| Previous | Contents | Index |
Clients may fail to connect to shares or lose existing connections. The shares must be set to permit client access. Share setup includes:
If a client fails to connect to a share or loses an existing connection, use the following procedure:
| Step 1: Collect Information | Step 2: Analyze the Problem | Step 3: Solve the Problem |
|---|---|---|
| Determine whether the client is connected but failing to access resources in the shares. For example, the client computer displays the connection to the server but is unable to list all the files and directories to which the client requires access. | Use the SHOW USER command to display the groups to which the user belongs. | To add the user to a group, use the MODIFY GROUP command to add the user name. |
| Use the SHOW SHARE command to display the groups allowed to access the share. | To let the user's group access a share, use the MODIFY SHARE/PERMISSIONS command. | |
| Use the SHOW FILE command to display access permissions on the resources. If the OpenVMS and PATHWORKS Advanced Server security model is enabled, use the OpenVMS command DIRECTORY/SECURITY to display the OpenVMS owner and protection information. | Use the PATHWORKS Advanced Server SET FILE/PERMISSIONS command to modify the permissions on the file to give the user or group access to the specific resource. Use the OpenVMS SET FILE/PROTECTION command to modify the RMS protections on a directory or file. | |
| Use the PATHWORKS Advanced Server SHOW HOSTMAP command to display host mapped user accounts. | Use the ADD HOSTMAP command to associate a PATHWORKS Advanced Server user account with an OpenVMS user account. | |
6.3.2.7 Printer Problems
Problems with the print software can occur after changes in hardware
configuration or print queues. The PATHWORKS Advanced Server provides
commands to modify and remove print jobs and print queues.
If a problem is specific to a print queue or print job, use the following procedure:
| Step 1: Collect Information | Step 2: Analyze the Problem | Step 3: Solve or the Problem |
|---|---|---|
| Obtain the physical printer name, the print queue name, and the specific print command used to submit the print job. | Use the SHOW PRINT JOBS command to display information about print jobs. | Use the SET PRINT JOB command to change the status of a print job or delete a print job. |
| During printer maintenance and when printers are off line, you may need to prevent users from submitting print jobs. | Use the SHOW PRINT QUEUE command to display information about the print queue, the print jobs in the print queue, and the status of the print queue. |
Use the following commands to control the print queue while you correct
the problem:
PAUSE PRINT QUEUE
|
6.3.2.8 User Account Problems
When one user reports a problem connecting to the server or a share,
establish whether the problem is caused by the PATHWORKS Advanced
Server user account definition. You can help users with password
problems immediately, by changing their passwords.
If a client reports a failure to log on to the network, use the following procedure:
| Step 1: Collect Information | Step 2: Analyze the Problem | Step 3: Solve or Report the Problem |
|---|---|---|
| Determine whether the user account is set up properly. | Use the SHOW USER command to display user account information. Look for logon restrictions, such as logon hours, which might give the client access only during specific hours of the day and days of the week. | Use the MODIFY USER command to change user account information like restricted hours. (See Section 3.3, Managing PATHWORKS Advanced Server User Accounts.) |
| Determine whether the user is entering the correct password. | Use the SET PASSWORD command to change a user account password. | |
6.3.2.9 Privileged User Problems
Users with responsibility for privileged operations, such as
administrators, printer operators, and server operators, may receive
error messages when attempting to use privileged commands and
procedures. Make sure the user is a member of the appropriate group.
If users are unable to perform privileged operations, use the following procedure:
| Step 1: Collect Information | Step 2: Analyze the Problem | Step 3: Solve the Problem |
|---|---|---|
| Determine whether users are in groups. | Use the SHOW USERS/FULL command to display the user accounts and predefined groups for operators and administrators. | If a PATHWORKS Advanced Server operator or administrator does not have the required user rights, use the MODIFY USER /ADD_TO_GROUP command to add the user to the appropriate groups. |
| Determine whether users are unable to perform administrative operations on a file, such as deleting the file, modifying file protections, and displaying directory information about the file. |
Use the SHOW FILES command to display the permissions set on the file.
Use this information to notify users of changes you plan to make to the file. |
Use the TAKE FILE OWNERSHIP command to obtain administrative control over a file and set permissions appropriately. (See Section 4.4.9, Taking Ownership of Files or Directories.) |
6.3.2.10 License Acquisition Problems
Clients may report performance problems in connecting to the server or
error messages during license verification. License assignment and
verification problems may be caused by:
The license server must be running on a node with sufficient resources to manage the license database and to respond to client requests for licenses. If users are reporting performance problems at boot time, the license system may be suffering from performance problems. You should run the standalone license server on a node designated for that purpose. See the Advanced Server for OpenVMS Guide to Managing Advanced Server Licenses for more information.
If one or more clients are refused a connection to the server, use the following procedure:
| Step 1: Collect Information | Step 2: Analyze the Problem | Step 3: Solve the Problem |
|---|---|---|
| Use the License Manager to determine whether appropriate licenses have been loaded. | If the client is validating its client-based licenses with the license server, and the client computer displays messages beginning with LIC nnn that the license request or license validation failed, check for valid licenses. | Upgrade the client license to the appropriate license. |
|
If there is no license on the server, and the Alerter service is
enabled, the problem is reported with an alert message. Examine the
license component log files. For more information on these log files,
refer to the Advanced Server for OpenVMS Guide to Managing Advanced Server Licenses.
Determine whether the number of licenses available to the client or group is sufficient |
Ensure that one or both of the following are true:
|
|
|
Determine whether the Explorer Map Network Drive on the Windows 95 or
Windows 98 client fails with the following message:
"The following error occurred while trying to connect to Drive: to path The network has responded incorrectly" Determine whether the Run command from the Start menu on the Windows 95 or Windows 98 client fails with one of the following messages: "An extended error has occurred" or "The network name cannot be found" |
The server is not configured with a license. | Add licenses to the server, or check client-based licenses to see that adequate licenses are available to the client. |
If your server was previously running PATHWORKS V5 for OpenVMS (LAN Manager), and you encounter a problem that is completely unsolvable, you can remove the newly installed software using the Rollback command procedure provided with PATHWORKS Advanced Server. The Rollback procedure must have been enabled during the server installation procedure. Refer to the PATHWORKS for OpenVMS (Advanced Server) Server Migration Guide for information about reverting to the previous version of the server.
Using the Rollback procedure restores your environment to PATHWORKS V5 for OpenVMS (LAN Manager) at the time of PATHWORKS Advanced Server installation. Therefore, information about changes made while PATHWORKS Advanced Server was running, like newly added users or changed permissions, will be lost. |
PATHWORKS Advanced Server provides you with a Configuration Manager to set up your server and modify its configuration. This chapter contains information about the Configuration Manager and how to use it, including:
After you install the server software, you can use the PATHWORKS Advanced Server Configuration Manager to modify the server software configuration and tune your server. The Configuration Manager is a character-cell user interface that allows you to modify server parameters. If you are using DECterm or an equivalent terminal emulator, you can access all the functions of the Configuration Manager using a mouse input device. If you are using a keyboard to control the Configuration Manager, refer to Section 7.7, Navigating the Configuration Manager Using a Keyboard for information about the keys you can use to control the Configuration Manager.
The server parameters you can modify using the Configuration Manager include:
Each type of parameter is presented on a separate screen by the
Configuration Manager. Each parameter is described in more detail in a
later section.
7.2 Starting the Configuration Manager
To start the Configuration Manager, log in to the OpenVMS SYSTEM account, and enter the following command:
$ ADMINISTER/CONFIGURATION |
The Basic Configuration Parameters Screen appears, as shown in the following Figure.
Figure 7-1 Basic Configuration Parameters Screen
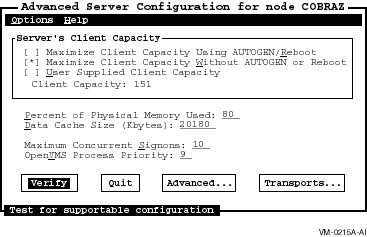
To exit the Configuration Manager, select one of the following buttons on the Basic Configuration Parameters screen.
To get help while running the Configuration Manager, select the Help menu at the top of the Basic Configuration Parameters screen.
From the Help menu, you can choose to display the following types of information:
The following sections describe each screen and each parameter in
detail.
7.3 Modifying Basic Configuration Parameters
The first screen that appears when you start the Configuration Manager
is the Basic Configuration Parameters screen. It allows you to change
the basic server configuration parameters, as described in the
following sections.
7.3.1 Specifying a Server's Client Capacity
Client capacity is the maximum number of client sessions the server can support at a time. You can enter a value, or you can let the Configuration Manager determine a value based on current resources.
To specify the client capacity:
On the Basic Configuration Parameters screen, select User-Supplied Client Capacity, then enter your new value in the Client Capacity edit box. The Configuration Manager may need to run AUTOGEN or reboot your system to make additional resources available to support such a configuration.
To allow the Configuration Manager to determine the appropriate setting:
Select one of the following:
To determine the maximum number of clients:
Use the following procedure:
After you determine the maximum number of clients the server will accommodate, be sure that the network transports you want to use can accept at least this many links. If not, configure the transports to accept more links.
For DECnet, the configuration change depends on the version of DECnet. For DECnet, the default maximum number of transport links is 32. For this version of DECnet, you can configure the transport to accept 100 links by entering the following commands:
$ MCR NCP DEFINE EXECUTOR MAXIMUM LINKS 100 $ MCR NCP SET EXECUTOR MAXIMUM LINKS 100 |
For DECnet-Plus, the default maximum number of transport links is 200. To raise this maximum to 300, enter the following commands:
$ MCR NCL SET NODE 0 NSP MAXIMUM RECEIVE BUFFERS 6000 $ MCR NCL SET NODE 0 NSP MAXIMUM TRANSPORT CONNECTIONS 300 |
Note that the number of receive buffers should be set to 20 *
n, where n is the maximum number of transport
connections. In addition, be sure to edit the NET$LOGICALS.COM file to
increase the NET$ACP quotas appropriately. For more information about
configuring the DECnet transport, refer to the DECnet for OpenVMS Network Management Utilities manual.
7.3.2 Specifying the Percent of Physical Memory Used
The Percent of Physical Memory Used parameter allows you to specify the maximum percentage of the system's physical memory that may be dedicated to server use, such as the data cache and the process working sets. You can specify from 1% to 100% of physical memory. If you set this parameter to too high a value, the rest of the OpenVMS operating system may not have enough memory to operate efficiently. The default setting is 80%.
To modify the percentage of physical memory the server may use:
On the Basic Configuration Parameters screen, enter the percent value
in the Percent of Physical Memory Used field.
7.3.3 Specifying Server Data Cache Size
The Server Data Cache Size parameter allows you to specify the size of the data cache for the server's file data. A proper setting can decrease the amount of disk I/O, improving server response. You can set this value from 512 Kbytes to 131,072 Kbytes (128 Mbytes). The default setting is 2048 Kbytes (2 Mbtyes).
To modify server data cache size:
On the Basic Configuration Parameters screen, enter the number of
Kbytes in the
Data Cache Size field.
7.3.4 Specifying the Maximum Number of Concurrent Signons
The Configuration Manager allows you to specify the maximum number of external authentication signon operations that can take place concurrently. External authentication allows PATHWORKS Advanced Server to do the logon validation for both PATHWORKS Advanced Server and OpenVMS user accounts.
You can enter any number from 2 through 999. The default value for this parameter is 10.
To modify the maximum number of concurrent signons:
On the Basic Configuration Parameters screen, enter the value in the
Maximum Concurrent Signons field.
7.3.5 Specifying OpenVMS Process Priority
The Configuration Manager allows you to specify the base priority assigned to main server processes for scheduling purposes. Values from 9 to 12 are most appropriate. Server processes below base priority 9 can be preempted by interactive processes, and processes above base priority 12 will not receive their priority boosts.
To change the base process priority for the server:
On the Basic Configuration Parameters screen, enter the value in the OpenVMS Process Priority field.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |