| Previous | Contents | Index |
This chapter describes the ACMS operator commands you can use to
install and run ACMS applications, modify active applications, and
cancel tasks. For reference information on the commands described in
this chapter, refer to Chapter 21.
9.1 Installing Applications
Before you can install an application, you must first be authorized by the Application Authorization Utility (AAU). See Chapter 4 for information on how to use the AAU to authorize users to install applications.
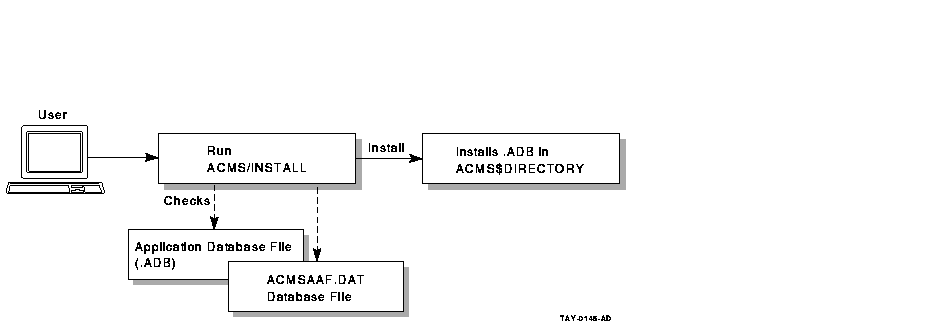
Once you are authorized by the AAU, install an application by issuing the ACMS/INSTALL command. You do not need any special OpenVMS privileges to install an application. The ACMS/INSTALL command installs applications in the directory pointed to by the logical name ACMS$DIRECTORY. All applications must be installed in ACMS$DIRECTORY before they can run on the ACMS system. When you enter the ACMS/INSTALL command, ACMS displays a message confirming that the application has been installed in ACMS$DIRECTORY. For example:
$ ACMS/INSTALL DISK1:[ACCOUNT]INVENTORY.ADB %ACMSINS-S-ADBINS, Application DISK1:[ACCOUNT] - INVENTORY.ADB has been installed in ACMS$DIRECTORY |
This command installs the application INVENTORY in ACMS$DIRECTORY.
Figure 9-1 shows the steps ACMS takes when installing an application.
Figure 9-1 Process of Installing an Application
If you attempt to install an application you are not authorized to install, ACMS displays the following messages, terminates the installation attempt, and returns you to DCL level:
%ACMSINS-E-INSFAIL, INSTALL command failed -SYSTEM-F-NOPRIV, no privilege for attempted operation $ |
Include either a file specification or the logical name of an application with the ACMS/INSTALL command. If you specify a logical name that is a search list, ACMS installs only the first available application in the search list.
When you install an application database file, the ACMS/INSTALL command checks the application authorization database file (ACMSAAF.DAT) to confirm that:
After checking the ACMSAAF.DAT file, AAU:
Once an application is installed, stop and restart ACMS to make the new version of the application available to users. Chapter 8 describes how to start and stop the ACMS system. If you are reinstalling an application, you must stop the application before you reinstall it.
After you stop and restart ACMS, you can run the application by using
the ACMS/START APPLICATION command. See Section 9.3 for information
on how to run an ACMS application.
9.2 Removing Applications
To delete an application from ACMS$DIRECTORY, specify the /REMOVE qualifier with the ACMS/INSTALL command and the file name of the application you want to remove. You must be authorized by the AAU before you can remove an application.
For example, you can delete the application installed in the example in the previous section by typing the following command. Once you enter this command, ACMS displays a message confirming that the application has been removed.
$ ACMS/INSTALL INVENTORY/REMOVE %ACMSINS-S-ADBINSREM, Application INVENTORY has been removed from ACMS$DIRECTORY $ |
When you specify the ACMS/INSTALL command with the /REMOVE qualifier to delete an application, ACMS does the following:
Specify only a file name when deleting an application from
ACMS$DIRECTORY; do not specify device, directory, or file type. When
you have a number of applications with different file names to remove
from ACMS$DIRECTORY, you must remove them one at a time. You cannot
specify more than one application, use the keyword $ALL, or use the
wildcard character (*) with the /REMOVE qualifier.
