![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/openvms_doc_banner_top.gif)
|
![[Site home]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home_off.gif)
![[Send comments]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments_off.gif)
![[Help with this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help_off.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs_off.gif)
![[OpenVMS site]](../../images/buttons/bn_openvms_off.gif)
![[Compaq site]](../../images/buttons/bn_compaq_off.gif)
|
| Updated: 11 December 1998 |
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/openvms_doc_banner_top.gif)
|
![[Site home]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home_off.gif)
![[Send comments]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments_off.gif)
![[Help with this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help_off.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs_off.gif)
![[OpenVMS site]](../../images/buttons/bn_openvms_off.gif)
![[Compaq site]](../../images/buttons/bn_compaq_off.gif)
|
| Updated: 11 December 1998 |
OpenVMS Alpha System Analysis Tools Manual
| Previous | Contents | Index |
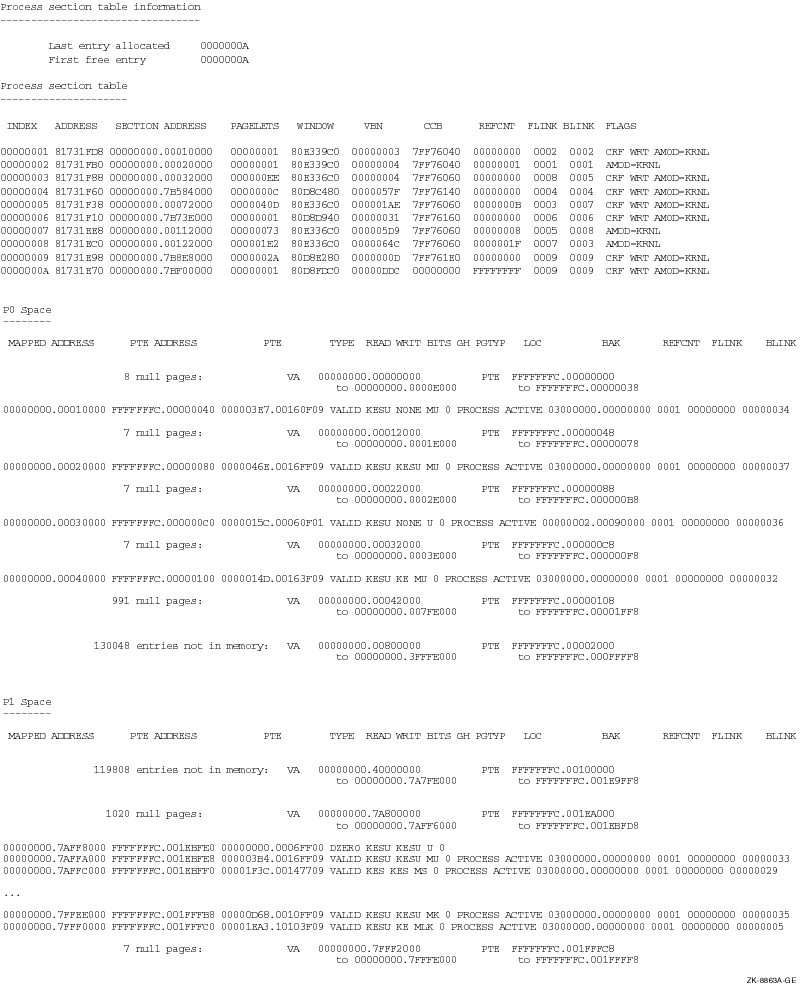
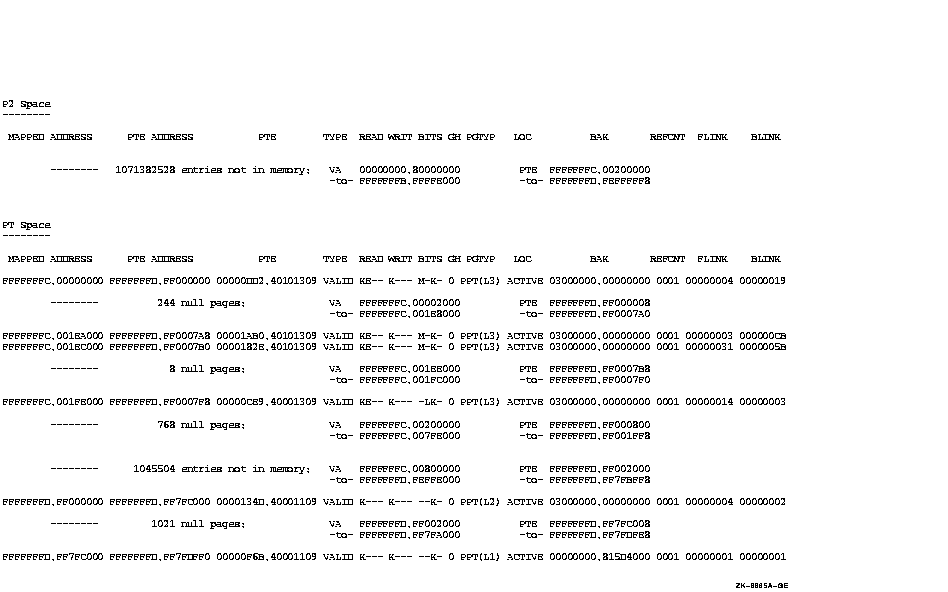
Process active channels
-----------------------
Channel Window Status Device/file accessed
------- ------ ------ --------------------
0010 00000000 DKB400:
0040 00000000 Busy OPA0:
0060 00000000 OPA0:
0090 80D83BC0 DKB400:(390,17,0)(section file)
00A0 80D8AF40 DKB400:(3888,39,0)(section file)
Process activated images
------------------------
IMCB Start End Sym Vect Type Image Name Major ID, Minor ID
-------- -------- -------- -------- --------- ------------------------------
7FF88480 00010000 000401FF 00000000 MAIN X 0,0
7FF8A4A0 80C03378 80C04E08 80C03378 GLBL SYS$PUBLIC_VECTORS 93,1959106
Total images = 2 Pages allocated = 24
Process Buffered Objects
------------------------
ADDRESS ACMODE SEQUENCE REFCNT PID PAGCNT BASE PVA BASE SVA
-------- ------ -------- -------- -------- -------- ---------- ----- --
No buffer objects for this proces
|
The SHOW PROCESS/ALL command displays information taken from the PCB of process VERIFICATION, and then proceeds to display the process header, the process registers, the process section table, the page tables of the process, images activated, and information about the I/O channels owned by the process. These displays may also be obtained by the /PCB, /PHD, /REGISTERS, /RDE, /PROCESS_SECTION_TABLE, /P0, /P1, /P2, /PT, /IMAGES, and /CHANNEL qualifiers, respectively.
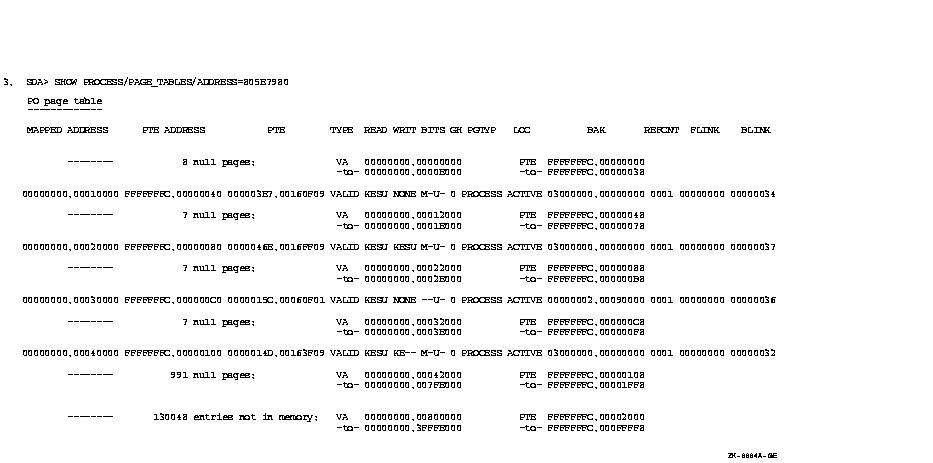
This example displays the page tables of a process whose PCB address is 805E7980.
4. SDA>SHOW PROCESS/BUFFER_OBJECTS
Process Buffered Objects
------------------------
ADDRESS ACMODE SEQUENCE REFCNT PID PAGCNT BASE PVA BASE SVA
-------- ------ -------- -------- -------- -------- ----------------- --------
805E4580 User 00000008 00000001 00010020 00000001 00000000.00020000 826BC000
805E7880 User 00000009 00000001 00010020 00000001 00000000.00020000 826BE000
8057AEC0 User 0000000A 00000001 00010020 00000001 00000000.00020000 826C0000
805E6EC0 User 0000000B 00000001 00010020 00000001 00000000.00020000 82764000
|
The SHOW PROCESS/BUFFER_OBJECTS command displays all the buffered objects that a process has created.
5. SDA>SHOW PROCESS/IMAGES
Process activated images
------------------------
IMCB Start End Sym Vect Type Image Name Major ID,Minor ID
-------- -------- -------- -------- ------------ -----------------------------
7FF78810 00010000 001107FF 00000000 MAIN SDA 0,0
7FF789B0 001E6000 002263FF 001E80B0 GLBL SHR LBRSHR 2,9
7FF76480 001A4000 001E43FF 001A4950 GLBL SHR SCRSHR 1,2900
7FF785A0 00112000 001A27FF 00186AE0 GLBL SHR SMGSHR 1,104
7FF78060 7FC06000 7FC67FFF 7FC144B0 GLBL SHR LIBRTL 1,1
Base End ImageOff Section Type
80400000 80481C00 00000000 System Resident Code
7FC06000 7FC16800 00090000 Shareable Address Data
7FC26000 7FC27000 000B0000 Read-Write Data
7FC36000 7FC3F600 000C0000 Shareable Read-Only Data
7FC46000 7FC46200 000D0000 Read-Write Data
7FC56000 7FC57000 000E0000 Demand Zero Data
7FC66000 7FC67400 000F0000 Read-Write Data
7FF78330 7FC76000 7FCA7FFF 7FC86000 GLBL SHR LIBOTS 1,3
Base End ImageOff Section Type
80482000 8048FA00 00020000 System Resident Code
7FC76000 7FC78600 00000000 Shareable Read-Only Data
7FC86000 7FC87C00 00010000 Shareable Address Data
7FCA6000 7FCA6200 00030000 Read-Write Data
7FF78130 80810110 8081C770 80810110 GLBL SYS$BASE_IMAGE 114,15303694
7FF784D0 80802A18 80803FF8 80802A18 GLBL SYS$PUBLIC_VECTORS 114,15295276
Total images = 8 Pages allocated = 344
|
The SHOW PROCESS/IMAGES command displays the address of the image control block; the start and end addresses of the image; the activation code; the protected and shareable flags; the image name; the major and minor IDs of the image; and the base, end, image offset, and section type for installed resident images.
Displays information about all resources in the system, or about a resource associated with a specific lock.
SHOW RESOURCE {/ADDRESS=n|/ALL (d)|
/BRIEF|/CACHED|/CONTENTION [=ALL]| /LOCKID=lock-id|/NAME=resource-name|
/STATUS=(keyword [keyword,])}
None.
/ADDRESS=n
Displays information from the resource block at the specified address./ALL
Displays information from all resource blocks (RSBs) in the system. This is the default behavior of the SHOW RESOURCE command./BRIEF
Displays a brief one line of the resource information./CACHED
Displays resource blocks that are no longer valid. The memory for these resources is saved so that later requests for resources can use them./CONTENTION [=ALL]
Displays only resources that have at least one lock on either the waiting or conversion queue. Unless the ALL keyword is specified, resources with locks on the waiting or conversion queues that are not participating in deadlock searches are ignored. (Locks not participating in deadlock searches are requested with either the LCK$M_NODLCKWT or LCK$M_NODLCKBLK flags.)/LOCKID=lock-id
Displays information on the resource associated with the lock with the specified lock-id./NAME=resource-name
Displays information about a specific resource./STATUS=(keyword [keyword,])
Displays only resources that have the specified status bits set in the RSB$L_STATUS field. Status keywords are as follows:
Keyword Meaning BRL Indicates byte range resource CHK_BTR Checks for better master CVTFULRNG Indicates full-range requests in convert queue CVTSUBRNG Indicates sub-range requests in convert queue DIR_IP Creates directory entry DIR_RQD Indicates directory entry required DIRENTRY Indicates entered in directory during failover RBLD_ACT Indicates lock rebuild active for this tree RBLD_IP Indicates rebuild operation in progress RBLD_RQD Indicates rebuild required for this resource tree RM_ACCEPT Accepts new master RM_DEFLECT Deflects remote interest RM_IP Indicates resource remaster in progress RM_PEND Indicates a pending resource remaster operation RM_RBLD Indicates to always rebuild resource tree RM_WAIT Blocks local activity VALCUR Indicates value block is current INVPEND Checks for value block invalidation VALINVLD Indicates value block invalid WTFULRNG Indicates full-range requests in wait queue WTSUBRNG Indicates a full-range requests in wait queue 2PC_IP Indicates a two-phase convert operation in progress
The SHOW RESOURCE command displays the information listed in Table 4-20 for each resource in the system or for the specific resource associated with the specified lock-id.
Table 4-20 Resource Information in the SHOW RESOURCE Display Field Contents Address of RSB Address of the resource block (RSB) that describes this resource. Parent RSB Address of the RSB that is the parent of this RSB. This field is 00000000 if the RSB itself is a parent block. Sub-RSB count Number of RSBs of which this RSB is the parent. This field is 0 if the RSB has no sub-RSBs. Lock Count The total count of all locks on the resource. BLKAST count Number of locks on this resource that have requested a blocking AST. GGMODE Indication of the most restrictive mode in which a lock on this resource has been granted. Table 4-21 shows the fields and values and their meanings. They are shown in order from the least restrictive mode to the most restrictive. For information on conflicting and incompatible lock modes, see the OpenVMS System Services Reference Manual.
CGMODE Indication of the most restrictive lock mode to which a lock on this resource is waiting to be converted. This does not include the mode for which the lock at the head of the conversion queue is waiting. FGMODE Indication of the full-range grant mode. CSID Cluster system identification number (CSID) and name of the node that owns the resource. RQSEQNM Sequence number of the request. Status The contents of the resource block status field. Resource Dump of the name of this resource, as stored at the end of the RSB. The first two columns are the hexadecimal representation of the name, with the least significant byte represented by the rightmost two digits in the rightmost column. The third column contains the ASCII representation of the name, the least significant byte being represented by the leftmost character in the column. Periods in this column represent values that correspond to nonprinting ASCII characters. Valblk Hexadecimal dump of the 16-byte block value block associated with this resource. Seqnum Sequence number associated with the resource's value block. If the number indicates that the value block is not valid, the words "Not valid" appear to the right of the number. Granted queue List of locks on this resource that have been granted. For each lock in the list, SDA displays the number of the lock and the lock mode in which the lock was granted. Conversion queue List of locks waiting to be converted from one mode to another. For each lock in the list, SDA displays the number of the lock, the mode in which the lock was granted, and the mode to which the lock is to be converted. Waiting queue List of locks waiting to be granted. For each lock in the list, SDA displays the number of the lock and the mode requested for that lock. Length Length in bytes of the resource name. Mode Processor mode of the namespace in which this RSB resides. Owner Owner of the resource. Certain resources, owned by the operating system, list "System" as the owner. Locks owned by a group have the number (in octal) of the owning group in this field.
| Value | Meaning |
|---|---|
| NL | Null mode. |
| CR | Concurrent-read mode. |
| CW | Concurrent-write mode. |
| PR | Protected-read mode. |
| PW | Protected-write mode. |
| EX | Exclusive mode. |
| #1 |
|---|
SDA> SHOW RESOURCE
Resource database
-----------------
RSB: FFFFFFFF.7FD47950 GGMODE: PR Status: VALID
Parent RSB: 00000000.00000000 CGMODE: PR
Sub-RSB count: 0 FGMODE: PR
Lock Count: 1 RQSEQNM: 0000
BLKAST count: 1 CSID: 00000000 (SWORKS)
Resource: 6D632445 48434143 CACHE$cm Valblk: 00000000 00000000
Length 24 525F534B 524F5753 SWORKS_R 00000000 00000000
Kernel mode 000027DA 4E455641 AVENÚ'..
System 00000000 00000000 ........ Seqnum: 00000000
Granted queue (Lock ID / Gr mode / Range):
0100042F PR 00000000-FFFFFFFF
Conversion queue (Lock ID / Gr mode / Range -> Rq mode / Range):
*** EMPTY QUEUE ***
Waiting queue (Lock ID / Rq mode / Range):
*** EMPTY QUEUE ***
Resource Database
-----------------
RSB: FFFFFFFF.7FA66A50 GGMODE: NL Status: VALID
Parent RSB: FFFFFFFF.7FD88350 CGMODE: NL
Sub-RSB count: 0 FGMODE: NL
Lock Count: 2 RQSEQNM: 004D
BLKAST count: 0 CSID: 00000000 (SWORKS)
Resource: 001E7324 42313146 F11B$s.. Valblk: 00000001 0000033A
Length 10 00000000 00000000 ........ 00000000 00000000
Kernel mode 00000000 00000000 ........
System 00000000 00000000 ........ Seqnum: 00000672
Granted queue (Lock ID / Gr mode / Range):
69000F80 NL 00000000-FFFFFFFF 01001810 NL 00000000-FFFFFFFF
Conversion queue (Lock ID / Gr mode / Range -> Rq mode / Range):
*** EMPTY QUEUE ***
Waiting queue (Lock ID / Rq mode / Range):
*** EMPTY QUEUE ***
.
.
.
|
The SHOW RESOURCE command displays information taken from the RSBs of all resources in the system. For instance, the RSB at FFFFFFFF.7FA66A5016 is a parent block with no sub-RSBs.
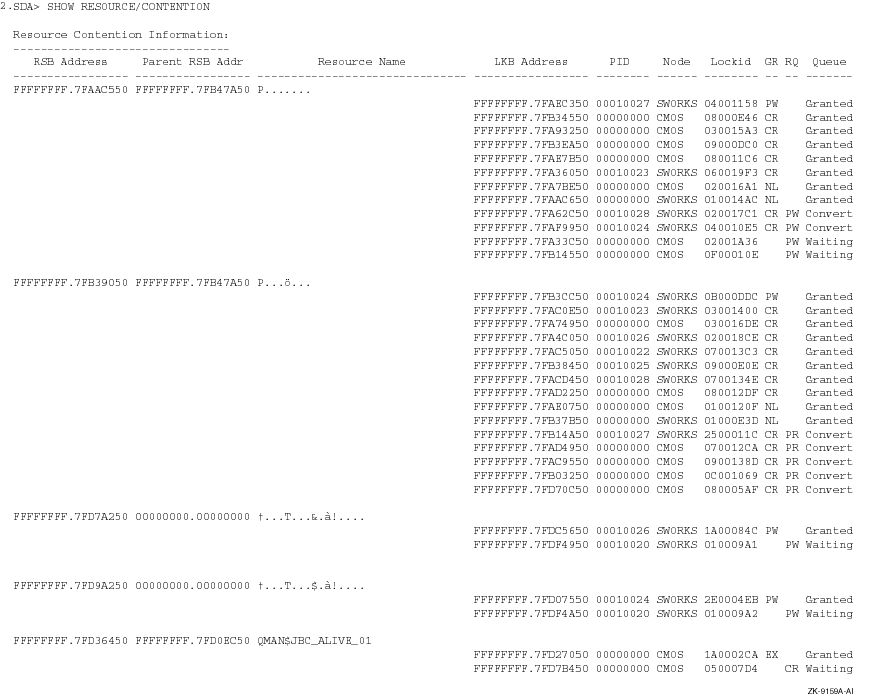
This example of the SHOW RESOURCE/CONTENTION commands shows all the resources for which there is contention, and which are not to be included in dead lock searches.
Displays information contained in the reserved memory descriptors. Reserved memory is used within the system by memory-resident global sections.
SHOW RMD [/QUALIFIERS]
None.
/ADDRESS=n
Displays a specific reserved memory descriptor entry, given its address./ALL
Displays information in all the reserved memory descriptors. This qualifier is the default.
The SHOW RMD displays information that resides in the reserved memory descriptors. Table 4-22 shows the fields and their meaning.
Table 4-22 RMD Fields Field Meaning ADDRESS Gives the address of the reserved memory descriptor. NAME Gives the name of the reserved memory descriptor. FLAGS Gives the settings of flags for specified reserved memory descriptor, as a hexadecimal number, then key flag bits are also displayed by name. GROUP Gives the UIC group that owns the reserved memory. This is given as -S- for system global reserved memory. PFN Gives starting page number of the reserved memory. COUNT Gives the number of pages reserved. IN_USE Gives the number of pages in use. ZERO_PFN Gives the next page number to be zeroed.
SDA> SHOW RMD
Reserved Memory Descriptor List
-------------------------------
ADDRESS NAME GROUP PFN COUNT IN_USE ZERO_PFN FLAGS
80D21200 MILORD2 -S- 00000000 00000100 00000000 00000000 00000000
80D21100 MILORD1 -S- 00000A00 00000080 00000000 00000A00 00000001 ALLOC
80D21280 MILORD2 -S- 00000000 00000001 00000000 00000000 00000040 PAGE_TABLES
80D21180 MILORD1 -S- 00000180 00000001 00000000 00000180 00000041 ALLOC PAGE_TABLES
|
Displays the RMS data structures selected by the SET RMS command to be included in the default display of the SHOW PROCESS/RMS command.
SHOW RMS
None.
None.
The SHOW RMS command lists the names of the data structures selected for the default display of the SHOW PROCESS/RMS command.For a description of the significance of the options listed in the SHOW RMS display, see the description of the SET RMS command and Table 4-2.
For an illustration of the information displayed by the SHOW PROCESS/RMS command, see the examples included in the description of the SHOW PROCESS command.
| #1 |
|---|
SDA> SHOW RMS
RMS Display Options: IFB,IRB,IDX,BDB,BDBSUM,ASB,CCB,WCB,FCB,FAB,RAB,NAM,
XAB,RLB,BLB,BLBSUM,GBD,GBH,FWA,GBDSUM,JFB,NWA,RU,DRC,SFSB,GBSB
Display RMS structures for all IFI values.
|
The SHOW RMS command displays the full set of options available for display by the SHOW PROCESS/RMS command. SDA, by default, selects the full set of RMS options at the beginning of an analysis.
| #2 |
|---|
SDA> SET RMS=(IFAB,CCB,WCB)
SDA> SHOW RMS
RMS Display Options: IFB,CCB,WCB
Display RMS structures for all IFI values.
|
The SET RMS command establishes the IFB, CCB, and WCB as the structures to be displayed when the SHOW PROCESS/RMS command is issued. The SHOW RMS command verifies this selection of RMS options.
Displays information about response IDs (RSPIDs) of all System Communications Services (SCS) connections or, optionally, a specific SCS connection.
SHOW RSPID [/CONNECTION=cdt-address]
None.
/CONNECTION=cdt-address
Displays RSPID information for the specific SCS connection whose connection descriptor table (CDT) address is provided in cdt-address. You can find the cdt-address for any active connection on the system in the CDT summary page display of the SHOW CONNECTIONS command. CDT addresses are also stored in many individual data structures related to SCS connections. These data structures include class driver request packets (CDRPs) and unit control blocks (UCBs) for class drivers that use SCS and cluster system blocks (CSBs) for the connection manager.
Whenever a local system application (SYSAP) requires a response from a remote SYSAP, a unique number, called an RSPID, is assigned to the response by the local system. The RSPID is transmitted in the original request (as a means of identification), and the remote SYSAP returns the same RSPID in its response to the original request.The SHOW RSPID command displays information taken from the response descriptor table (RDT), which lists the currently open local requests that require responses from SYSAPs at a remote node. For each RSPID, SDA displays the following information:
| #1 |
|---|
SDA> SHOW RSPID
--- Summary of Response Descriptor Table (RDT) 805E6F18 ---
RSPID CDRP Address CDT Address Local Process Name Remote Node
----- ------------ ----------- ------------------ -----------
39D00000 8062CC80 805E8710 VMS$VMScluster VANDQ1
EE210001 80637260 805E8C90 VMS$DISK_CL_DRVR ROMRDR
EE240002 806382E0 805E8DF0 VMS$DISK_CL_DRVR VANDQ1
EE440003 806393E0 805E8F50 VMS$TAPE_CL_DRVR VANDQ1
5DB90004 80636BC0 805E8870 VMS$VMScluster ROMRDR
5C260005 80664040 805E8870 VMS$VMScluster ROMRDR
38F80006 80664A80 805E8710 VMS$VMScluster VANDQ1
|
This example shows the default output for the SHOW RSPID command.
| #2 |
|---|
SDA> SHOW RSPID/CONNECTION=805E8F50
--- Summary of Response Descriptor Table (RDT) 805E6F18 ---
RSPID CDRP Address CDT Address Local Process Name Remote Node
----- ------------ ----------- ------------------ -----------
EE440003 806393E0 805E8F50 VMS$TAPE_CL_DRVR VANDQ1
|
This example shows the output for a SHOW RSPID/CONNECTION command.
| Previous | Next | Contents | Index |
![[Site home]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_home_off.gif)
![[Send comments]](../../images/buttons/bn_comments_off.gif)
![[Help with this site]](../../images/buttons/bn_site_help_off.gif)
![[How to order documentation]](../../images/buttons/bn_order_docs_off.gif)
![[OpenVMS site]](../../images/buttons/bn_openvms_off.gif)
![[Compaq site]](../../images/buttons/bn_compaq_off.gif)
|
![[OpenVMS documentation]](../../images/openvms_doc_banner_bottom.gif) |
|
Copyright © Compaq Computer Corporation 1998. All rights reserved. Legal |
6549PRO_016.HTML
|