![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 19 July 1999 | |
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
The Alpha object language currently defines seven types of header records. Each type is assigned a symbolic code with values between 0 and 6. All other values are illegal in an Alpha object module.
Table B-4 lists the various types of header records.
| Subtype | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Main module header (MHD) 1 | EMH$C_MHD | 0 |
| Language processor name header (LNM) 1 | EMH$C_LNM | 1 |
| Source file header (SRC) 2 | EMH$C_SRC | 2 |
| Title text header (TTL) 2 | EMH$C_TTL | 3 |
| Copyright header (CPR) 2 | EMH$C_CPR | 4 |
| Maintenance status header (MTC) 2 | EMH$C_MTC | 5 |
| General text header (GTX) 2 | EMH$C_GTX | 6 |
| Reserved to Digital | All others |
The content and format of the MHD and LNM header subtypes, both of which are required in each object module, are described in the following subsections. Figure B-2 depicts a module header with MHD and LNM subrecords.
Figure B-2 Module Header Record with Subrecords
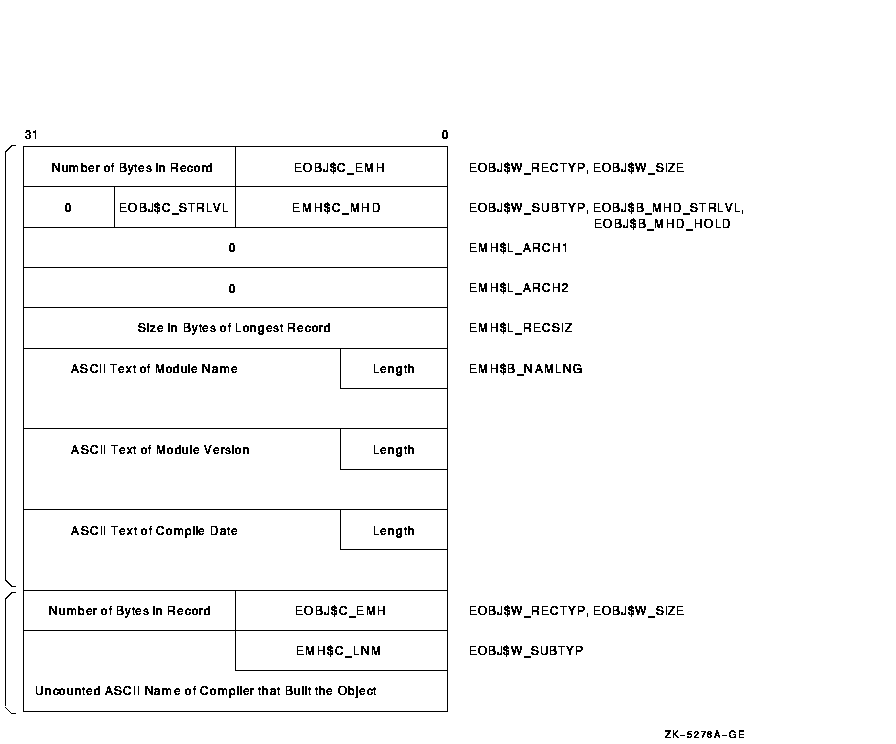
Though currently ignored by the linker, the header subtypes SRC, TTL, CPR, MTC, and GTX exist to allow the language processors to provide printable information within the object module for documentation purposes.
The format of the LNK, SRC, TTL, CPR, MTC, and GTX records consists of a record type field (EOBJ$W_RECTYP) containing the value EOBJ$C_EMH, a record size field (EOBJ$W_SIZE), a header subtype field (EOBJ$W_SUBTYP), and a field containing the uncounted ASCII text.
The content and format of the SRC and TTL records are depicted in
subsections B.2.3 and B.2.4, respectively. The contents
of these records, as well as the MTC record (which contains information
about the maintenance status of the object module), are displayed in an
object module analysis. (See the description of the ANALYZE/OBJECT
command in the OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.)
B.2.1 Main Module Header Record (EMH$C_MHD)
The main module header record, depicted in Figure B-2, is composed of the following fields. The name, symbolic representation, and length of each field are presented, followed by a symbolic value or an explanation of the contents of the field, where appropriate.
| RECORD TYPE | Name: EMH$W_RECTYP |
| Length: 2 bytes |
The field EMH$W_RECTYP redefines EOBJ$W_RECTYP. It must contain the value EOBJ$C_EMH.
| RECORD SIZE | Name: EMH$W_SIZE |
| Length: 2 bytes |
The field EMH$W_SIZE redefines EOBJ$W_SIZE. It is the size of the entire record, including the preceding record type field.
| HEADER TYPE | Name: EMH$W_HDRTYP |
| Length: 2 bytes |
The field EMH$W_HDRTYP redefines EOBJ$W_SUBTYP. It must contain a header subtype such as EMH$C_MHD (main module header) or EMH$C_LNM (language name and version).
