Display *dpy;
char *name, *program, *option;
main()
{
dpy = XOpenDisplay(0);
program = "xgr";
option = "foreground";
(1) name = XGetDefault(dpy, program, option);
printf("The default is '%s'.", name);
}
|
- The GET DEFAULT routine has the following
format:
property_name_return = XGetDefault(display, program_name,
option_name)
10.3 Storing Resources into a Database
Before the client can retrieve resources from a database, the client must create the database and store resources into it, unless the client is using an application or default database.
Example 10-2 illustrates how to create a database and add a single resource to it using the PUT LINE RESOURCE routine.
| Example 10-2 Creating and Storing into the Database |
|---|
.
.
.
Display *dpy;
char *name, *class;
(1)XrmDatabase graph_db = 0;
static void doCreateDatabase( );
/***** Create the database ******/
static void doCreateDatabase( )
{
int i;
(2) char *resource[] ={
"*Background.Color: light steel blue\n",
"*Foreground.Color: yellow\n",
"graph.window.height: 600\n",
"graph.window.width: 600\n",
"Graph.Font:
-Adobe-New Century Schoolbook-Bold-R-Normal--*-140-*-*-p-*-ISO8859-1\n",
"graph.gc.line.style: 2\n",
"graph.gc.line.width: 5\n",
"graph.gc.line.dashOffset: 0\n",
"graph.gc.line.dashes: 25\n"
};
(3) for (i = 0; i <= 8; i++)
XrmPutLineResource (&graph_db, resource[i]);
}
|
- The client assigns space for the database graph_db and initializes it to 0.
- The client creates the array resources.
- The PUT LINE RESOURCE routine adds a single
resource entry that is specified as a string and that contains both a
name and a value. If the database contains null, PUT LINE RESOURCE
creates a new database and returns a pointer to it.
The PUT LINE RESOURCE routine has the following format:
XrmPutLineResource(database, line)
Any white space before or after the name or colon in the line argument is ignored. The value is terminated by a new-line or null character. To allow values to contain embedded new-line characters, a \n is recognized and replaced by a new-line character.
10.4 Retrieving from the Resource Database
To retrieve a resource from the database, use the GET RESOURCE routine. The GET RESOURCE routine uses the resource manager value data structure. The resource manager value data structure defines database values. Database values consist of a size, an address, and a representation type. The size is specified in bytes. The representation type is a way to store data by some client-defined type, such as a string.
The following illustrates the resource manager value data structure:
typedef struct {
unsigned int size;
caddr_t addr;
} XrmValue, *XrmValuePtr:
|
Table 10-3 describes the members of the structure.
| Member Name | Contents |
|---|---|
| size | Size of the resource |
| addr | Address of the resource |
Example 10-3 illustrates how to create a client-defined routine that retrieves a resource from the database and returns the value to the calling routine. The resources are used to define graphics context values to draw a dashed line. See Chapter 4 for more information about defining graphics contexts.
In the following example, the fully-qualified name of the client is graph and its fully-qualified class is Graph.
| Example 10-3 Retrieving a Resource from the Database |
|---|
#include <decw$include/Xlib.h> #include <decw$include/Xutil.h> #include <decw$include/Xresource.h> Display *dpy; Window win; GC gc; Screen *screen; int n; char *name, *class; (1)XrmDatabase graph_db = 0; XrmValue value; (2)XrmString type; static void doInitialize( ); static char *doGetResource( ); static char *doDefineColor( ); static void doCreateDatabase( ); static void doCreateWindows( ); static void doCreateGraphicsContext( ); static void doLoadFont( ); static void doExpose( ); static void doMapWindows( ); static void doHandleEvents( ); static void doButtonPress( ); /***** The main program *****/ static int main() { doInitialize( ); doHandleEvents( ); } /***** doInitialize *****/ static void doInitialize( ) { dpy = XOpenDisplay(0); screen = DefaultScreenOfDisplay(dpy); doCreateDatabase( ); doCreateWindows( ); doCreateGraphicsContext( ); doLoadFont( ); doMapWindows( ); } /***** Create the database *****/ static void doCreateDatabase( ) { int i; char *resource[] ={ "*Background.Color: light steel blue\n", "*Foreground.Color: yellow\n", "graph.window.height: 600\n", "graph.window.width: 600\n", "Graph.Font: -Adobe-New Century Schoolbook-Bold-R-NormaL--*-140-*-*-P-*-ISO8859-1\n", "graph.gc.line.style: 2\n", "graph.gc.line.width: 5\n", "graph.gc.line.dashOffset: 0\n", "graph.gc.line.dashes: 25\n" }; for (i = 0; i <= 8; i++) XrmPutLineResource (&graph_db, resource[i]); XrmPutFileDatabase (graph_db, "graph_db.dat"); } /***** Get the resource *****/ (3)static char *doGetResource (name, class) { if (XrmGetResource (graph_db, name, class, &type, &value)){ printf("Returning '%s'.