | 2.5 picas |
| Right margin | Justified |
| Text Element Characteristics | |
| Headings | Numbered |
| Paragraphs | Flush left at gutter width |
| Figures, tables, and examples | Numbered, table of contents entry |
The MANUAL doctype designs require no doctype-specific tags, but accept the full range of DECdocument global tags. See the Using Global TagsUsing Global Tags for more information on global tags. Process a file with the MANUAL doctype by using one of the doctype keywords in the preceding list on the DOCUMENT command line. The following example shows how to process a file named MYMANUAL.SDML with the MANUAL doctype to create a reference manual.
$ DOCUMENT MYMANUAL MANUAL.REFERENCE LN03 |
6.1 Example of Using the MANUAL Doctype
This section contains a sample SDML file for producing a portion of a
manual. The example is for the first few pages of a hardware manual
created using the MANUAL.REFERENCE doctype. The output of this manual
sample shows the title page and some numbered headings and a table in
the body of the manual. You may find these samples useful in
understanding how global tags can be used in the MANUAL doctype to
create various kinds of manuals.
<FRONT_MATTER> <TITLE_PAGE> <TITLE>(Series III Overthruster\User Manual) <ABSTRACT> This book describes the Series III Overthruster, the Series III manual-override mode and the Overthruster monitor utilities. <ENDABSTRACT> <ENDTITLE_PAGE> <ENDFRONT_MATTER> <CHAPTER>(Introduction to the Overthruster\INTRO_CHAP) <P> The Series III Overthruster is an intelligent mass thrust device, designed to deliver controlled thrust from a ZX-300 type drive unit. The Series III family provides enhanced data collection and control utilities far superior to those present in the Series II. <HEAD1>(Series III Overthruster Models\thruster) <p> The Series III Overthruster family has three models. <REFERENCE>(MODEL_TAB) lists these models and the salient features of each. <TABLE>(Comparison of Series III Overthruster Models\MODEL_TAB) <TABLE_SETUP>(4\25\10\10) <TABLE_HEADS>(Feature\<SPAN>(3\LEFT)Models\ \ ) <TABLE_HEADS>( \SIII-O30\SIII-O50\SIII-O70) <TABLE_ROW>(Data Channels Supported\2\4\4) <TABLE_ROW>(I/O Control Processor \A-L35\J19\J19) <TABLE_ROW>(Drive Unit\ZX-301\ZX-301\ZX-310A) <TABLE_ROW>(Power Source\TY-100\TY-100A \TY-200) <TABLE_ROW>(Control Memory\128Kb\128Kb\512Kb) <TABLE_ROW>(Data Memory\ -- \ -- \512Kb) <ENDTABLE> <HEAD1>(Series III Overthruster Functional Description\thruster_func) <p> The Series III Overthruster is an intelligent mass thrust device in accordance with the DS8 architecture. |
Should you wish to create the output file yourself, you can obtain the file MANUAL_SAMPLE.SDML from directory DOC$ROOT:[EXAMPLES] and process it using the MANUAL doctype. Comparing the output to this SDML file may be helpful in understanding how to use these tags.
Chapter 7
Using the MILSPEC Doctype
DECdocument has two doctype designs for creating printed military documents, as shown in Figure 7-1, and one design for online documentation:
- MILSPEC.SECURITY
Use MILSPEC.SECURITY to produce documents requiring security classifications or to produce documents that conform to the U.S. Department of Defense standard DOD-STD-2167 or DOD-STD-2167A.
MILSPEC.SECURITY includes tags for security classification, numbering of figures and tables by section number, additional heading levels, 1- to 4-line running titles, single-line running feet, and the ability to use proportionally spaced fonts in code examples. - MILSPEC.DRAFT
Use MILSPEC.DRAFT to produce double-spaced draft documents. - MILSPEC.ONLINE
Use MILSPEC.ONLINE to produce documents that can be viewed with Bookreader. This doctype accepts all tags that are valid in MILSPEC.SECURITY. Refer to Chapter 8 for information about online documentation.
MILSPEC.ONLINE creates an online document in a 5.9 x 6.6 inch format with numbered headings and ragged right margin.
Table 7-1 lists the page layout of the MILSPEC doctype designs for printed documentation.
Figure 7-1 MILSPEC Doctype Designs

| Page Layout Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Running heads | Two-line running heading |
| Running feet | Sequential using Arabic numerals |
| Page numbering | Sequential using Arabic numerals |
| Trim size | 8 1/2 x 11 inches |
| Right margin | Justified |
| Text Element Characteristics | |
| Headings | Numbered using Arabic numerals |
| Paragraphs | Numbered using Arabic numerals |
| Figures, Examples | Numbered using Arabic numerals |
| Tables | Numbered using Roman numerals |
7.1 MILSPEC Template Files
DECdocument provides template files for MIL-STD-490A documents and for DOD-STD-2167 or DOD-STD-2167A Data Item Description documents in the directory DOC$TEMPLATES. Each template file contains all the headings, titles, and other text elements required by the MIL-STD-490A, DOD-STD-2167 and DOD-STD-2167A specifications for conforming documents. Comments in the template input files guide you in placing your information into the file. See Section 7.3, Section 7.4.1, and Section 7.4.2 for more information on using these templates.
Another source of templates exists. If you have the VAX
Language-Sensitive Editor (LSE) Version 2.0 or higher installed on your
system, you can access LSE templates for the DOD-STD-2167 or
DOD-STD-2167A Data Item Description documents and then expand the
appropriate placeholders to create source files for these doctypes.
7.2 MILSPEC Doctype Conformance and Format
The MILSPEC doctype produces documents conforming to United States Department of Defense Military Specification Standard MIL-STD-490A, published June 4, 1985, or documents conforming to United States Department of Defense Standard DOD-STD-2167, also published June 4, 1985.
The MILSPEC doctype provides 24 template SDML files for documents that conform to the Department of Defense standard DOD-STD-2167 for Data Item Descriptions. Data Item Descriptions are MIL-STD-490A documents that are specialized for a particular kind of information. DOD-STD-2167 specifies the exact form of each data item description. See Section 7.4.1 for more information on creating a DOD-STD-2167 document.
Documents produced using the MILSPEC doctype design have the following general format:
- Pages, formal figures, and formal tables are numbered sequentially throughout the document and are not numbered by chapter, section, or appendix.
- Paragraphs are numbered using the global numbered heading tags (<HEAD1> or <HEAD2>) to create the Arabic numerals. A period automatically ends the numbered paragraph headings.
- Formal tables are numbered using Roman numerals.
- The global <PREFACE> tag automatically generates a preface section heading of Foreword rather than Preface. All other DECdocument doctypes use the heading Preface.
- The table of contents begins on page ii rather than on page iii. All other DECdocument doctypes that support the automatic creation of tables of contents begin the table of contents on page iii.
- Appendixes are numbered using Roman numerals. Sections and paragraphs in an appendix are numbered in Arabic numerals. The Arabic numerals correspond to the appendix number multiplied by 10 if there are fewer than 10 such sections or paragraphs or by 100 if there are 10 or more sections or paragraphs. For example, in Appendix II, the first major paragraph would be paragraph 20.1, and the second paragraph would be 20.2.
The MILSPEC doctype accepts the full range of DECdocument global tags, with the exception of the <PART> and <PART_PAGE> tags. Table 7-2 summarizes the tags specific to the MILSPEC doctype, which are also used in the MILSPEC.SECURITY and MILSPEC.DRAFT doctype designs. See Section 7.5 for more information on any of these tags.
| Tag Name | Description |
|---|---|
| <SET_APPENDIX_NUMBER> | Overrides the default Roman numeral DECdocument usually assigns to an appendix. |
| <SIGNATURE_LINE> | Creates up to two rules on a line (one in each signature column) and places a name below each rule; each rule serves as a signatory line for the person listed below it. |
| <SIGNATURE_LIST> | Begins a 2-column listing of signature lines on the title page and places a heading above each column. You create each row of signature lines using the <SIGNATURE_LINE> tag in the context of the <SIGNATURE_LIST> tag. |
| <SPECIFICATION_INFO> | Creates a listing of information about the specification document on the title page and creates a 2-line running heading that lists the specification number and date for the rest of the document. |
| <SPEC_TITLE> | Creates a title with up to seven centered lines on the title page. |
| <SUBTITLE> | Creates a subtitle with up to seven centered lines on the title page. |
7.2.1 Example of Using the MILSPEC.SECURITY and MILSPEC.DRAFT Doctypes
This section contains a sample of the first pages of a specification
created using the MILSPEC doctype tags. This sample includes the title
page of the specification and the first page of text after the title
page.