| STRUCTURE LEVEL | Name: EMH$B_STRLVL |
| Length: 1 byte |
The structure level is EOBJ$C_STRLVL. Because the format of the MHD record never changes, the structure level field is provided so that changes in the format of other records can be made without recompiling every module that conformed to the previous format.
| ALIGNMENT BYTE | Name: EMH$B_TEMP |
| Length: 1 byte |
Alignment, must be zero.
| ARCHITECTURE | Name: EMH$L_ARCH1 |
| Length: 4 bytes |
Currently unused, must be zero.
| ARCHITECTURE | Name: EMH$L_ARCH2 |
| Length: 4 bytes |
Currently unused, must be zero.
| MAXIMUM RECORD SIZE | Name: EMH$L_RECSIZ |
| Length: 4 bytes |
This field contains the size in bytes of the longest record that can occur in the object module. This value may not exceed the maximum size of a record that is defined by the constant EOBJ$C_MAXRECSIZ, which is 8192 bytes.
| MODULE NAME LENGTH | Name: EMH$B_NAMLNG |
| Length: 1 byte |
This field contains the length in bytes of the module name.
| MODULE NAME | Name: EMH$T_NAME |
| Length: Variable, 1 to 31 bytes for object modules, 1 to 39 bytes for the module header at the beginning of a shareable image's global symbol table |
This field contains the module name in ASCII format.
| MODULE VERSION | Name: None |
| Length: Variable, 1 to 32 bytes, including the length byte |
This field contains the module version number as an ASCII counted string. The length byte must be present and contain 0 if there is no module version.
| CREATION TIME AND DATE | Name: None |
| Length: 17 bytes |
This field contains the module creation time and date in the fixed
format dd-mmm-yyyy hh:mm, where dd is the day of the month, mmm is the
standard 3-character abbreviation of the month, yyyy is the year, hh is
the hour (00 to 23), and mm is the minutes of the hour (00 to 59). Note
that a space is required after the year and that the total character
count for this time format is 17 characters (including hyphens (-), the
space, and the colon (:)).
B.2.2 Language Processor Name Header Record (EMH$C_LNM)
The language processor name header record is composed of the following fields:
| RECORD TYPE | Name: EMH$W_RECTYP |
| Length: 2 bytes |
EMH$W_RECTYP redefines EOBJ$W_RECTYP. The record type is EOBJ$C_EMH.
| RECORD SIZE | Name: EMH$W_SIZE |
| Length: 2 bytes |
The field EMH$W_SIZE redefines EOBJ$W_SIZE. It is the size of the entire record, including the preceding record type field.
| HEADER TYPE | Name: EMH$W_HDRTYP |
| Length: 2 bytes |
EMH$W_HDRTYP redefines EOBJ$W_SUBTYP. The header type is EMH$C_LNM.
| LANGUAGE NAME | Name: None |
| Length: Variable |
This field, which is generated by the language processor, contains the
name and version of the compiler that wrote the object module. It
consists of a variable-length string of ASCII characters and is
not preceded by a byte count of the string.
B.2.3 Source Files Header Record (EMH$C_SRC)
The contents of the source files header record, although ignored by the linker, are displayed in an object module analysis. (See the description of the ANALYZE/OBJECT command in the OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.) The source files header record is composed of the following fields:
| RECORD TYPE | Name: EMH$W_RECTYP |
| Length: 2 bytes |
EMH$W_RECTYP redefines EOBJ$W_RECTYP. The record type is EOBJ$C_EMH.
| RECORD SIZE | Name: EMH$W_SIZE |
| Length: 2 bytes |
The field EMH$W_SIZE redefines EOBJ$W_SIZE. It is the size of the entire record, including the preceding record type field.
| HEADER TYPE | Name: EMH$W_HDRTYP |
| Length: 2 bytes |
EMH$W_HDRTYP redefines EOBJ$W_SUBTYP. The header type is EMH$C_SRC.
| SOURCE FILES | Name: None |
| Length: Variable |
This field, which is generated by the compiler, contains the list of
file specifications from which the object module was created. It
consists of a variable-length string of ASCII characters and is
not preceded by a byte count of the string.