\n", value.addr); return value.addr; } else{ printf("no such entry in database"); exit (-1); } } /***** Create the windows *****/ static void doCreateWindows( ) { (4) int winW = atoi (doGetResource ("graph.window.width", "Graph.Window.Width")); int winH = atoi (doGetResource ("graph.window.height", "Graph.Window.Height")); int winX = (WidthOfScreen(screen)-winW)>>1; int winY = (HeightOfScreen(screen)-winH)>>1; XSetWindowAttributes xswa; /* Create the window */ xswa.event_mask = ExposureMask | ButtonPressMask; (5) xswa.background_pixel = doDefineColor(doGetResource( "graph.window.background.color", "Graph.Window.Background.Color")); win = XCreateWindow(dpy, RootWindowOfScreen(screen), winX, winY, winW, winH, 0, DefaultDepthOfScreen(screen), InputOutput, DefaultVisualOfScreen(screen), CWEventMask | CWBackPixel, &xswa); } /***** Create the graphics context *****/ static void doCreateGraphicsContext( ) { XGCValues xgcv; xgcv.foreground = doDefineColor(doGetResource("graph.gc.foreground.color", "Graph.GC.Foreground.Color")); xgcv.background = doDefineColor(doGetResource("graph.gc.background.color", "Graph.GC.Background.Color")); xgcv.line_width = atoi (doGetResource("graph.gc.line.width", "Graph.GC.Line.Width")); (6) xgcv.line_style = atoi (doGetResource("graph.gc.line.style", "Graph.GC.Line.Style")); xgcv.dash_offset = atoi (doGetResource("graph.gc.line.dashOffset", "Graph.GC.Line.Type")); xgcv.dashes = atoi (doGetResource("graph.gc.line.dashes", "Graph.GC.Line.Dashes")); gc = XCreateGC(dpy, win, GCForeground | GCBackground | GCLineWidth | GCLineStyle | GCDashOffset | GCDashList, &xgcv); } /***** Load the font for text writing *****/ static void doLoadFont( ) { Font font; char *fontname; fontname = doGetResource ("graph.font", "Graph.Font"); font = XLoadFont(dpy, fontname); XSetFont(dpy, gc, font); } . . . |
- The client assigns storage for a resource manager data structure.
- XrmString is a typedef defined in DECW$INCLUDE: XRESOURCE.H and declares type as a character string.
- The client-defined doGetResource
routine calls the GET RESOURCE routine and retrieves a resource from
the specified database. The client passes a fully-qualified name and
fully-qualified class. The address of the value member of the resource
manager value data structure is returned. Note that the value returned
points into database memory and therefore must not be freed or
modified.
The GET RESOURCE routine has the following format:
XrmGetResource(database_id, name_list_string, class_list_string,
repr_type_return, repr_value_return) - To specify the window height and width, the client calls doGetResource and passes the fully-qualified name and class of the resource to be returned. Because the value returned is a string, the C library function atoi converts it to an integer.
- The background pixel is defined by calling
the client-defined routine doGetResource, which returns the
value "light steel blue". The string is then passed to the
client-defined routine doDefineColor, which allocates the
color. See Chapter 5 for more information about defining colors.
- Values for the graphics context data structure members are set using strings returned by doGetResource and converted to an integer by atoi. Because the resource manager does not translate macros and constants, the integer for the constant LineDoubleDash is used. Refer to X.H for these values in the DECW$INCLUDE directory.
10.5 Merging and Storing Databases
The resource manager provides routines that merge two or more databases, store a copy of a database to a disk, and retrieve the database from the disk.
Use the MERGE DATABASES routine to merge two or more databases into one database. This routine is used to combine databases; for example, to combine a client-specific database of defaults and a database of user preferences. The MERGE DATABASES routine overwrites an identical database entry.
Use the PUT FILE DATABASE routine to store a copy of the specified database to disk in a specified file. To retrieve a database from the disk, use the GET FILE DATABASE routine.
Example 10-4 shows how to retrieve two databases from disk, to merge each database into a newly created database, and to store the new database in a disk file on the default directory.
Example 10-4 uses the database file graph_db created by Example 10-3. Assume that this database contains the default values for the client named graph. Assume that another database exists containing user preferences for several clients including values to be used for graph. This database is named user_pref_db and contains the following entries:
window1.background: dark blue window1.foreground: white window1.borderWidth: 1 window2.height: 50 window2.width: 400 graph.window.height: 600 graph.window.width: 600 graph.gc.line.width: 1 graph.gc.line.style: 2 graph.gc.line.dashOffset: 0 graph.gc.line.dashes: 25 Graph.Font: -Adobe-Helvetica-Bold-R-Normal--*-140-*-*-P-*-ISO8859-1 *Background.Color: light steel blue *Foreground.Color: yellow |
Note that in Example 10-4, the entry Graph.Font in "user_pref_db.dat" is identical to the entry in graph_db; however, the value of the font name has been changed. When the client merges the two databases, the value of Graph.Font in user_pref_db overwrites the value from graph_db.
| Example 10-4 Merging and Storing Databases |
|---|
#include <decw$include/Xlib.h>
#include <decw$include/Xresource.h>
main()
{
Display *dpy;
XrmDatabase graph_db, user_pref_db, result_db = 0;
XrmString type;
XrmValue value;
(1) graph_db = XrmGetFileDatabase("graph_db.dat");
(2) XrmMergeDatabases(graph_db, &result_db);
user_pref_db = XrmGetFileDatabase("user_pref_db.dat");
XrmMergeDatabases(user_pref_db, &result_db);
XrmGetResource(result_db, "graph.font", "Graph.Font", &type, &value);
printf("The answer is '%s'.", value.addr);
(3) XrmPutFileDatabase(result_db,"result_db.dat");
}
|
- The client retrieves a database from disk
and loads it into database memory.
The GET FILE DATABASE routine has the following format:
database_id_return = XrmGetFileDatabase(file_name) - The source database graph_db is
merged with the destination database result_db. Note that when
using the MERGE DATABASE routine, the source database is destroyed.
The MERGE DATABASE routine has the following format:
XrmMergeDatabases(src_database_id, dst_database_id) - The client calls the PUT FILE DATABASE to
write the database result_db to disk on the default directory.
The PUT FILE DATABASE routine has the following format:
XrmPutFileDatabase(database_id, file_name)
10.6 Using Representations for Strings
Most uses of the resource manager involve defining names, classes, and types as string constants; however, strings are not stored in the database as ASCII text. All strings are converted from strings to quarks. A quark is an integer and is used as a shorthand form of the string constant. A quark is also referred to as a representation. Converting from a string to a quark is controlled by the type of resource manager routine used.
The resource manager provides two types of routines for most resource manager functions: string routines and quark routines. String routines are convenience functions that convert all strings to quarks each time the routine is called. For example, when the client calls the PUT RESOURCE routine, the resource manager first converts the string and the value to quarks and then calls Q PUT RESOURCE to add them to the database. Although conversion is transparent to the user when using these routines, performance is slower because a conversion occurs each time a string routine is called. (See Example 10-3 for an illustration of these types of routines.)
Quark routines, on the other hand, operate directly on the quarks that are in the database. Although the client must use conversion routines to change the string to a quark, performance is increased because conversion takes place only once. In addition, quark routines compare integers, which is much faster than string comparisons.
