![[Compaq]](../../images/hp.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/hp_ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 15 July 2002 | |
![[Compaq]](../../images/hp.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/hp_ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
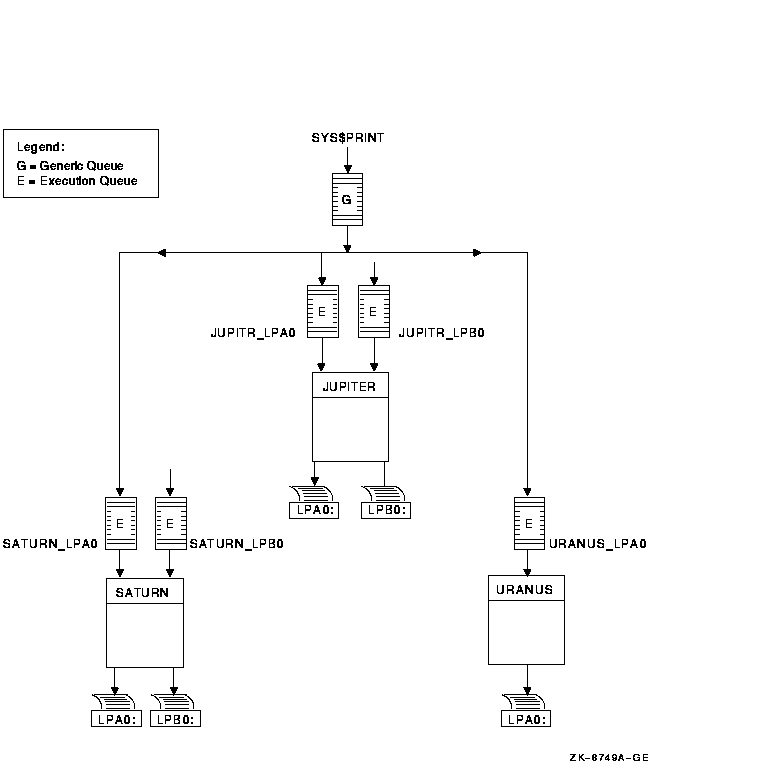
Figure 14-8 shows a typical OpenVMS Cluster output queue configuration. For information about OpenVMS Cluster queue configurations, refer to OpenVMS Cluster Systems.
Figure 14-8 Output Queue Configuration in an OpenVMS Cluster
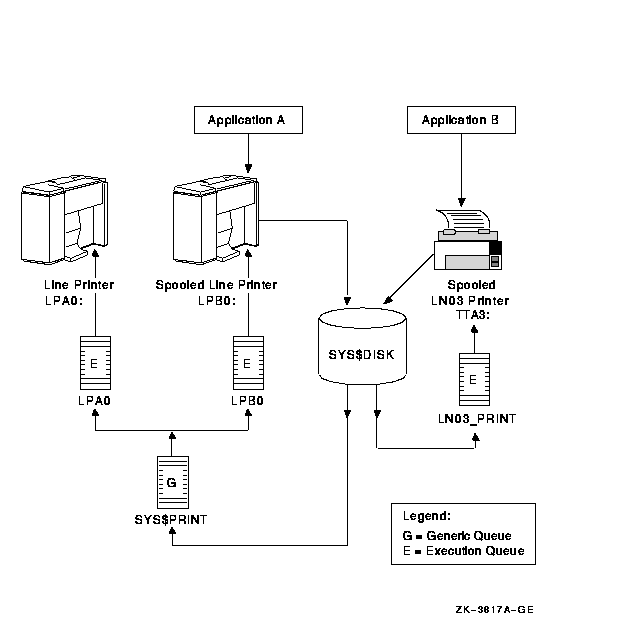
If your system runs application programs that write output directly to a printer rather than submit it to an output queue, or if you will be using LAT queues, spool your printers. Spooling your printers causes application programs to write output to an intermediate storage device so that the printer remains available to other users while the program is running.
Figure 14-9 shows an output configuration with spooled printers.
Figure 14-9 Queue Configuration with Spooled Devices
For more information about spooling printers, see Section 8.8.2.1.
14.2.2.8 Distributing Printing
The OpenVMS batch and print queuing system enables users to print files on output devices attached to the local system or OpenVMS Cluster system.