B.2.4 Title Text Header Record (EMH$C_TTL)
The contents of the title text header record, although ignored by the linker, are displayed in an object module analysis. (See the description of the ANALYZE/OBJECT command in the OpenVMS DCL Dictionary.) The title text header record is composed of the following fields:
| RECORD TYPE | Name: EMH$W_RECTYP |
| Length: 2 bytes |
EMH$W_RECTYP redefines EOBJ$W_RECTYP. The record type is EOBJ$C_EMH.
| RECORD SIZE | Name: EMH$W_SIZE |
| Length: 2 bytes |
The field EMH$W_SIZE redefines EOBJ$W_SIZE. It is the size of the entire record, including the preceding record type field.
| HEADER TYPE | Name: EMH$W_HDRTYP |
| Length: 2 bytes |
EMH$W_HDRTYP redefines EOBJ$W_SUBTYP. The header type is EMH$C_TTL.
| TITLE TEXT | Name: None |
| Length: Variable |
This field, which is generated by the language processor, contains a
brief description of the object module. It consists of a
variable-length string of ASCII characters and is not preceded
by a byte count of the string.
B.3 Global Symbol Directory Records (EOBJ$C_EGSD)
GSD records contain information that the linker uses to build link-time structures describing symbol references, symbol definitions, procedure definitions, and psect definitions. These structures are used to build the global symbol table, the debugger symbol table, and image sections, including the fix-up section.
At least one GSD record must appear in each object module.
A GSD record consists of a type field (EGSD$W_RECTYP), a size field (EGSD$W_RECSIZ), a quadword-alignment field (EGSD$L_ALIGNLW), and one or more GSD subrecords. Each subrecord consists of a type field, a size field, and one or more fields that differ depending on the type value. Each GSD subrecord must start on a quadword boundary. The beginning of the GSD record is filled out to a quadword by the EGSD$L_ALIGNLW field. This places the first subrecord on a quadword boundary. Each subrecord must be filled out to a quadword boundary by padding with zeros so that the following subrecord is also quadword aligned. Any padding must be reflected in the record's total byte count.
Table B-5 lists each type of GSD subrecord together with its symbolic representation and its corresponding numeric value.
| GSD Subrecord | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Program section definition | EGSD$C_PSC | 0 |
| Global symbol specification | EGSD$C_SYM | 1 |
| Random identity check | EGSD$C_IDC | 2 |
| Reserved to Digital | 3--4 | |
| Shareable program section definition 1 | EGSD$C_SPSC | 5 |
| Vectored symbol definition 2 | EGSD$C_SYMV | 6 |
| Masked symbol definition 2 | EGSD$C_SYMM | 7 |
| Universal symbol definition 1 | EGSD$C_SYMG | 8 |
| Reserved to Digital | All others |
A single GSD record must contain at least one of the above types of
subrecords. The number of subrecords in a GSD record is limited by the
maximum record size specified in the header field EMH$L_RECSIZ.
Figure B-1 shows the general format of a GSD record that contains
two subrecords. Note that the RECORD TYPE and RECORD SIZE fields appear
only once at the beginning of the record, regardless of how many
subrecords there are. The RECORD SIZE field counts all of the bytes in
the record, including the RECORD TYPE and RECORD SIZE fields
themselves, and all of the GSD subrecords. Each GSD subrecord includes
a GSD SUBRECORD TYPE and GSD SUBRECORD SIZE field. The RECORD TYPE and
RECORD SIZE fields for the GSD record are not listed in the following
sections, which describe each subrecord, and are not shown in the
diagrams.
B.3.1 Program Section Definition Subrecords (EGSD$C_PSC, EGSD$C_SPSC)
The linker assigns program sections an identifying index number as it processes each successive psect definition, that is, each EGSD$C_PSC subrecord. The linker assigns these numbers in sequential order, assigning 0 to the first program section it encounters, 1 to the second, and so on, up to the maximum allowable limit of 65,535 (216 --1) within any single object module.
Program sections are referred to by other object language records by means of this program section index. For example, the global symbol specification subrecord (EGSD$C_SYM) contains a field that specifies the program section index. This field is used to locate the program section containing storage for the symbol. Text information and relocation (TIR) commands also use the program section index.
Care is required to ensure that program sections are defined to the
linker (and thus assigned an index) in the proper order so that other
object language records that reference a program section by means of
the index are in fact referencing the correct program section. Program
sections may be referenced before they are defined, although it is good
practice to define the program sections first when possible.
B.3.1.1 Normal Program Section Definition Subrecord (EGSD$C_PSC)
Figure B-3 depicts the format of a program section definition subrecord, showing the fields it contains and providing a description of each.
Figure B-3 GSD Subrecord for a Program Section Definition
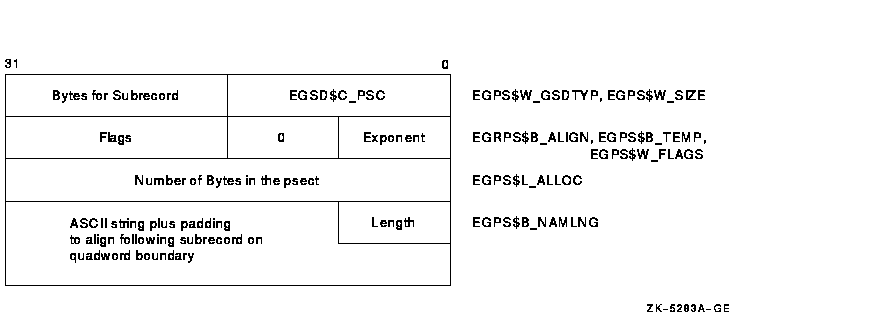
| GSD SUBRECORD TYPE | Name: EGPS$W_GSDTYP |
| Length: 2 bytes |
The GSD type is EGSD$C_PSC.
| GSD SUBRECORD SIZE | Name: EGPS$W_SIZE |
| Length: 2 bytes |
This field contains the size of the entire subrecord, including the preceding type field and any padding used to quadword align the following record.
| PSECT ALIGNMENT | Name: EGPS$B_ALIGN |
| Length: 1 byte |
This field specifies the virtual address boundary at which the program section is placed. Each contribution to a particular program section may specify its own alignment. If the contributions have different alignments, the greatest alignment is used to align the entire program section. The flags field of an overlaid program section has the EGPS$V_OVR bit set.
The alignment field contains a value between 0 and 16, which is interpreted as a power of 2; the value of this expression is the alignment in bytes between 1 and 64K. Table B-6 illustrates some common alignment field values.
| Value | Alignment in Bytes | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | (BYTE) |
| 1 | 2 | (WORD) |
| 2 | 4 | (LONGWORD) |
| 3 | 8 | (QUADWORD) |
| 4 | 16 | (OCTAWORD) |
| 9 | 512 | (PAGELET) |
| 13 | 8K | (8K BIG PAGE) |
| 16 | 64K | (64K BIG PAGE) |
| ALIGNMENT BYTE | Name: EGPS$B_TEMP |
| Length: 1 byte |
Field alignment byte. Must be 0.
| FLAGS | Name: EGPS$W_FLAGS |
| Length: 2 bytes |
This field is a word-length bit field, each bit indicating (when set) that the program section has the corresponding attribute. (See Section 3.2 for a description of program section attributes.) The following table lists the numbers, names, and corresponding meanings of each bit in the field:
| Bit | Name | Meaning if Set |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | EGPS$V_PIC | Not meaningful. For compatability reasons, the linker still sorts psects on this attribute when building image sections. This bit should never be the only distinguishing attribute between two different psects. If two psects have exactly the same attributes except for EGSP$V_PIC, then the psect attributes should be changed so that they match. |
| 1 | EGPS$V_LIB | Program section is defined in the symbol table of a shareable image, to which this image is bound. This bit is used by the linker and should not be set in user-defined program sections. |
| 2 | EGPS$V_OVR | Contributions to this program section by more than one module are overlaid. If this bit is set, EGPS$V_REL and EGPS$V_GBL must also be set. An overlaid program section must not be referenced by the ESDF$L_PSINDX field of a symbol definition. |
| 3 | EGPS$V_REL | Program section is relocatable. If this bit is not set, the program section is absolute and therefore contains only symbol definitions. Note that memory is not allocated for absolute program sections. |
| 4 | EGPS$V_GBL | Program section is global. |
| 5 | EGPS$V_SHR | Program section is shareable between two or more active processes. |
| 6 | EGPS$V_EXE | Program section is executable. |
| 7 | EGPS$V_RD | Program section is readable. This attribute is currently ignored by the linker. |
| 8 | EGPS$V_WRT | Program section is writable. |
| 9 | EGPS$V_VEC | Program section contains change mode dispatch vectors or message vectors. This bit is normally left clear and set by the programmer with the linker option PSECT_ATTRIBUTE=psect-name,VEC |
| 10 | EGPS$V_NOMOD | Program section contains unmodified data and can be included in a demand-zero image section. |
| 11 | EGPS$V_COM | Program section defines conditional storage for a symbol with the EGSD$V_COMM bit set. If this bit is set, EGPS$V_OVR, EGPS$V_REL, and EGPS$V_GBL must also be set. |
| 12--15 | Reserved to Digital. |
| ALLOCATION | Name: EGPS$L_ALLOC |
| Length: 4 bytes |
This field contains the length in bytes of this module's contribution to the program section. If the program section is absolute, the value of the allocation field must be 0.
| PSECT NAME LENGTH | Name: EGPS$B_NAMLNG |
| Length: 1 byte |
This field contains the length in bytes of the program section name.
| PSECT NAME | Name: EGPS$T_NAME |
| Length: Variable, 1 to 31 bytes |
This field contains the name of the program section in ASCII format. Note that program section names are limited to 31 bytes, while symbol names are limited to 64 bytes. Compilers that implement global symbols as overlaid program sections (as opposed to global symbol definitions with storage allocated by a concatenated program section) must be aware of this restriction.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
| privacy and legal statement | ||
| 4548PRO_021.HTML | ||