![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/openvms_doc_banner_top.gif)
|
![[Site home]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home_off.gif)
![[Send comments]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments_off.gif)
![[Help with this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help_off.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs_off.gif)
![[OpenVMS site]](../../images/buttons/bn_openvms_off.gif)
![[Compaq site]](../../images/buttons/bn_compaq_off.gif)
|
| Updated: 11 December 1998 |
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/openvms_doc_banner_top.gif)
|
![[Site home]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home_off.gif)
![[Send comments]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments_off.gif)
![[Help with this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help_off.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs_off.gif)
![[OpenVMS site]](../../images/buttons/bn_openvms_off.gif)
![[Compaq site]](../../images/buttons/bn_compaq_off.gif)
|
| Updated: 11 December 1998 |
OpenVMS I/O User's Reference Manual
| Previous | Contents | Index |
On VAX and Alpha systems, an application program assigns a channel to
the generic SCSI class driver using the standard call to the $ASSIGN
system service, as described in the OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual. The application
program specifies a device name and a word to receive the channel
number.
8.8 Issuing a $QIO Request to the Generic Class Driver
The format of the Queue I/O Request ($QIO) system service that initiates a request to the SCSI generic class driver is as follows. This explanation concentrates on the special elements of a $QIO request to the SCSI generic class driver. For a detailed description of the $QIO system service, see the OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual.
$QIO [efn] ,chan ,func ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm]
,p1 ,p2 [,p3] [,p4] [,p5] [,p6]
|
SYS$QIO ([efn] ,chan ,func ,iosb ,[astadr] ,[astprm]
,p1 ,p2 [,p3] [,p4] [,p5] [,p6])
|
chan
I/O channel assigned to the device to which the request is directed. The chan argument is a word value containing the number of the channel, as returned by the Assign I/O Channel ($ASSIGN) system service.func
Longword value containing the IO$_DIAGNOSE function code. Only the IO$_DIAGNOSE function code is implemented in the generic SCSI class driver.iosb
I/O status block. The iosb argument is required in a request to the generic SCSI class driver; it has the following format:
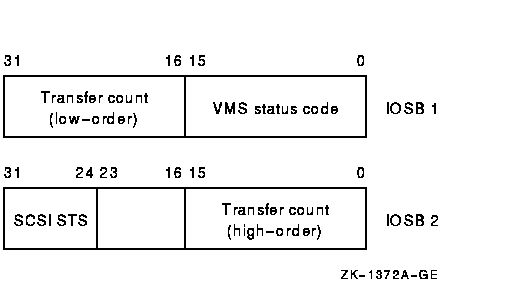
The status code provides the final status indicating the success or failure of the SCSI command. The SCSI status byte contains the status value returned from the target device, as defined in the ANSI SCSI specification. The transfer count field specifies the actual number of bytes transferred during the SCSI bus DATA IN or DATA OUT phase.

opcode
Currently, the only supported opcode is 1, indicating a pass-through function. Other opcode values are reserved for future expansion.flags
Bit map having the following format:
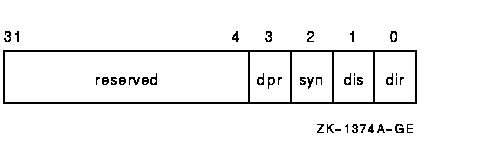
Bits in the flags bit map are defined as follows:
| Field | Definition |
|---|---|
| dir |
Direction of transfer.
If this bit is set, the target is expected at some time to enter the DATA IN phase to send data to the host. To facilitate this, the port driver maps the specified data buffer for write access. If this bit is clear, the target is expected at some time to enter the DATA OUT phase to receive data from the host. To facilitate this, the port driver maps the specified data buffer for read access. The generic SCSI class driver ignores the dir flag if either the SCSI data address or SCSI data length field of the generic SCSI descriptor is zero. |
| dis |
Enable disconnection.
If this bit is set, the target device is allowed to disconnect during the execution of the command. If this bit is clear, the target cannot disconnect during the execution of the command. Note that targets that hold on to the bus for long periods of time without disconnecting can adversely affect system performance. See Section 8.5.2 for additional information. |
| syn |
Enable synchronous mode.
If this bit is set, the port driver uses synchronous mode for data transfers, if both the host and target allow this mode of operation. If this bit is clear, or synchronous mode is not supported by either the host or target, the port driver uses asynchronous mode for data transfers. See Section 8.5.1 for additional information. |
| dpr |
Disable port retry.
If this bit is clear, the port driver retries, up to three times, any command that fails with a timeout, bus parity, or invalid phase transition error. If this bit is set, the port driver does not retry commands for which it detects failure. See Section 8.5.3 for additional information. |
If the dir bit is set in the flags field, data is written into this buffer during the execution of the command. Otherwise, data is read from this buffer and sent to the target device.
If the SCSI command requires no data to be transferred, then the SCSI data address field should be clear.
If the SCSI command requires no data to be transferred, then this field should be clear.
For example, suppose an application program is using the generic class driver to read the first 2 bytes of a disk block. The length field in the SCSI READ command contains 1 (indicating one logical block, or 512 bytes), while the SCSI data length field contains a 2. The SCSI pad length field must contain the difference, 510 bytes.
For most transfers, this field should contain 0. Failure to initialize the SCSI pad length field properly causes port driver timeouts and SCSI bus resets.
See Section 8.5.4 for additional information.
See Section 8.5.4 for additional information.
8.9 Generic SCSI Class Driver Device Information
A call to the Get Device/Volume Information ($GETDVI) system service returns the following information for any device serviced by the generic SCSI class driver. (See the description of the $GETDVI system service in the OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual.)
$GETDVI returns the following device characteristics when you specify the item code DVI$_DEVCHAR:
| DEV$M_AVL | Available device |
| DEV$M_IDV | Input device |
| DEV$M_ODV | Output device |
| DEV$M_SHR | Shareable device |
| DEV$M_RND | Random-access device |
DVI$DEVCLASS returns the device class, which is DC$_MISC; DVI$DEVTYPE
returns the device type, which is DT$_GENERIC_SCSI.
8.10 Call a Generic SCSI Class Driver
Example 8-1 is an application that uses the generic SCSI class driver to send a SCSI INQUIRY command to a device.
| Example 8-1 Generic SCSI Class Driver Call Example |
|---|
/*
GKTEST.C
This program uses the SCSI generic class driver to send an inquiry command
to a device on the SCSI bus.
*/
#include ctype
/* Define the descriptor used to pass the SCSI information to GKDRIVER */
#define OPCODE 0
#define FLAGS 1
#define COMMAND_ADDRESS 2
#define COMMAND_LENGTH 3
#define DATA_ADDRESS 4
#define DATA_LENGTH 5
#define PAD_LENGTH 6
#define PHASE_TIMEOUT 7
#define DISCONNECT_TIMEOUT 8
#define FLAGS_READ 1
#define FLAGS_DISCONNECT 2
#define GK_EFN 1
#define SCSI_STATUS_MASK 0X3E
#define INQUIRY_OPCODE 0x12
#define INQUIRY_DATA_LENGTH 0x30
globalvalue
IO$_DIAGNOSE;
short
gk_chan,
transfer_length;
int
i,
status,
gk_device_desc[2],
gk_iosb[2],
gk_desc[15];
char
scsi_status,
inquiry_command[6] = {INQUIRY_OPCODE, 0, 0, 0, INQUIRY_DATA_LENGTH, 0},
inquiry_data[INQUIRY_DATA_LENGTH],
gk_device[] = {"GKA0"};
main ()
{
/* Assign a channel to GKA0 */
gk_device_desc[0] = 4;
gk_device_desc[1] = &gk_device[0];
status = sys$assign (&gk_device_desc[0], &gk_chan, 0, 0);
if (!(status & 1)) sys$exit (status);
/* Set up the descriptor with the SCSI information to be sent to the target */
gk_desc[OPCODE] = 1;
gk_desc[FLAGS] = FLAGS_READ + FLAGS_DISCONNECT;
gk_desc[COMMAND_ADDRESS] = &inquiry_command[0];
gk_desc[COMMAND_LENGTH] = 6;
gk_desc[DATA_ADDRESS] = &inquiry_data[0];
gk_desc[DATA_LENGTH] = INQUIRY_DATA_LENGTH;
gk_desc[PAD_LENGTH] = 0;
gk_desc[PHASE_TIMEOUT] = 0;
gk_desc[DISCONNECT_TIMEOUT] = 0;
for (i=9; i<15; i++) gk_desc[i] = 0; /* Clear reserved fields */
/* Issue the QIO to send the inquiry command and receive the inquiry data */
status = sys$qiow (GK_EFN, gk_chan, IO$_DIAGNOSE, gk_iosb, 0, 0,
&gk_desc[0], 15*4, 0, 0, 0, 0);
/* Check the various returned status values */
if (!(status & 1)) sys$exit (status);
if (!(gk_iosb[0] & 1)) sys$exit (gk_iosb[0] & 0xffff);
scsi_status = (gk_iosb[1] >> 24) & SCSI_STATUS_MASK;
if (scsi_status) {
printf ("Bad SCSI status returned: %02.2x\n", scsi_status);
sys$exit (1);
}
/* The command succeeded. Display the SCSI data returned from the target */
transfer_length = gk_iosb[0] >> 16;
printf ("SCSI inquiry data returned: ");
for (i=0; i<transfer_length; i++) {
if (isprint (inquiry_data[i]))
printf ("%c", inquiry_data[i]);
else
printf (".");
}
printf ("\n");
}
|
This chapter has been updated for OpenVMS Version 7.2.
