![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 19 July 1999 | |
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
The read or write attributes subfunction is controlled by the attribute list specified by P5. The list consists of a variable number of two longword control blocks, terminated by a 0 longword, as shown in Figure 1-6. The maximum number of attribute control blocks in one list is 30. Table 1-6 describes the attribute control block fields.
Figure 1-6 Attribute Control Block Format
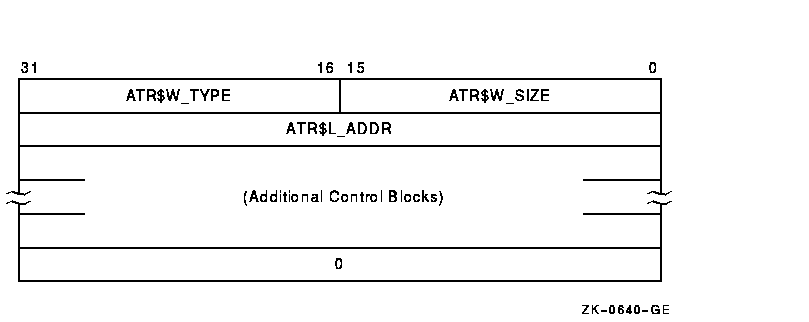
| Field | Meaning |
|---|---|
| ATR$W_SIZE | Specifies the number of bytes of the attribute to be transferred. Legal values are from 0 to the maximum size of the particular attribute (see Table 1-7). |
| ATR$W_TYPE | Identifies the individual attribute to be read or written. |
| ATR$L_ADDR | Contains the buffer address of the memory space to or from which the attribute is to be transferred. The attribute buffer must be writable. |
Table 1-7 lists the valid attributes for ACP-QIO functions. The maximum size (in bytes) is determined by the required attribute configuration. For example, the Radix-50 file name (ATR$S_FILNAM) uses only 6 bytes, but it is always accompanied by the file type and file version, so a total of 10 bytes is required. Each attribute has two names: one for the code (for example, ATR$C_UCHAR) and one for the size (for example, ATR$S_UCHAR).
| Attribute Name6 | Maximum Size (bytes) | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| ATR$C_UCHAR 2 3 | 4 | 4-byte file characteristics. (The file characteristics bits are listed following this table.) |
| ATR$C_RECATTR 4 | 32 | Record attribute area. Section 1.4 describes the record attribute area in detail. |
| ATR$C_FILNAM | 10 | 6-byte Radix-50 file name plus ATR$C_FILTYP and ATR$C_FILVER. |
| ATR$C_FILTYP | 4 | 2-byte Radix-50 file type plus ATR$C_FILVER. |
| ATR$C_FILVER | 2 | 2-byte binary version number. |
| ATR$C_EXPDAT 2 | 7 | Expiration date in ASCII. Format: DDMMMYY. |
| ATR$C_STATBLK | 32 | Statistics block. This attribute is read only. Section 1.5 describes the statistics block in detail. |
| ATR$C_HEADER | 512 | Complete file header. This attribute is read only. |
| ATR$C_BLOCKSIZE | 2 | Magnetic tape block size. |
| ATR$C_USERLABEL | 80 | User file label. This attribute is not supported for disk devices. |
| ATR$C_ASCDATES 2 3 | 35 | Revision count (2 binary bytes), revision date, creation date, and expiration date, in ASCII. Format: DDMMMYY (revision date), HHMMSS (time), DDMMMYY (creation date), HHMMSS (time), DDMMMYY (expiration date). (The format contains no embedded spaces or commas.) |
| ATR$C_ALCONTROL | 14 | Compatibility mode allocation data. |
| ATR$C_ENDLBLAST | 4 | End of magnetic tape label processing; provides AST control block. |
| ATR$C_ASCNAME | 86 |
Disk: file name, type, and version, in ASCII, including punctuation.
Format: name.type;version.
Magnetic tape: contains 17-character file identifier (ANSI a); no version number. Overrides all other file name and file type specifications if supplied on input operations. If specified on an access operation and you want only a value to be returned, specify (in ATR$W_SIZE) a buffer of greater than 17 bytes. |
| ATR$C_CREDATE 2 | 8 | 64-bit creation date and time. |
| ATR$C_REVDATE 2 4 | 8 | 64-bit revision date and time. |
| ATR$C_EXPDATE 2 | 8 | 64-bit expiration date and time. |
| ATR$C_BAKDATE 4 5 8 10 | 8 | 64-bit backup date and time. |
| ATR$C_UIC 2 | 4 | 4-byte file owner UIC. |
| ATR$C_FPRO 2 4 | 2 | File protection. |
| ATR$C_RPRO 10 | 2 | 2-byte record protection. |
| ATR$C_ACLEVEL 2 4 5 10 | 1 | File access level. |
| ATR$C_SEMASK 10 | 8 | File security mask and limit. |
| ATR$C_UIC_RO | 4 | 4-byte file owner UIC. This attribute is read only. |
| ATR$C_DIRSEQ 10 | 2 | Directory update sequence count. |
| ATR$C_BACKLINK 10 | 6 | File back link pointer. |
| ATR$C_JOURNAL 10 | 1 | Journal control flags. |
| ATR$C_HDR1_ACC | 1 | ANSI magnetic tape header label accessibility character. |
| ATR$C_ADDACLENT 7 10 11 | 255 | Adds an ACE to the beginning of the ACL when the ACE context value is 0; to the end of the ACL when the ACE context value is --1; or at a location pointed to by a prior ACL$C_FNDACETYP or ACL$C_FNDACLENT. |
| ATR$C_DELACLENT 7 10 11 | 255 | Deletes an access control entry pointed to by the buffer address or, if the buffer address is 0, the ACE pointed to by a prior ACL$C_FNDACETYP or ACL$C_FNDACLENT. |
| ATR$C_MODACLENT 7 10 11 | 255 | Replaces the ACE pointed to by a prior ACL$C_FNDACETYP or ACL$C_FNDACLENT with the ACE pointed to by its buffer address. |
| ATR$C_FNDACLENT 10 11 | 255 | Locates an ACE pointed to by its buffer address. |
| ATR$C_FNDACETYP 10 11 | 255 | Locates an ACE of the type pointed to by its buffer address. |
| ATR$C_DELETEACL 7 10 11 | 255 | Deletes the entire ACL with the exception of protected ACEs. |
| ATR$C_READACL 10 11 | 512 | Reads the entire ACL or as much as will fit in the supplied buffer. Only complete ACEs are transferred. |
| ATR$C_ACLLENGTH 10 11 | 4 | Returns the size, in bytes, of the object's ACL. |
| ATR$C_READACE 10 11 | 255 | Reads the ACE pointed to by ACL$C_FNDACETYP or ACL$C_FNDACLENT into the buffer. |
| ATR$C_RESERVED 9 10 | 380 | Modifies the reserve area. |
| ATR$C_HIGHWATER 10 | 4 | High-water mark (user read-only). |
| ATR$C_PRIVS_USED 10 | 4 | Privileges used to gain access. This attribute can only be retrieved on the initial file access or create operation. |
| ATR$C_MATCHING_ACE 8 10 | 255 | ACE used to gain access (if any). This attribute can only be retrieved on the initial file access or create operation. |
| ATR$C_ACCESS_MODE | 1 | Access mode for following attribute descriptors. |
| ATR$C_FILE_SPEC 10 | 512 | Convert FID to file specification. |
| ATR$C_BUFFER_OFFSET 3 | 2 | Offset length for ANSI magnetic tape header label buffer. |
| ATR$C_DELETE_ALL 7 10 11 | 255 | Delete the entire ACL, including protected entries. |
| ATR$C_GRANT_ACE 10 11 | 255 | Return an ACE that grants or denies access to the object. |
| ATR$C_NEXT_ACE 10 11 | 4 | Advance to the next ACE in the ACL. |
Table 1-8 lists the bits contained in the file characteristics longword, which is read with the ATR$C_UCHAR attribute.
| FCH$M_NOBACKUP | Do not back up file. |
| FCH$M_READCHECK | Verify all read operations. |
| FCH$M_WRITCHECK | Verify all write operations. |
| FCH$M_CONTIGB | Keep file as contiguous as possible. |
| FCH$M_LOCKED | File is deaccess-locked. |
| FCH$M_CONTIG | File is contiguous. |
| FCH$M_BADACL | File's ACL is corrupt. |
| FCH$M_SPOOL | File is an intermediate spool file. |
| FCH$M_DIRECTORY | File is a directory. |
| FCH$M_BADBLOCK | File contains bad blocks. |
| FCH$M_MARKDEL | File is marked for deletion. |
| FCH$M_ERASE | Erase file contents before deletion. |
| FCH$M_ASSOCIATED 1 | File has an associated file. |
| FCH$M_EXISTENCE 1 | Suppress existence of file. |
| FCH$M_NOMOVE | Disable movefile operations on this file. |
| FCH$M_NOSHELVABLE | File is not shelvable. |
| FCH$M_SHELVED | File is shelved. |
Figure 1-7 shows the format of the record attributes area.
Figure 1-7 ACP-QIO Record Attributes Area

Table 1-9 lists the record attributes values and their meanings.
| Field Value | Meaning | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FAT$B_RTYPE | Record type. Contains FAT$V_RTYPE and FAT$V_FILEORG. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$V_RTYPE |
Record type. The following bit values are defined:
|
||||||||||||||
| FAT$V_FILEORG |
File organization. The following bit values are defined:
|
||||||||||||||
| FAT$B_RATTRIB |
Record attributes. The following bit values are defined:
|
||||||||||||||
| FAT$W_RSIZE | Record size in bytes. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$L_HIBLK 2 |
Highest allocated VBN. The ACP maintains this field when the file is
extended or truncated. Attempts to modify this field in a write
attributes operation are ignored.
|
||||||||||||||
| FAT$L_EFBLK 2 3 |
End-of-file VBN
|
||||||||||||||
| FAT$W_FFBYTE 3 | First free byte in FAT$L_EFBLK. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$B_BKTSIZE | Bucket size in blocks. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$B_VFCSIZE | Size in bytes of fixed-length control for VFC records. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$W_MAXREC | Maximum record size in bytes. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$W_DEFEXT | Default extend quantity. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$W_GBC | Global buffer count. | ||||||||||||||
| FAT$W_VERSIONS | Default version limit; valid only if the file is a directory. |
Figure 1-8 shows the format of the attributes statistics block. Table 1-10 lists the contents of this block.
Figure 1-8 ACP--QIO Attributes Statistics Block
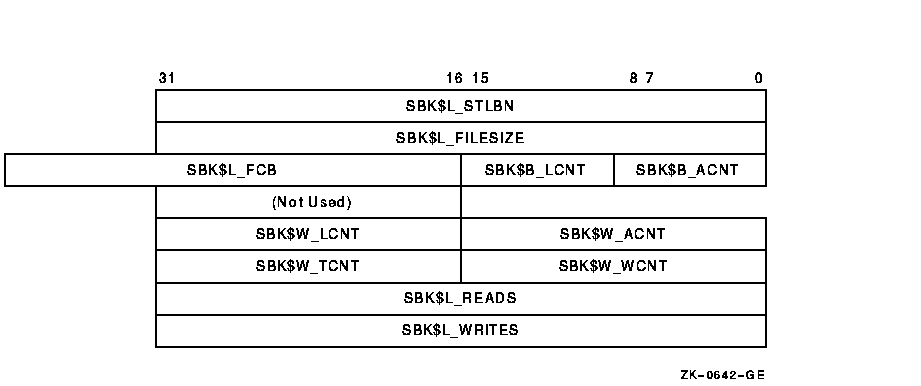
| Field | Subfields | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| SBK$L_STLBN | Contains the starting LBN of the file if the file is contiguous. If the file is not contiguous, this field contains a value of 0. The LBN appears as an inverted longword (the high- and low-order 16 bits are transposed for PDP-11 compatibility). The following subfields are defined: | |
| SBK$W_STLBNH | Starting LBN (high-order 16 bits) | |
| SBK$W_STLBNL | Starting LBN (low-order 16 bits) | |
| SBK$L_FILESIZE | Contains the size of the file in blocks. The file size appears as an inverted longword (the high- and low-order 16 bits are transposed for PDP-11 compatibility). The following subfields are defined: | |
| SBK$W_FILESIZH | File size (high-order 16 bits) | |
| SBK$W_FILESIZL | File size (low-order 16 bits) | |
| SBK$B_ACNT 1 | Access count (low byte). Field is for PDP-11 compatibility. | |
| SBK$B_LCNT 1 | Lock count (low byte). Field is for PDP-11 compatibility. | |
| SBK$L_FCB | System pool address of the file's file control block. | |
| SBK$W_ACNT 1 | Access count (number of channels with file open currently). | |
| SBK$W_LCNT 1 | Lock count (the number of access operations that have locked the file against writers). | |
| SBK$W_WCNT 1 | Writer count (the number of channels that currently have the file open for write). | |
| SBK$W_TCNT 1 | Truncate lock count (the number of access operations that have locked the file against truncation). | |
| SBK$L_READS | Number of read operations executed for the file on this channel. | |
| SBK$L_WRITES | Number of write operations executed for the file on this channel. |
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
| privacy and legal statement | ||
| 6136PRO_002.HTML | ||