![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 19 July 1999 | |
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
To establish print queues, you must determine the type of queue configuration that best suits your OpenVMS Cluster system. You have several alternatives that depend on the number and type of print devices you have on each computer and on how you want print jobs to be processed. For example, you need to decide:
Once you determine the appropriate strategy for your cluster, you can create your queues. Figure 7-1 shows the printer configuration for a cluster consisting of the active computers JUPITR, SATURN, and URANUS.
Figure 7-1 Sample Printer Configuration
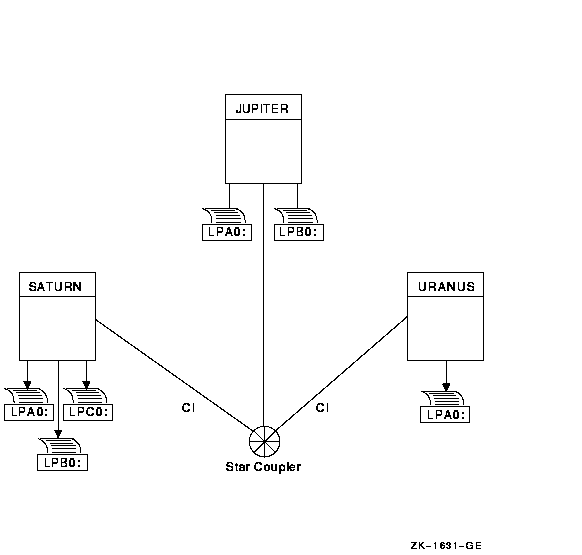
You set up OpenVMS Cluster print queues using the same method that you
would use for a standalone computer. However, in an OpenVMS Cluster
system, you must provide a unique name for each queue you create.
7.7.2 Command Format
You create and name a print queue by specifying the INITIALIZE/QUEUE command at the DCL prompt in the following format:
INITIALIZE/QUEUE/ON=node-name::device[/START][/NAME_OF_MANAGER=name-of-manager] queue-name |
| Qualifier | Description |
|---|---|
| /ON | Specifies the computer and printer to which the queue is assigned. If you specify the /START qualifier, the queue is started. |
| /NAME_OF_MANAGER | If you are running multiple queue managers, you should also specify the queue manager with the qualifier. |
You can also use the autostart feature to simplify startup and ensure high availability of execution queues in an OpenVMS Cluster. If the node on which the autostart queue is running leaves the OpenVMS Cluster, the queue automatically fails over to the next available node on which autostart is enabled. Autostart is particularly useful on LAT queues. Because LAT printers are usually shared among users of multiple systems or in OpenVMS Cluster systems, many users are affected if a LAT queue is unavailable.
Format for creating autostart queues:
Create an autostart queue with a list of nodes on which the queue can run by specifying the DCL command INITIALIZE/QUEUE in the following format:
INITIALIZE/QUEUE/AUTOSTART_ON=(node-name::device:,node-name::device:,...) queue-name |
When you use the /AUTOSTART_ON qualifier, you must initially activate the queue for autostart, either by specifying the /START qualifier with the INITIALIZE /QUEUE command or by entering a START/QUEUE command. However, the queue cannot begin processing jobs until the ENABLE AUTOSTART /QUEUES command is entered for a node on which the queue can run. Generic queues cannot be autostart queues.
Rules: Generic queues cannot be autostart queues. Note that you cannot specify both /ON and /AUTOSTART_ON.
Reference: Refer to Section 7.13 for information
about setting the time at which autostart is disabled.
7.7.4 Examples
The following commands make the local print queue assignments for JUPITR shown in Figure 7-2 and start the queues:
$ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/ON=JUPITR::LPA0/START/NAME_OF_MANAGER=PRINT_MANAGER JUPITR_LPA0 $ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/ON=JUPITR::LPB0/START/NAME_OF_MANAGER=PRINT_MANAGER JUPITR_LPB0 |
Figure 7-2 Print Queue Configuration

The clusterwide queue database enables you to establish generic queues
that function throughout the cluster. Jobs queued to clusterwide
generic queues are placed in any assigned print queue that is
available, regardless of its location in the cluster. However, the file
queued for printing must be accessible to the computer to which the
printer is connected.
7.8.1 Sample Configuration
Figure 7-3 illustrates a clusterwide generic print queue in which the queues for all LPA0 printers in the cluster are assigned to a clusterwide generic queue named SYS$PRINT.
A clusterwide generic print queue needs to be initialized and started only once. The most efficient way to start your queues is to create a common command procedure that is executed by each OpenVMS Cluster computer (see Section 7.12.3).
Figure 7-3 Clusterwide Generic Print Queue Configuration
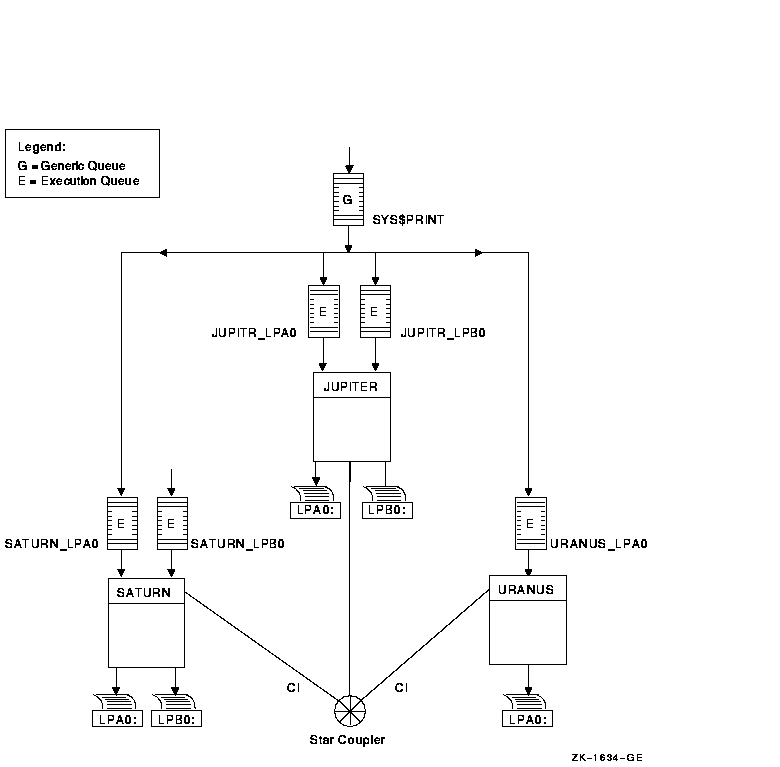
The following command initializes and starts the clusterwide generic queue SYS$PRINT:
$ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/GENERIC=(JUPITR_LPA0,SATURN_LPA0,URANUS_LPA0)/START SYS$PRINT |
Jobs queued to SYS$PRINT are placed in whichever assigned print queue
is available. Thus, in this example, a print job from JUPITR that is
queued to SYS$PRINT can be queued to JUPITR_LPA0, SATURN_LPA0, or
URANUS_LPA0.
7.9 Setting Up Execution Batch Queues
Generally, you set up execution batch queues on each OpenVMS Cluster
computer using the same procedures you use for a standalone computer.
For more detailed information about how to do this, see the
OpenVMS System Manager's Manual.
7.9.1 Before You Begin
Before you establish batch queues, you should decide which type of queue configuration best suits your cluster. As system manager, you are responsible for setting up batch queues to maintain efficient batch job processing on the cluster. For example, you should do the following:
Once you determine the strategy that best suits your needs, you can create a command procedure to set up your queues. Figure 7-4 shows a batch queue configuration for a cluster consisting of computers JUPITR, SATURN, and URANUS.
Figure 7-4 Sample Batch Queue Configuration
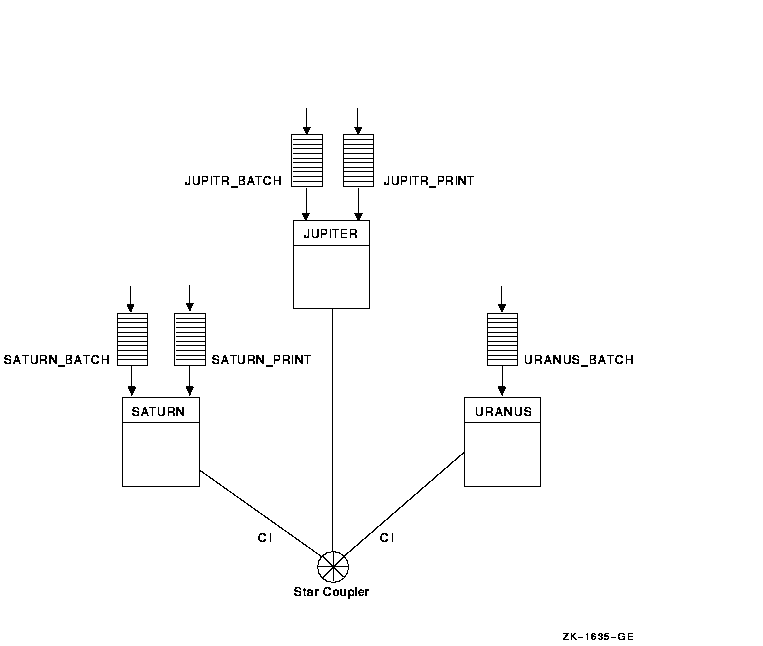
7.9.2 Batch Command Format
You create a batch queue with a unique name by specifying the DCL
command INITIALIZE/QUEUE/BATCH in the following format:
INITIALIZE/QUEUE/BATCH/ON=node::[/START][/NAME_OF_MANAGER=name-of-manager] queue-name |
| Qualifier | Description |
|---|---|
| /ON | Specifies the computer on which the batch queue runs. |
| /START | Starts the queue. |
| /NAME_OF_MANAGER | Specifies the name of the queue manager if you are running multiple queue managers. |
You can initialize and start an autostart batch queue by specifying the DCL command INITIALIZE/QUEUE/BATCH. Use the following command format:
INITIALIZE/QUEUE/BATCH/AUTOSTART_ON=node::queue-name |
When you use the /AUTOSTART_ON qualifier, you must initially activate the queue for autostart, either by specifying the /START qualifier with the INITIALIZE/QUEUE command or by entering a START/QUEUE command. However, the queue cannot begin processing jobs until the ENABLE AUTOSTART /QUEUES command is entered for a node on which the queue can run.
Rule: Generic queues cannot be autostart queues. Note
that you cannot specify both /ON and /AUTOSTART_ON.
7.9.4 Examples
The following commands make the local batch queue assignments for JUPITR, SATURN, and URANUS shown in Figure 7-4:
$ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/BATCH/ON=JUPITR::/START/NAME_OF_MANAGER=BATCH_QUEUE JUPITR_BATCH $ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/BATCH/ON=SATURN::/START/NAME_OF_MANAGER=BATCH_QUEUE SATURN_BATCH $ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/BATCH/ON=URANUS::/START/NAME_OF_MANAGER=BATCH_QUEUE URANUS_BATCH |
Because batch jobs on each OpenVMS Cluster computer are queued to
SYS$BATCH by default, you should consider defining a logical name to
establish this queue as a clusterwide generic batch queue that
distributes batch job processing throughout the cluster (see
Example 7-2). Note, however, that you should do this only if you have
a common-environment cluster.
7.10 Setting Up Clusterwide Generic Batch Queues
In an OpenVMS Cluster system, you can distribute batch processing among computers to balance the use of processing resources. You can achieve this workload distribution by assigning local batch queues to one or more clusterwide generic batch queues. These generic batch queues control batch processing across the cluster by placing batch jobs in assigned batch queues that are available. You can create a clusterwide generic batch queue as shown in Example 7-2.
A clusterwide generic batch queue needs to be initialized and started
only once. The most efficient way to perform these operations is to
create a common command procedure that is executed by each OpenVMS
Cluster computer (see Example 7-2).
7.10.1 Sample Configuration
In Figure 7-5, batch queues from each OpenVMS Cluster computer are assigned to a clusterwide generic batch queue named SYS$BATCH. Users can submit a job to a specific queue (for example, JUPITR_BATCH or SATURN_BATCH), or, if they have no special preference, they can submit it by default to the clusterwide generic queue SYS$BATCH. The generic queue in turn places the job in an available assigned queue in the cluster.
If more than one assigned queue is available, the operating system selects the queue that minimizes the ratio (executing jobs/job limit) for all assigned queues.
Figure 7-5 Clusterwide Generic Batch Queue Configuration
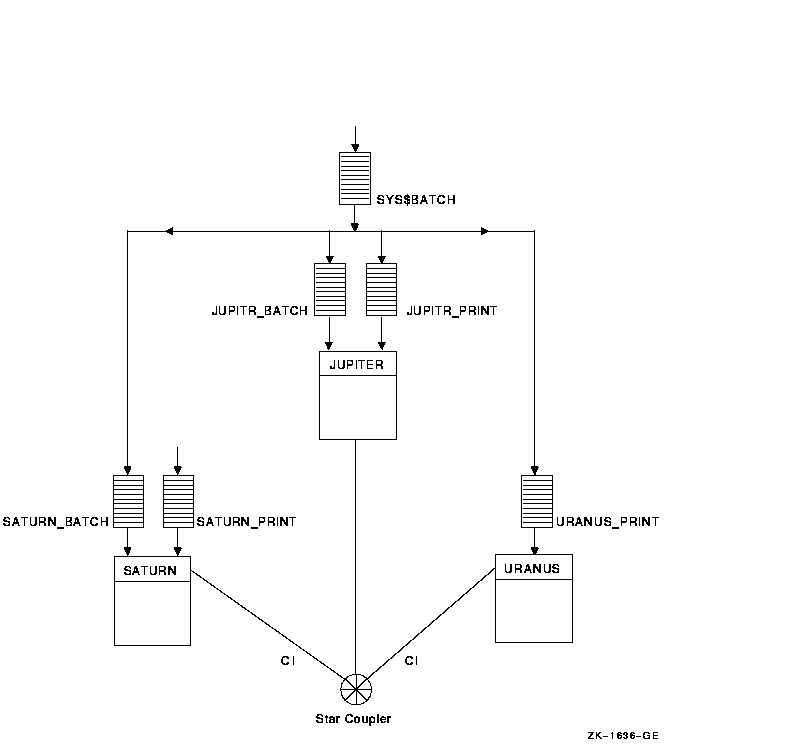
Normally, you use local batch execution queues during startup to run
batch jobs to start layered products. For this reason, these queues
must be started before the ENABLE AUTOSTART command is executed, as
shown in the command procedure in Example 7-1.
7.11.1 Startup Command Procedure
Start the local batch execution queue in each node's startup command procedure SYSTARTUP_VMS.COM. If you use a common startup command procedure, add commands similar to the following to your procedure:
$ SUBMIT/PRIORITY=255/NOIDENT/NOLOG/QUEUE=node_BATCH LAYERED_PRODUCT.COM $ START/QUEUE node_BATCH $ DEFINE/SYSTEM/EXECUTIVE SYS$BATCH node_BATCH |
Submitting the startup command procedure LAYERED_PRODUCT.COM as a high-priority batch job before the queue starts ensures that the job is executed immediately, regardless of the job limit on the queue. If the queue is started before the command procedure was submitted, the queue might reach its job limit by scheduling user batch jobs, and the startup job would have to wait.
7.12 Using a Common Command Procedure
Once you have created queues, you must start them to begin processing
batch and print jobs. In addition, you must make sure the queues are
started each time the system reboots, by enabling autostart for
autostart queues or by entering START/QUEUE commands for nonautostart
queues. To do so, create a command procedure containing the necessary
commands.
7.12.1 Command Procedure
You can create a common command procedure named, for example,
QSTARTUP.COM, and store it on a shared disk. With this method, each
node can share the same copy of the common QSTARTUP.COM procedure. Each
node invokes the common QSTARTUP.COM procedure from the common version
of SYSTARTUP. You can also include the commands to start queues in the
common SYSTARTUP file instead of in a separate QSTARTUP.COM file.
7.12.2 Examples
Example 7-1 shows commands used to create OpenVMS Cluster queues.
| Example 7-1 Sample Commands for Creating OpenVMS Cluster Queues | |||
|---|---|---|---|
$ (1) $ DEFINE/FORM LN_FORM 10 /WIDTH=80 /STOCK=DEFAULT /TRUNCATE $ DEFINE/CHARACTERISTIC 2ND_FLOOR 2 . . . (2) $ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/AUTOSTART_ON=(JUPITR::LPA0:)/START JUPITR_PRINT $ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/AUTOSTART_ON=(SATURN::LPA0:)/START SATURN_PRINT $ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/AUTOSTART_ON=(URANUS::LPA0:)/START URANUS_PRINT . . . (3) $ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/BATCH/START/ON=JUPITR:: JUPITR_BATCH $ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/BATCH/START/ON=SATURN:: SATURN_BATCH $ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/BATCH/START/ON=URANUS:: URANUS_BATCH . . . (4) $ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/START - _$ /AUTOSTART_ON=(JUPITR::LTA1:,SATURN::LTA1,URANUS::LTA1) - _$ /PROCESSOR=LATSYM /FORM_MOUNTED=LN_FORM - _$ /RETAIN=ERROR /DEFAULT=(NOBURST,FLAG=ONE,NOTRAILER) - _$ /RECORD_BLOCKING LN03$PRINT $ $ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/START - _$ /AUTOSTART_ON=(JUPITR::LTA2:,SATURN::LTA2,URANUS::LTA2) - _$ /PROCESSOR=LATSYM /RETAIN=ERROR - _$ /DEFAULT=(NOBURST,FLAG=ONE,NOTRAILER) /RECORD_BLOCKING - _$ /CHARACTERISTIC=2ND_FLOOR LA210$PRINT $ (5) $ ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES/ON=SATURN $ ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES/ON=JUPITR $ ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES/ON=URANUS (6) $ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/START SYS$PRINT - _$ /GENERIC=(JUPITR_PRINT,SATURN_PRINT,URANUS_PRINT) $ (7) $ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/BATCH/START SYS$BATCH - _$ /GENERIC=(JUPITR_BATCH,SATURN_BATCH,URANUS_BATCH) $ |
Following are descriptions of each command or group of commands in Example 7-1.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| (1) | Define all printer forms and characteristics. |
| (2) |
Initialize local print queues. In the example, these queues are
autostart queues and are started automatically when the node executes
the ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES command. Although the /START qualifier is
specified to activate the autostart queues, they do not begin
processing jobs until autostart is enabled.
To enable autostart each time the system reboots, add the ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES command to your queue startup command procedure, as shown in Example 7-2. |
| (3) | Initialize and start local batch queues on all nodes, including satellite nodes. In this example, the local batch queues are not autostart queues. |
| (4) |
Initialize queues for remote LAT printers. In the example, these queues
are autostart queues and are set up to run on one of three nodes. The
queues are started on the first of those three nodes to execute the
ENABLE AUTOSTART command.
You must establish the logical devices LTA1 and LTA2 in the LAT startup command procedure LAT$SYSTARTUP.COM on each node on which the autostart queue can run. For more information, see the description of editing LAT$SYSTARTUP.COM in the OpenVMS System Manager's Manual. Although the /START qualifier is specified to activate these autostart queues, they will not begin processing jobs until autostart is enabled. |
| (5) | Enable autostart to start the autostart queues automatically. In the example, autostart is enabled on node SATURN first, so the queue manager starts the autostart queues that are set up to run on one of several nodes. |
| (6) | Initialize and start the generic output queue SYS$PRINT. This is a nonautostart queue (generic queues cannot be autostart queues). However, generic queues are not stopped automatically when a system is shut down, so you do not need to restart the queue each time a node reboots. |
| (7) | Initialize and start the generic batch queue SYS$BATCH. Because this is a generic queue, it is not stopped when the node shuts down. Therefore, you do not need to restart the queue each time a node reboots. |
7.12.3 Example
Example 7-2 illustrates the use of a common QSTARTUP command
procedure on a shared disk.
| Example 7-2 Common Procedure to Start OpenVMS Cluster Queues | |||
|---|---|---|---|
$!
$! QSTARTUP.COM -- Common procedure to set up cluster queues
$!
$!
(1)
$ NODE = F$GETSYI("NODENAME")
$!
$! Determine the node-specific subroutine
$!
$ IF (NODE .NES. "JUPITR") .AND. (NODE .NES. "SATURN") .AND. (NODE .NES. "URANUS")
$ THEN
$ GOSUB SATELLITE_STARTUP
$ ELSE
(2)
$!
$! Configure remote LAT devices.
$!
$ SET TERMINAL LTA1: /PERM /DEVICE=LN03 /WIDTH=255 /PAGE=60 -
/LOWERCASE /NOBROAD
$ SET TERMINAL LTA2: /PERM /DEVICE=LA210 /WIDTH=255 /PAGE=66 -
/NOBROAD
$ SET DEVICE LTA1: /SPOOLED=(LN03$PRINT,SYS$SYSDEVICE:)
$ SET DEVICE LTA2: /SPOOLED=(LA210$PRINT,SYS$SYSDEVICE:)
(3)
$ START/QUEUE/BATCH 'NODE'_BATCH
$ GOSUB 'NODE'_STARTUP
$ ENDIF
$ GOTO ENDING
$!
$! Node-specific subroutines start here
$!
(4)
$ SATELLITE_STARTUP:
$!
$! Start a batch queue for satellites.
$!
$ START/QUEUE/BATCH 'NODE'_BATCH
$ RETURN
$!
(5)
$JUPITR_STARTUP:
$!
$! Node-specific startup for JUPITR::
$! Setup local devices and start nonautostart queues here
$!
$ SET PRINTER/PAGE=66 LPA0:
$ RETURN
$!
$SATURN_STARTUP:
$!
$! Node-specific startup for SATURN::
$! Setup local devices and start nonautostart queues here
$!
.
.
.
$ RETURN
$!
$URANUS_STARTUP:
$!
$! Node-specific startup for URANUS::
$! Setup local devices and start nonautostart queues here
$!
.
.
.
$ RETURN
$!
$ENDING:
(6)
$! Enable autostart to start all autostart queues
$!
$ ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES
$ EXIT
|
Following are descriptions of each phase of the common QSTARTUP.COM command procedure in Example 7-2.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| (1) | Determine the name of the node executing the procedure. |
| (2) |
On all large nodes, set up remote devices connected by the LAT. The
queues for these devices are autostart queues and are started
automatically when the ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES command is executed at
the end of this procedure.
In the example, these autostart queues were set up to run on one of three nodes. The queues start when the first of those nodes executes the ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES command. The queue remains running as long as one of those nodes is running and has autostart enabled. |
| (3) | On large nodes, start the local batch queue. In the example, the local batch queues are nonautostart queues and must be started explicitly with START/QUEUE commands. |
| (4) | On satellite nodes, start the local batch queue. |
| (5) | Each node executes its own subroutine. On node JUPITR, set up the line printer device LPA0:. The queue for this device is an autostart queue and is started automatically when the ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES command is executed. |
| (6) | Enable autostart to start all autostart queues. |
By default, the shutdown procedure disables autostart at the beginning
of the shutdown sequence. Autostart is disabled to allow autostart
queues with failover lists to fail over to another node. Autostart also
prevents any autostart queue running on another node in the cluster to
fail over to the node being shut down.
7.13.1 Options
You can change the time at which autostart is disabled in the shutdown sequence in one of two ways:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Define the logical name SHUTDOWN$DISABLE_AUTOSTART as follows:
$ DEFINE/SYSTEM/EXECUTIVE SHUTDOWN$DISABLE_AUTOSTART - Set the value of number-of-minutes to the number of minutes before shutdown when autostart is to be disabled. You can add this logical name definition to SYLOGICALS.COM. The value of number-of-minutes is the default value for the node. If this number is greater than the number of minutes specified for the entire shutdown sequence, autostart is disabled at the beginning of the sequence. |
| 2 | Specify the DISABLE_AUTOSTART number-of-minutes option during the shutdown procedure. (The value you specify for number-of-minutes overrides the value specified for the SHUTDOWN$DISABLE_AUTOSTART logical name.) |
Reference: See the OpenVMS System Manager's Manual for more information about changing the time at which autostart is disabled during the shutdown sequence.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
| privacy and legal statement | ||
| 4477PRO_012.HTML | ||