The Distributed Queuing Service (DQS) layered product extends the printing capabilities of the OpenVMS queuing system to a distributed environment. DQS enables users to print files on output devices attached to remote nodes in your network.
For more information, refer to the DQS documentation or your Compaq
support representative.
14.3 Planning Your Queue Setup
You must create queues for users to submit jobs; you must start the queues so that jobs can begin processing. To set up and start queues, follow these steps:
| Step | Task | For More Information |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Make sure you have started the queue manager and created the queue database. | Section 13.5 |
| 2 | If your configuration includes output queues, set up output devices and create a command procedure to set up the devices on reboot. | Section 14.3.1 |
| 3 | If you plan to use any queue options, such as forms, characteristics, and banner pages, determine the qualifiers needed to specify those options. In addition, define any forms and characteristics you will use before you create queues. (Because of the length of the instructions for this step, the corresponding section in the manual follows the section for step 5.) | Section 14.6 |
| 4 | Create and start queues. | Section 14.4 |
| 5 | Create a command procedure to perform the necessary setup tasks each time your system reboots. | Section 14.5 |
Before creating output queues, you must set up the devices to which the queues will direct output.
$ SET PRINTER/TAB/PAGE=66/WIDTH=132/LOWER/FF/NOCR - _$ /FALLBACK/NOWRAP/NOTAB LPA0:(1) $ SET TERMINAL/SPEED=9600/PAGE=100/WIDTH=200/DEVICE=LN03/NOBROADCAST - _$ /NOECHO/HARDCOPY/NOTYPE_AHEAD/NOFORM/NOWRAP/PASTHRU/PERMANENT LTA3331:(2) $ SET DEVICE/SPOOLED=(LPA0,SYS$SYSDEVICE) LPA0:(3) $ SET DEVICE/SPOOLED=(LN03_1,SYS$SYSDEVICE) LTA3331:(4) |
This example performs the following actions:
Create queues in the following order:
For detailed instructions on creating and starting queues, see the following sections:
| Task | For More Information |
|---|---|
| Autostart execution queues | Section 14.4.1 |
| Nonautostart execution queues | Section 14.4.2 |
| Generic queues | Section 14.4.3 |
To create and start an autostart execution queue, complete these tasks:
$ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/START/DEFAULT=(NOBURST,FLAG=ALL,TRAILER=ONE) - _$ /AUTOSTART_ON=(LILITH::LPA0:,SMITTN::LPA0:) LPA0(1) $ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/START/DEVICE=TERMINAL/ - _$ /AUTOSTART_ON=(LILITH::LTA3331:,SMITTN::LTA555:) - _$ /RECORD_BLOCKING/BLOCK_LIMIT=600/CHARACTERISTICS=(EAST)- _$ /SEPARATE=(NOBURST,NOTRAILER,NOFLAG,RESET=ANSI$RESET) - _$ /DEFAULT=(NOFEED,NOBURST,FLAG=ONE,NOTRAILER,FORM=MEMO) - _$ /LIBRARY=LN03LIBRARY /PROCESSOR=LATSYM LN03_1(2) $ ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES(3) $ ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES/ON_NODE=SMITTN(4) |
The commands in this example perform the following tasks:
Detailed explanations of each task follow.
14.4.1.1 Creating an Autostart Queue
To create an autostart execution queue, use the /AUTOSTART_ON qualifier with the INITIALIZE/QUEUE command, as shown in the following table:
The system does not check the node name you specify as node:: to determine if it is an existing node name, so be sure to specify the node name correctly. |
How to Specify a Failover List
As the table indicates, to specify a failover list:
You must activate an autostart queue in one of the following ways:
|
INITIALIZE/QUEUE/START/AUTOSTART_ON[/qualifiers,...] queue-name |
|
START/QUEUE[/qualifiers,...] queue-name |
How to Start a Deactivated Queue
To start an autostart queue that has been deactivated by STOP/QUEUE/NEXT or STOP/QUEUE/RESET, enter START/QUEUE. The queue is then automatically started by the queue manager either:
You must enable autostart on a node to start autostart queues. You can do this either before or after you create an autostart queue. Perform the following steps to enable autostart:
$ ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES |
The ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES command starts only valid, active autostart queues capable of running on a node. If an autostart queue does not start when you enter this command, the queue might not be active for autostart. You must activate autostart queues, as explained in Section 14.4.1.2. |
How to Start Stopped Autostart Queues
You can start all stopped active autostart queues on a node by enabling autostart for queues with ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES. Including a separate START/QUEUE command to start an active autostart queue is not necessary.
