![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/openvms_doc_banner_top.gif)
|
![[Site home]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home_off.gif)
![[Send comments]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments_off.gif)
![[Help with this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help_off.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs_off.gif)
![[OpenVMS site]](../../images/buttons/bn_openvms_off.gif)
![[Compaq site]](../../images/buttons/bn_compaq_off.gif)
|
| Updated: 11 December 1998 |
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/openvms_doc_banner_top.gif)
|
![[Site home]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home_off.gif)
![[Send comments]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments_off.gif)
![[Help with this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help_off.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs_off.gif)
![[OpenVMS site]](../../images/buttons/bn_openvms_off.gif)
![[Compaq site]](../../images/buttons/bn_compaq_off.gif)
|
| Updated: 11 December 1998 |
OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual
| Previous | Contents | Index |
Adding a specific CPU to the process affinity mask indicates that the kernel thread is able to execute only on that CPU or on the others specified in the mask. Affinity scheduling takes effect as soon as the affinity mask becomes nonzero, limiting the CPU selection for the kernel thread to what is specified and available. Thread selection and execution is still subject to standard capability requirements, but only the affinity CPU set is considered when looking for an available site. When the affinity mask is cleared, all CPUs are again considered available and affinity is deactivated.
Either modify_mask or prev_mask, or both, must be specified as arguments. If modify_mask is specified, then select_mask must be specified as an argument. If modify_mask is not specified, then no modifications are made to the affinity mask for the specified kernel thread. In this case, select_mask is ignored. If prev_mask is not specified, then no previous mask is returned.
No service changes will be allowed if the specified kernel thread will transition from a runnable to blocked state. The CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU bit in the flags argument requires that the final thread state be runnable regardless of previous state; otherwise, interim changes that maintain a blocked state are allowed if the thread is already in one.
The caller must have the ALTPRI privilege to call SYS$PROCESS_AFFINITY to modify its own affinity mask. To modify another processí affinity mask, the caller must have:
To call SYS$PROCESS_AFFINITY simply to retrieve the specific process or global mask, the caller need only have the following privileges:
$CPU_CAPABILITIES
$PROCESS_CAPABILITIES
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_BADPARAM One of more arguments has an invalid value. SS$_ACCVIO The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more arguments. SS$_NOPRIV Insufficient privilege for attempted operation. SS$_NOSUCHTHREAD The specified kernel thread does not exist. SS$_NONEXPR The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process identification was specified. SS$_IVLOGNAM The process name string has a length of 0 or has more than 15 characters. SS$_CPUCAP No CPU can run the specified process with new affinities. SS$_INSFARG Fewer than the required number of arguments were specified or no operation was specified.
On Alpha systems, allows modification of the user capability set for a specified kernel thread, or for the global user capability process default.This service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$PROCESS_CAPABILITIES [pidadr] [,prcnam] [,select_mask] [,modify_mask] [,prev_mask] [,flags]
int sys$process_capabilities (unsigned int *pidadr, void *prcnam, struct _generic_64 *select_mask, struct _generic_64 *modify_mask, struct _generic_64 *prev_mask, struct _generic_64 *flags);
pidadr
OpenVMS usage: process_id type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Process identification (PID) of a kernel thread whose user capability mask is to be modified or returned. The pidadr argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a longword that contains the PID.Process selection is made through a combination of the pidadr and prcnam arguments. If neither are specified or if both have a zero value, the service operations are made to the user capability mask of the current kernel thread of the calling process. The pidadr argument takes precedence over the prcnam argument where both are supplied in the service call.
If the constant CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY is specified in flags, then the user portion of the default process user capability mask is modified or returned instead, regardless of the values specified in pidadr.
prcnam
OpenVMS usage: process_name type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor
Process name of the process whose user capability mask is to be modified or returned. The prcnam argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a character string descriptor pointing to the process name string. A process can be identified with a 1- to 15-character string. The service operations are made to the user capability mask of the initial thread of the specified process.You can use the prcnam argument only if the process identified by the descriptor has the same UIC group number as the calling process. To obtain information about processes in other groups, the pidadr argument must be used.
If pidadr and prcnam are both specified, then prcnam is ignored. If neither argument is specified, then the context of the current kernel thread of the calling process is modified or returned.
select_mask
OpenVMS usage: mask_quadword type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Mask specifying which bits of the specified process's user capability mask are to be modified. The select_mask argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword bit vector wherein a bit, when set, specifies that the corresponding user capability is to be modified.The individual user capability bits in select_mask can be referenced by their symbolic bit constant names, CAP$M_USER1 through CAP$M_USER16. These constants (not zero-relative) specify the position in the mask quadword that corresponds to the bit name. Multiple capabilities can be selected by ORing together the appropriate bits.
Alternatively, the constant CAP$K_ALL_USER, when specified as the select_mask argument, selects all user capabilities.
modify_mask
OpenVMS usage: mask_quadword type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Mask specifying the settings for those capabilities selected in the select_mask argument. The modify_mask argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword bit vector wherein a bit, when set, specifies that the corresponding user capability is to be added to the specified kernel thread; when clear, the corresponding user capability is to be removed.The symbolic bit constants CAP$M_USER1 through CAP$M_USER16 can be used to modify the appropriate bit position in modify_mask. Multiple capabilities can be modified by ORing together the appropriate bits.
To add a specific user capability to a kernel thread, that bit position must be set in both select_mask and modify_mask. To remove a specific user capability from a kernel thread, that bit position must be set in select_mask and clear in modify_mask.
The symbolic constant CAP$K_ALL_USER_ADD, when specified in modify_mask, indicates that all capabilities specified in select_mask are to be added to the appropriate capability set. The symbolic constant CAP$K_ALL_USER_REMOVE indicates that all specified capabilities are to be removed from the set.
prev_mask
OpenVMS usage: mask_quadword type: quadword (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Previous user capability mask for the specified process or thread before execution of this call to $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES. The prev_mask argument is the 32- or 64-bit address of a quadword into which $PROCESS_CAPABILITIES writes the previous bit mask. If CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY is set in the flags argument, then prev_mask will contain the user portion of the global default capability mask.flags
OpenVMS usage: mask_quadword type: quadword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference
Options selected for the user capability modification. The flags argument is a quadword bit vector wherein a bit corresponds to an option. Only the bits specified below are used; the remainder of the quadword bits are reserved and must be zero.Each option (bit) has a symbolic name, defined by the $CAPDEF macro. The flags argument is constructed by performing a logical OR operation using the symbolic names of each desired option. The following table describes the symbolic name of each option.
Symbolic Name Description CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY Indicates that the specified operations are to be performed on the global context cell instead of on a specific kernel thread. This bit supersedes any individual kernel thread specified in pidadr or prcnam. Specifying this bit constant applies the service operations to the capabilities for all newly created processes. CAP$M_FLAG_PERMANENT Indicates whether to modify the permanent user process capabilities in addition to the current image copy. If CAP$M_FLAG_PERMANENT is set, then both the permanent and current user process capabilities are modified. If this bit is clear or flags is unspecified, then just the current image process capabilities are modified. This bit also determines which of the capability masks are returned in prev_mask. If set, the permanent mask, used to reinitialize the current set at image rundown, is returned. If the bit is clear or the flags argument is not specified, the current running mask is returned.
CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU Determines whether the kernel thread can be left in a non-runnable state under some circumstances. No operation of this service will allow a transition from runnable to blocked state; however, if the kernel thread is already at a blocked state, this bit determines whether the result of the operation must leave it runnable. If CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU is set or flags is unspecified, the kernel thread will be checked to ensure it can safely run on one of the CPUs in the active set; otherwise, any state operations on kernel threads already in a blocked state will be allowed.
The Modify Process User Capabilities system service, based on the arguments select_mask and modify_mask, adds or removes user capabilities for the specified kernel thread. If specified, the previous capability mask is returned in prev_mask. With the modify_mask argument, multiple user capabilities for a kernel thread can be added or removed in the same system service call.Either modify_mask or prev_mask, or both, must be specified as arguments. If modify_mask is specified, then select_mask must be specified as an argument. If modify_mask is not specified, then no modifications are made to the user capability mask for the specified kernel thread. In this case, select_mask is ignored. If prev_mask is not specified, then no previous mask is returned.
No service changes will be allowed if the specified kernel thread will transition from a runnable to blocked state. The CAP$M_FLAG_CHECK_CPU bit in the flags argument requires that the final thread state be runnable regardless of previous state; otherwise, interim changes that maintain a blocked state are allowed if the thread is already in one.
If the symbolic bit constant CAP$M_FLAG_DEFAULT_ONLY is set in the flags argument, the user capability modifications or the mask read requests are made only to the global initialization cell regardless of what process selections values are specified in the pidadr and prcnam arguments.
The caller must have the ALTPRI privilege to call SYS$PROCESS_CAPABILITIES to modify its own user capability mask. To modify another processí user capability mask, the caller must have:
- ALTPRI---To modify any process with a matching UIC
- ALTPRI and GROUP---To modify any process in the same UIC group
- ALTPRI and WORLD---To modify any process
To call SYS$PROCESS_CAPABILITIES simply to retrieve the specific process or global mask, the caller need only have the following privileges:
- None---To retrieve the state of itself or any process with a matching UIC
- GROUP---To retrieve the state of any process in the same UIC group
- WORLD---To retrieve the state of any process
$CPU_CAPABILITIES
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_BADPARAM One of more arguments has an invalid value. SS$_ACCVIO The service cannot access the locations specified by one or more arguments. SS$_NOSUCHTHREAD The specified kernel thread does not exist. SS$_NONEXPR The specified process does not exist, or an invalid process identification was specified. SS$_IVLOGNAM The process name string has a length of 0 or more than 15 characters. SS$_NOPRIV Insufficient privilege for attempted operation. SS$_CPUCAP No CPU can run the specified process with new capabilities. SS$_INSFARG Fewer than the required number of arguments were specified or no operation was specified.
Creates and initializes a process context that is used by $GETJPI to scan processes on the local system or across the nodes in an OpenVMS Cluster system.On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$PROCESS_SCAN pidctx [,itmlst]
int sys$process_scan (unsigned int *pidctx, void *itmlst);
pidctx
OpenVMS usage: process_id type: longword (unsigned) access: modify mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
Context value supplied by $PROCESS_SCAN to be used as the pidadr argument of $GETJPI. The pidctx argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a longword that is to receive the process context longword. This longword normally contains 0 or a previous context. If it contains a previous context, the old context is deleted. If it contains a value other than 0 or a previous context, the old value is ignored.itmlst
OpenVMS usage: 32-bit item_list_3 or 64-bit item_list_64b type: longword (unsigned) for 32-bit; quadword (unsigned) for 64-bit access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
Item list specifying selection criteria to be used by the scan or to control the scan.The itmlst argument is the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) or the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) of a list of item descriptors, each of which describes one selection criterion or control option. Within each selection criterion you can include several item entries. An item list in 32-bit format is terminated by a longword of 0; an item list in 64-bit format is terminated by a quadword of 0. All items in an item list must be of the same format---either 32-bit or 64-bit.
The information in the item list is passed to the item descriptor in one of two ways. If the item descriptor can always hold the actual value of the selection criterion, the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor and the buffer length is specified as 0. If the item descriptor points to the actual value of the selection criterion, the address of the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor and you must specify the buffer length for the selection criterion. Each item code description specifies whether the information is passed by value or by reference.
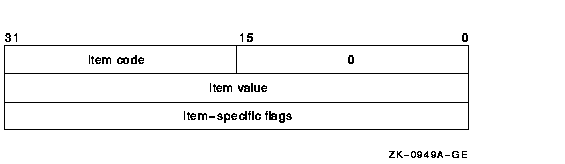
The following diagram depicts the format of a 32-bit item descriptor that passes the selection criterion as a value.
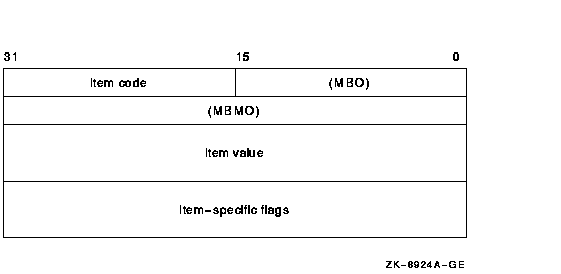
The following diagram depicts the format of a 64-bit item descriptor that passes the selection criterion as a value.
The following diagram depicts the format of a 32-bit item descriptor that passes the selection criterion by reference.

The following diagram depicts the format of a 64-bit item descriptor that passes the selection criterion by reference.
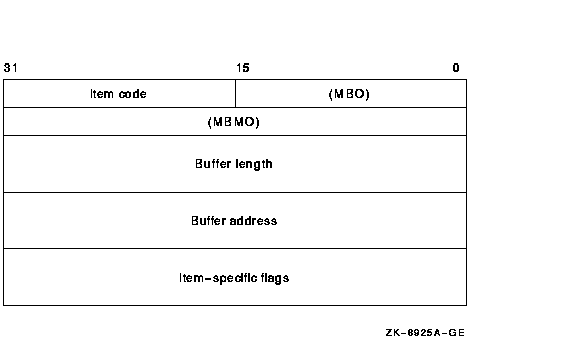
The following table defines the item descriptor fields.
| Descriptor Field | Definition | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer length | Buffer length is specified in a different way for the two types of item descriptors. | ||||
|
|||||
| Item code |
A word containing the selection criterion. These codes are defined by
the $PSCANDEF macro.
Each item code is described after this list of descriptor fields. |
||||
| Item value | A longword containing the actual value of the selection criterion. When you specify an item code that is passed by value, $PROCESS_SCAN searches for the actual value contained in the item list. See the description of the buffer address field for information about item codes that are passed by reference. | ||||
| Buffer address | A longword containing the user-supplied address of the buffer from which $PROCESS_SCAN retrieves information needed by the scan. When you specify an item code that is passed by reference, $PROCESS_SCAN uses the address as a pointer to the actual value. See the description of the item value field for information about item codes that are passed by value. | ||||
| Item-specific flags |
A longword that contains flags to help control selection information.
Item-specific flags, for example EQL or NEQ, are used to specify how
the value specified in the item descriptor is compared to the process
value.
These flags are defined by the $PSCANDEF macro. Some flags are common to multiple item codes; other flags are specific to an individual item code. See the description of each item code to determine which flags are used. For item codes that describe bit masks or character strings, these flags control how the bit mask or character string is compared with that in the process. By default, they are compared for equality. For item codes that describe integers, these flags specify an arithmetic comparison of an integer item with the process attribute. For example, a PSCAN$M_GTR selection specifying the value 4 for the item code PSCAN$_PRIB finds only the processes with a base priority above 4. Without one of these flags, the comparison is for equality. |
||||
| MBO | Must be 1. | ||||
| MBMO | Must be --1. |
PSCAN$_ACCOUNT
When you specify PSCAN$_ACCOUNT, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the account field.If the string supplied in the item descriptor is shorter than the account field, the string is blank-padded for the comparison unless the item-specific flag PSCAN$M_PREFIX_MATCH is present.
Because the information is a character string, the selection value is passed by reference. The length of the buffer is placed in the first word of the item descriptor and the address of the buffer is placed in the second longword.
Although the current length of the account field is 8 bytes, the PSCAN$_ACCOUNT buffer can be up to 64 bytes in length. If the buffer length is 0 or greater than 64, the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
PSCAN$_AUTHPRI
When you specify PSCAN$_AUTHPRI, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the authorized base priority field.This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table SYS-14.
PSCAN$_CURPRIV
When you specify PSCAN$_CURPRIV, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the current privilege field. Privilege bits are defined by the $PRVDEF macro.Because the bit mask information is too long to be passed by value, the information is passed by reference. The privilege buffer must be exactly 8 bytes, otherwise the SS$_IVBUFLEN error is returned.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table SYS-14.
PSCAN$_GETJPI_BUFFER_SIZE
When you specify PSCAN$_GETJPI_BUFFER_SIZE, you determine the size of a buffer to be used by $GETJPI to process multiple requests in a single message. Using this item code can greatly improve the performance of scans on remote nodes, because fewer messages are needed. This item code is ignored during scans on the local node.This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. The buffer length must be specified as 0. The buffer is allocated by $PROCESS_SCAN; you do not have to allocate a buffer.
If you use PSCAN$_GETJPI_BUFFER_SIZE with $PROCESS_SCAN, all calls to $GETJPI using the context established by $PROCESS_SCAN must request the same item code information. Because $GETJPI locates information for more than one process at a time, it is not possible to change the item codes or the length of the buffers used in the $GETJPI item list. $GETJPI checks each call and returns the error SS$_BADPARAM if an attempt is made to change the item list during a buffered process scan. However, the buffer addresses can be changed between $GETJPI calls.
Because the locating and buffering of information by $GETJPI is transparent to a calling program, you are not required to change the way $GETJPI is called when you use this item code.
The $GETJPI buffer uses the process quota BYTLM. If the buffer is too large for the process quota, $GETJPI (not $PROCESS_SCAN) returns the error SS$_EXBYTLM. If the buffer specified is not large enough to contain the data for at least one process, $GETJPI returns the error SS$_BADPARAM.
No item-specific flags are used with PSCAN$_GETJPI_BUFFER_SIZE.
PSCAN$_GRP
When you specify PSCAN$_GRP, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the UIC group number.This integer item code is passed by value; the value is placed in the second longword of the item descriptor. Because the value of the group number is a word, the high-order word of the value is ignored. The buffer length must be specified as 0.
The flags that can be used with this item code are listed in Table SYS-14.
PSCAN$_HW_MODEL
When you specify PSCAN$_HW_MODEL, $GETJPI returns information about processes that match the specified CPU hardware model number.
Previous Next Contents Index
![[Site home]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home_off.gif)
![[Send comments]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments_off.gif)
![[Help with this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help_off.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs_off.gif)
![[OpenVMS site]](../../images/buttons/bn_openvms_off.gif)
![[Compaq site]](../../images/buttons/bn_compaq_off.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/openvms_doc_banner_bottom.gif)
Copyright © Compaq Computer Corporation 1998. All rights reserved.
Legal4527PRO_072.HTML