This chapter describes the QIO interface of local area network (LAN) drivers that control the LAN devices.
In addition to the QIO interface, the OpenVMS operating system supports
another interface into LAN drivers. The VMS Communications Interface
(VCI) provides a privileged interface that is optimized for network
transfers.
9.1 Local Area Network (LAN) Terminology
The following is a list of terms relevant to local area networks:
Section 9.2.1 and Section 9.2.2 show the communication devices
supported on the OpenVMS operating system.
9.2.1 OpenVMS VAX Lan Devices
On VAX systems, Table 9-1 lists the supported devices.
| Medium | Bus | Device | Device Name | DECnet Name | Device Type | Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSMA/CD | XMI | DEMNA | EXc0 | MNA | DT$_EX_DEMNA | V5.3 |
| CSMA/CD | Local | SGEC | EZc0 | ISA | DT$_EZ_SGEC | V5.3 |
| CSMA/CD | Local | LANCE | ESc0 | SVA | DT$_ES_LANCE | V4.4 |
| CSMA/CD | TurboChannel | PMAD | ECc0 | MXE | DT$_EC_PMAD | V5.5-2HW |
| CSMA/CD | TurboChannel | DELTA | ECc0 | MXE | DT$_EC_PMAD | V5.5-2HW |
| CSMA/CD | QBUS | DESQA | ESc0 | SVA | DT$_ES_LANCE | V5.0 |
| CSMA/CD | QBUS | DELQA | XQc0 | QNA | DT$_XQ_DELOA | V5.0 |
| CSMA/CD | QBUS | DEQTA | XQc0 | QNA | DT$_XQ_DEQTA | V5.3 |
| CSMA/CD | QBUS | DEQNA | XQc0 | QNA | DT$_DEQNA | V4.0 |
| CSMA/CD | QBUS | KFE52 | EFc0 | KFE | DT$_FT_NI | V5.4 |
| CSMA/CD | UNIBUS | DEUNA | XEc0 | UNA | DT$_DEUNA | V4.0 |
| CSMA/CD | UNIBUS | DELUA | XEc0 | UNA | DT$_DELUA | V4.0 |
| CSMA/CD | BI | DEBNA | ETc0 | BNA | DT$_ET_DEBNA | V4.4 |
| CSMA/CD | BI | DEBNK | ETc0 | BNA | DT$_ET_DEBNA | V4.4 |
| CSMA/CD | BI | DEBNT | ETc0 | BNA | DT$_ET_DEBNA | V4.4 |
| CSMA/CD | BI | DEBNI | ETc0 | BNA | DT$_ET_DEBNI | V5.2 |
| FDDI | XMI | DEMFA | FXc0 | MFA | DT$_FX_DEMFA | V5.4-3 |
| FDDI | TurboChannel | DEFZA | FCc0 | FZA | DT$_FC_DEFZA | V5.5-2HW |
| FDDI | TurboChannel | DEFTA | FCc0 | FZA | DT$_FC_DEFTA | V6.0 |
| FDDI | QBUS | DEFQA | FQc0 | FQA | DT$_FQ_DEFQA | V6.1 |
The DEQTA device is also known as the DELQA-YM. Also note that the device name is the name of the template device which is used by applications to identify the LAN device. The "c" in the device name indicates the controller letter, for example, A, B, and so on. |
On Alpha systems, Table 9-2 lists the supported devices.
| Medium | Bus | Device | Device Name | DECnet Name | Device Type | Version |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSMA/CD | XMI | DEMNA | EXc0 | MNA | DT$_EX_DEMNA | V1.0 |
| CSMA/CD | CBUS | TGEC | EZc0 | ISA | DT$_EZ_TGEC | V1.0 |
| CSMA/CD | TurboChannel | COREIO | ESc0 | SVA | DT$_ES_LANCE | V1.0 |
| CSMA/CD | TurboChannel | PMAD | ECc0 | MXE | DT$_EC_PMAD | V1.0 |
| CSMA/CD | TurboChannel | DELTA | ECc0 | MXE | DT$_EY_NITC2 | V6.1 |
| CSMA/CD | EISA | DE422 | ERc0 | ERA | DT$_ER_DE422 | V1.5 |
| CSMA/CD | EISA | DE425 | ERc0 | ETA | DT$_ER_TULILP | V6.1 |
| CSMA/CD | ISA | DE200 | ERc0 | ERA | DT$_ER_LANCE | V6.1 |
| CSMA/CD | ISA | DE201 | ERc0 | ERA | DT$_ER_LANCE | V6.1 |
| CSMA/CD | ISA | DE202 | ERc0 | ERA | DT$_ER_LANCE | V6.1 |
| CSMA/CD | ISA | DE203 | ERc0 | ERA | DT$_ER_LEMAC | V6.2 |
| CSMA/CD | ISA | DE204 | ERc0 | ERA | DT$_ER_LEMAC | V6.2 |
| CSMA/CD | ISA | DE205 | ERc0 | ERA | DT$_ER_LEMAC | V6.2 |
| CSMA/CD | PCI | Tulip | EWc0 | EWA | DT$_EW_TULIP | V6.1 |
| CSMA/CD | PCI | DE434 | EWc0 | EWA | DT$_EW_DE435 | V6.1 |
| CSMA/CD | PCI | DE435 | EWc0 | EWA | DT$_EW_DE435 | V6.1 |
| CSMA/CD | PCI | DE436 | EWc0 | EWA | DT$_EW_DE435 | V6.1 |
| CSMA/CD | PCI | DE450 | EWc0 | EWA | DT$_EW_DE450 | V6.2 |
| CSMA/CD | PCI | DE500-XA | EWc0 | EWA | DT$_EW_DE500 | V6.2 |
| CSMA/CD | PCI | DE500-AA | EWC0 | EWA | DT$_EW_DE500 | V6.2 |
| CSMA/CD | PCI | DE500-BA | EWc0 | EWA | DT$_EW_DE500 | V6.2 |
| CSMA/CD | PCI | DE504-BA | EWc0 | EWA | DT$_EW_DE504 | V7.1-1H1 |
| CSMA/CD | PCI | DE500-FA | EWc0 | EWA | DT$_EW_DE500 | V7.1 |
| CSMA/CD | PCMCIA | 3COM 3C589B | EOc0 | CEC | DT$_EO_3C589 | V6.2-1H2 |
| CSMA/CD | PCI | DEGPA-SA | EWc0 | EWA | DT$_EW_DEGPA | V7.1-2 |
| FDDI | XMI | DEMFA | FXc0 | MFA | DT$_FX_DEMFA | V1.0 |
| FDDI | FutureBus+ | DEFAA | FAc0 | FAA | DT$_FA_DEFAA | V1.5 |
| FDDI | TurboChannel | DEFZA | FCc0 | FZA | DT$_FC_DEFZA | V1.0 |
| FDDI | TurboChannel | DEFTA | FCc0 | FZA | DT$_FC_DEFTA | V1.5 |
| FDDI | EISA | DEFEA | FRc0 | FEA | DT$_FR_DEFEA | V1.5-1H1 |
| FDDI | PCI | DEFPA | FWc0 | FPA | DT$_FW_DEFPA | V6.2 |
| TokenRing | TurboChannel | DETRA | ICc0 | TRA | DT$_IC_DETRA | V6.1 |
| TokenRing | EISA | DW300 | IRc0 | TRE | DT$_IR_DW300 | V6.1 |
| TokenRing | ISA | DW110 | IRc0 | TRE | DT$_IR_DW300 | V6.2 |
| TokenRing | PCI | PBXNP-AA | IWc0 | TRE | DT$_IW_TI380PCI | V6.2-1H1 |
| TokenRing | PCI | PBXNP-DA | IWc0 | TRE | DT$_IW_RACORE | V7.1-1H1 |
| ATM | TurboChannel | DGLTA |
HCc0
/ELc0 |
ELA |
DT$_HC_OTTO | V6.2 |
| ATM | PCI | DGLPB |
HWc0
/ELc0 |
ELA |
DT$_HW_OTTO | V7.1-1H1 |
| ATM | PCI | DGLPA |
HWc0
/ELc0 |
ELA |
DT$_HW_METEOR | V7.1-2 |
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |
![[Site home]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home_off.gif)
![[Send comments]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments_off.gif)
![[Help with this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help_off.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs_off.gif)
![[OpenVMS site]](../../images/buttons/bn_openvms_off.gif)
![[Compaq site]](../../images/buttons/bn_compaq_off.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/openvms_doc_banner_bottom.gif) |
|
Copyright © Compaq Computer Corporation 1998. All rights reserved. Legal |
6136PRO_028.HTML
|