9.3 Starting Applications
Once the ACMS system is up and running, you can start ACMS applications provided you have the OpenVMS OPER privilege. When you start an application, ACMS starts the application execution controller and allocates the resources the application needs. The tasks in the application are then ready for terminal users to select. Terminal users cannot select tasks that belong to an application that is not started.
The ACMS/START APPLICATION command starts one or more applications. Use the command interactively or include it in a command file. For example, the following command starts the application DEPARTMENT:
$ ACMS/START APPLICATION DEPARTMENT |
Starting an application interactively helps you control the use of
resources and the availability of required files and databases. You can
start an application whenever ACMS is active.
9.4 Stopping Applications
The ACMS/STOP APPLICATION command stops the applications you name. You must have the OpenVMS OPER privilege to stop an application. When you stop an application, ACMS stops the application execution controller and releases the resources for the application. The tasks in the application are no longer available for users to select.
You might want to stop one or more ACMS applications if you:
Unless you specify the /CANCEL qualifier, the ACMS/STOP APPLICATION command does not execute until all tasks in that application finish executing. Before using the /CANCEL qualifier, use the DCL REPLY command to ask users to finish their tasks. Then, use the ACMS/SHOW TASK command to check that users have stopped their tasks. Finally, issue the ACMS/STOP APPLICATION /CANCEL command to stop any remaining active tasks.
The following command cancels all active tasks in the INVENTORY and ACCOUNTING applications and then stops those applications.
$ ACMS/STOP APPLICATION INVENTORY, ACCOUNTING /CANCEL |
ACMS allows you to display information about applications in static or dynamic mode. Static mode displays information reflecting an application's state for an instant in time---that is, the instant in time at which the command executes. Dynamic mode displays information about an application continually as it executes. The following sections describe how to display information about your application in either mode.
To get information about software errors that occur during the
execution of ACMS application programs, use the ACMS Software Event Log
Utility Program (SWLUP) which is discussed in Chapter 13.
9.5.1 Displaying Static Information
The ACMS/SHOW APPLICATION command displays information about active applications in static mode. You can specify the name of one or several applications with the ACMS/SHOW APPLICATION command. If you do not include the name of an application, ACMS displays information about all currently active applications. Example 9-1 displays information about the application INVENTORY.
| Example 9-1 ACMS/SHOW APPLICATION Command |
|---|
$ ACMS/SHOW APPLICATION INVENTORY ACMS V4.0 CURRENT APPLICATIONS Time: 1-MAY-1994 17:19:40.84 (1)Application Name: INVENTORY (2) Object Name: ACMS01EXC001000 (3) User Name: ACMS (4) PID: 22000123 (5) Max Task Count: 655 (6) Max SP Count: 35 (7) Cur Task Count: 0 (8) Cur SP Count: 7 (9) Auditing: ON (10) SP Mon. Interval: 5) (11) (12) (13) (14) (15) (16) Server Name max SPs min SPs active free waiting SPs SPs tasks INVSRV05 5 0 0 0 0 INVSRV02 1 0 1 0 4 INVSRV06 5 1 1 0 3 INVSRV04 5 2 0 2 0 INVSRV01 5 2 1 1 0 INVSRV03 5 1 1 0 0 |
The following is a description of the numbered items in Example 9-1:
Use the /POOL, /SERVER_ATTRIBUTES, or /TASK_ATTRIBUTES qualifier with the ACMS/SHOW APPLICATION command to display, respectively, pool information, the current settings of modifiable server attributes, and the current settings of modifiable task attributes for an application. Example 9-2 displays pool information for the application TEST.
| Example 9-2 ACMS/SHOW APPLICATION/POOL TEST Command |
|---|
$ ACMS/SHOW APPLICATION/POOL TEST
ACMS V4.0 CURRENT APPLICATIONS Time: 1-MAY-1994 11:21:04.50
Application Name: TEST State: STARTED
Object Name: ACMS01EXC008000
User Name: ACMS$EXC PID: 25C01337
Max Task Count: 65535 Max SP Count: 5
Cur Task Count: 0 Cur SP Count: 2
Auditing: ON SP Mon. Interval: 5
Application Workspace and Control Pools
(1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6)
Pool Pool Free (pct.) Largest Allocation Garbage
type size bytes block failures collections
Group/User workspace pools
(7) Control pool 65536 64848 (98%) 32768 0 0
(8) Workspace pool 131072 130560 (99%) 65536 0 0
(9) TEST_GRP01
(10) Control pool 25600 25088 (98%) 16384 0 0
(11) Workspace pool 179200 178688 (99%) 65536 0 0
TEST_GRP02
Control pool 25600 25088 (98%) 16384 0 0
Workspace pool 179200 178688 (99%) 65536 0 0
DBMS_GRP
Control pool 25600 25088 (98%) 16384 0 0
Workspace pool 179200 178688 (99%) 65536 0 0
|
The following is a description of the numbered items in Example 9-2:
Use the information in the pool display to determine the correct sizes
for the ACMSGEN parameters for control and workspace pools. See
Chapter 11 for more information.
9.5.2 Displaying Dynamic Information
Dynamically display information about a single application by using the ACMS/SHOW APPLICATION/CONTINUOUS command. ACMS/SHOW APPLICATION/CONTINUOUS command allows you to:
When you specify the ACMS/SHOW APPLICATION/CONTINUOUS command, specify the file name of a started application. If you do not specify an application name, ACMS returns an error. Specify only the file name; do not include device, directory, or file type. You cannot specify more than one application name with the ACMS/SHOW APPLICATION/CONTINUOUS command. Example 9-3 displays dynamic information about the application STORAGE.
| Example 9-3 ACMS/SHOW APPLICATION/CONTINUOUS Command |
|---|
$ ACMS/SHOW APPLICATION/CONTINUOUS STORAGE
ACMS V4.0 ACMS CONTINUOUS APPLICATION MONITOR NODE::MYNODE
1-MAY-1994 07:52:04.62
(1) Name: STORAGE
(2) Process: ACMS01EXC015000
(3) User: ACMS$EXC (4) PID: 22E00563
(5) Max Tasks: 65535 (6) Max SPs: 22
(7) Cur Tasks: 15 (8) Cur SPs: 13
(9) (10) (11) (12) (13) (14)
SERVER NAME Min SP/Max SP Current Average Minimum Maximum
TESTSRV01 3/3
Active Servers 0 0 0 1
Free Servers 3 1 0 3
Waiting Tasks 0 2 0 28
TLOAD001S 3/3
Active Servers 2 1 0 3
Free Servers 1 1 0 3
Waiting Tasks 0 12 0 92
|
You can control the video display by using the control and arrow keys. Press [Ctrl/C], [Ctrl/Y], or [Ctrl/Z] to terminate the display. Press [Ctrl/W] to refresh the screen. The up and down arrow keys scroll the screen forward and backward.
The following is a description of the numbered items in Example 9-3:
ACMS refreshes the screen every 30 seconds by default. If you want the screen to refresh at a different interval, specify in seconds the interval you prefer. For example, the following command causes new information for the BOOKSALES application to display on your terminal screen every 300 seconds (5 minutes):
$ ACMS/SHOW APPLICATION/CONTINUOUS/INTERVAL=300 BOOKSALES |
Begin or end a continuous application display with the /BEGINNING_TIME and /ENDING_TIME qualifiers. Both qualifiers let you specify times in OpenVMS absolute time format, delta time format, or a combination of the two. Refer to OpenVMS DCL Dictionary for information about how to create valid time formats.
There are occasions when having hardcopy records of application information is useful. The /OUTPUT qualifier requests ACMS to copy application data to a file you name. Then either display the file at your terminal or print it. If you do not specify a file, ACMS stores information in the file ACMSSHOW.LIS in your current default directory. When you do not use the /OUTPUT qualifier, ACMS sends output to the default output device defined by the SYS$OUTPUT logical name.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |