




A system administrator may choose to add a standalone help volume to the desktop when an application does not provide integrated help or a customized environment provides a supplemental help volume. See "Standalone Help." for instructions to install a standalone volume on the desktop.
If your application's help volume includes execution links, it is recommended that the author define execution aliases in an application defaults file. This takes advantage of the Help System's default execution policy which will automatically execute links with execution aliases. However, if the help volume is viewed as an independent volume using a separate information viewer, such as the Help Viewer, the Help System will display a confirmation dialog box when an execution link is selected.
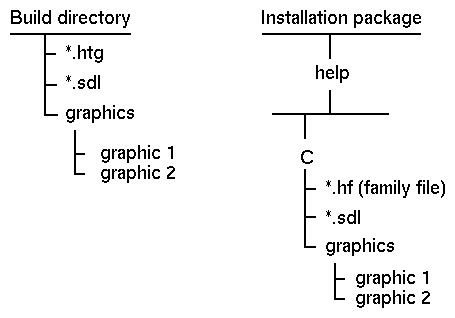
Figure 13-1 shows a typical installation package for an application and its help files. Help files are grouped in a separate help subdirectory which contains a default language directory (C is the default). The run-time help file, family file, and graphics files are located in this directory.
Figure 13-1 Application installation package

If your application provides online help in multiple languages, you should create a language subdirectory to accommodate each language (where language matches the user's LANG environment variable). For example, an application that provides both an English and German user interface stores its corresponding online help in two subdirectories: C for English and german for German.
You don't need to ship the volume.htg or any additional files generated by the HelpTag software.
A run-time help file does not include actual graphic images. Instead, it contains a "reference" to the location of each graphic file. When you run HelpTag, the dthelptag compiler incorporates the relative path names of the graphics files into the help volume.
When the help files are installed, the graphics files must be in the same relative position as when the run-time file was built. Otherwise, the help volume will be unable to locate the graphics files. For example, if your graphics files are in a subdirectory named graphics one level below your volume.htg file, then your installation package must preserve that relative position. The graphics files must be placed in a subdirectory named graphics one level below the volume.sdl file.
Figure 13-2 Relationship of build directories and installation package
hf). A family file briefly describes your help volume and includes copyright information. It can also be used to group one or more related volumes into a single product category. If you want your help volume to be accessible from the desktop browser volume, then you must provide a family file in your installation package. To create a family file, see "To Create a Help Family."
dtappintegrate, registers your application and its help files by creating symbolic links between the installed application files and specific desktop directories. Application registration ensures that your help files are located in the directory search paths used by the Help System. Registration enables two important features of the Help System:
If you register a help family with one or more help volumes, you make your help available for general browsing from the Front Panel Help Viewer. This allows access to application-specific help without using the application. Or, if you are writing standalone help, this is the only way for users to get to your help.
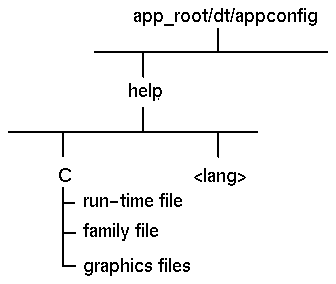
/etc/dt/appconfig/help/language directory.Remember that the run-time help file and its graphics files must be installed in the same relative position as when the help volume was built. See "Graphics Files." to review the installation of graphics files.
dt/appconfig/help/language to the /etc/dt/appconfig/help/language directory. Refer to the CDE Advanced User's and System Administrator's Guide for detailed instructions for application registration.
Here are the recommended commands for creating the run-time file:
dthelptag -clean volume
dthelptag volume nomemo onerror=stop
The -clean option removes files from any previous dthelptag command, the nomemo option ensures that writer's memos are not displayed, and the onerror=stop option stops processing if any parser errors occur. You should not distribute a help volume that has any parser errors.
Each hyperlink displays the proper topic or performs the correct action.
Execution aliases are defined as resources in the application's application defaults file. An execution alias associates a name with a shell command to be executed. If you have used execution links in your help volume, coordinate with the application developer to add these resources to the application defaults file. For more information, refer to "Execution Aliases."
The graphics have been tested on various color, grayscale, and monochrome displays.
Each graphics file must be installed in the same relative position to the .sdl file that it was in relative to the.htg file when the HelpTag software was run.
The dtappintegrate script was run to create symbolic links from the installation directory to the registration directory.
The family file is installed with the other help files. When dtappintegrate is run, it creates a symbolic link for the family file. Registering a family file for your help volume is optional. However, if you choose not to register a family file, your help volume will not be accessible from the Front Panel Help Viewer.
App-class*helpVolume: volume
App-class*helpOnHelpVolume: help-on-help-volume
The helpVolume resource identifies the help volume for your application.The helpOnHelpVolume identifies the help volume that contains the help on using the help system.
An author defines execution aliases as application resources. An execution alias associates a name with a shell command to be executed. If execution links have been used in the help volume, check with the author to identify the resources that need to be added. For more information, refer to "Execution Aliases."
App-class*DtHelpDialogWidget*onHelpDialog*rows: rows
App-class*DtHelpDialogWidget*onHelpDialog*columns: columns
App-class*DtHelpDialogWidget*definitionBox*rows: rows
App-class*DtHelpDialogWidget*definitionBox*columns: columns
The onHelpDialog resources control the size of the quick help dialogs used to display Help on Help. The definitionBox resources control the size of the quick help dialog used for definition links.
In most cases an application can rely on the default font resources. However, when custom fonts are used, they must be defined in the application-defaults file. Sample font schemes are provided in the /usr/dt/dthelp/fontschemes directory. See Chapter 14, "Native Language Support," for additional information about font schemes.