When a node reboots, autostart is disabled until you enter ENABLE
AUTOSTART/QUEUES.
14.4.1.4 Adding Commands to Your Startup Procedure
Compaq recommends that you add ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES to your startup procedure on all of your nodes. Add this command following the commands that configure printer devices and mount important disks. Adding the command eliminates the necessity of adding it later, if you need to add autostart queues or add nodes to autostart queue failover lists.
The following example illustrates some sample commands that you might add to a node's SYSTARTUP_VMS.COM procedure:
$! Start the nonautostart batch queue $ START/QUEUE SYS$BATCH $! Start all autostart queues $ ENABLE AUTOSTART/QUEUES |
For more examples, see the SYS$MANAGER:SYSTARTUP_VMS.COM template on
your system disk.
14.4.2 Creating and Starting Nonautostart Execution Queues
This section describes how to create and start a nonautostart queue.
The following example creates a batch queue named SYS$BATCH and starts the queue on LILITH:
$ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/START/BATCH/ON=LILITH::SYS$BATCH |
To create a nonautostart execution queue, use the /ON qualifier with the INITIALIZE/QUEUE command, as shown in the following table:
| Type of Queue | Command |
|---|---|
| Output queues |
INITIALIZE/QUEUE/ON=node::device: queue-name
For node::, specify the node on which the queue is to execute. For device:, specify the device to which the queue's output is sent. |
| Batch queues |
INITIALIZE/QUEUE/BATCH/ON=node:: queue-name
The /BATCH qualifier is required to create a batch queue. For node::, specify the node on which the queue is to execute. |
You must start a nonautostart queue in one of the following ways:
|
INITIALIZE/QUEUE/START/ON[/qualifiers,...] queue-name |
|
START/QUEUE[/qualifiers,...] queue-name |
For each nonautostart queue, you must include a START/QUEUE command
naming the queue in your startup command procedure.
This section describes how to create and start a generic queue.
14.4.3.1 Creating a Generic Queue
To create a generic queue, use the /GENERIC qualifier with the INITIALIZE/QUEUE command, as shown in the following table:
| Type of Queue | Command |
|---|---|
| Output queue |
INITIALIZE/QUEUE/GENERIC[=(queue-name[,...])] queue-name
The /GENERIC qualifier specifies that the queue is a generic queue. For the first queue-name, specify the execution queue to which the generic queue sends jobs. For the second queue-name, specify the generic queue to which output is sent. |
| Batch queues |
INITIALIZE/QUEUE/BATCH/GENERIC[=(queue-name[,...]) queue-name
The /BATCH qualifier is required to create a batch queue. For queue-name, specify the execution queue to which the generic queue sends jobs. The execution queue must be a batch queue. |
You can also set up a generic queue without explicitly naming the execution queues to which it may send jobs. Instead, use the /ENABLE_GENERIC qualifier with INITIALIZE/QUEUE, START/QUEUE, or SET QUEUE for the execution. This method is not normally recommended. However, if your queue configuration is simple, you can use this method.
The following example creates a generic queue (LN03_PRINT), which lists execution queues to which LN03_PRINT sends jobs:
$ INITIALIZE/QUEUE/GENERIC=(LN03_1,LN03_2,LN03_3) LN03_PRINT |
You must start a generic queue in one of the following ways:
|
INITIALIZE/QUEUE/START/GENERIC(=queue-name[,...])[/qualifiers, ...] queue-name |
|
START/QUEUE[/qualifiers,...] queue-name |
Information about forms, characteristics, and queues is stored in the queue database. For this reason, creating forms, queues, and characteristics each time the node or OpenVMS Cluster system reboots is unnecessary. However, you must start nonautostart execution queues and enable autostart each time a node reboots. To do so, create a command procedure.
If your configuration is simple, you can add the commands to the site-specific startup command procedure SYSTARTUP_VMS.COM. If your configuration requires a large number of commands, create a separate command procedure and execute it from SYSTARTUP_VMS.COM.
Generic queues are not automatically stopped when a node shuts down. Therefore, including commands to start generic queues in your startup command procedure is unnecessary.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/hp_bn_comments.gif)
|
| privacy and legal statement | ||
| 6017PRO_059.HTML | ||