![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/openvms_doc_banner_top.gif)
|
![[Site home]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home_off.gif)
![[Send comments]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments_off.gif)
![[Help with this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help_off.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs_off.gif)
![[OpenVMS site]](../../images/buttons/bn_openvms_off.gif)
![[Compaq site]](../../images/buttons/bn_compaq_off.gif)
|
| Updated: 11 December 1998 |
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/openvms_doc_banner_top.gif)
|
![[Site home]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home_off.gif)
![[Send comments]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments_off.gif)
![[Help with this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help_off.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs_off.gif)
![[OpenVMS site]](../../images/buttons/bn_openvms_off.gif)
![[Compaq site]](../../images/buttons/bn_compaq_off.gif)
|
| Updated: 11 December 1998 |
Order Number: AA--QSBGB--TE
Alpha privileged-code applications link against the system base image (SYS$BASE_IMAGE.EXE) on OpenVMS Alpha. This guide explains the changes that might impact Alpha privileged-code applications as a result of the OpenVMS Alpha 64-bit virtual addressing and kernel threads support provided in OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0.
Privileged-code applications from versions prior to OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 might require the source-code changes described in this guide.
Revision/Update Information: This manual supersedes the OpenVMS Alpha Guide to Upgrading Privileged-Code Applications, Version 7.0
Software Version: OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1
Digital Equipment Corporation
Maynard,
Massachusetts
Digital Equipment Corporation makes no representations that the use of its products in the manner described in this publication will not infringe on existing or future patent rights, nor do the descriptions contained in this publication imply the granting of licenses to make, use, or sell equipment or software in accordance with the description.
Possession, use, or copying of the software described in this publication is authorized only pursuant to a valid written license from Digital or an authorized sublicensor.
Digital conducts its business in a manner that conserves the environment and protects the safety and health of its employees, customers, and the community.
© Digital Equipment Corporation 1996. All rights reserved.
The following are trademarks of Digital Equipment Corporation: Bookreader, DECdirect, DECwindows, Digital, OpenVMS, OpenVMS Cluster, VAX, VAX DOCUMENT, VAXcluster, VMS, and the DIGITAL logo.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective holders.
ZK6466
The OpenVMS documentation set is available on CD-ROM.
| Contents | Index |
Alpha privileged-code applications link against the system base image (SYS$BASE_IMAGE.EXE) on OpenVMS Alpha. This guide explains the changes that might impact Alpha privileged-code applications as a result of the OpenVMS Alpha 64-bit virtual addressing and kernel threads support provided in OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0.
This guide is intended to help developers using privileged-code interfaces understand how the changes in OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 might affect their applications and device drivers.
Nonprivileged code applications should not require any source code changes and should run without modification on OpenVMS Alpha Versions 7.0 and 7.1.
The information in this document applies only to privileged-code applications on OpenVMS Alpha systems; applications on OpenVMS VAX systems are not affected.
Privileged-code applications and device drivers that were recompiled and relinked to run on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 do not require source-code changes and do not have to be recompiled and relinked to run on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1. However, privileged-code applications from releases prior to OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 that were not recompiled and relinked for OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0, might need to be recompiled and relinked to run on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1 and might require source-code changes as described in this guide. For more information about recompiling and relinking privileged-code applications and device drivers for OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.1, see OpenVMS Version 7.1 Release Notes. |
This guide is intended for system programmers who use privileged-mode interfaces in their applications.
The guide is divided into three parts:
For more information about how to use this guide, see Chapter 1.
For additional information on the Open Systems Software Group (OSSG) products and services, access the Digital OpenVMS World Wide Web site. Use the following URL:
http://www.openvms.digital.com |
Digital welcomes your comments on this manual.
Print or edit the online form SYS$HELP:OPENVMSDOC_COMMENTS.TXT and send us your comments by:
| Internet | openvmsdoc@zko.mts.dec.com |
| Fax | 603 881-0120, Attention: OSSG Documentation, ZKO3-4/U08 |
|
OSSG Documentation Group, ZKO3-4/U08
110 Spit Brook Rd. Nashua, NH 03062-2698 |
Use the following table to order additional documentation or information. If you need help deciding which documentation best meets your needs, call 800-DIGITAL (800-344-4825).
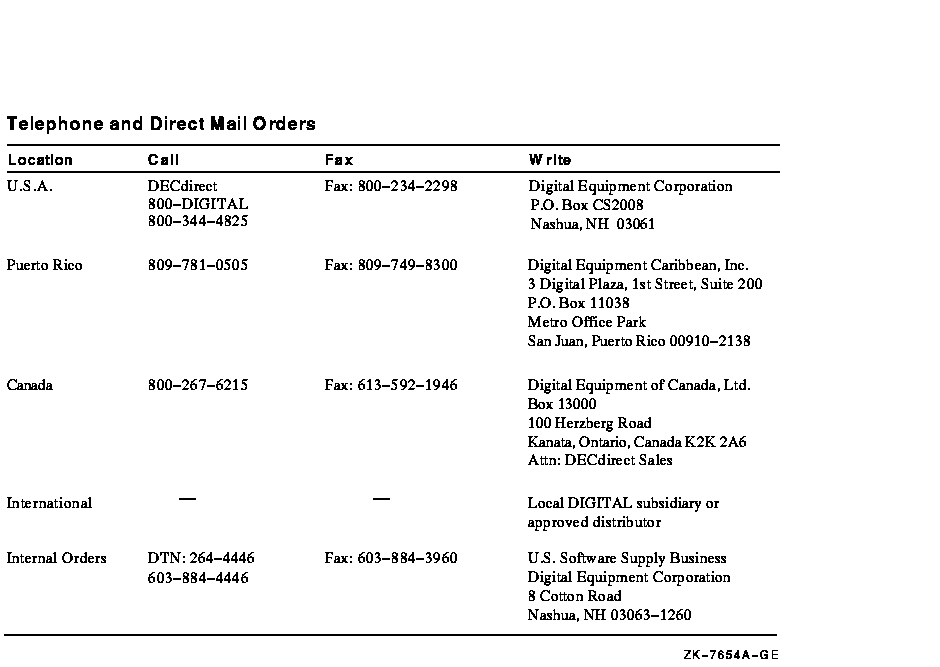
The name of the OpenVMS AXP operating system has been changed to the OpenVMS Alpha operating system. Any references to OpenVMS AXP or AXP are synonymous with OpenVMS Alpha or Alpha.
The following conventions are also used in this manual:
| Ctrl/ x | A sequence such as Ctrl/ x indicates that you must hold down the key labeled Ctrl while you press another key or a pointing device button. |
|
PF1
x or
GOLD x |
A sequence such as PF1
x or GOLD
x indicates that you must first press and release the key
labeled PF1 or GOLD and then press and release another key or a
pointing device button.
GOLD key sequences can also have a slash (/), dash (--), or underscore (_) as a delimiter in EVE commands. |
| [Return] | In examples, a key name enclosed in a box indicates that you press a key on the keyboard. (In text, a key name is not enclosed in a box.) |
| ... |
Horizontal ellipsis points in examples indicate one of the following
possibilities:
|
|
.
. . |
Vertical ellipsis points indicate the omission of items from a code example or command format; the items are omitted because they are not important to the topic being discussed. |
| ( ) | In command format descriptions, parentheses indicate that, if you choose more than one option, you must enclose the choices in parentheses. |
| [ ] | In command format descriptions, brackets indicate optional elements. You can choose one, none, or all of the options. (Brackets are not optional, however, in the syntax of a directory name in an OpenVMS file specification or in the syntax of a substring specification in an assignment statement.) |
| { } | In command format descriptions, braces indicate a required choice of options; you must choose one of the options listed. |
| text style |
This text style represents the introduction of a new term or the name
of an argument, an attribute, or a reason.
This style is also used to show user input in Bookreader versions of the manual. |
| italic text | Italic text indicates important information, complete titles of manuals, or variables. Variables include information that varies in system output (Internal error number), in command lines (/PRODUCER= name), and in command parameters in text (where device-name contains up to five alphanumeric characters). |
| UPPERCASE TEXT | Uppercase text indicates a command, the name of a routine, the name of a file, or the abbreviation for a system privilege. |
| Monospace type |
Monospace type indicates code examples and interactive screen displays.
In the C programming language, monospace type in text identifies the following elements: keywords, the names of independently compiled external functions and files, syntax summaries, and references to variables or identifiers introduced in an example. |
| - | A hyphen at the end of a command format description, command line, or code line indicates that the command or statement continues on the following line. |
| numbers | All numbers in text are assumed to be decimal unless otherwise noted. Nondecimal radixes---binary, octal, or hexadecimal---are explicitly indicated. |
OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 includes significant changes to OpenVMS Alpha privileged interfaces and data structures, mostly as a result of support for 64-bit virtual addresses and kernel threads.
For 64-bit virtual addresses, these changes are part of the infrastructure work needed to enable processes to grow their virtual address space beyond the existing 1 GB limit of P0 space and the 1 GB limit of P1 space to include P2 space, making a total of 8TB. Likewise, S2 is the extension of system space.
Kernel threads support causes significant changes to the process structure within OpenVMS (most notably to the process control block (PCB)). Although kernel threads support does not explicitly change any application programming interfaces (APIs) within OpenVMS, it does change the use of the PCB in such a way that some existing privileged code may be impacted.
As a result of these changes, some privileged-code applications might need to make source-code changes to run on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0.
This chapter briefly describes OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 64-bit virtual
address and kernel threads support and suggests how you should use this
guide to ensure that your privileged-code application runs successfully
on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0.
1.1 Quick Description of OpenVMS Alpha 64-Bit Virtual Addressing
OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 provides support for 64-bit virtual addresses, which makes more of the 64-bit virtual address space defined by the Alpha architecture available to the OpenVMS Alpha operating system and to application programs. The 64-bit address features allow processes to map and access data beyond the previous limits of 32-bit virtual addresses. Both process-private and system virtual address space now extend to 8 TB.
In addition to the dramatic increase in virtual address space, OpenVMS Alpha 7.0 significantly increases the amount of physical memory that can be used by individual processes.
Many tools and languages supported by OpenVMS Alpha (including the Debugger, run-time library routines, and DEC C) are enhanced to support 64-bit virtual addressing. Input and output operations can be performed directly to and from the 64-bit addressable space by means of RMS services, the $QIO system service, and most of the device drivers supplied with OpenVMS Alpha systems.
Underlying this are new system services that allow an application to allocate and manage the 64-bit virtual address space that is available for process-private use.
For more information about OpenVMS Alpha 64-bit virtual address
features, see the OpenVMS Alpha Guide to 64-Bit Addressing and VLM Features.
1.2 Quick Description of OpenVMS Alpha Kernel Threads
OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 provides kernel threads features, which extend process scheduling capabilities to allow threads of a process to run concurrently on multiple CPUs in a multiprocessor system. The only interface to kernel threads is through the DECthreads package. Existing threaded code that uses either the CMA API or the POSIX threads API should run without change and gain the advantages provided by the kernel threads project.
Kernel threads allows a multithreaded process to execute code flows independently on more than one CPU at a time. This allows a threaded application to make better use of multiple CPUs in an SMP system. DECthreads uses these independent execution contexts as virtual CPUs and schedules application threads on them. OpenVMS then schedules the execution contexts (kernel threads) onto physical CPUs. By providing a callback mechanism from the OpenVMS scheduler to the DECthreads thread scheduler, scheduling latencies inherent in user-mode-only thread managers is greatly reduced. OpenVMS informs DECthreads when a thread has blocked in the kernel. Using this information, DECthreads can then opt to schedule some other ready thread.
For more information about kernel threads, refer to the Bookreader
version of the OpenVMS Programming Concepts Manual and Chapter 6 in this guide.
1.3 How to Use This Guide
Read Part I to learn about the changes that might be required for privileged-code applications to run on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0.
Refer to Part II for information about enhancing customer-written system services and device drivers with OpenVMS Version 7.0 features.
Refer to the Appendixes for more information about some of the data structures and routines mentioned throughout this guide.
The new features provided in OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 have required corresponding changes in internal system interfaces and data structures. These internal changes might require changes in some privileged software.
This chapter contains recommendations for upgrading privileged-code
applications to ensure that they run on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0. Once
your application is running on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0, you can
enhance it as described in Part II.
2.1 Recommendations for Upgrading Privileged-Code Applications
To ensure that a privileged-code application runs on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0, do the following:
This section summarizes OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 changes to the kernel that may require source changes in customer-written drivers and inner-mode software. The recommendations in bold face type indicate how each change can be handled.
The remaining sections in this chapter contain more details about these changes.
All device drivers, VCI clients, and inner-mode components must be recompiled and relinked to run on OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0. |
A few necessary source changes might not always be immediately identified by compile-time or link-time warnings. Some of these are:
This section describes OpenVMS Alpha Version 7.0 changes to the I/O
subsystem that might require source changes to device drivers.
2.2.1 Impact of IRPE Data Structure Changes
As described in Section A.9, the I/O Request Packet Extension (IRPE) structure now manages a single additional locked-down buffer instead of two. The general approach to deal with this change is to use a chain of additional IRPE structures.
Current users of the IRPE may be depending on the fact that a buffer locked for direct I/O could be fully described by the irp$l_svapte, irp$l_boff, and irp$l_bcnt values. For example, it is not uncommon for an IRPE to be used in this fashion:
This approach no longer works correctly. As described in Appendix A, the DIOBM structure that is embedded in the IRP will be needed as well. Moreover, it may not be sufficient to simply copy the DIOBM from the IRP to the IRPE. In particular, the irp$l_svapte may need to be modified if the DIOBM is moved.
The general approach to this change is to lock the buffer using the IRPE directly. This approach is shown in some detail in the following example:
irpe->irpe$b_type = DYN$C_IRPE; (1) irpe->irpe$l_driver_p0 = (int) irp; (2) status = exe_std$readlock( irp, pcb, ucb, ccb, (3) buf1, buf1_len, lock_err_rtn (4) ); if( !$VMS_STATUS_SUCCESS(status) ) return status; irpe->irpe$b_rmod = irp->irp$b_rmod; (5) status = exe_std$readlock( (IRP *)irpe, pcb, ucb, ccb, (6) buf2, buf2_len, lock_err_rtn ); if( !$VMS_STATUS_SUCCESS(status) ) return status; |
This approach is easily generalized to more buffers and IRPEs. The only thing omitted from this example is the code that allocates and links together the IRPEs. The following example shows the associated error callback routine in its entirety; it can handle an arbitrary number of IRPEs.
void lock_err_rtn (IRP *const lock_irp, (1) PCB *const pcb, UCB *const ucb, CCB *const ccb, const int errsts, IRP **real_irp_p (2) ) { IRP *irp; if( lock_irp->irp$b_type == DYN$C_IRPE ) irp = (IRP *) ((IRPE *)lock_irp)->irpe$l_driver_p0; (3) else irp = lock_irp; exe_std$lock_err_cleanup (irp); (4) *real_irp_p = irp; (5) return; } |
| Next | Contents | Index |
![[Site home]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home_off.gif)
![[Send comments]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments_off.gif)
![[Help with this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help_off.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs_off.gif)
![[OpenVMS site]](../../images/buttons/bn_openvms_off.gif)
![[Compaq site]](../../images/buttons/bn_compaq_off.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/openvms_doc_banner_bottom.gif) |
|
Copyright © Compaq Computer Corporation 1998. All rights reserved. Legal |
6466PRO.HTML
|