Note that <SET_HEADINGS> is used within the <DOCUMENT_ATTRIBUTES> tag to cause running headings to be centered. Also note that the <SECURITY> and <HIGHEST_SECURITY_CLASS> tags are used to label text elements with security classifications.
The SDML code for the specification is shown first, followed by the output from that SDML code when processed for a POSTSCRIPT destination and the MILSPEC.SECURITY doctype, and then followed by the output when processed for a POSTSCRIPT destination and the MILSPEC.DRAFT doctype.
<DOCUMENT_ATTRIBUTES> <SET_HEADINGS>(CENTERED) <ENDDOCUMENT_ATTRIBUTES> <FRONT_MATTER> <TITLE_PAGE> <SPECIFICATION_INFO>(12345B\a142-b4\<DATE>\Part I of Three Parts) <ONLINE_TITLE>(PDS For the Overthruster Monitor System) <SPEC_TITLE>(Preliminary Development Specification \For the Overthruster Monitor System \Series (Series Configuration Number) \Order Number (Approved Order Number)) <SUBTITLE>(Submitted Under\Contract A00000--11--A--2222\<highest_security_class>) <set_security_class>(C_LEVEL\CL\C_LEVEL\5) <SIGNATURE_LIST>(Authenticated by:\Approved by:) <SIGNATURE_LINE>(Procurer\Program Manager) <SIGNATURE_LINE>(Date\Technical Director) <SIGNATURE_LINE>(\Consultant) <ENDSIGNATURE_LIST> <ENDTITLE_PAGE> <COMMENT>(<endsecurity>) <CONTENTS_FILE> <ENDFRONT_MATTER> <CHAPTER>(Scope\first_sec) <HEAD1>(Scope\scope_head) <P> This document establishes all specifications for the design and production of the Overthruster Monitor System (USN-122-233x) by our Corporation. <HEAD1>(Purpose\purpose_sec) <P> The purpose of this document is to specify all design and production dimensions of the Overthruster Monitor System. This will ensure that all essential requirements are met and that all concerns are addressed. <set_security_class>(C_LEVEL\CL\C_LEVEL\5) <HEAD2>(Primary Purpose\Primary_purpose_sec) <P> The primary purpose is to enrich the quality dimension of our product. <COMMENT>(<endsecurity>) <HEAD3>(Secondary Purpose\secondary_purpose_sec) <P> The secondary purpose is to create a corporate strategy for the product that encompasses the goals established in <REFERENCE>(primary_purpose_sec\VALUE). <P> <ELLIPSIS> <P> Production of the Overthruster Monitor System will necessitate a reorganization of our current production strategy. In order to produce the projected quantities of the Overthruster Monitor System we will have to make the changes summarized in <REFERENCE>(OMS_tab). <set_security_class>(C_LEVEL\CL\C_LEVEL\5) <TABLE>(Overthruster Monitor System <oparen>OMS<cparen> Production Line Impact\OMS_tab) <TABLE_ATTRIBUTES>(WIDE) <TABLE_SETUP>(2\18) <TABLE_HEADS>(Production<LINE>Line Name\Production<LINE>Line Modification) <TABLE_ROW>(Alpha<LINE> (System Units) \100% conversion from Series II OMS production to Series III OMS production.) <TABLE_ROW>(Beta<LINE> (Unit Stands) \Increase production 30% and designate 50% of that production for the Overthruster Monitor System sales.) <TABLE_ROW>(Gamma<LINE> (Model I Power Supplies) \Phase out production over 6-month time frame. <COMMENT>(<endsecurity>) <set_security_class>(S_LEVEL\SL\S_LEVEL\6) Will be modified to produce the new Model IIA Power Supply. <COMMENT>(<endsecurity>) ) <TABLE_ROW>(Omega<LINE> (Model IIA Power Supplies) \Increase production by 35% until Gamma comes on-line in 6 months.) <ENDTABLE> |
Should you wish to create the output file yourself, you can obtain the file MILSPEC_SECURE_SAMPLE.SDML from directory DOC$ROOT:[EXAMPLES] and process it using the MILSPEC.SECURITY doctype. Comparing the output to this SDML file may be helpful in understanding how to use these tags.
Should you wish to create the output file yourself, you can obtain the file MILSPEC_DRAFT_SAMPLE.SDML from directory DOC$ROOT:[EXAMPLES] and process it using the MILSPEC.DRAFT doctype. Comparing the output to this SDML file may be helpful in understanding how to use these tags.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |