How to Integrate with Calendar





The Calendar API is an implementation of the X.400 Application Programming Interface Association's (XAPIA) Calendaring and Scheduling API (CSA API). CSA API defines a set of high-level functions so that applications that are calendar enabled can access the varied features of the calendaring and scheduling service. For more information about the latest XAPIA Specification, contact the X.400 API Association, 800 El Camino Real, Mountain View, California 94043.
This chapter describes the Calendar API in these sections:
The number of function calls provided is minimal. A single set of functions manage multiple types of calendar entries.
Table 10-1 Derivation of C Naming Conventions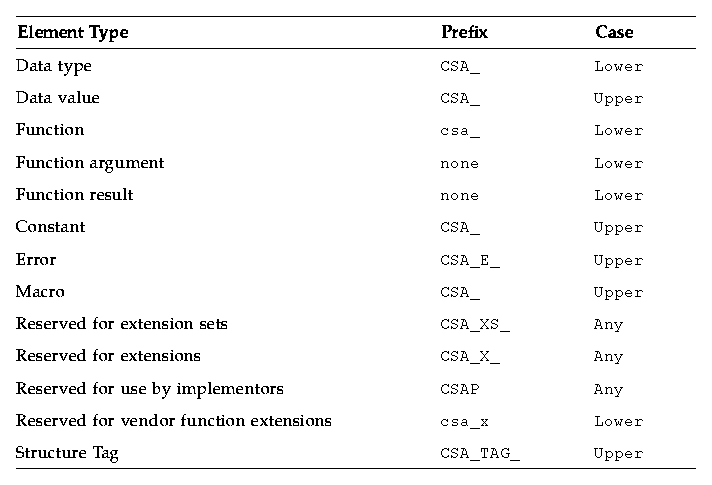
Elements with the prefix CSAP (any case) are reserved for internal proprietary use by implementors of the CSA service. They are not intended for direct use by programs written using the CSA interface.
The prefixes CSA_XS_, CSA_X_ (in either uppercase or lowercase), and csa_x are reserved for extensions of the interface by vendors or groups. The specification defines these interface extensions as extensions to the base set of functions.
For constant data values, an additional string is usually appended to CSA_ to indicate the data structure or function for the constant data value.
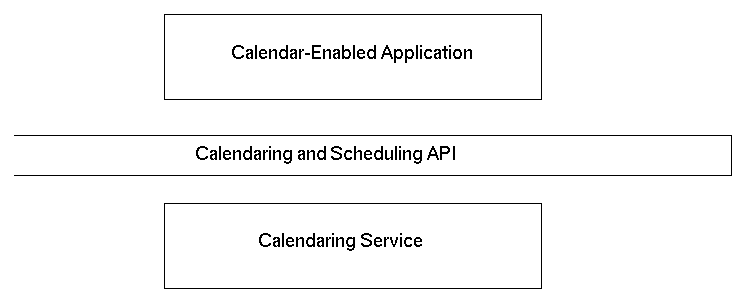
The CSA interface is defined between a calendar-enabled application and a calendaring service. All functions in this interface are designed to be independent of the calendaring service; however, the API does allow protocol-specific extensions to the common functions to be invoked through the use of extensions. See "Extensions" for more information. The relationship of the CSA interface to a calendar-enabled application and the calendar service is shown in Figure 10-1.
Figure 10-1 Positioning of the Calendaring and Scheduling API
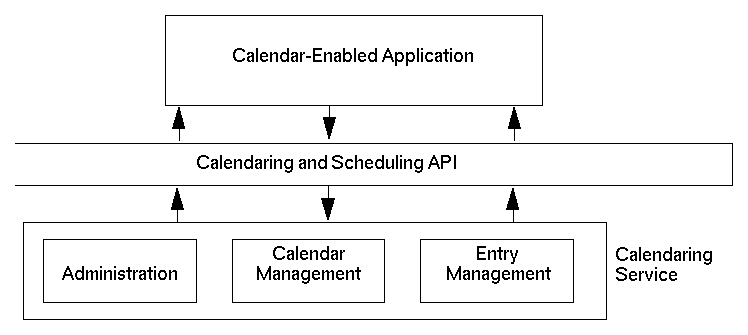
The model of the CSA interface can be divided into three components: administration, calendar management, and entry management. These components are shown in Figure 10-2.
Figure 10-2 Components of the Calendaring and Scheduling API
Access to the calendaring service is established through a calendaring session. The session provides for a valid connection to the calendaring service and assists in ensuring the integrity of the calendaring information maintained by the service. A calendar-enabled application logs on to an individual calendar within the calendaring service to establish a valid session or connection. The session is terminated by the calendar-enabled application logging off from the calendar.
The calendaring service maintains one or more calendars. The calendar service provides some level of administration support for these calendars. A calendar-enabled application might access a list of the calendars maintained by a particular calendar service. In addition, the calendar service might provide support for the archive and restore of calendar information into some implementation-specific, persistent format. Where a calendar service provides support for maintaining more than one calendar, support functions are defined for creating and deleting calendars. In addition, functions are provided to support administering the characteristics of the calendar.
The majority of the functions within the CSA interface manage individual calendar entries. Calendar entries may be either events, to dos, or memos. Entries can be added, deleted, updated, and read from a particular calendar. A calendar-enabled application can also add reminders to calendar entries.
The calendar attributes are a set of named values that may represent common, implementation-specific, or application-specific administrative characteristics about the calendar. For example, time zone, name, owner, and access rights to the calendar can be specified in individual calendar attributes.
The calendar entries are the primary components of a calendar. The three classes of calendar entries follow:
The calendar attributes and entry attributes consist of a name, type, and value tuple. Common attributes defined by the specification can be extended. Implementations can define implementation-specific attributes. In addition, some implementations may provide the capability for applications to define application-specific attributes. The CDE implementation supports application defined attributes.
The organizer role enables the user to delete the entry or view and change entry attributes of those calendar entries for which the user is specified as the organizer. The organizer defaults to the calendar user who created the entry.
The sponsor role enables the user to delete the entry or view and change entry attributes for those calendar entries for which the user is specified as the sponsor. The sponsor is the calendar user who effectively owns the calendar entry.
In addition to these roles, an access right can be set to limit access to free time searches; view, insert, or change calendar attributes; or view, insert or change entries, depending on whether they are classified as public, confidential, or private. The entry classification acts as a secondary filter on accessibility.
The csa_list_calendars() function is used to list the names of the calendars managed by a particular calendar service.
The csa_query_configuration() function is used to list information about the current calendar service configuration. This information can include the character set, line terminator characters for text strings, default service name, default authorization user identifier for the specified calendar service, an indicator of whether a password is needed to authenticate the user identifier, an indicator of whether the common extensions for user interface dialogs is supported, and the CSA specification supported by the implementation.
The CSA implementation provides support for managing the memory for calendar objects and attributes that are returned by the service. The csa_free() function is used to free up this memory after it is no longer needed. It is the responsibility of the application to free up the memory allocated and managed by the calendar service.
The application can also list, read, and update calendar attributes using the csa_list_calendar_attributes(), csa_read_calendar_attributes(), and csa_update_calendar_attributes() functions. The application can register callback functions for receiving notification of a calendar logon, calendar deletion, update of calendar attributes, addition of a new calendar entry, deletion of a calendar entry, and update of a calendar entry. The callback function is only registered for the duration of the calendar session. In any case, this information may be invaluable for some calendar administration applications.
The csa_add_entry() function is used to add new entries to a calendar. The csa_delete_entry() function is used to delete an entry in a calendar. The csa_ list_entries() function is used to enumerate the calendar entries that match a particular set of entry attribute criteria. The csa_read_entry_attributes() function is used to get either all or a set of entry attribute values associated with a particular calendar entry.
To add an entry to a calendar, a calendar-enabled application must first establish a session with the calendaring service using the csa_logon() function. Then the application invokes the csa_add_entry() function to specify the new entry. The calendar-enabled application is responsible for composing the attributes used in the csa_add_entry() function. The session is terminated using the csa_logoff() function.
The entry attributes in an individual calendar entry can be enumerated with the csa_list_entry_attributes() function. The values of one or more attributes can be read with the csa_ read_entry_attributes() function. Individual entry attributes can be modified with the csa_update_entry_attributes() function.
Memory allocated by the CSA implementation for retrieved calendar information is released by passing the associated memory pointers to the csa_free() function.
Some calendar entries are associated with a recurring activity. The csa_list_entry_sequence() function can be used to enumerate the other recurring calendar entries. This function returns a list of entry handles for the recurring entries.
The CDE calendar server provides support for alarms or reminders to be associated with calendar entries. Reminders can take the form of audio reminders from the terminal speaker, flashing reminders presented on the terminal screen, mail reminders sent to the calendar user, or pop-up reminders presented on the terminal screen. The calendar service manages the reminders, but it is the responsibility of the calendar application to retrieve the reminder information and act on it. The csa_read_next_reminder() function is used to read the information about the next scheduled type of reminder.
Extensions that are additional parameters to a function call may be input or output. That is, the extension may be passed as input parameters from the application to the CSA service or passed as output parameters from CSA service to the application. If an extension is an input parameter, the application allocates memory for the extension structure and any other structures associated with the extension. If an extension is an output parameter, the CSA service allocates the storage for the extension result, if necessary. In this case, the application must free the allocated storage with a csa_free() call.
If an extension that is not supported is requested, CSA_E_UNSUPPORTED_FUNCTION_EXT is returned.
Table 10-2 CSA Data Structures
Table 10-3 CSA Calendar Attributes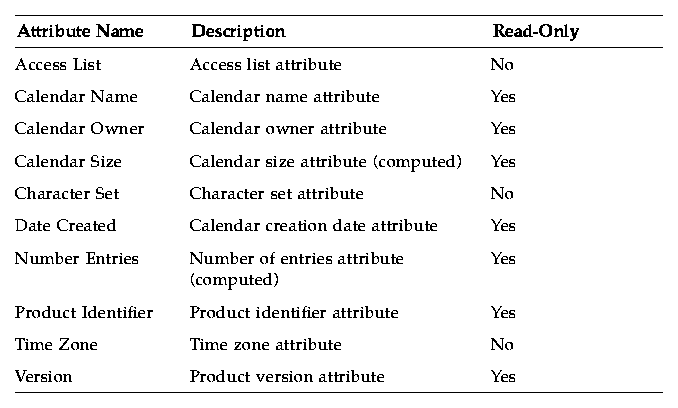
The following section provides additional information about the calendar attributes listed in Table 10-3.
When a new calendar is added and if no access list is specified, the default access list contains a special user world and its corresponding access right is CSA_VIEW_PUBLIC_ENTRIES, which provides access right to list and read calendar entries with public classification. The special user world includes all users.
The calendar name is specified when the calendar is created using csa_add_calendar(). It becomes read-only and cannot be changed after the calendar is created.
The calendar owner is set to the user who is running the application that calls csa_add_calendar() to create the calendar. It becomes read-only and cannot be changed after the calendar is created.
The CDE common locale name should be used to set this value.
This read-only attribute shows the version number of the server managing the calendar. This attribute is a CSA_VALUE_UINT32 type of attribute.
This read-only attribute shows the data version of the calendar. This attribute is a CSA_VALUE_UINT32 type of attribute.
Table 10-4 CSA Entry Attributes 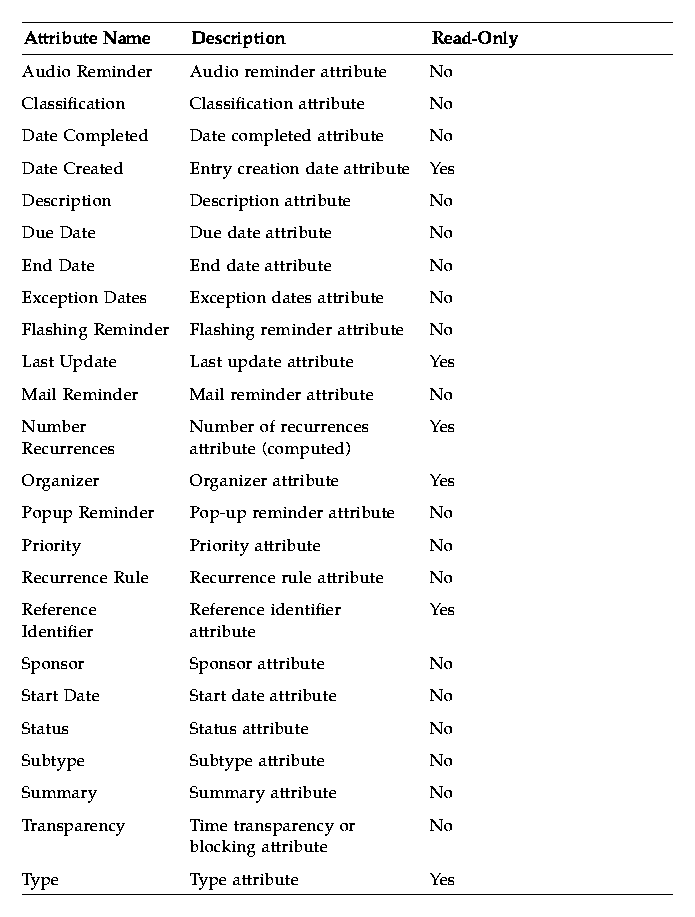
The following section provides additional information about the entry attributes listed in Table 10-4.
The organizer of an entry is set to the user who is running the application that calls csa_add_entry() to add the entry to the calendar. It becomes read-only and cannot be changed after the entry is added.
The reference identifier of an entry is a string that contains a unique identifier of the entry within the calendar as well as the name and location of the calendar. The format is n:calendar@location where n is a number that uniquely identifies the entry within the calendar, calendar is the name of the calendar, and location is the name of the machine where the calendar is stored.
The CDE implementation defines the following additional status values:
CSA_X_DT_STATUS_ACTIVE
CSA_X_DT_STATUS_DELETE_PENDING
CSA_X_DT_STATUS_ADD_PENDING
CSA_X_DT_STATUS_COMMITTED
CSA_X_DT_STATUS_CANCELLED
The value becomes read-only and cannot be changed after the entry is added. The CDE implementation defines the following additional type value:
CSA_X_DT_TYPE_OTHER
The value of this attribute indicates whether the start and end time of the entry should be shown to the user. It can be modified using csa_update_entry_attributes(). This attribute is a CSA_VALUE_SINT32 type of attribute.
The frequency of recurrence of the entry, which indicates how often the entry repeats. This is a read-only attribute and is derived from the entry attribute Recurrence Rule.
This attribute is a CSA_VALUE_UINT32 type of attribute.
The following values are defined:
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_ONETIME
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_DAILY
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_WEEKLY
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_BIWEEKLY
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_MONTHLY_BY_WEEKDAY
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_MONTHLY_BY_DATE
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_YEARLY
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_EVERY_NDAY
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_EVERY_NWEEK
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_EVERY_NMONTH
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_MON_TO_FRI
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_MONWEDFRI
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_TUETHUR
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_WEEKDAYCOMBO
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_OTHER
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_OTHER_WEEKLY
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_OTHER_MONTHLY
CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_OTHER_YEARLY
This attribute shows the number of times an entry repeats. This is a read-only attribute and is derived from the entry attribute Recurrence Rule. This attribute is a CSA_VALUE_UINT32 type of attribute.
This attribute tells how often an entry with repeat types CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_EVERY_NDAY, CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_EVERY_NWEEK, or CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_EVERY_NMONTH repeats. This is a read-only attribute, and is derived from the entry attribute Recurrence Rule. For example, if the value of this attribute is 3 and the repeat type is CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_EVERY_NWEEK, the entry repeats every three weeks. This attribute is a CSA_VALUE_UINT32 type of attribute.
If the entry's repeat type is CSA_X_DT_REPEAT_MONTHLY_BY_WEEKDAY, this attribute tells in which week the entry repeats. This is a read-only attribute and is derived from the entry attribute Recurrence Rule. This attribute is a CSA_VALUE_SINT32 type of attribute.
This entry attribute shows the end date of the sequence. This is a read-only attribute and is derived from the entry attribute Recurrence Rule. This attribute is a CSA_VALUE_DATE_TIME type of attribute.
The calendar attribute, CSA_CAL_ATTR_CHARACTER_SET, is used to store the locale information of the calendar.
CSA_return_code
csa_free(
CSA_buffer memory
);
CSA_return_code
csa_list_calendars(
CSA_service_reference calendar_service,
CSA_uint32 *number_names,
CSA_calendar_user **calendar_names,
CSA_extension *list_calendars_extensions
);
A host name where the server runs should be passed in calendar_server.
CSA_return_code
csa_logon(
CSA_service_reference calendar_service,
CSA_calendar_user *user,
CSA_string password,
CSA_string character_set,
CSA_string required_csa_version,
CSA_session_handle *session,
CSA_extension *logon_extensions
);
Arguments calendar_service, password, character_set, and required_csa_version are not used.The calendar_address field of the CSA_calendar_user structure pointed to by user specifies the calendar to log onto. The format is calendar@location where calendar is the name of the calendar and location is the host name where the calendar is stored.
The CDE-defined extension CSA_X_DT_GET_USER_ACCESS_EXT is supported. This extension can be used to get the access rights the calling user has with respect to the calendar. The user's access rights is returned in the item_data field of the extension structure.
CSA_return_code
csa_logoff(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA-extension *logoff_extensions
);
CSA_return_code
csa_query_configuration(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_enum item,
CSA_buffer *reference,
CSA_extension *query_configuration_extensions
);
The following items are not supported by this implementation of CDE:CSA_CONFIG_CHARACTER_SET
CSA_CONFIG_LINE_TERM
CSA_CONFIG_VER_IMPLEM
CSA_return_code
csa_add_calendar(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_calendar_user *user,
CSA_uint32 number_attributes,
CSA_attribute *calendar_attributes,
CSA_extension *add_calendar_extensions
);
The first argument session is ignored.The calendar_address field of the CSA_calendar_user structure pointed to by user specifies the name and the location of the calendar to be created. The format is calendar@location where calendar is the name of the calendar and location is the host name where the calendar is to be stored; for example, my_calendar@my_host.
CSA_return_code
csa_call_callbacks(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_flags reason,
CSA_extension *call_callbacks_extensions
);
CSA_return_code
csa_delete_calendar
CSA_session_handle session,
csa_extension *delete_calendar_extensions
);
CSA_return_code
csa_list_calendar_attributes(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_uint32 *number_names,
CSA_attribute_reference **calendar_attributes_names,
CSA_extension *list_calendar_attributes_extensions
);
CSA_return_code
csa_read_calendar_attributes(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_uint32 number_names,
CSA_attribute_reference *attribute_names,
CSA_uint32 *number_attributes,
CSA_attribute **calendar_attributes,
CSA_extension *read_calendar_attributes_extensions
);
CSA_return_code
csa_register_callback(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_flags reason,
CSA_callback callback,
CSA_buffer client_data,
CSA_extension *register_callback_extensions
);
CSA_return_code
csa_unregister_callback(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_flags reason,
CSA_callback callback,
CSA_buffer client_data,
CSA_extension *unregister_callback_extensions
);
CSA_return_code
csa_update_calendar_attributes(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_uint32 number_attributes,
CSA_attribute *calendar_attributes,
CSA_extension *update_calendar_attributes_extensions
);
CSA_return_code
csa_add_entry(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_uint32 number_attributes,
CSA_attribute *entry_attributes,
CSA_entry_handle *entry,
CSA_extension *add_entry_extensions
);
CSA_return_code
csa_delete_entry(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_entry_handle entry,
CSA_enum delete_scope,
CSA_extension *delete_entry_extensions
);
CSA_return_code
csa_list_entries(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_uint32 number_attributes,
CSA_attribute *entry_attributes,
CSA_enum *list_operators,
CSA_uint32 *number_entries,
CSA_entry_handle **entries,
CSA_extension *list_entries_extensions
);
The following information details more about the operators specified in list_operators:Only the operators CSA_MATCH_ANY and CSA_MATCH_EQUAL_TO are supported for the attribute value types CSA_VALUE_REMINDER, CSA_VALUE_CALENDAR_USER, and CSA_VALUE_DATE_TIME_RANGE.
Only the operators CSA_MATCH_ANY, CSA_MATCH_EQUAL_TO, CSA_MATCH_NOT_EQUAL_TO, and CSA_MATCH_CONTAIN are supported for the attribute value type CSA_VALUE_STRING. The operator CSA_MATCH_CONTAIN only applies to CSA_VALUE_STRING type of attributes.
Matching of attributes with the value types CSA_VALUE_OPAQUE_DATA, CSA_VALUE_ACCESS_LIST, CSA_VALUE_ATTENDEE_LIST, and, CSA_VALUE_DATE_TIME_LIST are not supported. The only exception is the attribute CSA_ENTRY_ATTR_REFERENCE_IDENTIFIER. The operator CSA_MATCH_EQUAL_TO is supported for this attribute.
CSA_return_code
csa_list_entry_attributes(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_entry_handle entry,
CSA_uint32 *number_names,
CSA_attribute_reference **entry_attribute_names,
CSA_extension *list_entry_attributes_extensions
);
CSA_return_code
csa_list_entry_sequence(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_entry_handle entry,
CSA_date_time_range time_range,
CSA_uint32 *number_entries,
CSA_entry_handle **entry_list,
CSA_extension *list_entry_sequences_extensions
);
CSA_E_INVALID_PARAMETER is returned if the specified entry is a one-time entry.
CSA_return_code
csa_read_entry_attributes(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_entry_handle entry,
CSA_uint32 number_names,
CSA_attribute_reference *attribute_names,
CSA_uint32 *number_attributes,
CSA_attribute **entry_attributes,
CSA_extension *read_entry_attributes_extensions
);
CSA_return_code
csa_read_next_reminder(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_uint32 number_names,
CSA_attribute_reference *reminder_names,
CSA_date_time given_time,
CSA_uint32 *number_reminders,
CSA_remainder_reference **reminder_references,
CSA_extension *read_next_reminder_extensions
);
CSA_return_code
csa_update_entry_attributes(
CSA_session_handle session,
CSA_entry_handle entry,
CSA_enum update_scope,
CSA_boolean update_propagation,
CSA_uint32 number_attributes,
CSA_attribute *entry_attributes,
CSA_entry_handle *new_entry,
CSA_extension *update_entry_attributes_extensions
);
Update propagation is not supported; the update_propagation argument should be set to CSA_FALSE.




