![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 30 March 2001 | |
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
Provides a process with an I/O channel so input/output operations can be performed on a device, or establishes a logical link with a remote node on a network.On Alpha systems, this service accepts 64-bit addresses.
SYS$ASSIGN devnam ,chan ,[acmode] ,[mbxnam] ,[flags]
int sys$assign (void *devnam, unsigned short int *chan, unsigned int acmode, void *mbxnam,...);
devnam
OpenVMS usage: device_name type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (VAX)
Name of the device to which $ASSIGN is to assign a channel. The devnam argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of a character string descriptor pointing to the device name string.If the device name contains a double colon (::), the system assigns a channel to the first available network device (NET:) and performs an access function on the network.
chan
OpenVMS usage: channel type: word (unsigned) access: write only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit reference (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit reference (VAX)
Number of the channel that is assigned. The chan argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of a word into which $ASSIGN writes the channel number.acmode
OpenVMS usage: access_mode type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Access mode to be associated with the channel. The acmode argument specifies the access mode. The $PSLDEF macro defines the following symbols for the four access modes:
Symbol Access Mode Numeric Value PSL$C_KERNEL Kernel 0 PSL$C_EXEC Executive 1 PSL$C_SUPER Supervisor 2 PSL$C_USER User 3 The specified access mode and the access mode of the caller are compared. The less privileged (but the higher numeric valued) of the two access modes becomes the access mode associated with the assigned channel. I/O operations on the channel can be performed only from equal and more privileged access modes. For more information, refer to the section on access modes in the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual.
mbxnam
OpenVMS usage: device_name type: character-coded text string access: read only mechanism: by 32- or 64-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (Alpha) mechanism: by 32-bit descriptor--fixed-length string descriptor (VAX)
Logical name of the mailbox to be associated with the device. The mbxnam argument is the 32- or 64-bit address (on Alpha systems) or the 32-bit address (on VAX systems) of a character string descriptor pointing to the logical name string.If you specify mbxnam as 0, no mailbox is associated with the device. This is the default.
You must specify the mbxnam argument when performing a nontransparent, task-to-task, network operation.
Only the owner of a device can associate a mailbox with the device; the owner of a device is the process that has allocated the device, whether implicitly or explicitly. Only one mailbox can be associated with a device at any one time.
For unshareable, nonspooled devices, an implicit $ALLOCATE is done. This requires read, write, or control access to the device.
A mailbox cannot be associated with a device if the device has foreign (DEV$M_FOR) or shareable (DEV$M_SHR) characteristics.
A mailbox is disassociated from a device when the channel that associated it is deassigned.
If a mailbox is associated with a device, the device driver can send status information to the mailbox. For example, if the device is a terminal, this information might indicate dialup, hangup, or the reception of unsolicited input; if the device is a network device, it might indicate that the network is connected or perhaps that the line is down.
For details on the nature and format of the information returned to the mailbox, refer to the OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
flags
OpenVMS usage: mask_longword type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
An optional device-specific argument. The flags argument is a longword bit mask.For more information on the applicability of the flags argument for a particular device, refer to the OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual.
The Assign I/O Channel service provides a process with an I/O channel so input/output operations can be performed on a device. This service also establishes a logical link with a remote node on a network.Channels remain assigned until they are explicitly deassigned with the Deassign I/O Channel ($DASSGN) service or, if they are user-mode channels, until the image that assigned the channel exits.
The $ASSIGN service establishes a path to a device but does not check whether the caller can actually perform input/output operations to the device. Privilege and protection restrictions can be applied by the device drivers.
The calling process must have NETMBX privilege to perform network operations, and system dynamic memory is required if the target device is on a remote system.
Note that you should use the SHARE privilege with caution. Applications, application protocols, and device drivers coded to expect only exclusive access can encounter unexpected and errant behavior when access to the device is unexpectedly shared. Unless the SHARE privilege is explicitly supported by the application, the application protocol, and the device driver, its use is generally discouraged. Refer to the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual for additional information.
If the target of the assignment is on a remote node, the process needs sufficient buffer quota to allocate a network control block.
