Order Number: AA--PSVEG--TE
This manual describes how system maintainers (system managers, data center operators, and application programmers) with system privileges can create DECprint Supervisor print queues to provide printing services for the users of PostScript printers, customize the DECprint Supervisor printing system, and test the printing system. This manual also describes common problems with PostScript printing and how to solve them.
Revision/Update Information: This guide supersedes AA--PSVEF--TE.
Operating System & Versions:
OpenVMS Alpha, Version 6.2, 7.2-2, 7.3 or 7.3-1
OpenVMS VAX, Version 5.5-2, 7.2 or 7.3
Software Version: Compaq DECprint Supervisor (DCPS) for OpenVMS, Version 2.1
Compaq Computer Corporation
Houston, Texas
© 2002 Compaq Information Technologies Group, L.P.
Compaq, the Compaq logo, Alpha, DCPS, DECnet, OpenVMS, VAX and VMS are trademarks of Compaq Information Technologies Group, L.P. in the U.S. and/or other countries.
Microsoft and Windows are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries.
All other product names mentioned herin may be trademarks of their respective companies.
Confidential computer software. Valid license from Compaq required for possession, use, or copying. Consistent with FAR 12.211 and 12.212, Commercial Computer Software, Computer Software Documentation, and Technical Data for Commercial Items are licensed to the U.S. Government under vendor's standard commercial license.
Compaq shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein. The information is provided "as is" without warranty of any kind and is subject to change without notice. The warranties for Compaq products are set forth in the express limited warranty statements accompanying such products. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty.
The DECprint Supervisor documentation set is available on CD-ROM.
| Contents | Index |
This manual is for OpenVMS system managers and data center operators. Using this guide, you can create and modify print queues, maintain the print jobs and print queues, and set up printing environments to meet the needs of the printing system users.
This guide is also intended for advanced users and applications programmers who customize the printing system using form definitions, setup modules, and layup definition files. The DECprint Supervisor for OpenVMS User's Guide describes how users access the features of the printing system.
Be sure to read the DECprint Supervisor for OpenVMS Software Installation Guide if you have not installed the DECprint Supervisor software.
For information about additional PostScript printing documentation and how to order documentation, refer to the Ordering Additional Documentation appendix in this manual.
The following conventions are used throughout this document:
| Convention | Meaning |
|---|---|
| UPPERCASE | Uppercase characters indicate DCL commands, qualifiers, and parameters. |
| italics | Italic characters in command examples indicate that you are to substitute a word or value of your choice. |
| bold | Bold characters are PostScript operators or error message prefix strings. Bold in examples shows the characters that you should enter as part of the procedure. |
| [] | Brackets indicate that the enclosed item is optional. |
| Ctrl/ x | This symbol indicates a control key sequence. Press the key labeled Ctrl while you simultaneously press another key, represented by x. |
| [Return] | This symbol indicates that you should press the Return key. |
The DECprint Supervisor software allows people to use and manage networked PostScript printers. For example, it allows users to:
The system manager makes the printing system easier to use by providing:
Starting with DCPS V2.0, the need for DCPS-OPEN and DCPS-PLUS licenses has been eliminated. The right to use all features of DCPS is now included with the OpenVMS operating system license. |
DCPS also provides the following features:
$ PRINT/PARAMETERS=(PAGE_SIZE=n,SHEET_SIZE=m) file-spec |
$ PRINT/PARAMETERS=(LAYUP=option=value) |
$ PRINT/PARAMETERS=(PAGE_LIMIT="n,m") $ PRINT/PARAMETERS=(NUMBER_UP=n) |
The version of DCPS software currently running on your system is
printed on job and file separator pages, as well as in the logical name
DCPS$VERSION. If DCPS$VERSION is undefined, DCPS has not been started
on the system.
1.2 DECprint Supervisor Software Components
The DECprint Supervisor software includes the following components:
The DECprint Supervisor symbiont is used in place of the OpenVMS print symbiont, PRTSMB. The software is distributed as executable image files, text, and help files.
Figure 1-1 illustrates the process by which print jobs are produced on an OpenVMS system and delivered to the printer.
