![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif)
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
| Document revision date: 19 July 1999 | |
![[Compaq]](../../images/compaq.gif) |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/ovmsdoc_sec_head.gif)
|
|
| Previous | Contents | Index |
This section lists the function codes and function modifiers for the mailbox driver.
| Functions | Arguments | Modifiers |
|---|---|---|
|
IO$_READVBLK
IO$_READLBLK IO$_READPBLK IO$_WRITEVBLK IO$_WRITELBLK IO$_WRITEPBLK |
P1---buffer
####address P2---buffer size |
IO$M_NOW
IO$M_NORSWAIT 1 IO$M_READERCHECK 1 IO$M_WRITERCHECK 2 IO$M_STREAM 2 |
| IO$_WRITEOF | None |
IO$M_NOW
IO$M_READERCHECK IO$M_STREAM |
|
IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_READATTN
IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_WRTATTN IO$_SETMODE!IO$MB_ROOM_NOTIFY |
P1---AST address
P2---AST parameter P3---access mode |
None |
|
+IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_READERWAIT
+IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_WRITERWAIT |
None | None |
| IO$_SETMODE!IO$M_SETPROT |
P2---volume
####protection ####mask |
None |
|
+IO$_SENSEMODE!IO$M_READERCHECK
+IO$_SENSEMODE!IO$M_WRITERCHECK |
None | None |
| QIO Status Returns in R0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| SS$_ACCVIO | SS$_EXQUOTA | SS$_ILLIOFUNC | SS$INSFMEM |
| SS$MBFULL | SS$_MBTOOSML | SS$_NOPRIV | SS$_NORMAL |
| IOSB Status Returns | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| SS$_ABORT | SS$_BUFFEROVF | SS$_CANCEL | SS$_ENDOFFILE |
| SS$_NOREADER | SS$_NORMAL | SS$_NOWRITER | |
This section lists the function codes and function modifiers for the terminal driver.
| Functions | Arguments | Modifiers |
|---|---|---|
|
IO$_READVBLK
IO$_READLBLK IO$_READPROMPT |
P1---buffer address
P2---buffer size P3---timeout P4---read terminator ####block address P5---prompt string ####buffer address P6---prompt string ####buffer size 1 |
IO$M_NOECHO
IO$M_CVTLOW IO$M_NOFILTR IO$M_TIMED IO$M_PURGE IO$M_DSABLMBX IO$M_TRMNOECHO IO$M_ESCAPE |
| IO$_READVBLK |
P1---buffer address
P2---buffer size P3---access mode to ####probe itemlist P4---(zero) P5---itemlist buffer ####address P6---itemlist buffer ####size |
IO$M_EXTEND 2 |
|
IO$_WRITEVBLK
IO$_WRITELBLK IO$_WRITEPBLK |
P1---buffer address
P2---buffer size P3---(ignored) P4---carriage control ####specifier 3 |
IO$M_CANCTRLO
IO$M_ENABLMBX IO$M_NOFORMAT IO$M_REFRESH IO$M_BREAKTHRU |
|
IO$_SETMODE
IO$_SETCHAR |
P1---characteristics
####buffer address P2---characteristics ####buffer size P3---speed specifier P4---fill specifier P5---parity flags |
|
|
IO$_SETMODE
IO$_SETCHAR |
None | IO$M_HANGUP |
| IO$_SETMODE |
P1---buffer address
P2---buffer size |
IO$M_BRDCST |
|
IO$_SETMODE
IO$_SETCHAR |
P1---AST service
####routine address P2---AST parameter P3---access mode to ####deliver AST |
IO$M_CTRLCAST
IO$M_CTRLYAST |
|
IO$_SETMODE
IO$_SETCHAR |
P1---AST service
####routine address P2---character mask ####address P3---access mode to ####deliver AST |
IO$M_OUTBAND
IO$M_TT_ABORT 4 IO$M_INCLUDE 4 |
|
IO$_SETMODE
IO$_SETCHAR |
P1---address of
####control signals |
IO$M_SET_MODEM
5
IO$M_MAINT |
|
IO$_SETMODE
IO$_SETCHAR |
None |
IO$M_LOOP
5
IO$M_UNLOOP 5 IO$M_MAINT |
| IO$_TTY_PORT |
IO$M_LT_CONNECT
IO$M_LT_DISCON |
|
| IO$_TTY_PORT |
P1---itemlist
6
####address P2---queued status |
IO$M_LT_MAP_PORT |
| IO$_TTY_PORT |
P1---service name
####descriptor ####address P2---service rating |
IO$M_LT_RATING |
| IO$_TTY_PORT |
P1---itemlist
####address P2---itemlist ####length P3---entity type P4---entity string ####descriptor |
IO$M_LT_SENSEMODE |
| IO$_TTY_PORT |
P1---itemlist
####address P2---itemlist ####length P3---entity type P4---entity string ####descriptor |
IO$M_LT_SETMODE |
|
IO$_SENSEMODE
IO$_SENSECHAR |
P1---characteristics
####buffer address P2---characteristics ####buffer size |
IO$M_TYPEAHDCNT |
|
IO$_SENSEMODE
IO$_SENSECHAR |
P1---address of input
####modem signal ####block |
IO$M_RD_MODEM |
| IO$_SENSEMODE |
P1---buffer address
P2---buffer size |
IO$M_BRDCST |
| QIO Status Returns | ||
|---|---|---|
| SS$_ABORT | SS$_BADESCAPE | SS$_BADPARAM |
| SS$_CANCEL | SS$_CHANINTLK | SS$_CONTROLC |
| SS$_CONTROLO | SS$_CONTROLY | SS$_DATAOVERUN |
| SS$_INCOMPAT | SS$_NORMAL | SS$_PARITY |
| SS$_PARTESCAPE | SS$_TIMEOUT | |
This section lists the function codes and function modifiers for the local area network drivers.
| Functions | Arguments | Modifiers |
|---|---|---|
|
IO$_READLBLK
IO$_READVBLK IO$_READPBLK IO$_WRITELBLK IO$_WRITEVBLK IO$_WRITEPBLK |
P1---buffer address
P2---buffer size P4---802 format fields (optional) 3 P5---destination address (optional) 3 |
IO$M_NOW
1
IO$M_RESPONSE 2 |
|
IO$_SETMODE
IO$_SETCHAR |
P2---extended characteristics buffer (optional) 4 |
IO$M_CTRL
IO$M_STARTUP IO$M_SHUTDOWN |
|
IO$_SETMODE
IO$_SETCHAR |
P1---AST service address
P3 -- access mode to deliver AST |
IO$M_ATTNAST |
|
IO$_SENSEMODE
IO$_SENSECHAR |
P1---device characteristics buffer (optional)
P2---extended characteristics buffer (optional) |
IO$M_CTRL |
| QIO Status Returns | ||
|---|---|---|
| SS$_ABORT | SS$_ACCVIO | SS$_BADPARAM |
| SS$_BUFFEROVF | SS$_COMMHARD | SS$_CTRLERR |
| SS$_DATACHECK | SS$_DATAOVERUN | SS$_DEVACTIVE |
| SS$_DEVALLOC | SS$_DEVINACT | SS$_DEVOFFLINE |
| SS$_DEVREQERR | SS$_DISCONNECT | SS$_DUPUNIT |
| SS$_ENDOFFILE | SS$_EXQUOTA | SS$_INSFMEM |
| SS$_INSFMAPREG | SS$_IVBUFLEN | SS$_MEDOFL |
| SS$_NOPRIV | SS$_NORMAL | SS$_OPINCOMPL |
| SS$_TIMEOUT | SS$_TOOMUCHDATA |
This section lists the function codes and parameters for the $IO_SETUP system service.
| Functions | Arguments |
|---|---|
|
IO$_READVBLK
IO$_READLBLK IO$_WRITEVBLK IO$_WRITELBLK |
bufobj - user's buffer
iosobj---I/O Status Area (IOSA) astadr---Completion AST routine flags---longword mask return_fandle---fandle address |
This section lists the function codes and function modifiers for Fast Path.
| Functions | Arguments | Modifiers |
|---|---|---|
| IO$_SETPRFPATH |
P1---CPU mask
None |
IO$M_PREFERRED_CPU
IO$M_SYS_ASSIGNABLE |
This is a new appendix for OpenVMS Version 7.2.
As of OpenVMS Version 7.0, the $QIO IO$_DIAGNOSE function has been enhanced to support 64-bit addressing for the following SCSI class drivers: GKDRIVER, DKDRIVER, and MKDRIVER. This means that the virtual addresses specified within the S2DGB may now be 64-bit virtual addresses if the user application requests it.
The $QIO IO$_DIAGNOSE arguments are still as follows:
| Argument | Use |
|---|---|
| P1 | S2DGB base address |
| P2 | S2DGB length |
| P3 | Reserved, should be zero |
| P4 | Reserved, should be zero |
| P5 | Reserved, should be zero |
| P6 | Reserved, should be zero |
The SCSI Diagnose Buffer (S2DGB) defined in STARLET now allows two formats, one for 32-bit addressing and one for 64-bit addressing. The 32-bit format is identical to the one supported on OpenVMS Alpha Version 6.2. Figure B-1 shows the 32-bit S2DGB format. Figure B-2 shows the 64-bit S2DGB format.
Figure B-1 OpenVMS SCSI-2 Diagnose Buffer (S2DGB) 32-Bit Layout

Figure B-2 OpenVMS SCSI-2 Diagnose Buffer (S2DGB) 64-Bit Layout

A user application must specify which one of the two S2DGB formats is to be used by passing a format value in S2DGB$L_OPCODE. Specifically, S2DGB$L_OPCODE must be assigned a value of either OP_XCDB32 (= 1) to request 32-bit format, or OP_XCDB64 (= 2) to request 64-bit format. Once the value of OP_XCDB64 has been specified, the user application is obligated to use the 64-bit S2DGB format and, in particular, to use the 64-bit names for S2DGB fields as described below. Likewise, an opcode value of OP_XCDB32 obligates the user application to use the 32-bit names for the fields.
The correct length of the structure is defined by the constant S2DGB$K_XCDB32_LENGTH (value: 60-decimal), as well as by the constant S2DGB$K_XCDB64_LENGTH (value: 60-decimal).
The fields in the S2DGB are in the sections that follow. Whenever a field has two different names for the 32-bit and 64-bit cases, the 32-bit name is given first, and the 64-bit name is given after it in parentheses. Also, except for fields which contain addresses, all fields are unsigned longwords.
This field should contain either S2DGB$K_OP_XCDB32 or S2DGB$K_OP_XCDB64, depending on whether the user application intends to supply 32-bit virtual addresses or 64-bit virtual addresses, respectively, in the other fields of the S2DGB.
This field should contain the bit fields shown in the following table. Note that these bit definitions start at bit 0 and omit no bits. This is required for compatibility with the IO$_DIAGNOSE interface available in OpenVMS Alpha Version 6.1 and earlier.
| Bit Field | Description |
|---|---|
| S2DGB$V_READ | This bit should be 1 if the operation being performed is a read. If the operation is a write, this bit should be 0. |
| S2DGB$V_DISCPRIV | This bit should contain the DiscPriv bit value to be used in the IDENTIFY message sent with this operation. If S2DGB$V_TAGGED_REQ is 1, then this bit should be ignored. Note that this bit may be ignored by some ports. |
| S2DGB$V_SYNCHRONOUS | This bit is ignored since its value is beyond the control of the user in SCSI-2 drivers. |
| S2DGB$V_OBSOLETE1 | This bit is ignored. In previous releases, it represented the disabling of command retries, which is now beyond the control of the user in SCSI-2 drivers. |
| S2DGB$V_TAGGED_REQ |
When this bit is 1, the operation is processed as using tagged command
queuing and S2DGB$V_TAG should define the tag value to be used. When
this bit is 0, the operation is processed without benefit of tagged
command queuing. Ports that do not support tagged command queuing
always behave as if this bit is 0. Note that some ports simulate
untagged operations using appropriately tagged operations. If
S2DGB$V_TAGGED_REQ is 1, then this 3-bit field should contain one of
the following coded constant values:
|
| S2DGB$V_AUTOSENSE | When this bit is 1, S2DGB$L_32SENSEADDR and S2DGB$L_32SENSELEN should contain a valid sense buffer address and length. If a CHECK CONDITION or COMMAND TERMINATED status is returned, REQUEST SENSE data will be returned in the buffer defined by S2DGB$L_32SENSEADDR and S2DGB$L_32SENSELEN. |
| When S2DGB$V_AUTOSENSE is 0, the buffer described by S2DGB$L_32SENSEADDR and S2DGB$L_32SENSELEN is ignored. In such cases, the class driver saves the autosense data in pool and returns it to the next IO$_DIAGNOSE, if and only if that IO$_DIAGNOSE has a REQUEST SENSE CDB. | |
| All other bits in S2DGB$L_FLAGS should be zero. |
S2DGB$L_32CDBADDR (S2DGB$PQ_64CDBADDR)
This field should contain the 32-bit (or 64-bit) virtual address of the SCSI command data block (CDB) to be sent to the target by this IO$_DIAGNOSE operation.
Note that S2DGB$L_32CDBADDR is a pointer to a longword, while S2DGB$PQ_64CDBADDR is a pointer to a quadword.
S2DGB$L_32CDBLEN (S2DGB$L_64CDBLEN)
This field should contain the number of bytes in the SCSI command data block (CDB) to be sent to the target by this IO$_DIAGNOSE operation. (Legal values: 2 to 248. However, some ports may restrict CDBs to smaller lengths. Recommended values: 2 to 16.)
S2DGB$L_32DATADDR (S2DGB$PQ_64DATADDR)
This field should contain the 32-bit (or 64-bit) virtual address of the DATAIN or DATAOUT buffer to be used with this SCSI operation. If the CDB being sent to the target does not use a DATAIN or DATAOUT buffer, then this field should be zero.
Note that S2DGB$L_32DATADDR is a pointer to a longword, while S2DGB$PQ_64DATADDR is a pointer to a quadword.
S2DGB$L_32DATLEN (S2DGB$L_64DATLEN)
This field should contain the number of bytes in the DATAIN or DATAOUT buffer associated with this operation. If the CDB being sent to the target does not use a DATAIN or DATAOUT buffer, then this field should be zero. (Legal values: 0 to UCB$L_MAXBCNT. Recommended values: 0 to 65,536. All ports are required to support at least 65,536 byte data transfers.)
S2DGB$L_32PADCNT (S2DGB$L_64PADCNT)
This field should contain the number of padding DATAIN or DATAOUT bytes required by this operation. (Legal values: 0 to the maximum number of bytes in a disk block on this system minus one. Current legal values: 0 to 511.)
S2DGB$L_32PHSTMO (S2DGB$L_64PHSTMO)
This field should contain the number of seconds that the port driver should wait for a phase transition to occur or for delivery of an expected interrupt. If S2DGB$V_ TAGGED_REQ is 1 or this field contains a 0 or 1, then the current phase transition timeout setting will not be changed. (Legal values: 0 to 300 [5 minutes].)
S2DGB$L_32DSCTMO (S2DGB$L_64DSCTMO)
This field should contain the number of seconds that the port driver should wait for a disconnected transaction to reconnect. If S2DGB$V_TAGGED_REQ is 1 or this field contains a 0 or 1, then the current disconnect timeout setting will not be changed. (Legal values: 0 to 65,535 [about 18 hours].)
S2DGB$L_32SENSEADDR (S2DGB$PQ_64SENSEADDR)
If S2DGB$V_AUTOSENSE is 1, then this field should contain the 32-bit (or 64-bit) virtual address of the sense buffer to be used by this SCSI operation. If S2DGB$V_AUTOSENSE is 0, this field will be ignored.
Note that S2DGB$L_32SENSEADDR is a pointer to a longword, while S2DGB$PQ_64SENSEADDR is a pointer to a quadword.
S2DGB$L_32SENSELEN (S2DGB$L_64SENSELEN)
If S2DGB$V_AUTOSENSE is 1, then this field should contain the number of bytes in the sense buffer associated with this operation. (Legal values: 0 to 255. Note: a value of 0 instructs the class driver to discard any sense data received. Recommended value: 18. Some ports may restrict the number of sense bytes to 18.) If S2DGB$V_AUTOSENSE is 0, this field will be ignored.
The following example shows how to set up a 64-bit S2DGB:
#include <s2dgbdef.h> /* Define S2DGB */
#include <far_pointers.h> /* Define VOID_PQ */
S2DGB diag_desc;
/* Set up some default S2DGB descriptor values */
diag_desc.s2dgb$l_opcode = OP_XCDB64 /* Use 64-bits */
diag_desc.s2dgb$l_flags = (S2DGB$M_READ | /* Flags*/
S2DGB$M_TAGGED_REQ |
S2DGB$M_AUTOSENSE);
diag_desc.s2dgb$v_tag = S2DGB$K_SIMPLE; /* SIMPLE que tag */
diag_desc.s2dgb$pq_64cdbaddr = (VOID_PQ)(&cdb[0]);/* Command addr */
diag_desc.s2dgb$l_64cdblen = 6; /* Command length */
diag_desc.s2dgb$pq_64dataddr = (VOID_PQ)(&buf[0]);/* Data addr */
diag_desc.s2dgb$l_64datlen = 20; /* Data length */
diag_desc.s2dgb$l_64padcnt = 0; /* Pad length */
diag_desc.s2dgb$l_64phstmo = 20; /* Phase timeout */
diag_desc.s2dgb$l_64dsctmo = 10; /* Disc timeout */
diag_desc.s2dgb$pq_64senseaddr = (VOID_PQ)(&asn[0]);/* Autosense addr */
diag_desc.s2dgb$l_64senselen = 255; /* Sense length */
diag_desc.s2dgb$l_reserved_1 = 0; /* Reserved */
.
.
.
status = sys$qiow(0, target_chan, IO$_DIAGNOSE, &iosb, 0, 0,
&diag_desc, S2DGB$K_XCDB64_LENGTH, 0, 0, 0, 0);
|
If all arguments are valid, the class driver will invoke the necessary port functions to send the CDB, transfer the data, and return, save or discard sense data as defined by the input S2DGB. Upon completion, the return IOSB will have the following format:
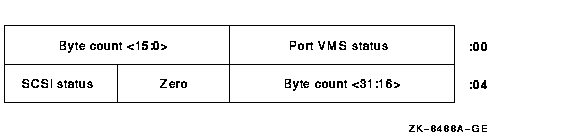
The DKDRIVER, GKDRIVER, and MKDRIVER class drivers, which implement other QIO functions, might intermix other tagged requests with IO$_DIAGNOSE requests. The order in which requests are sent generally matches the order in which requests are presented to the driver. An exception to this ordering occurs when the driver receives REQUEST SENSE for which autosense data previously has been recovered and stored. In this case, the IO$_DIAGNOSE will complete immediately and no command will be sent to the target.
The DKDRIVER, GKDRIVER, and MKDRIVER class drivers permit only one IO$_DIAGNOSE operation to be active (in the start I/O routine) at a given time, except as described in the next paragraph. However, applications must single thread IO$_DIAGNOSE requests in order to properly detect the presence of sense data and send the required REQUEST SENSE command. This is consistent with the VAX IO$_DIAGNOSE behavior. For example, if three reads are issued with no waiting and the first read gets a CHECK CONDITION, the sense data will be discarded by the target when the second read arrives.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |
![[Go to the documentation home page]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs.gif)
![[Help on this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help.gif)
![[How to contact us]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments.gif)
|
| privacy and legal statement | ||
| 6136PRO_037.HTML | ||