$ALLOC, $BRKTHRU, $BRKTHRUW, $CANCEL, $CREMBX, $DALLOC, $DASSGN, $DELMBX, $DEVICE_SCAN, $DISMOU, $GETDVI, $GETDVIW, $GETMSG, $GETQUI, $GETQUIW, $INIT_VOL, $MOUNT, $PUTMSG, $QIO, $QIOW, $SNDERR, $SNDJBC, $SNDJBCW, $SNDOPR
SS$_NORMAL The service completed successfully. SS$_REMOTE The service completed successfully. A logical link is established with the target on a remote node. SS$_ABORT A physical line went down during a network connect operation. SS$_ACCVIO The device or mailbox name string or string descriptor cannot be read by the caller, or the channel number cannot be written by the caller. SS$_CONNECFAIL For network operations, the connection to a network object timed out or failed. SS$_DEVACTIVE You specified a mailbox name, but a mailbox is already associated with the device. SS$_DEVALLOC The device is allocated to another process. SS$_DEVNOTMBX You specified a logical name for the associated mailbox, but the logical name refers to a device that is not a mailbox. SS$_DEVOFFLINE For network operations, the physical link is shutting down. SS$_EXQUOTA The target of the assignment is on a remote node and the process has insufficient buffer quota to allocate a network control block. SS$_FILALRACC For network operations, a logical link already exists on the channel. SS$_INSFMEM The target of the assignment is on a remote node and there is insufficient system dynamic memory to complete the request. SS$_INVLOGIN For network operations, the access control information was found to be invalid at the remote node. SS$_IVDEVNAM No device name was specified, the logical name translation failed, or the device or mailbox name string contains invalid characters. If the device name is a target on a remote node, this status code indicates that the network connect block has an invalid format. SS$_IVLOGNAM The device or mailbox name string has a length of 0 or has more than 63 characters. SS$_LINKEXIT For network operations, the network partner task was started, but exited before confirming the logical link (that is, $ASSIGN to SYS$NET). SS$_NOIOCHAN No I/O channel is available for assignment. SS$_NOLINKS For network operations, no logical links are available. The maximum number of logical links as set for the Network Control Program (NCP) executor MAXIMUM LINKS parameter was exceeded. SS$_NOPRIV For network operations, the issuing task does not have the required privilege to perform network operations or to confirm the specified logical link. SS$_NOSUCHDEV The specified device or mailbox does not exist, or, for DECnet for OpenVMS operations, the network device driver is not loaded (for example, the DECnet for OpenVMS software is not currently running on the local node). SS$_NOSUCHNODE The specified network node is nonexistent or unavailable. SS$_NOSUCHOBJ For network operations, the network object number is unknown at the remote node; for a TASK= connect, the named DCL command procedure file cannot be found at the remote node. SS$_NOSUCHUSER For network operations, the remote node could not recognize the login information supplied with the connection request. SS$_PROTOCOL For network operations, a network protocol error occurred, most likely because of a network software error. SS$_REJECT The network connect was rejected by the network software or by the partner at the remote node, or the target image exited before the connect confirm could be issued. SS$_REMRSRC For network operations, the link could not be established because system resources at the remote node were insufficient. SS$_SHUT For network operations, the local or remote node is no longer accepting connections. SS$_THIRDPARTY For network operations, the logical link connection was terminated by a third party (for example, the system manager). SS$_TOOMUCHDATA For network operations, the task specified too much optional or interrupt data. SS$_UNREACHABLE For network operations, the remote node is currently unreachable.
Appends an event message to the system security audit log file or sends an alarm to a security operator terminal.
SYS$AUDIT_EVENT [efn] ,[flags] ,itmlst ,[audsts] ,[astadr] ,[astprm]
int sys$audit_event (unsigned int efn, unsigned int flags, void *itmlst, unsigned int *audsts, void (*astadr)(__unknown_params), int astprm);
efn
OpenVMS usage: ef_number type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Number of the event flag to be set when the audit completes. The efn argument is a longword containing the number of the event flag; however, $AUDIT_EVENT uses only the low-order byte. If efn is not specified, event flag 0 is used.Upon request initiation, $AUDIT_EVENT clears the specified event flag.
flags
OpenVMS usage: mask_longword type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by value
Flags specifying options for the $AUDIT_EVENT system operation. The flags argument is a longword bit mask, where each bit corresponds to an option.Each flag option has a symbolic name. The $NSADEF macro defines the following symbolic names:
Symbolic Name Description NSA$M_ACL Specifies an event generated by an Alarm ACE or Audit ACE. This flag is reserved to Compaq. NSA$M_FLUSH Specifies that all messages in the audit server buffer be written to the audit log file. NSA$M_INTERNAL Specifies that the $AUDIT_EVENT call originates in the context of a trusted computing base (TCB) component. The auditing components use this flag to indicate that internal auditing failures should result in a SECAUDTCB bugcheck. This flag is reserved to Compaq. NSA$M_MANDATORY Specifies that an audit is to be performed, regardless of system alarm and audit settings. NSA$M_NOEVTCHECK Specifies that an audit is to be performed, regardless of the system alarm or audit settings. This flag is similar to the NSA$M_MANDATORY bit but, unlike the NSA$M_MANDATORY bit, this flag is not reflected in the NSA$W_FLAGS field in the resulting audit record on disk. NSA$M_SERVER Indicates that the call originates in a TCB server process and that the event should be audited regardless of the state of a process-specific, no-audit bit. Trusted servers use this flag to override the no-audit bit when they want to perform explicit auditing on behalf of a client process. This flag is reserved to Compaq.
itmlst
OpenVMS usage: item_list_3 type: longword (unsigned) access: read only mechanism: by reference
Item list specifying information to include in the audit record. The itmlst argument is the address of a list of item descriptors. The list of item descriptors is terminated by a longword of 0.The item list for all calls to $AUDIT_EVENT must include the following item codes:
- NSA$_EVENT_TYPE (see Table SYS-2)
- NSA$_EVENT_SUBTYPE (see Table SYS-2)
- At least one of the NSA$_ALARM_NAME item code or the NSA$_AUDIT_NAME item code.
- If the event being reported is an object access (NSA$C_MSG_OBJ_ACCESS) or an object delete (NSA$C_MSG_OBJ_DELETE), the NSA$_FINAL_STATUS, NSA$_ACCESS_DESIRED, and NSA$_OBJECT_CLASS item codes must be specified.
- If the event being reported is an object create (NSA$C_MSG_OBJ_CREATE), the NSA$_FINAL_STATUS and NSA$_OBJECT_CLASS item codes must be specified.
- If the event being reported is a privilege audit (NSA$C_MSG_PRVAUD), the NSA$_PRIVS_USED or the NSA$_PRIVS_MISSING item code must be specified.
- If the audit event being reported is a deaccess event (NSA$C_MSG_OBJ_DEACCESS), the NSA$_OBJECT_CLASS item code must be specified.
The item list is a standard format item list. The following diagram depicts the general structure of an item descriptor:
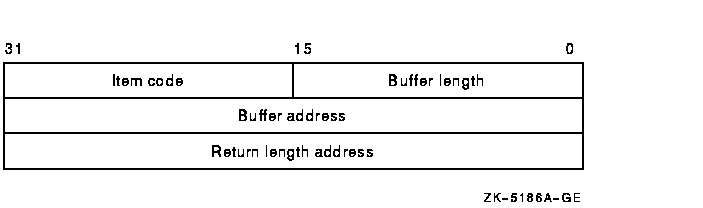
The following table defines the item descriptor fields:
| Descriptor Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| Buffer length | A word specifying the length (in bytes) of the buffer; the buffer supplies information to be used by $AUDIT_EVENT. The required length of the buffer varies, depending on the item code specified; each item code description specifies the required length. |
| Item code | A word containing a symbolic code describing the nature of the information currently in the buffer. The location of the buffer is pointed to by the buffer address field. Each item code has a symbolic name. This section provides a detailed description of item codes following the description of arguments. |
| Buffer address | A longword containing the address of the buffer that specifies the information. |
| Return length address | Not currently used; this field is reserved to Compaq. You must specify 0. |
See the Item Codes section for a description of the $AUDIT_EVENT item codes.
| OpenVMS usage: | cond_value_type |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | write only |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The audsts argument is valid only when the service returns success and the status is not SS$_EVTNOTENAB. In addition, the caller must either make use of the astadr argument or use the $AUDIT_EVENTW service before attempting to access audsts.
| OpenVMS usage: | ast_procedure |
| type: | procedure value |
| access: | call without stack unwinding |
| mechanism: | by reference |
The AST routine executes in the access mode of the caller of $AUDIT_EVENT.
| OpenVMS usage: | user_arg |
| type: | longword (unsigned) |
| access: | read only |
| mechanism: | by value |
NSA$_ALARM_NAME
NSA$_ALARM_NAME is a string of 1 to 32 characters specifying an alarm journal name to receive the record. To direct an event to the system alarm journal (that is, all enabled security operator terminals), use the string SECURITY.NSA$_AUDIT_NAME
NSA$_AUDIT_NAME is a string of 1 to 65 characters specifying the journal file to receive the audit record. To direct an event to the system audit journal, use the string SECURITY.NSA$_CHAIN
NSA$_CHAIN is a longword value specifying the item list to process immediately after the current one. The buffer address field in the item descriptor specifies the address of the next item list to be processed. Anything after NSA$_CHAIN is ignored.NSA$_EVENT_FACILITY
NSA$_EVENT_FACILITY is a word value specifying the facility generating the event. All operating system events are audited as facility zero.NSA$_EVENT_SUBTYPE
NSA$_EVENT_SUBTYPE is a longword value specifying an event message subtype. See Table SYS-2 for a list of valid event subtypes.NSA$_EVENT_TYPE
NSA$_EVENT_TYPE is a longword value specifying an event message type. See Table SYS-2 for a list of valid event types.
Table SYS-2 Description of$AUDIT_EVENT Types and Subtypes Symbol of Event Type Meaning NSA$C_MSG_AUDIT Systemwide change to auditing Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_AUDIT_DISABLED
NSA$C_AUDIT_ENABLED
NSA$C_AUDIT_INITIATE
NSA$C_AUDIT_TERMINATE
NSA$C_AUDIT_LOG_FINAL
NSA$C_AUDIT_LOG_FIRST
Audit events disabled
Audit events enabled
Audit server startup
Audit server shutdown
Final entry in audit log (forward link)
First entry in audit log (backward link)NSA$C_MSG_BREAKIN Break-in attempt detected Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_DETACHED
NSA$C_DIALUP
NSA$C_LOCAL
NSA$C_NETWORK
NSA$C_REMOTE
Detached process
Dialup interactive process
Local interactive process
Network server process
Interactive process from another network nodeNSA$C_MSG_CONNECTION Logical link connection or termination Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_CNX_ABORT
NSA$C_CNX_ACCEPT
NSA$C_CNX_DECNET_CREATE
NSA$C_CNX_DECNET_DELETE
NSA$C_CNX_DISCONNECT
NSA$C_CNX_IPC_CLOSE
NSA$C_CNX_IPC_OPEN
NSA$C_CNX_REJECT
NSA$C_CNX_REQUEST
NSA$C_CNX_INC_REQUEST
NSA$C_CNX_INC_ACCEPT
NSA$C_CNX_INC_REJECT
NSA$C_CNX_INC_DISCONNECT
NSA$C_CNX_INC_ABORT
Connection aborted
Connection accepted
DECnet for OpenVMS logical link created
DECnet for OpenVMS logical link disconnected
Connection disconnected
Interprocess communication association closed
Interprocess communication association opened
Connection rejected
Connection requested
Incoming connection requested
Incoming connection accepted
Incoming connection rejected
Incoming connection disconnected
Incoming connection abortedNSA$C_MSG_INSTALL Use of the Install utility (INSTALL) Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_INSTALL_ADD
NSA$C_INSTALL_REMOVE
Known image installed
Known image deletedNSA$C_MSG_LOGFAIL Login failure Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_BATCH
NSA$C_DETACHED
NSA$C_DIALUP
NSA$C_LOCAL
NSA$C_NETWORK
NSA$C_REMOTE
NSA$C_SUBPROCESS
Batch process
Detached process
Dialup interactive process
Local interactive process
Network server process
Interactive process from another network node
SubprocessNSA$C_MSG_LOGIN Successful login Subtype and Meaning
See subtypes for NSA$C_MSG_
LOGFAILNSA$C_MSG_LOGOUT Successful logout Subtype and Meaning
See subtypes for NSA$C_MSG_
LOGFAILNSA$C_MSG_MOUNT Volume mount or dismount Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_VOL_DISMOUNT
NSA$C_VOL_MOUNT
Volume dismount
Volume mountNSA$C_MSG_NCP Modification to network configuration database Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_NCP_COMMAND
Network Control Program (NCP) command issuedNSA$C_MSG_NETPROXY Modification to network proxy database Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_NETPROXY_ADD
NSA$C_NETPROXY_DELETE
NSA$C_NETPROXY_MODIFY
Record added to network proxy database
Record removed from network proxy database
Record modified in network proxy databaseNSA$C_MSG_OBJ_ACCESS Object access attempted Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_OBJ_ACCESS
Object access attemptedNSA$C_MSG_OBJ_CREATE Object created Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_OBJ_CREATE
Object createdNSA$C_MSG_OBJ_DEACCESS Object deaccessed Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_OBJ_DEACCESS
Object deaccessedNSA$C_MSG_OBJ_DELETE Object deleted Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_OBJ_DELETE
Object deletedNSA$C_MSG_PROCESS Process control system service issued Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_PRC_CANWAK
NSA$C_PRC_CREPRC
NSA$C_PRC_DELPRC
NSA$C_PRC_FORCEX
NSA$C_PRC_GETJPI
NSA$C_PRC_GRANTID
NSA$C_PRC_RESUME
NSA$C_PRC_REVOKID
NSA$C_PRC_SCHDWK
NSA$C_PRC_SETPRI
NSA$C_PRC_SIGPRC
NSA$C_PRC_SUSPND
NSA$C_PRC_WAKE
NSA$C_PRC_PRCTERM
Process wakeup canceled
Process created
Process deleted
Process exit forced
Process information gathered
Process identifier granted
Process resumed
Process identifier revoked
Process wakeup scheduled
Process priority altered
Process exception issued
Process suspended
Process wakeup issued
Process termination notification requestedNSA$C_MSG_PRVAUD Attempt to use privilege Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_PRVAUD_FAILURE
NSA$C_PRVAUD_SUCCESS
Unsuccessful use of privilege
Successful use of privilegeNSA$C_MSG_RIGHTSDB Modification to rights database Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_RDB_ADD_ID
NSA$C_RDB_CREATE
NSA$C_RDB_GRANT_ID
NSA$C_RDB_MOD_HOLDER
NSA$C_RDB_MOD_ID
NSA$C_RDB_REM_ID
NSA$C_RDB_REVOKE_ID
Identifier added to rights database
Rights database created
Identifier given to user
List of identifier holders modified
Identifier name or attributes modified
Identifier removed from rights database
Identifier revoked from userNSA$C_MSG_SYSGEN Modification of a system parameter using the System Generation utility (SYSGEN) Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_SYSGEN_SET
System parameter modifiedNSA$C_MSG_SYSTIME Modification to system time Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_SYSTIM_SET
NSA$C_SYSTIM_CAL
System time set
System time calibratedNSA$C_MSG_SYSUAF Modification to system user authorization file (SYSUAF) Subtype and Meaning
NSA$C_SYSUAF_ADD
NSA$C_SYSUAF_COPY
NSA$C_SYSUAF_DELETE
NSA$C_SYSUAF_MODIFY
NSA$C_SYSUAF_RENAME
Record added to SYSUAF
Record copied in SYSUAF
Record deleted from SYSUAF
Record modified in SYSUAF
Record renamed in SYSUAFNSA$_FIELD_NAME
NSA$_FIELD_NAME is a string of 1 to 256 characters specifying the name of the field being modified. This is used in combination with NSA$_ORIGINAL_DATA and NSA$_NEW_DATA.NSA$_MESSAGE
NSA$_MESSAGE specifies a system message code. The $FORMAT_AUDIT service will use the $GETMSG service to translate the message into text. The resulting text is inserted into the formatted audit message, with the "Event information:" prefix. For example, the operating system uses this item code to supply the privilege audit text associated with privilege audit events; this keeps the audit records small. By default, the $GETMSG service can only translate resident system messages. You can use the NSA$_MSGFILNAM item code to specify the name of an application or site-specific message file.NSA$_MSGFILNAM
NSA$_MSGFILNAM is a string of 1 to 255 characters specifying the message file containing the translation for the message code in NSA$_MESSAGE. The default file specification is SYS$MESSAGE:.EXE. By default, $FORMAT_AUDIT uses the resident system message file.NSA$_NEW_DATA
NSA$_NEW_DATA is a string of 1 to n characters specifying the contents of the field named in NSA$_FIELD_NAME after the event occurred. NSA$_ORIGINAL_DATA contains the field contents prior to the event.NSA$_NOP
NSA$_NOP specifies that the item list entry should be ignored. This item code allows you to build a static item list and then remove those entries that do not apply to the current event.NSA$_ORIGINAL_DATA
NSA$_ORIGINAL_DATA is a string of 1 to n characters specifying the contents of the field named in NSA$_FIELD_NAME before the event occurred. NSA$_NEW_DATA contains the field contents following the event.NSA$_SENSITIVE_FIELD_NAME
NSA$_SENSITIVE_FIELD_NAME is a string of 1 to 256 characters specifying the name of the field being modified. This is used in combination with NSA$_SENSITIVE_ORIG_DATA and NSA$_SENSITIVE_NEW_DATA. Use NSA$_SENSITIVE_FIELD_NAME to prevent sensitive information, such as passwords, from being displayed in an alarm message. Sensitive information is written to the audit log.NSA$_SENSITIVE_NEW_DATA
NSA$_SENSITIVE_NEW_DATA is a string of 1 to n characters specifying the contents of the field named in NSA$_SENSITIVE_FIELD_NAME after the event occurred. NSA$_SENSITIVE_ORIG_DATA contains the field contents prior to the event. Use NSA$_SENSITIVE_NEW_DATA to prevent sensitive information from being displayed in an alarm message. Sensitive information is written to the audit log.NSA$_SENSITIVE_ORIG_DATA
NSA$_SENSITIVE_ORIG_DATA is a string of 1 to n characters specifying the contents of the field named in NSA$_SENSITIVE_FIELD_NAME before the event occurred. NSA$_SENSITIVE_NEW_DATA contains the field contents following the event. Use NSA$_SENSITIVE_FIELD_NAME to prevent sensitive information from being displayed in an alarm message. Sensitive information is written to the audit log.NSA$_SUPPRESS
NSA$_SUPPRESS is a longword bit mask directing $AUDIT_EVENT to ignore the defaults for the following values and either omit the information from the event record or use the value provided in another parameter. The bits in the mask inhibit the use of default values for the following item codes:
NSA$V_ACCOUNT_NAME NAS$V_PROCESS_NAME NSA$V_FINAL_STATUS NSA$V_SUBJECT_CLASS NSA$V_IMAGE_NAME NSA$V_SUBJECT_OWNER NSA$V_PARENT_ID NSA$V_SYSTEM_ID NSA$V_PARENT_NAME NSA$V_SYSTEM_OWNER NSA$V_PARENT_OWNER NSA$V_TERMINAL NSA$V_PARENT_USERNAME NSA$V_TIME_STAMP NSA$V_PROCESS_ID NSA$V_USERNAME
Previous Next Contents Index
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
privacy and legal statement 4527PRO_004.HTML