Figure 1-1 DECprint Supervisor Software Components
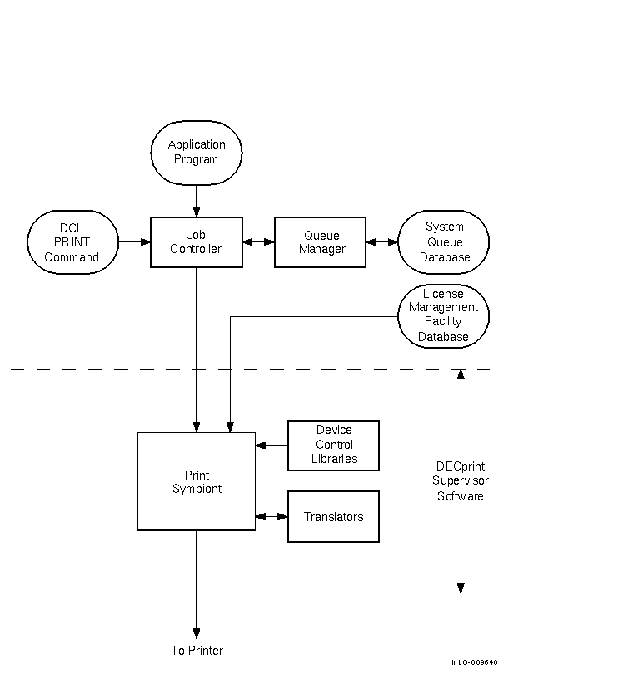
The software components of a DECprint Supervisor printing system are described
in the following sections.
1.2.1 The Print Symbiont
Users send jobs to the printer using the DCL PRINT command or using an application program that generates the OpenVMS system service call SYS$SNDJBC. The print symbiont manages the print jobs. The DECprint Supervisor software performs the following operations:
For example, suppose a user issues the following PRINT command:
$ PRINT/QUEUE=POST3/NOTIFY THORNTON.TXT |
The PRINT command line is translated to system service calls, which are sent to the job controller. The calls are converted to job controller data structures, which are then passed to the symbiont for processing. The symbiont sends the processed arguments and file data to the printer and notifies the user by displaying messages about the status of the print job.
See the DECprint Supervisor for OpenVMS User's Guide for information about the PRINT command and its
qualifiers.
1.2.2 Device Control Libraries
A device control library is an OpenVMS text library that contains setup modules. The symbiont uses modules from the device control library to implement the various PRINT parameters. The DECprint Supervisor software extracts the appropriate module, depending on the qualifier that either appears on the PRINT command line or is associated with a print queue, and inserts the module into the data stream.
The device control library also contains modules that the symbiont does not automatically use. Some of these modules contain PostScript procedures, for example, to include an error handler in a print job or to extend the findfont procedure to recognize alternate character encodings. These are described in the DECprint Supervisor for OpenVMS User's Guide.
You can create setup modules to be used on your own systems. When you create setup modules, you must store them in a device control library other than the DCPS$DEVCTL library. Create a device control library as described in Chapter 7 and add your library to the device control library search list defined in DCPS$STARTUP.COM.
When you create a site-specific device control library for your custom
setup modules, the contents of your library are retained from one
version of the DECprint Supervisor software to the next. The standard device
control library, DCPS$DEVCTL, is overwritten when you upgrade from one
version of the software to the next.
1.2.3 Translators
When a print job submits a print file that is not PostScript (or PCL, if your printer has a native PCL interpreter), the symbiont invokes a translator to translate the user's input file into PostScript. (Refer to Chapter 4 for more information about customizing the printing system for certain types of files.)
DECprint Supervisor software can detect the file data type automatically. You need not specify the data type on the PRINT command line. Translation to PostScript for successful printing is automatic. It is not necessary to maintain generic print queues for default data types.
The system manager can associate a default data type with a generic print queue, allowing users to print files by specifying the generic queue name. See Chapter 3 for more information.
If DCPS incorrectly identifies the data type of a file, you can identify the data type on the command line:
$ PRINT MYFILE.MEM /PARAMETERS=DATA_TYPE=ANSI $ PRINT MYFILE.POST /PARAMETERS=DATA_TYPE=POSTSCRIPT |
If you are installing DECprint Supervisor for the first time, or installing new printers, read this chapter. You may also find this chapter useful if you are changing the setup of an existing printer. The following sections describe how to set up your printers to work with DECprint Supervisor software.
| Non-PrintServer printers | Section 2.1 |
| DIGITAL PrintServer printers | Section 2.2 |
If you are changing the setup of a printer for which a DECprint Supervisor queue already exists, you must first stop the associated queue using the STOP /QUEUE /NEXT or STOP /QUEUE /RESET command. |
You can connect PostScript printers other than DIGITAL PrintServer printers to your OpenVMS system in a number of ways:
If your printer is connected via the network, multiple systems can access it.
The devices that can be used with DECprint Supervisor software are listed in the Software Product Description (SPD).
Your printer may contain a network interface card (NIC) or may be accessable to the network via a print server of a terminal server.
Printers can be configured as network printers if:
Network printing has the following implications:
Raw TCP/IP is a network protocol that utilizes the TCP/IP protocol directly without any additional interpretation of the TCP data stream. It is supported by many printer Network Interface Cards (NICs), print servers, and terminal servers.
There are other printer protocols that layer upon TCP/IP, including CPAP (Common Printer Access Protocol), LPD, and Telnet. DCPS uses CPAP to communicate with DIGITAL PrintServer printers.
DCPS does not support the Telnet or LPD protocols. |
To communicate with your printer using raw TCP/IP, the NIC, print server, or terminal server that you use to connect your printer to the network must provide a raw TCP/IP port. Further, this raw TCP/IP port must support bi-directional communication between the printer and your OpenVMS system. DCPS does not work with unidirectional ports, such as those found on the NICs for the DEClaser 3500 and 5100 printers, the RapidPrint 200, and Hewlett-Packard JetDirect cards that interface with the printer via its XIO (versus MIO) slot.
Before you can communicate with your printer via TCP/IP, you must
define an IP address for it. You may also assign a name to the address.
Refer to the printer documentation for information on setting the
printer's IP address. Refer to Compaq TCP/IP Services for OpenVMS,
Process Software MultiNet for OpenVMS, or Process Software TCPware
documentation for information on configuring your OpenVMS system's
TCP/IP environment. If your printer is connected through a print server
or terminal server, you must configure the IP address of the server.
You also need to configure the connection between the printer and the
server (for example, you may need to perform actions similar to those
described in Section 2.1.1.2.2 for LAT printers). Refer to documentation for
your terminal server or printer server for information on configuring
its network and printer interfaces.
2.1.1.2 LAT Printers
2.1.1.2.1 Configuring the Printer for LAT Access
To configure serial printers as network printers through a LAT connection to the Ethernet, change the following:
You can also change the printer password and printer name. These
changes are optional and explained in Section 2.1.3.3 and Section 2.1.3.4.
2.1.1.2.2 Setting DECserver LAT Port Characteristics
The process for configuring non-DECserver LAT devices is not described here, but many LAT devices use the same commands used by a DECserver device. Refer to the online help or other documentation for your NIC, terminal server, or print server for more information. |
To change DECserver port characteristics, you need privileged status on the DECserver device. Once you have privileged status, use the DEFINE PORT and SET PORT commands.
The DEFINE command changes the port's characteristics in the server's permanent database. These changes do not take effect until the next login for the port.
SET commands take effect immediately, but only alter the port's characteristics for the current session. For example, to change the INPUT SPEED and OUTPUT SPEED values on PORT_6 to 19200 baud (on a DECserver 200), issue the following commands from the console server manager:
LOCAL> SET PRIVILEGED PASSWORD> password LOCAL> SET PORT 6 SPEED 19200 LOCAL> DEFINE PORT 6 SPEED 19200 |
DECprint Supervisor supplies a sample command file for this purpose, if using LAT. This command file sets the characteristics for a DECserver with the Terminal Server Manager (TSM) software, and records data in the TSM database. (TSM is a software product available separately from Compaq.) The command file is:
This command file provides examples of characteristics for DECserver 100, DECserver 200, and DECserver 500 devices. |
For information about the commands and procedures for your DECserver device, refer to your DECserver management guide.
Make sure the DECserver port characteristics match the settings on your printer. Table 2-1 and Table 2-2 list DECserver port characteristics that must match the settings on your printer.
| Character size | 8 |
| Parity | None |
| Input speed | 9600 |
| Output speed | 9600 |
Make sure the queue limit is not set to 0, which disables queuing.
| Characteristic | Default Settings |
|---|---|
| ACCESS | REMOTE |
| AUTOBAUD | DISABLED |
| AUTOCONNECT | DISABLED |
| AUTOPROMPT | DISABLED |
| BREAK | DISABLED |
| BROADCAST | DISABLED |
| FLOW CONTROL | XON |
| INPUT FLOW CONTROL 1 | ENABLED |
| OUTPUT FLOW CONTROL 1 | ENABLED |
| INACTIVITY LOGOUT | DISABLED |
| LOSS NOTIFICATION | DISABLED |
| MESSAGE CODES | DISABLED |
| QUEUING | ENABLED |
| VERIFICATION | DISABLED |
On many versions of DECserver devices, QUEUING is not a port characteristic, but is a server characteristic whose default is ENABLED. |
| Next | Contents | Index |