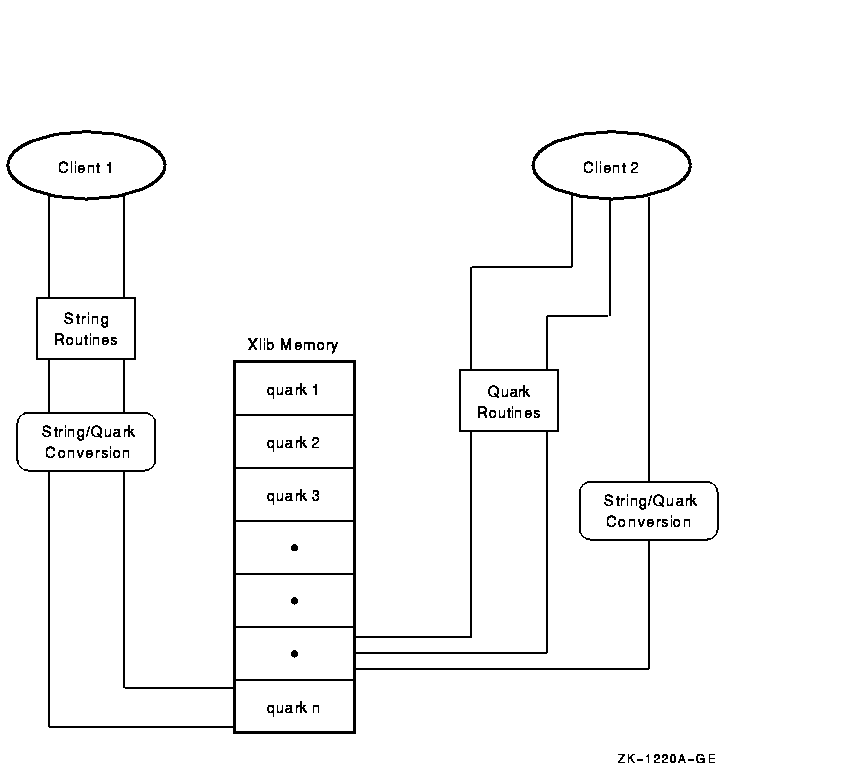
Figure 10-3 illustrates how string and quark routines operate on the database. Client 1 uses string routines that perform a string/quark conversion with each routine call. Client 2 converts the string directly and then uses quark routines to manipulate the database.
Figure 10-3 String and Quark Routines Operation
10.6.1 Converting a String to a Quark
Before using quark routines, the database is created and the strings are converted to quarks. Each string is converted and placed in a quark list where each name or class component in the string is converted to an integer. In addition, a binding list is created that indicates whether the component is separated by a period or an asterisk. When a component is separated by a period, it is bound tightly. The component is bound loosely when separated by an asterisk.
The following example shows the binding list for the string "graph.window*height". Because a period is implicit if neither a period nor asterisk appears at the beginning of the string, the following binding list is formed from the string ".graph.window*height". Refer to Table 10-2 for more information about resource manager rules.
XrmBindTightly XrmBindTightly XrmBindLoosely |
Example 10-5 shows how to allocate space for the binding and quark lists, to convert resources and values, and to put the resources and values into the specified database.
| Example 10-5 Converting a String to a Quark |
|---|
#include <decw$include/Xresource.h>
.
.
.
XrmDatabase graph_db;
(1)XrmBinding bindings[5];
(2)XrmQuark quarks[5];
.
.
.
/***** Create the database *****/
static void doCreateDatabase( )
{
int i;
char *resource[] ={
"*Background.Color",
"*Foreground.Color",
};
char *value_str[] ={
"light steel blue",
"yellow",
};
for (i = 0; i <= 1; i++){
(3) XrmStringToBindingQuarkList(resource[i], &bindings, &quarks);
(4) XrmQPutStringResource(&graph_db, &bindings, &quarks, value_str[i]);
}
|
- Allocate space for a binding list.
- Allocate space for a quark list.
- The client calls the STRING TO BINDING QUARK
LIST routine to convert the string to a quark list and a binding list.
The STRING TO BINDING QUARK LIST routine has the following format:
XrmStringToBindingQuarkList(value_name, binding_list_id_ret,
repr_list_id_ret) - The client calls the Q PUT STRING RESOURCE
routine to add the binding list, quark list, and a resource value to
the specified database. If the database is a null value, a new resource
database is created.
The Q PUT STRING RESOURCE routine has the following format:
XrmQPutStringResource(database_id, binding_list_id,
repr_list_id, value_name)
10.6.2 Retrieving Resources with Quarks
Once the string has been converted to a quark, other quark routines can be used to query, to compare, and to return values from the database. Although this causes an increase in code, performance is increased for programs that do many such operations.
Example 10-6 shows how to use the following quark routines: STRING TO NAME LIST, STRING TO CLASS LIST, and Q GET RESOURCE. The following example is modified from the example in Section 10.4 to use these routines.
| Example 10-6 Retrieving Quarks |
|---|
#include <decw$include/Xresource.h>
.
.
.
Display *dpy;
Window win;
GC gc;
Screen *screen;
XrmDatabase graph_db = 0;
XrmValue value;
(1) XrmRepresentation type;
XrmBinding bindings[5];
XrmQuark quarks[5];
XrmNameList names[5];
XrmClassList classes[5];
static void doInitialize( );
static char *doQGetResource( );
static char *doDefineColor( );
static void doCreateDatabase( );
static void doCreateWindows( );
static void doCreateGraphicsContext( );
static void doLoadFont( );
static void doExpose( );
static void doMapWindows( );
static void doHandleEvents( );
static void doButtonPress( );
/***** The main program *****/
static int main()
{
doInitialize( );
doHandleEvents( );
}
/***** doInitialize *****/
static void doInitialize( )
{
dpy = XOpenDisplay(0);
screen = DefaultScreenOfDisplay(dpy);
doCreateDatabase( );
doCreateWindows( );
doCreateGraphicsContext( );
doLoadFont( );
doMapWindows( );
}
/***** Create the database *******/
static void doCreateDatabase( )
{
int i;
char *resource[] ={
"*Background.Color",
"*Foreground.Color",
"graph.window.height",
"graph.window.width",
"Graph.Font",
"graph.gc.line.style",
"graph.gc.line.width",
"graph.gc.line.dashOffset",
"graph.gc.line.dashes"
};
char *value_str[] ={
"light steel blue",
"yellow",
"600",
"600",
"-Adobe-New Century Schoolbook-Bold-R-Normal--*-140-*-*-P-*-ISO8859-1",
"2",
"5",
"0",
"25"
};
for (i = 0; i <= 8; i++){
XrmStringToBindingQuarkList(resource[i], &bindings, &quarks);
XrmQPutStringResource(&graph_db, &bindings, &quarks, value_str[i]);
}
XrmPutFileDatabase(graph_db, "graph_db.dat");
}
/***** Get the resource *****/
static doGetResource ( )
{
(2) if (XrmQGetResource (graph_db, names, classes, &type, &value)){
printf("Returning '%s'.\n", value.addr);
return value.addr;
}
else{
printf("no such entry in database");
exit (-1);
}
}
/***** Create the windows *****/
static void doCreateWindows( )
{
int winW;
int winH;
int winX;
int winY;
XSetWindowAttributes xswa;
(3) XrmStringToNameList("graph.window.width", &names);
(4) XrmStringToClassList("Graph.Window.Width", &classes);
(5) winW = atoi (doGetResource ( ) );
XrmStringToNameList("graph.window.height", &names);
XrmStringToClassList("Graph.Window.Height", &classes);
winH = atoi (doGetResource ( ) );
winX = (WidthOfScreen(screen)-winW)>>1;
winY = (HeightOfScreen(screen)-winH)>>1;
/* Create the window */
xswa.event_mask = ExposureMask | ButtonPressMask;
XrmStringToNameList("graph.window.background.color", &names);
XrmStringToClassList("Graph.Window.Background.Color", &classes);
xswa.background_pixel = doDefineColor(doGetResource( ) );
win = XCreateWindow(dpy, RootWindowOfScreen(screen),
winX, winY, winW, winH, 0,
DefaultDepthOfScreen(screen), InputOutput,
DefaultVisualOfScreen(screen), CWEventMask | CWBackPixel, &xswa);
}
/***** Create the graphics context *****/
static void doCreateGraphicsContext( )
{
XGCValues xgcv;
XrmStringToNameList("graph.gc.foreground.color", &names);
XrmStringToClassList("Graph.GC.Foreground.Color", &classes);
xgcv.foreground = doDefineColor(doGetResource( ) );
XrmStringToNameList("graph.gc.background.color", &names);
XrmStringToClassList("Graph.GC.Background.Color", &classes);
xgcv.background = doDefineColor(doGetResource( ) );
XrmStringToNameList("graph.gc.line.width", &names);
XrmStringToClassList("Graph.GC.Line.Width", &classes);
xgcv.line_width = atoi (doGetResource( ) );
XrmStringToNameList("graph.gc.line.style", &names);
XrmStringToClassList("Graph.Line.Style", &classes);
xgcv.line_style = atoi (doGetResource( ) );
XrmStringToNameList("graph.gc.line.dashOffset", &names);
XrmStringToClassList("Graph.GC.Line.Type", &classes);
xgcv.dash_offset = atoi (doGetResource( ) );
XrmStringToNameList("graph.gc.line.dashes", &names);
XrmStringToClassList("Graph.Line.Dashes", &classes);
xgcv.dashes = atoi (doGetResource( ) );
gc = XCreateGC(dpy, win, GCForeground | GCBackground
| GCLineWidth | GCLineStyle | GCDashOffset | GCDashList, &xgcv);
}
/***** Load the font for text writing *****/
static void doLoadFont( )
{
Font font;
char *fontname;
XrmStringToNameList("graph.font", &names);
XrmStringToClassList("Graph.Font", &classes);
fontname = doGetResource ( );
font = XLoadFont(dpy, fontname);
XSetFont(dpy, gc, font);
}
.
.
.
|
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |